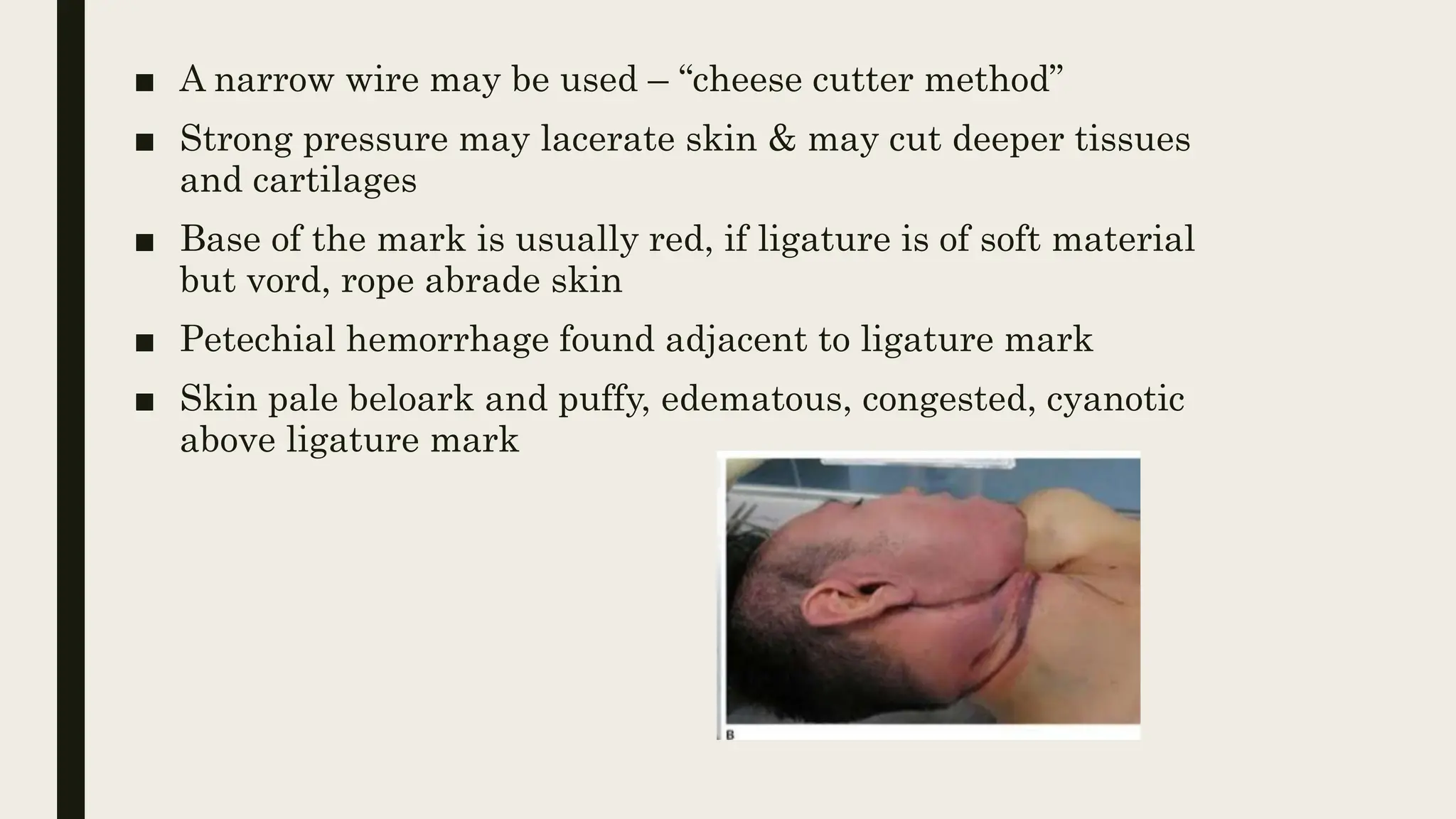
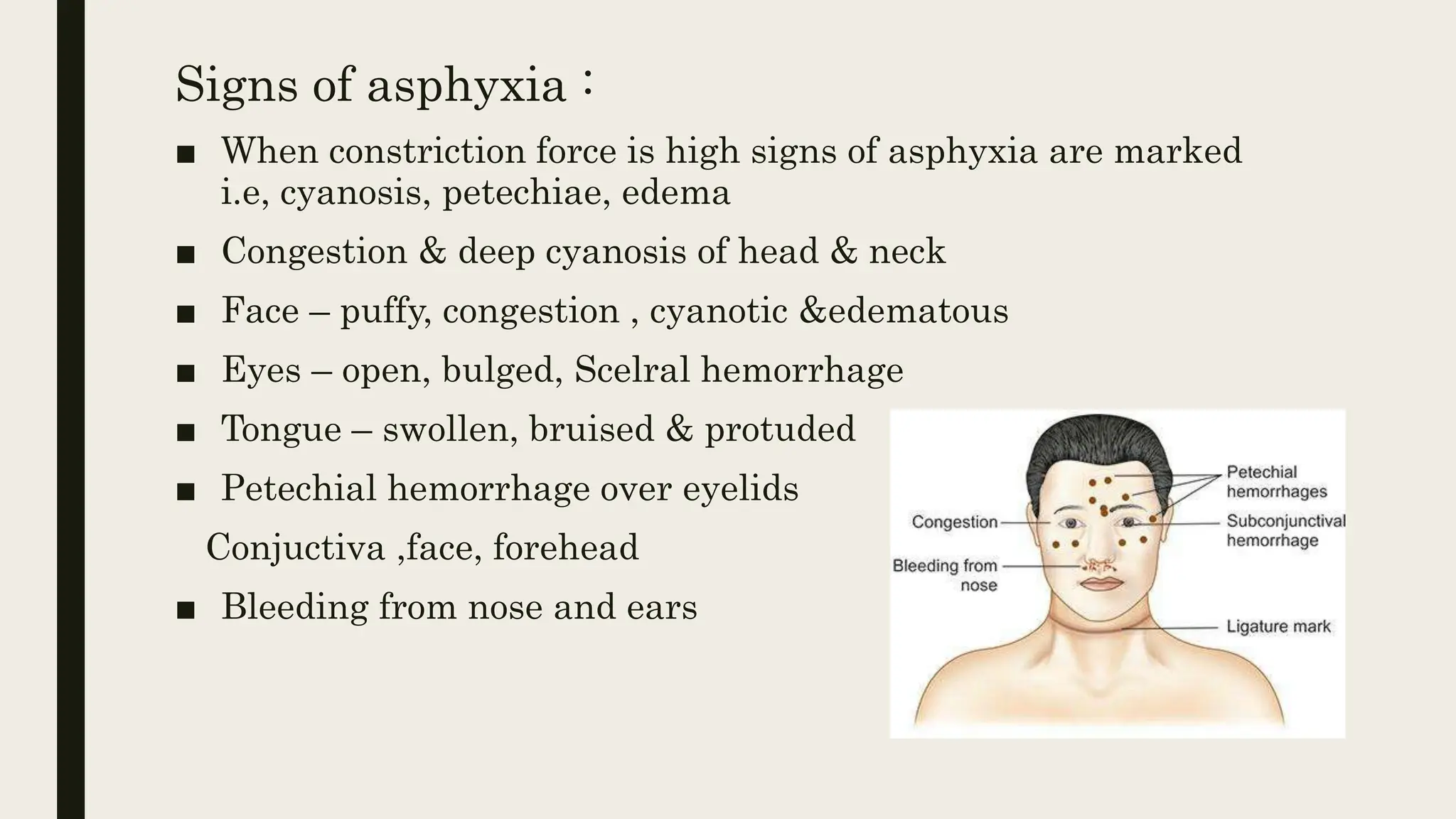
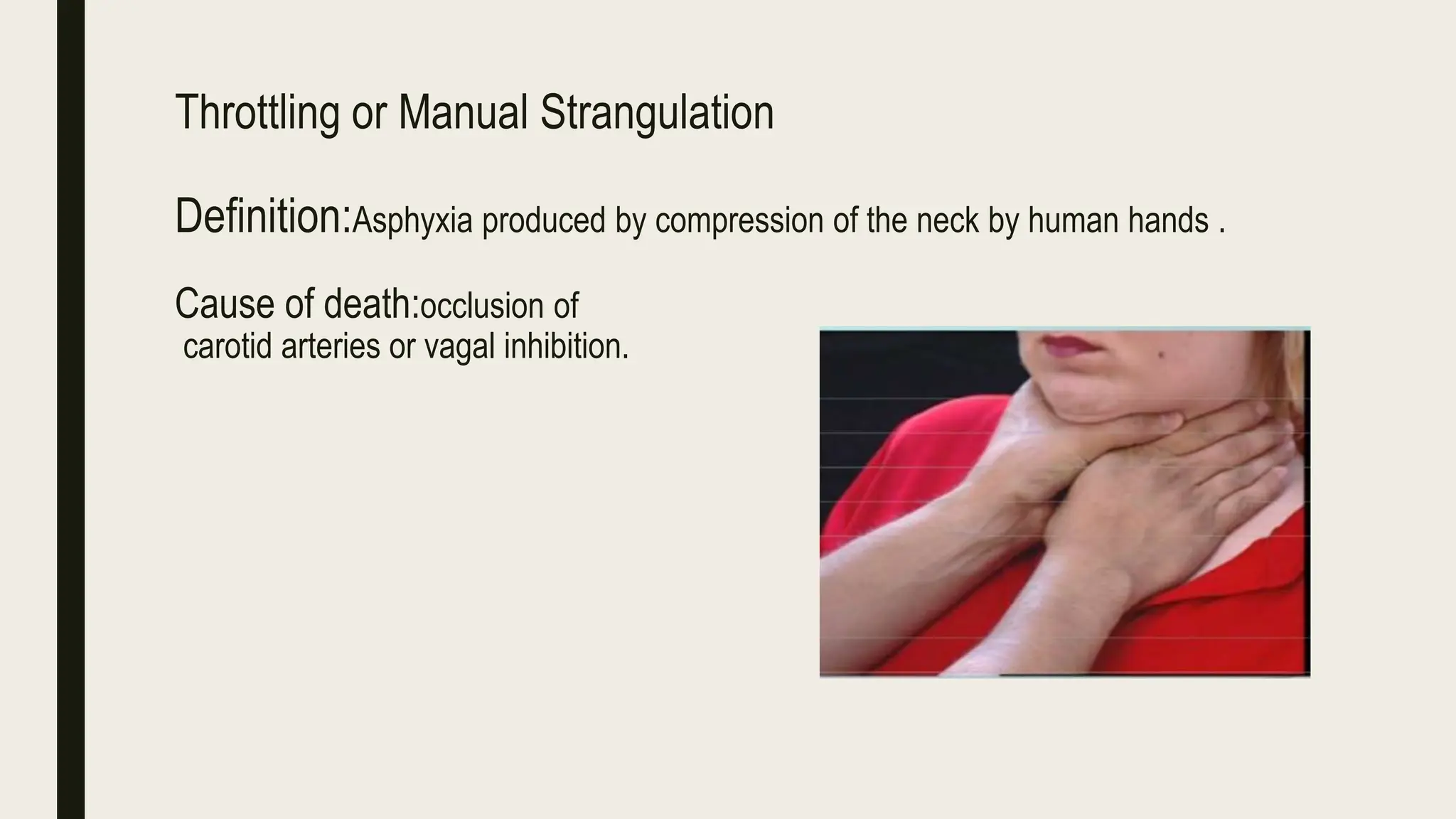
This document discusses different types of strangulation including strangulation by ligature, manual strangulation, garroting, mugging, and bansdola. It provides details on the definition, causes of death, and postmortem appearances of strangulation by ligature and manual strangulation. Signs of asphyxia, ligature marks, bruising and fractures that may be seen externally and internally are described. The medicolegal importance of determining whether cases are homicide, accidental, or suicidal is also mentioned.