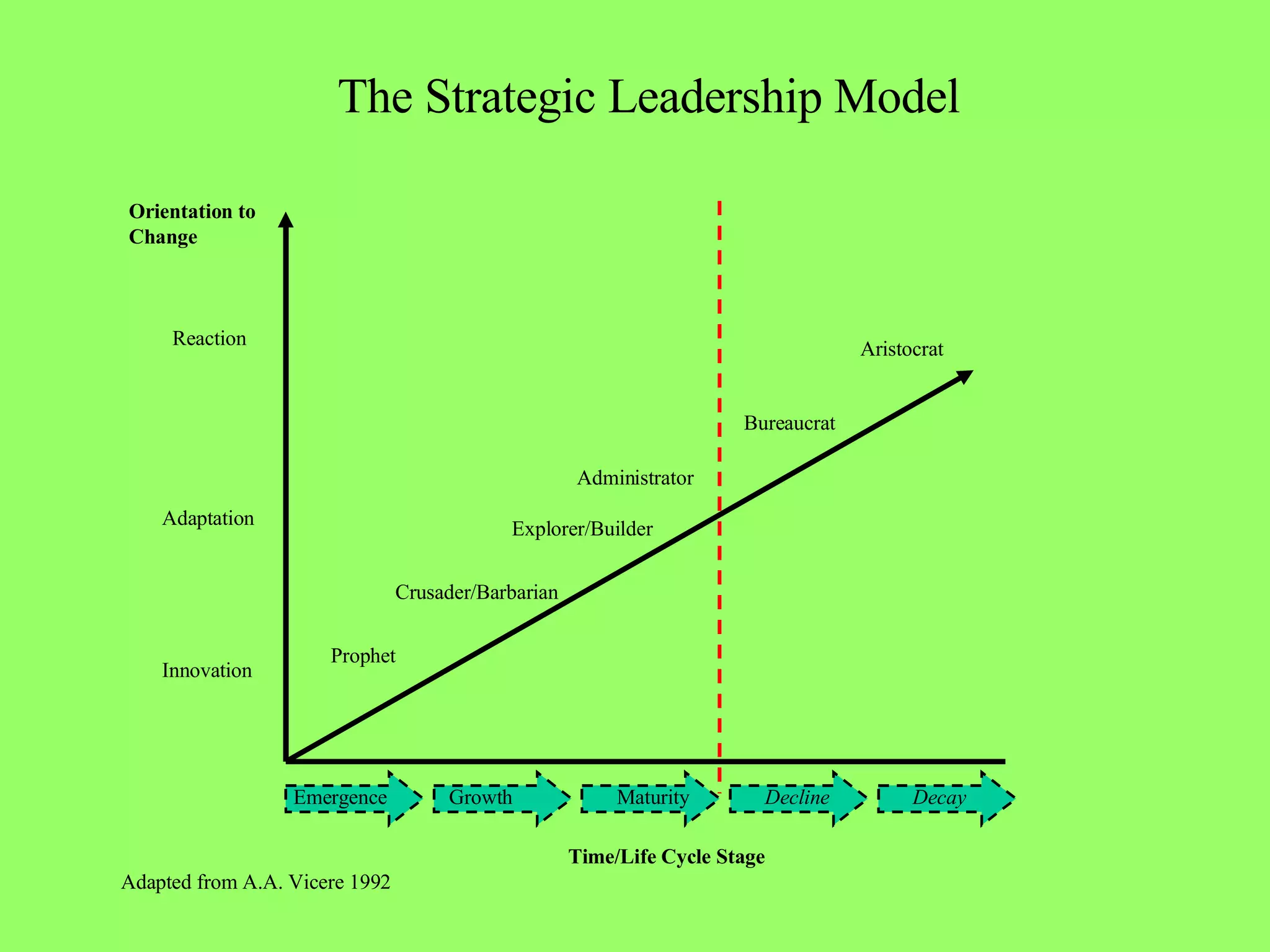
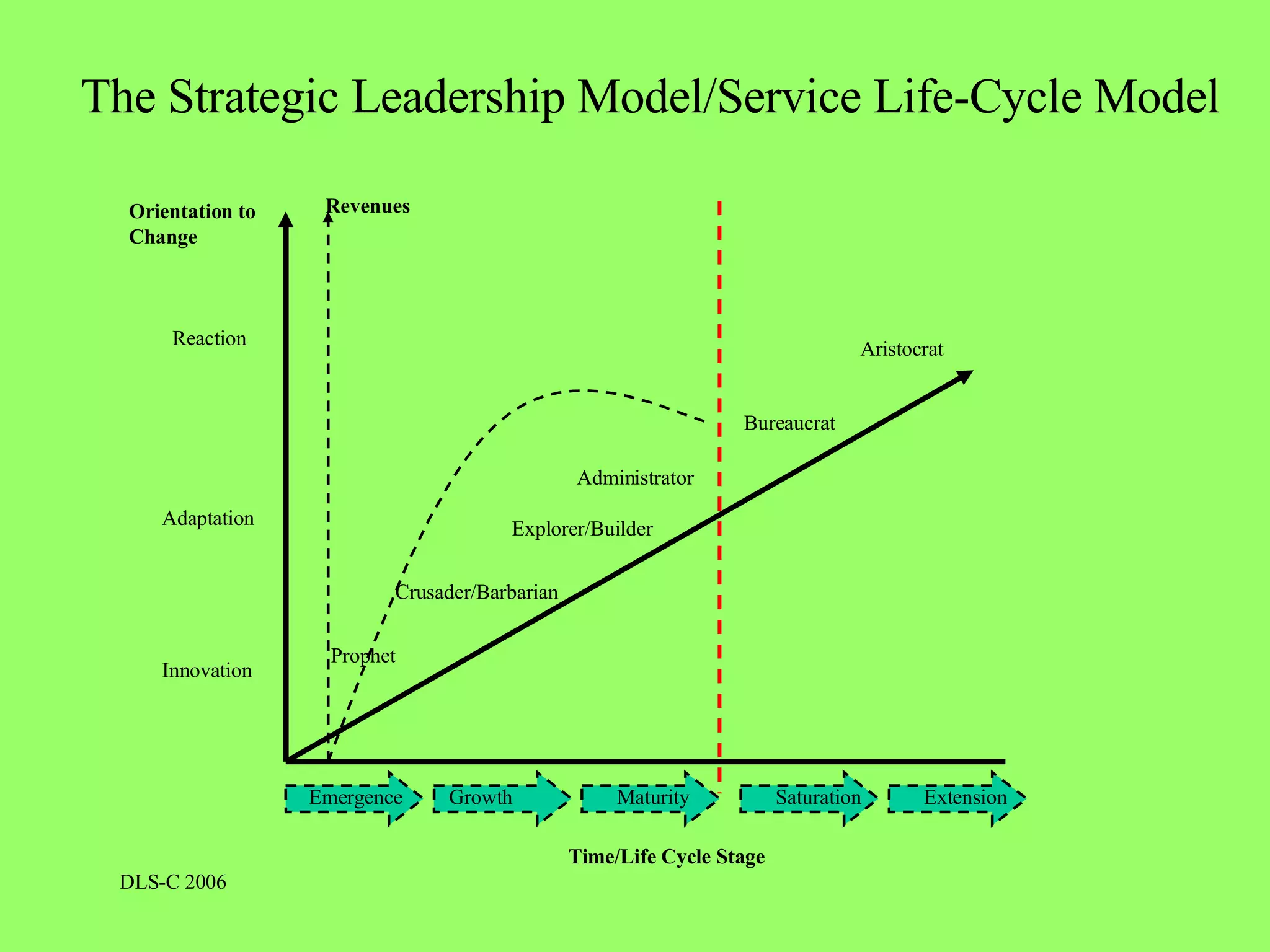
The document discusses different models of leadership and factors that contribute to effective leadership. It describes various leadership styles that are suited to different stages in an organization's lifecycle. It also discusses the need for a balanced leadership approach that incorporates innovation to enable organizations to adapt to constant and rapid change.