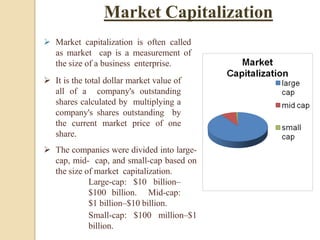
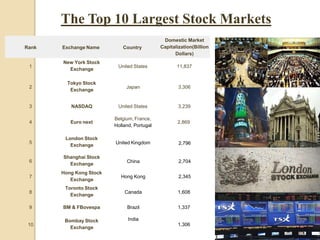
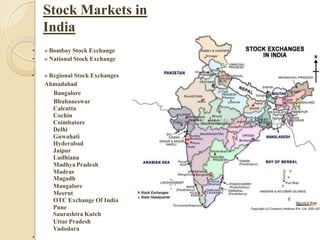
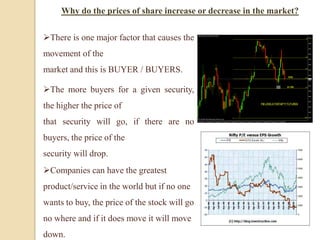
The stock market and share market are essentially the same thing. They both refer to an exchange where buyers and sellers can trade stocks or shares, which are units of ownership in a company. A stock market provides liquidity for these transactions. The major stock markets in India are the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE). Investors can analyze companies through fundamental and technical analysis to determine when to buy and sell stocks.