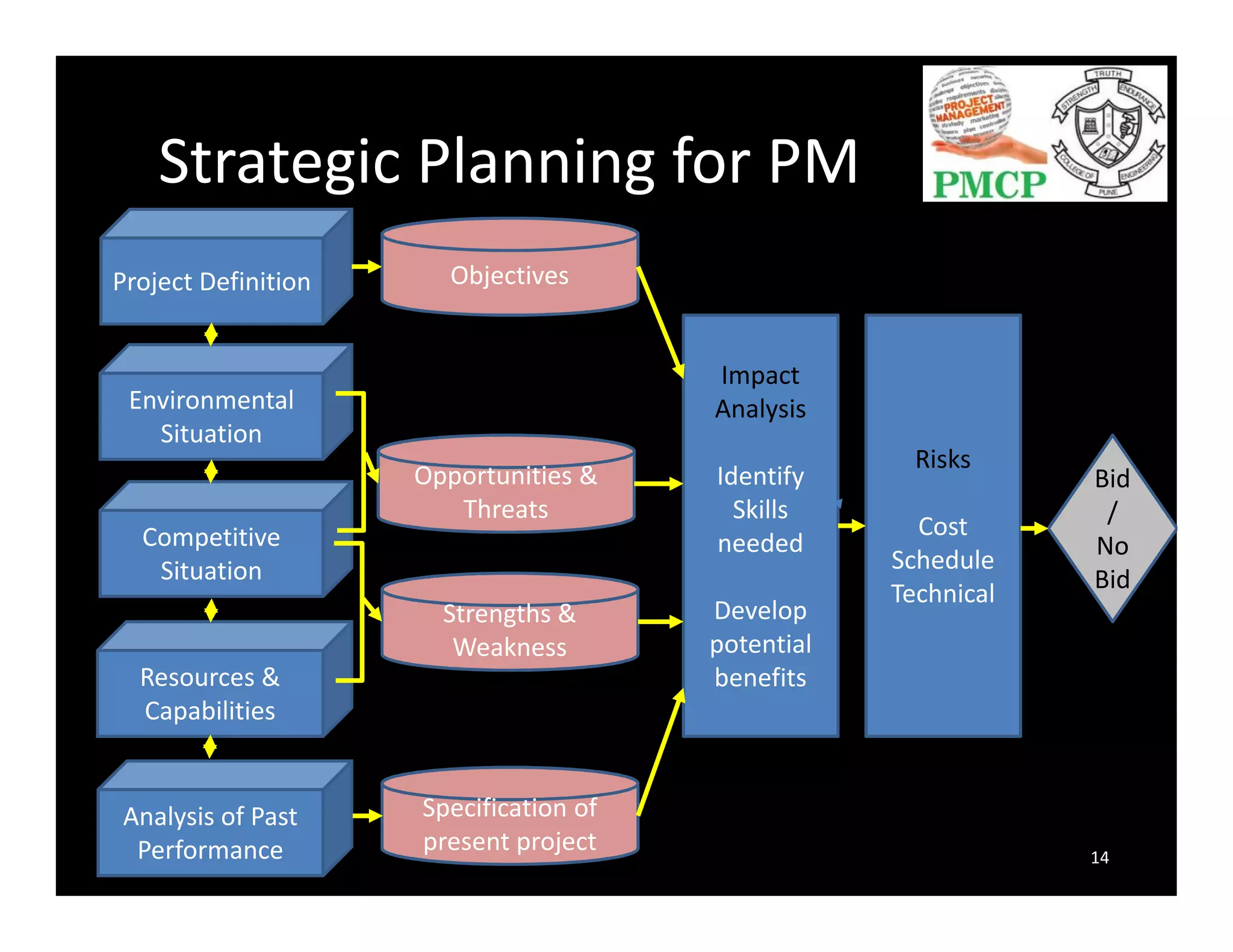
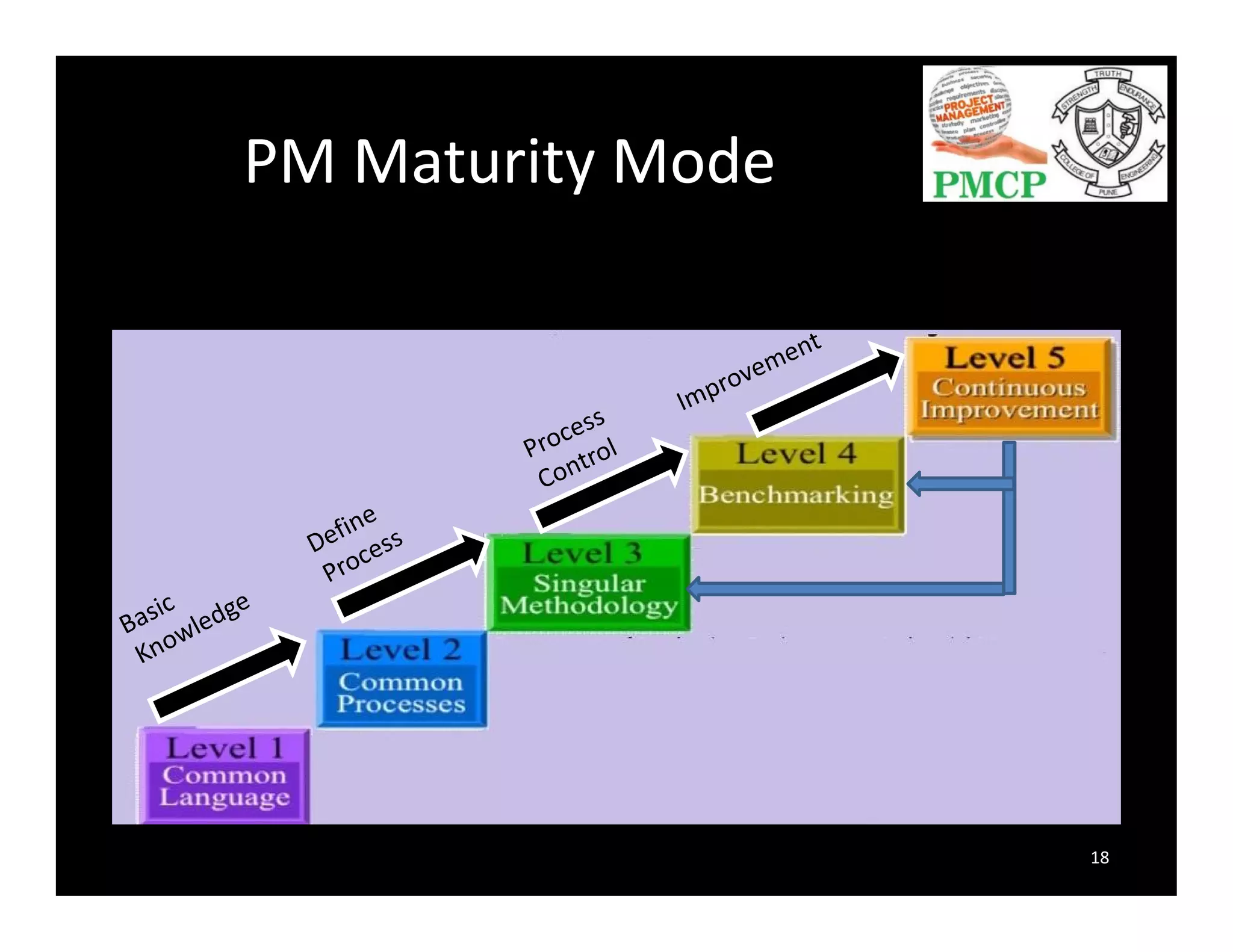
The document discusses the significance of strategic planning in project management (PM) and its evolution from being merely a scheduling tool to a recognized core competency. It outlines a PM maturity model consisting of five levels, describing behaviors, actions, and benefits at each level, and emphasizes the importance of a structured approach to enhance PM practices. It also highlights the challenges organizations face in PM, such as scope creep and misaligned schedules, and stresses the necessity for continuous communication and improvement.