1. A stool analysis examines the waste residue of undigested food and materials, intestinal secretions, epithelial cells, bacteria, and inorganic materials that are excreted in feces.
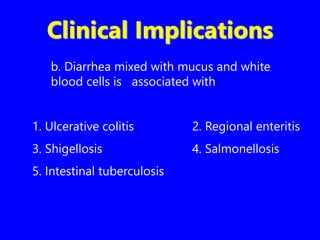
2. The color, consistency, presence of blood, mucus, fat, or parasites can provide clinical implications about gastrointestinal diseases and malabsorption syndromes.
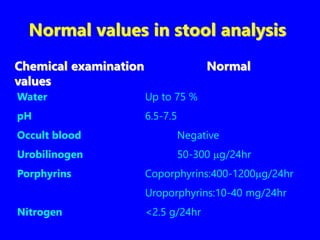
3. Chemical analyses of pH, urobilinogen, porphyrins, electrolytes, fat, and enzymes like trypsin in stool samples can help diagnose conditions affecting the liver, pancreas, and absorption of nutrients in the bowels.