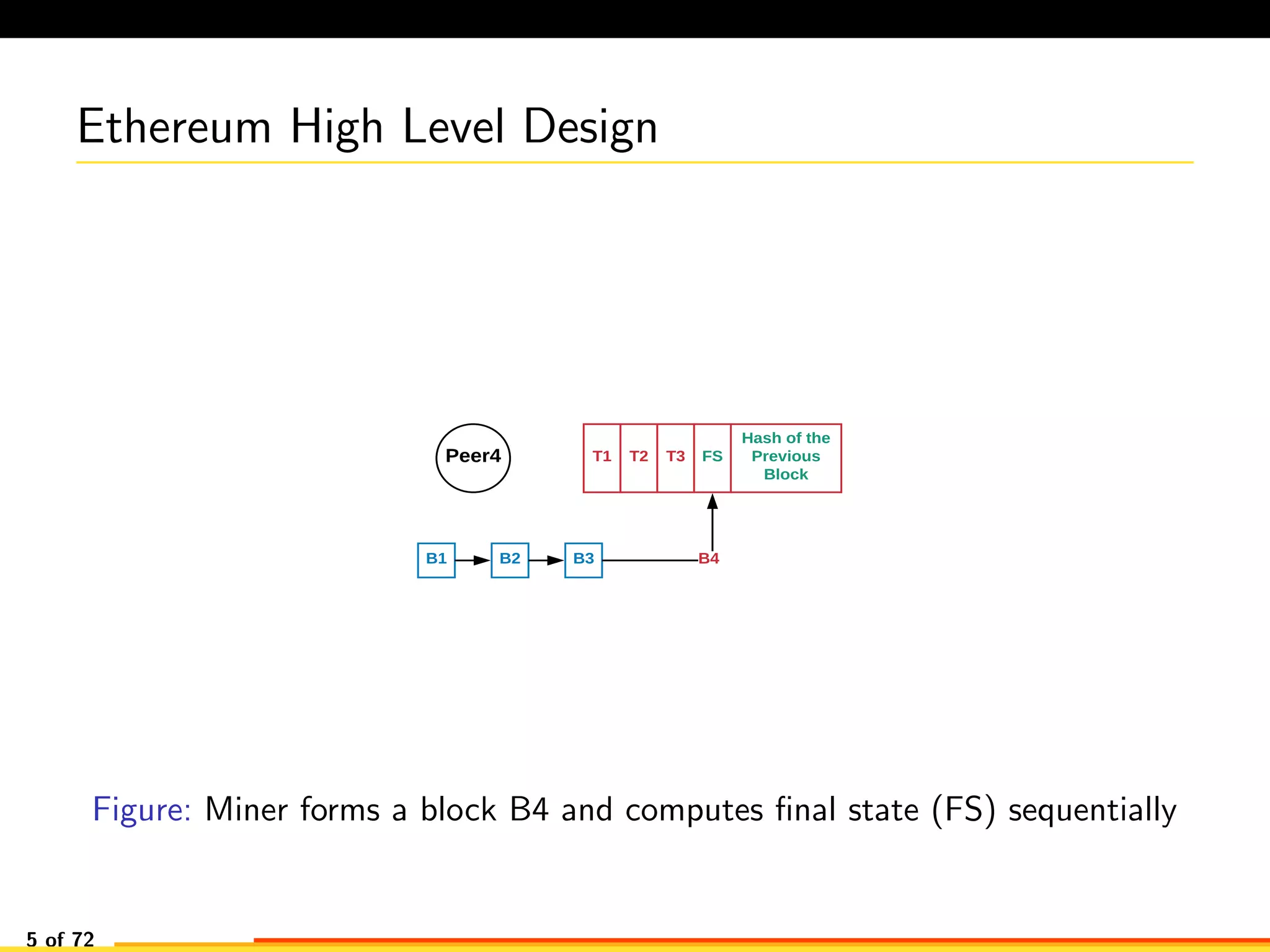
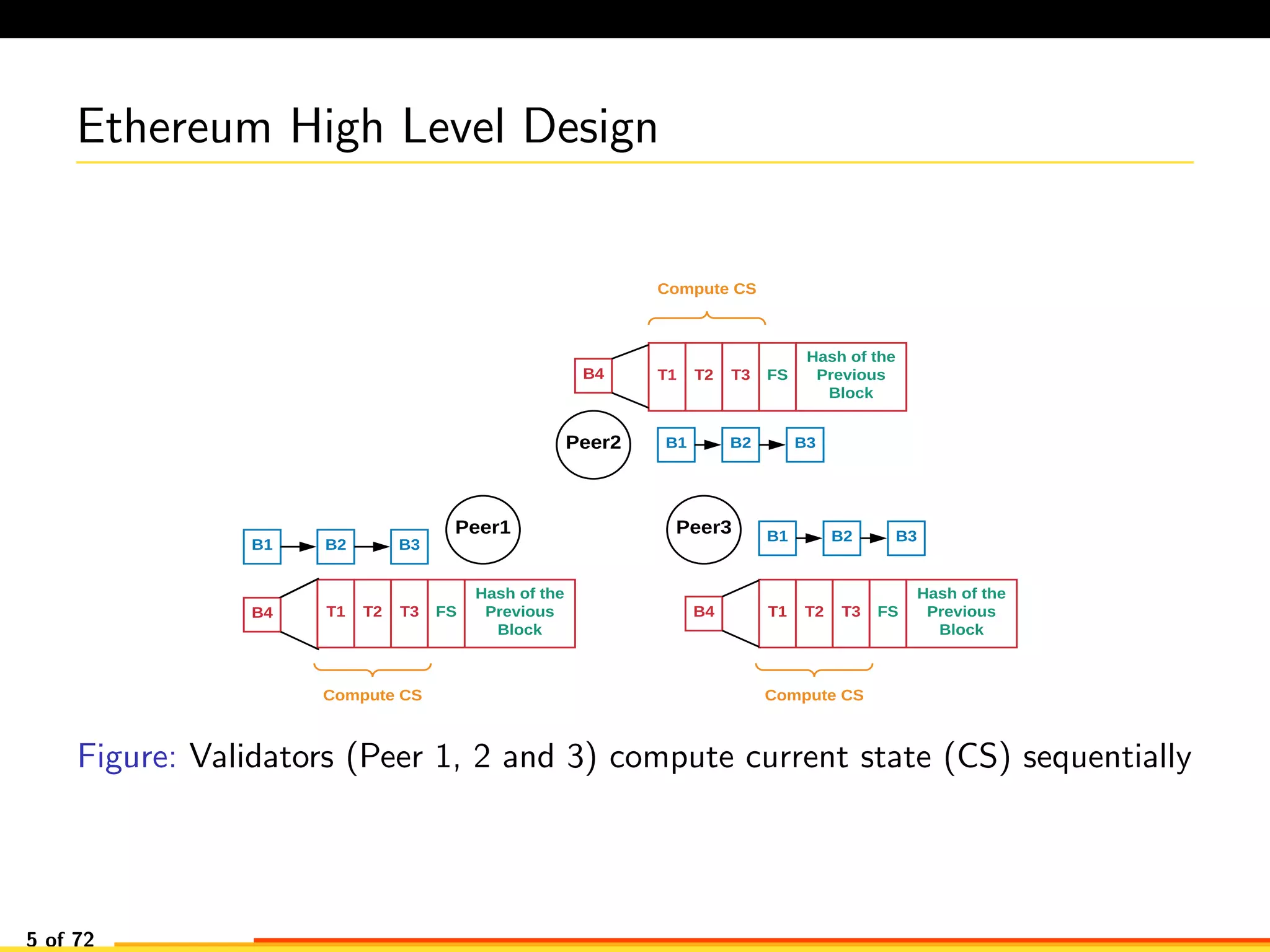
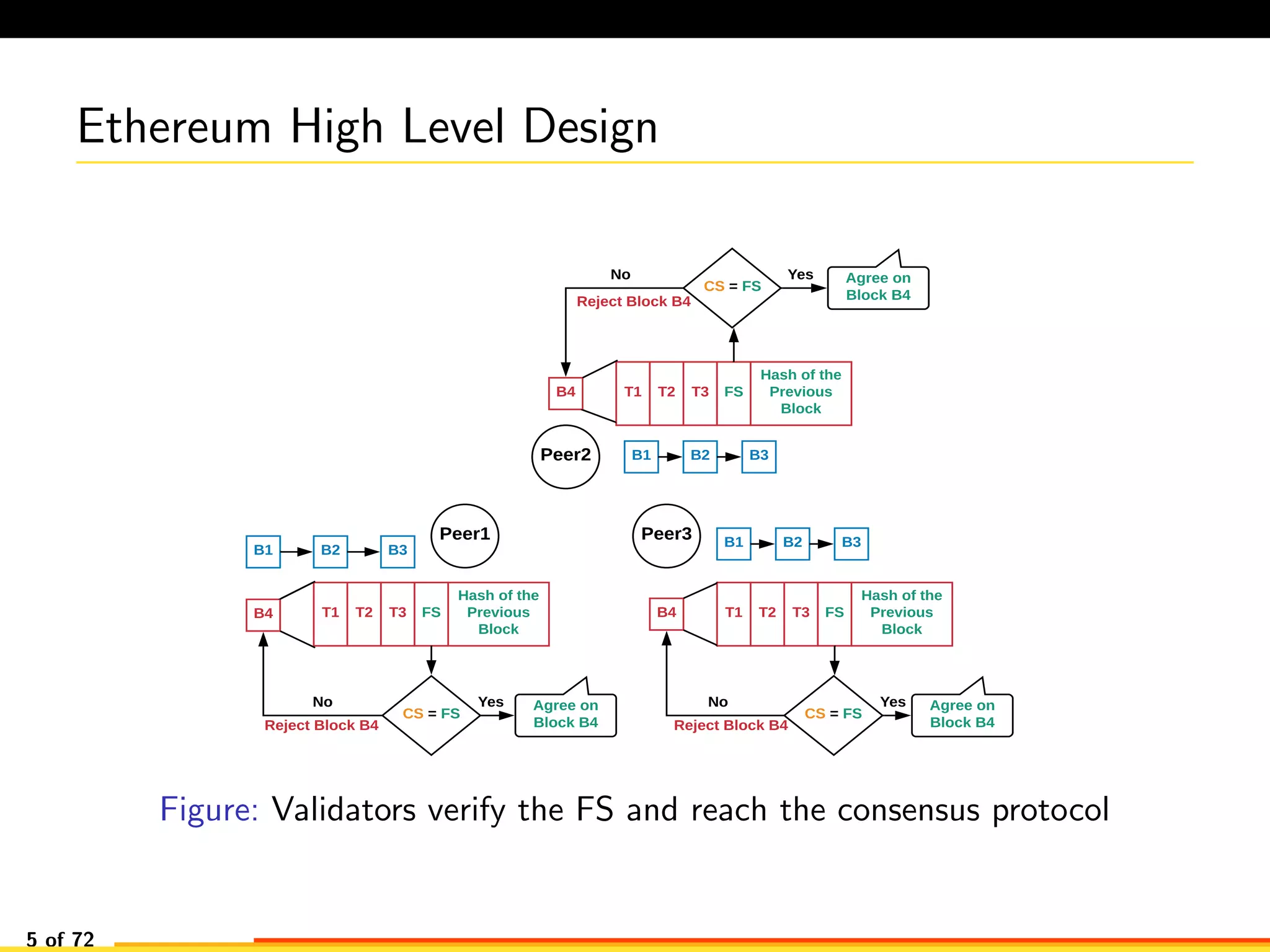
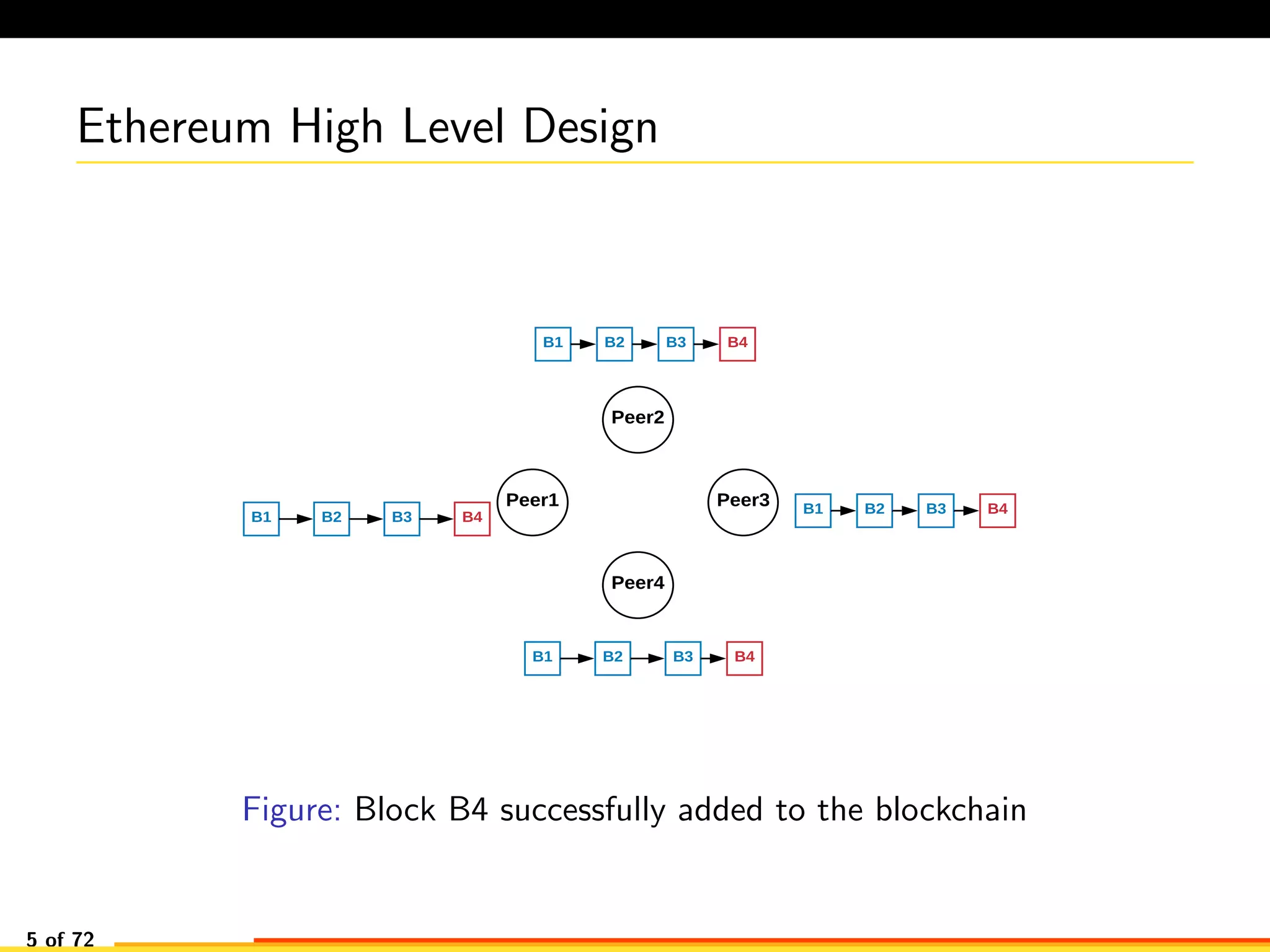
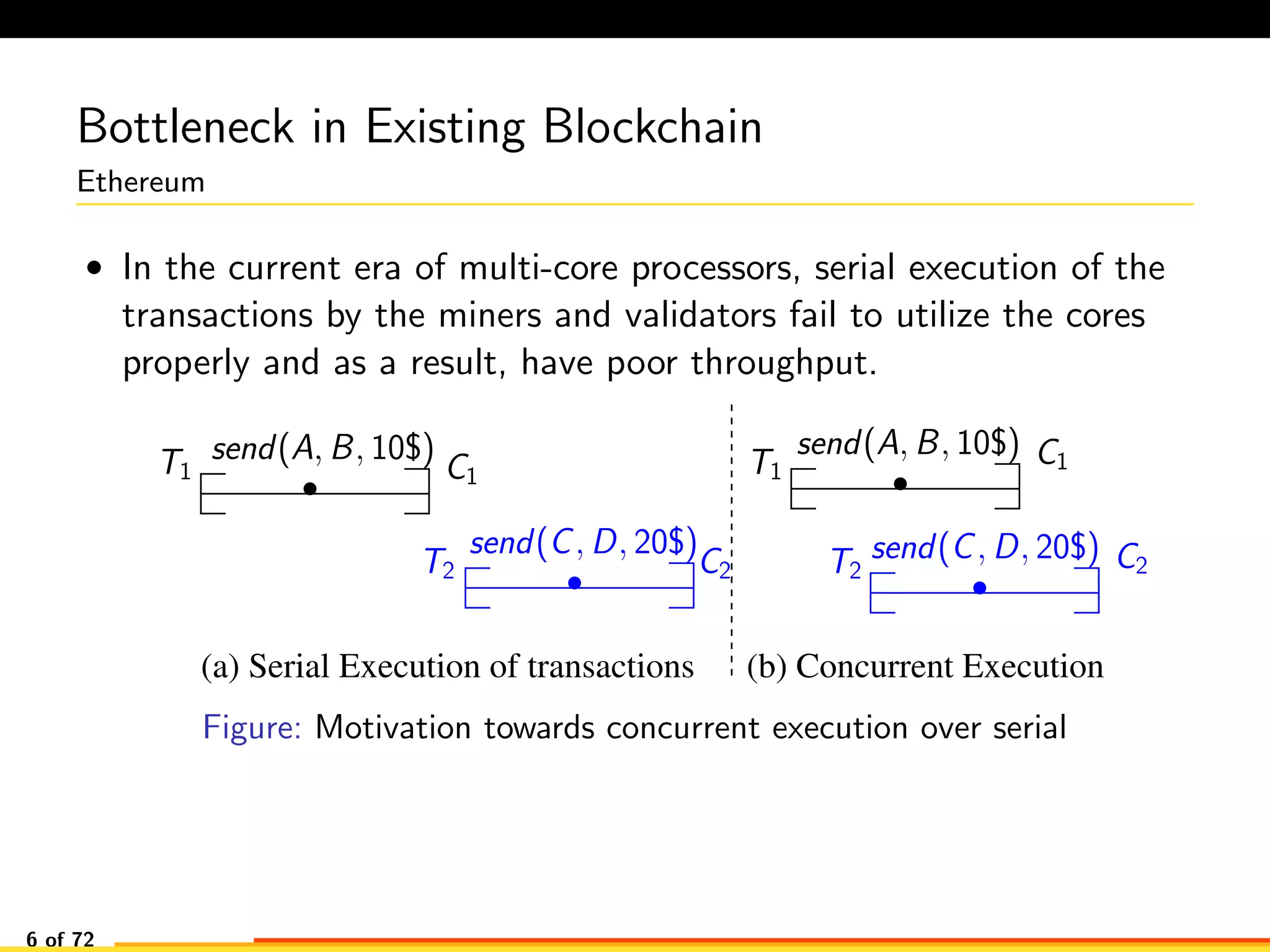
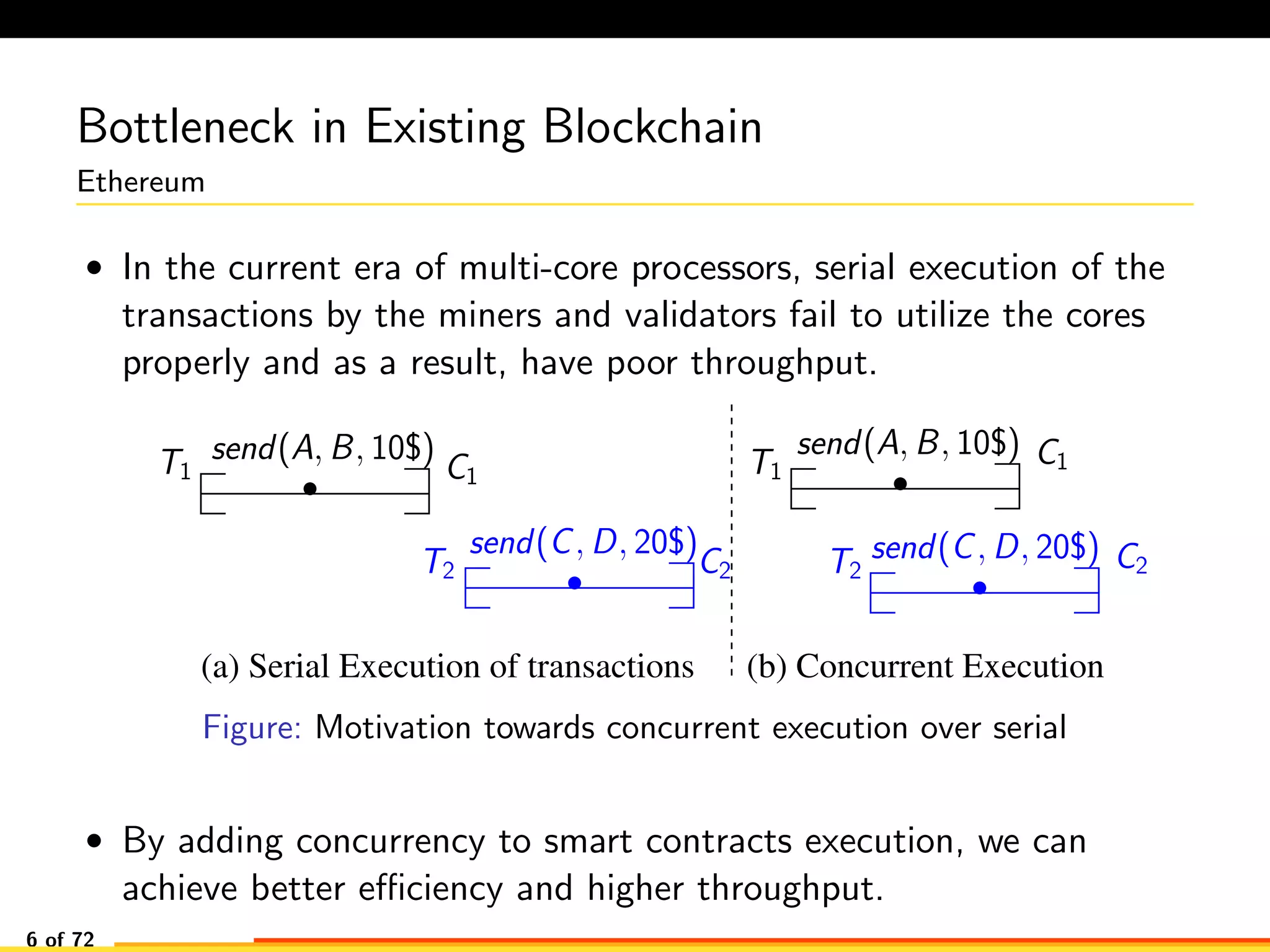
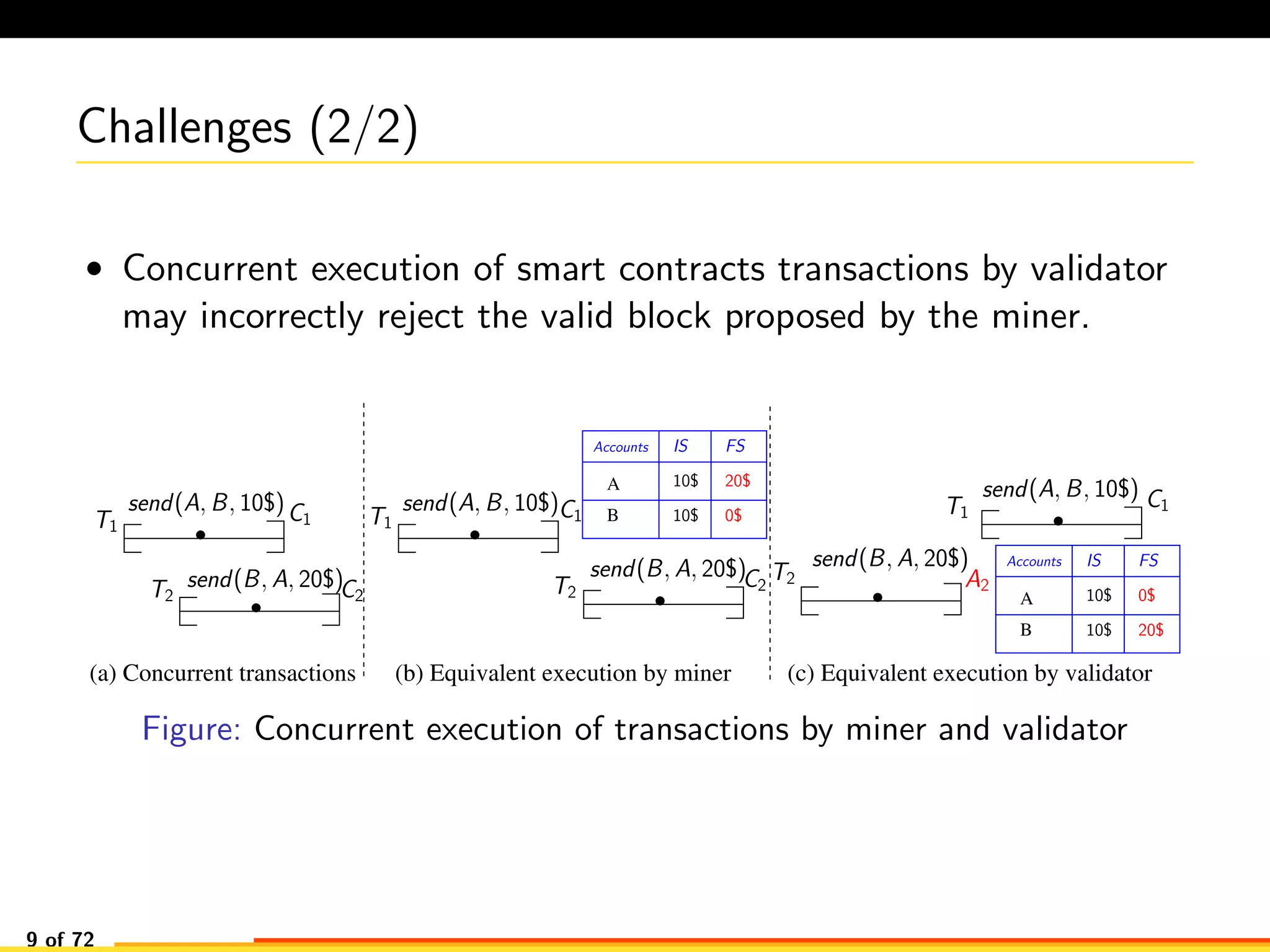
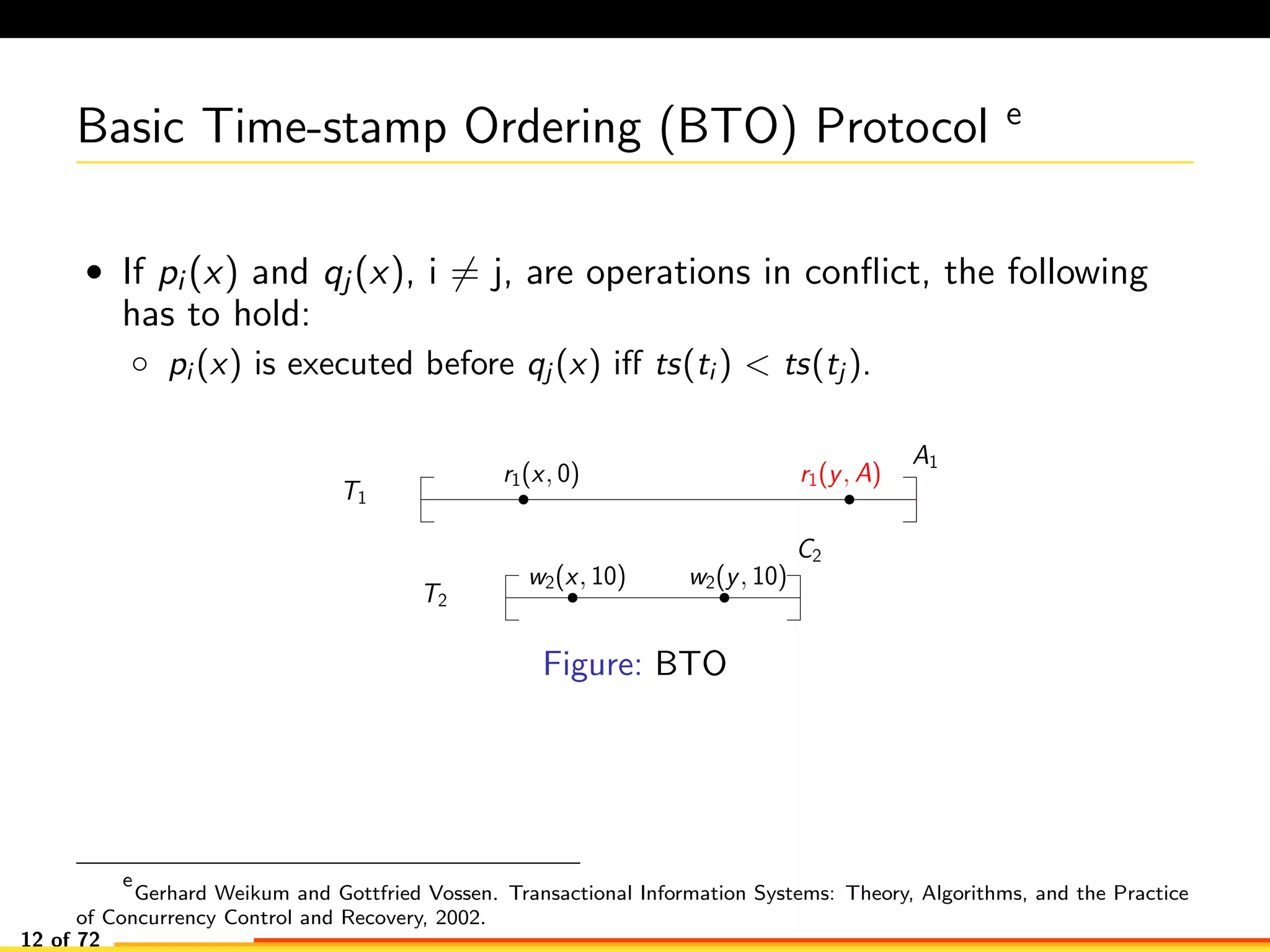
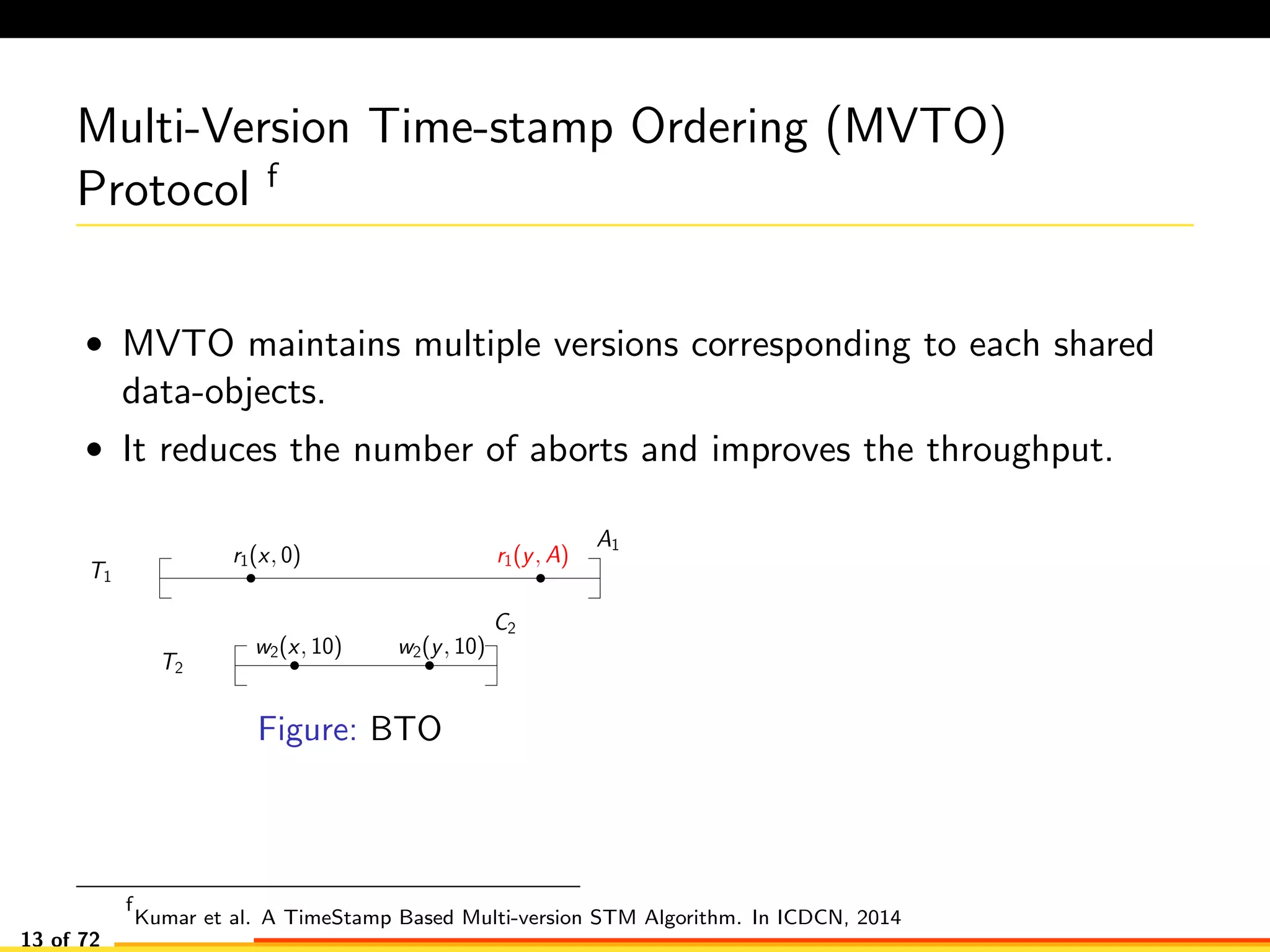
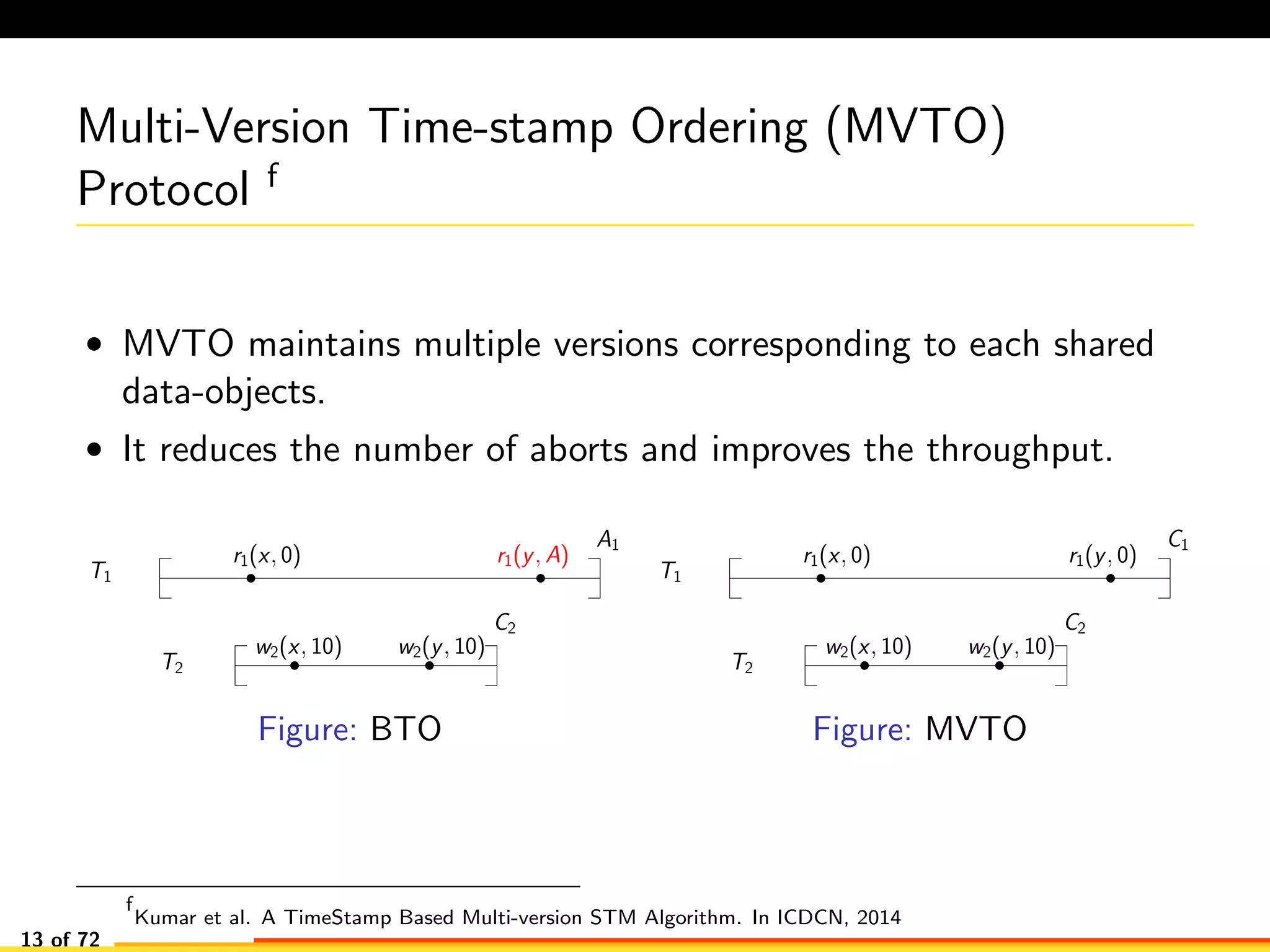
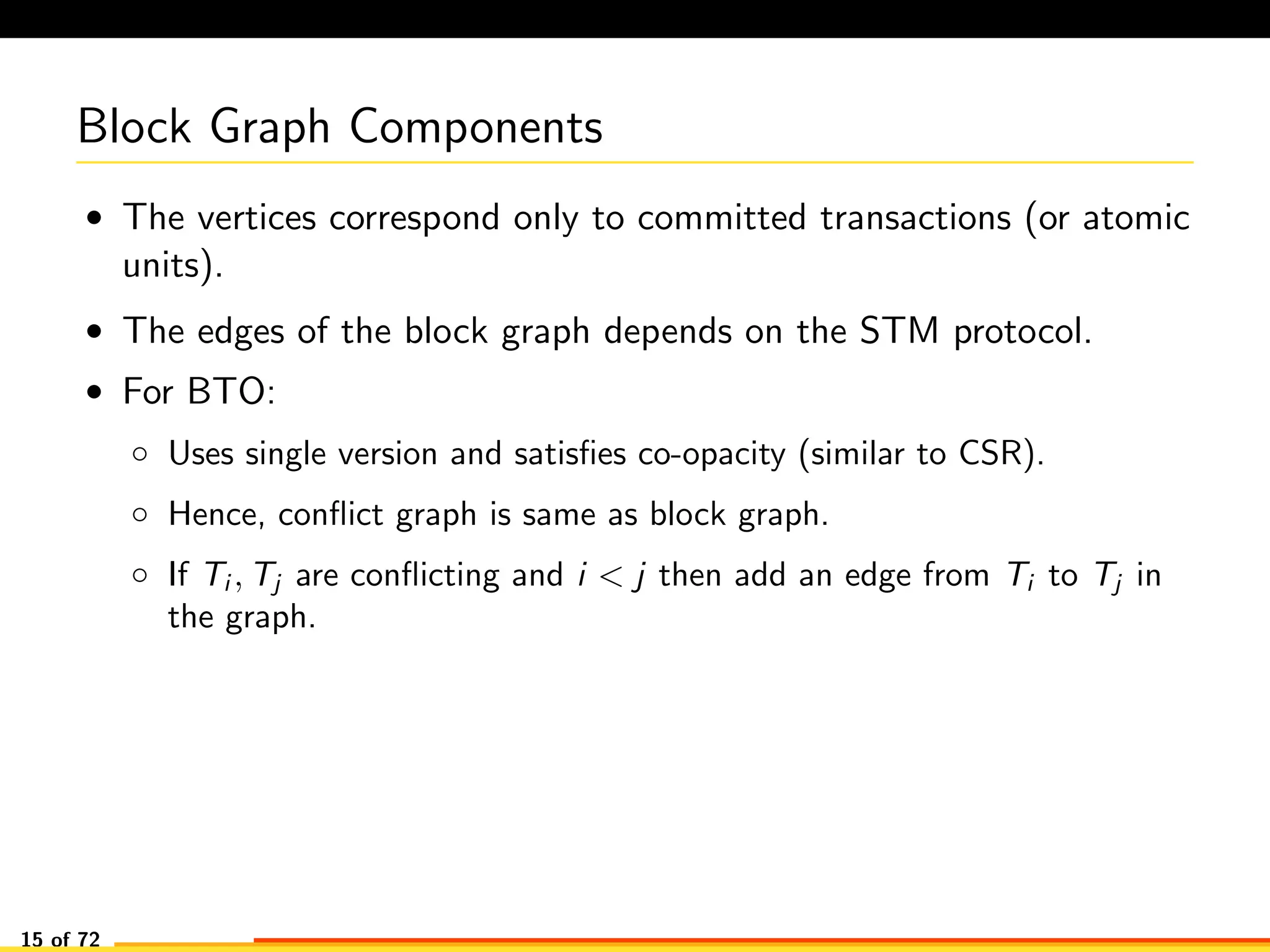
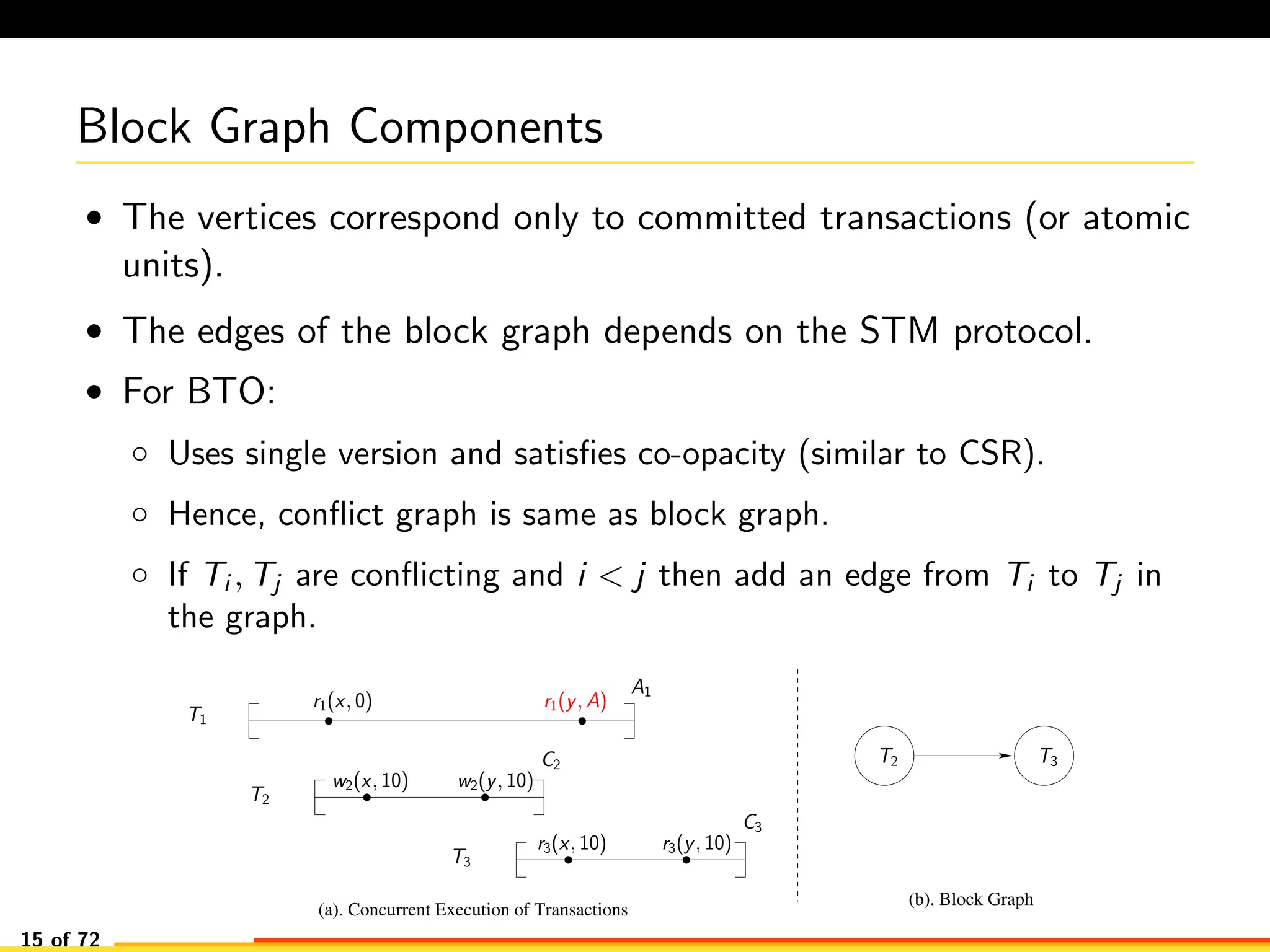
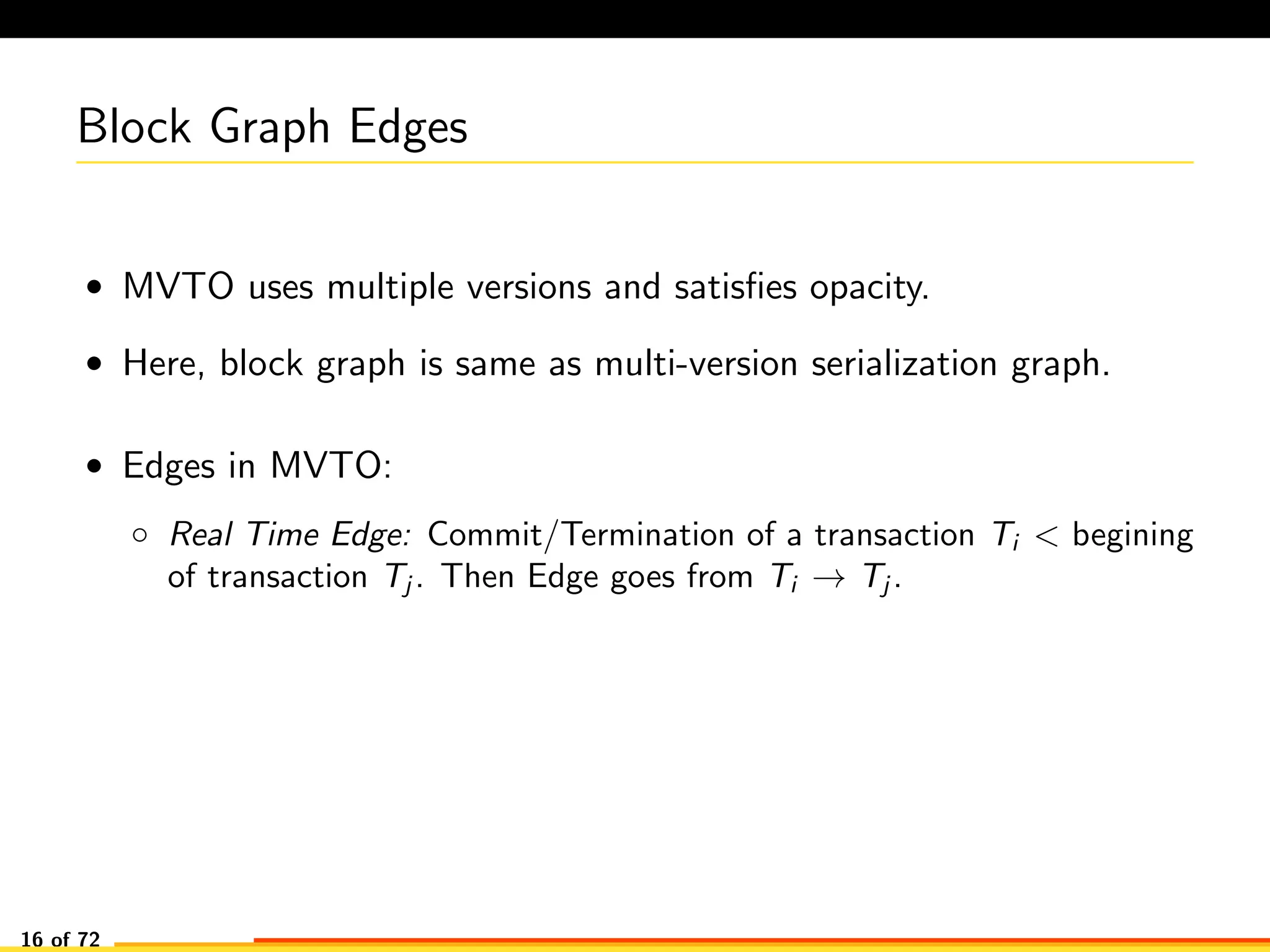
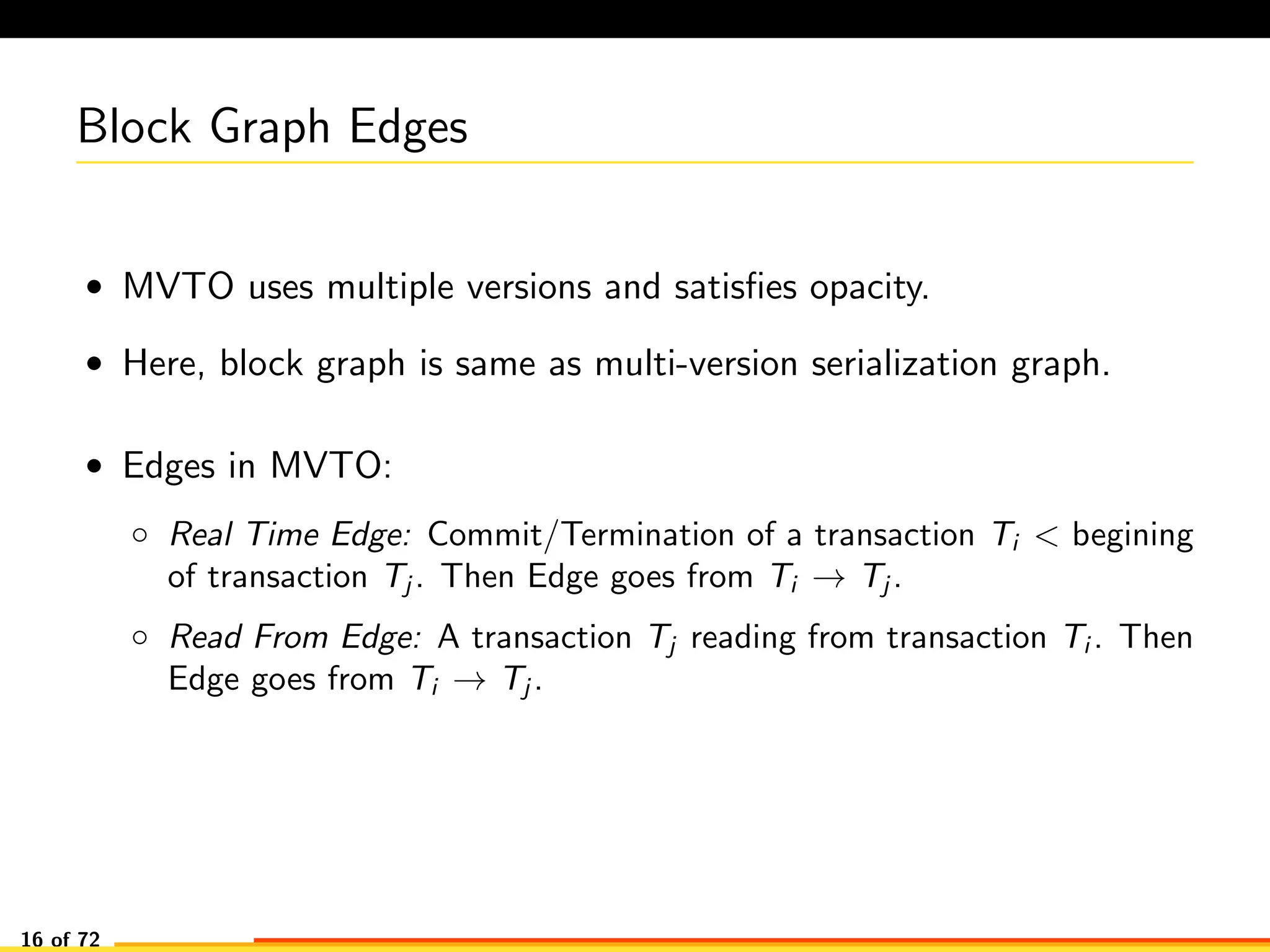
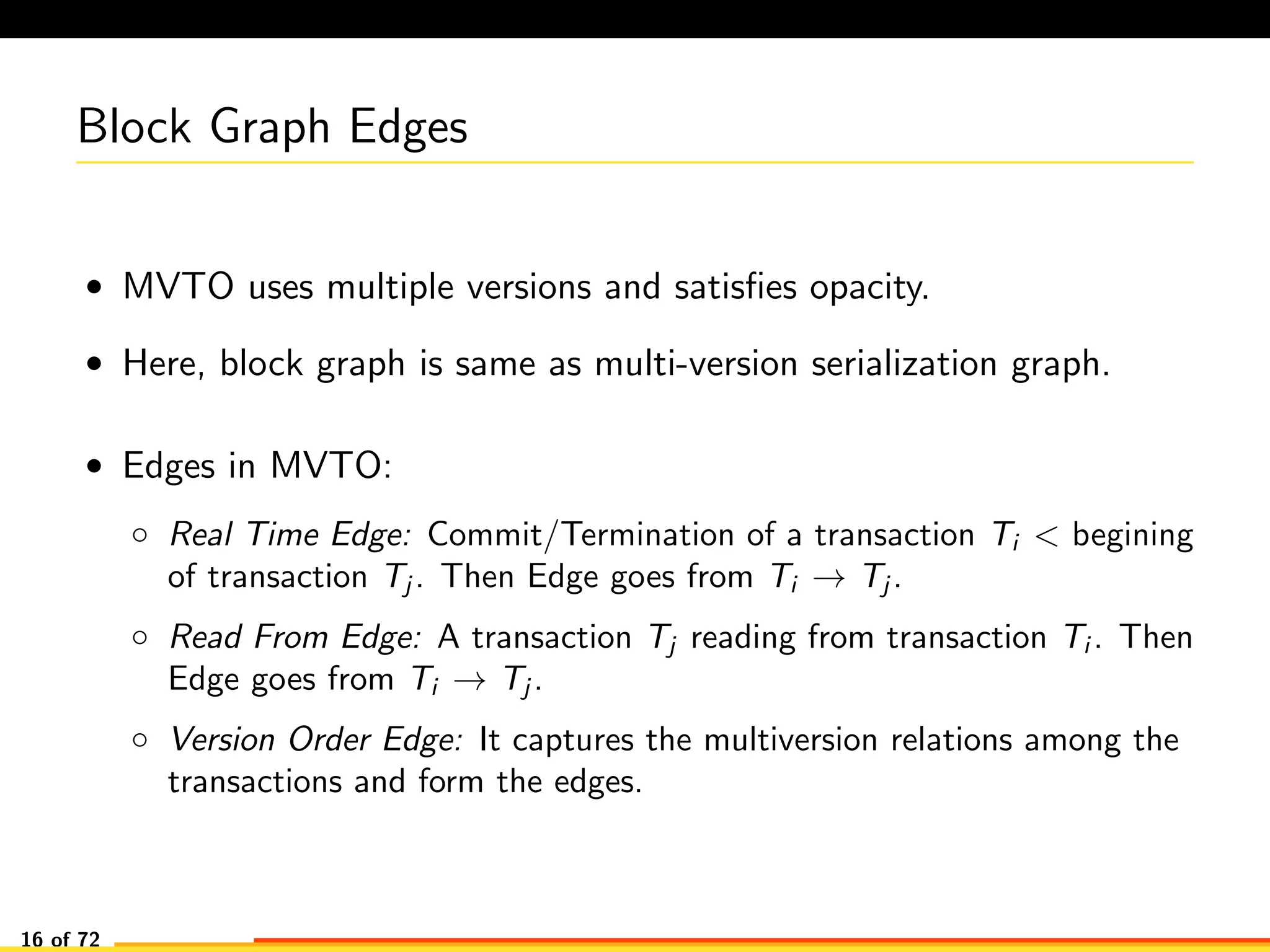
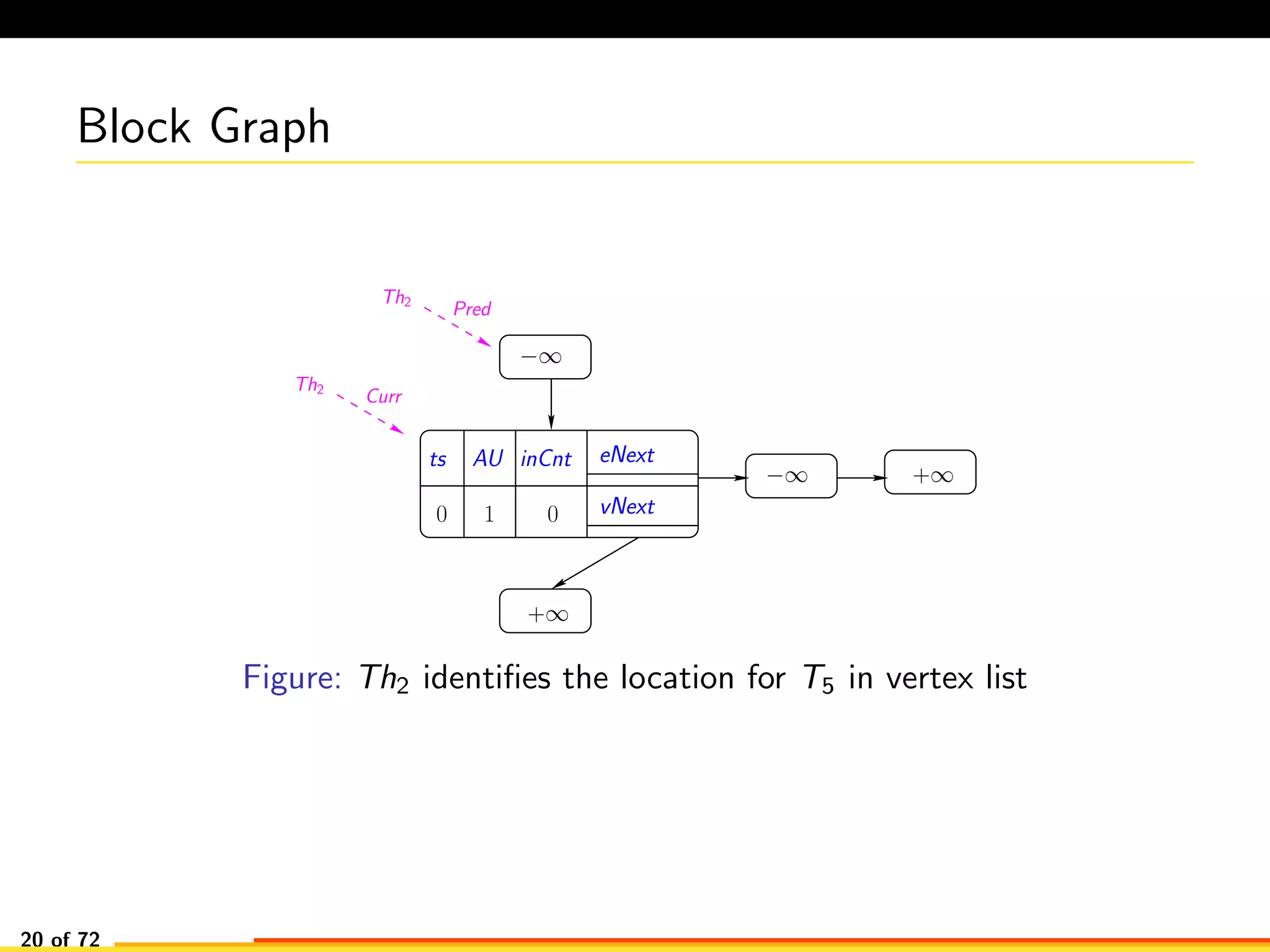
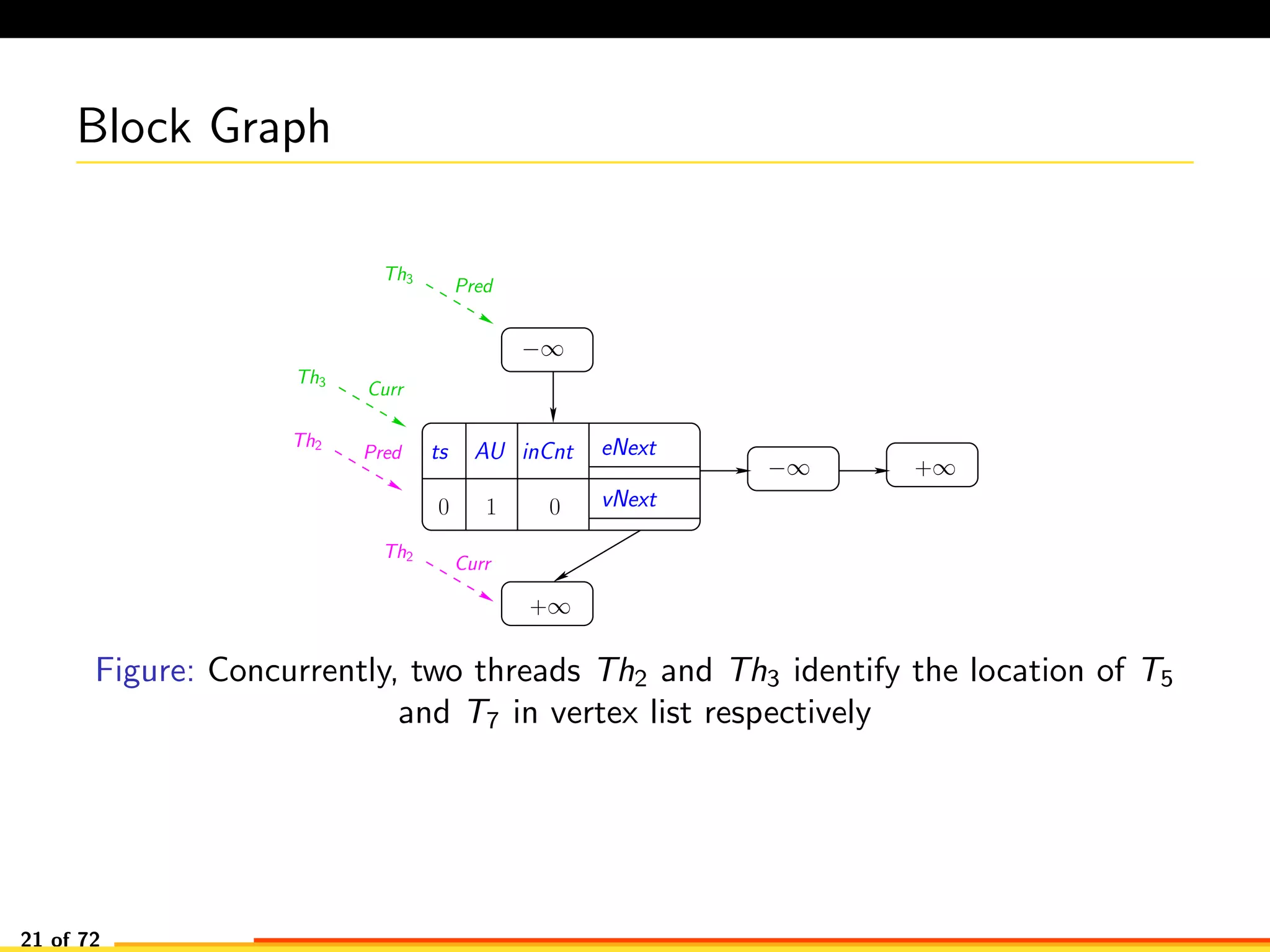
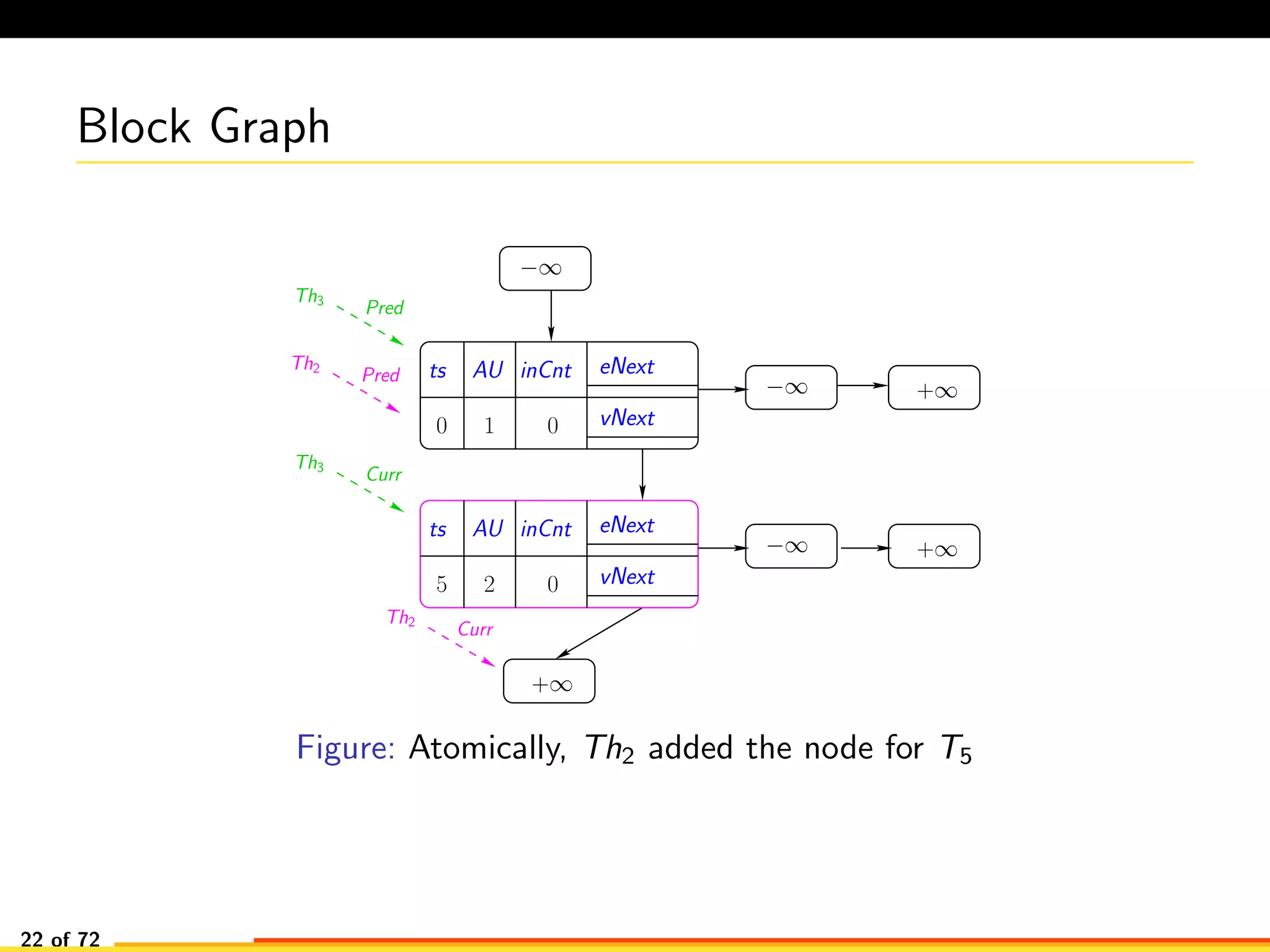
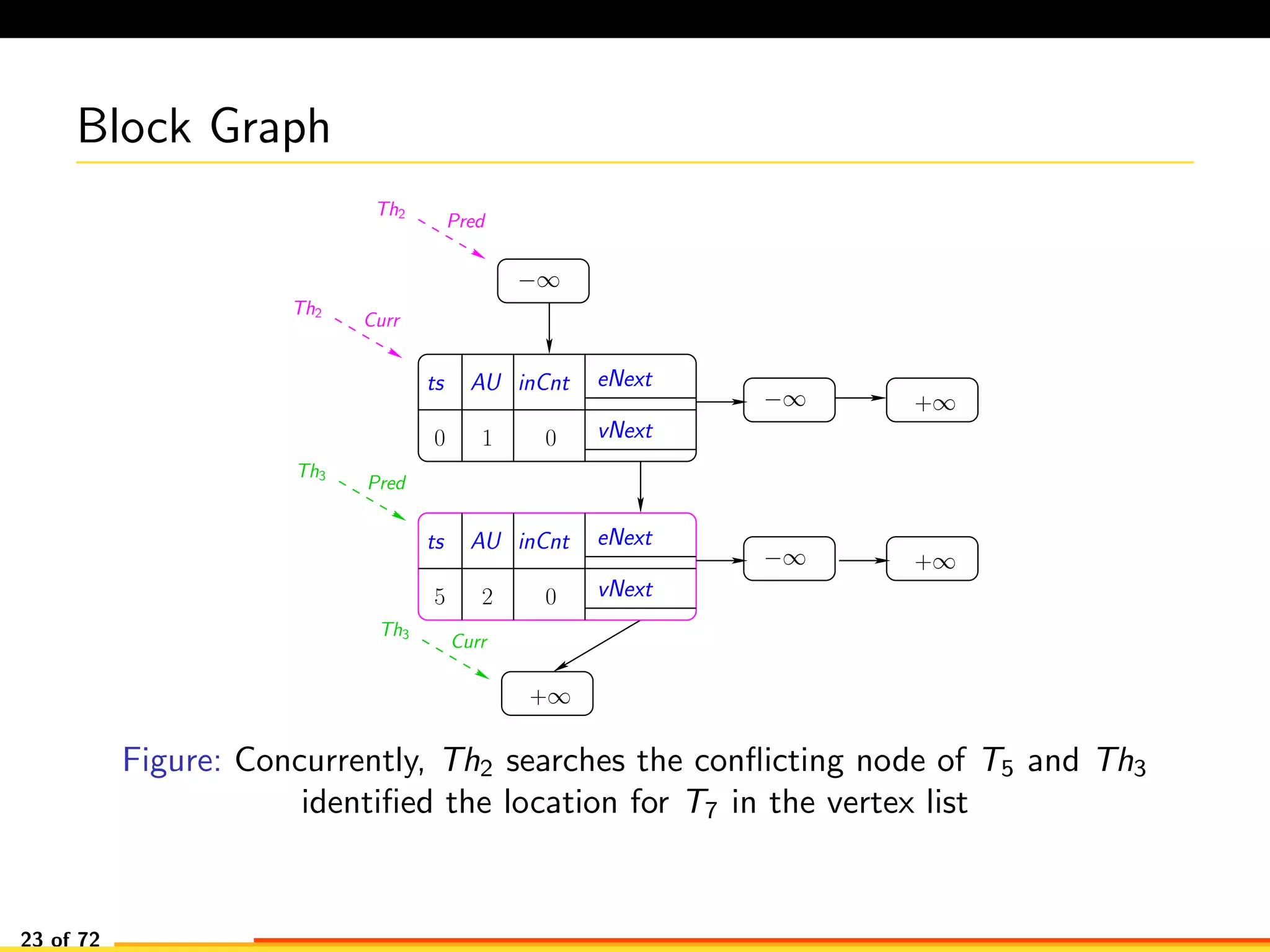
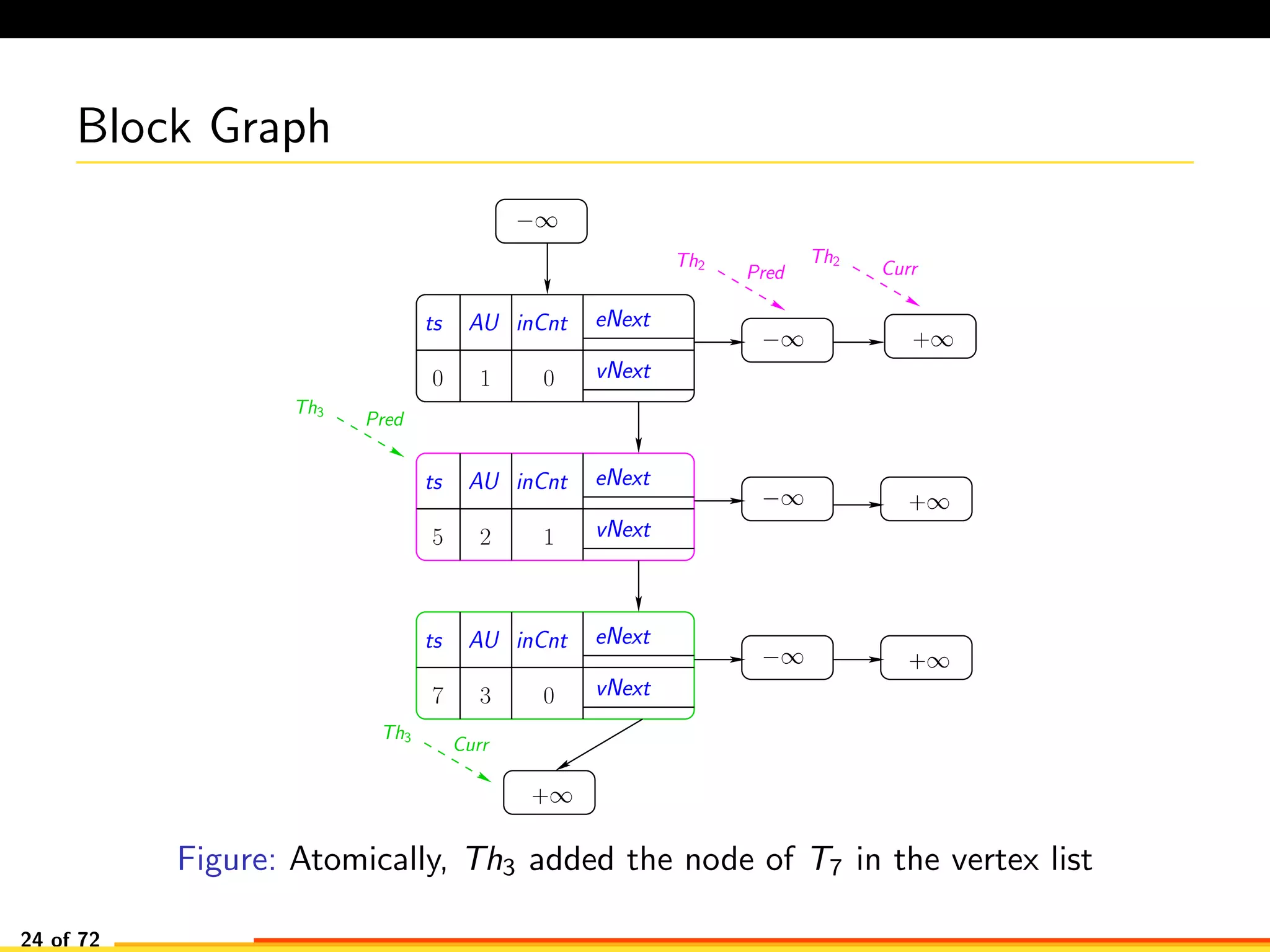
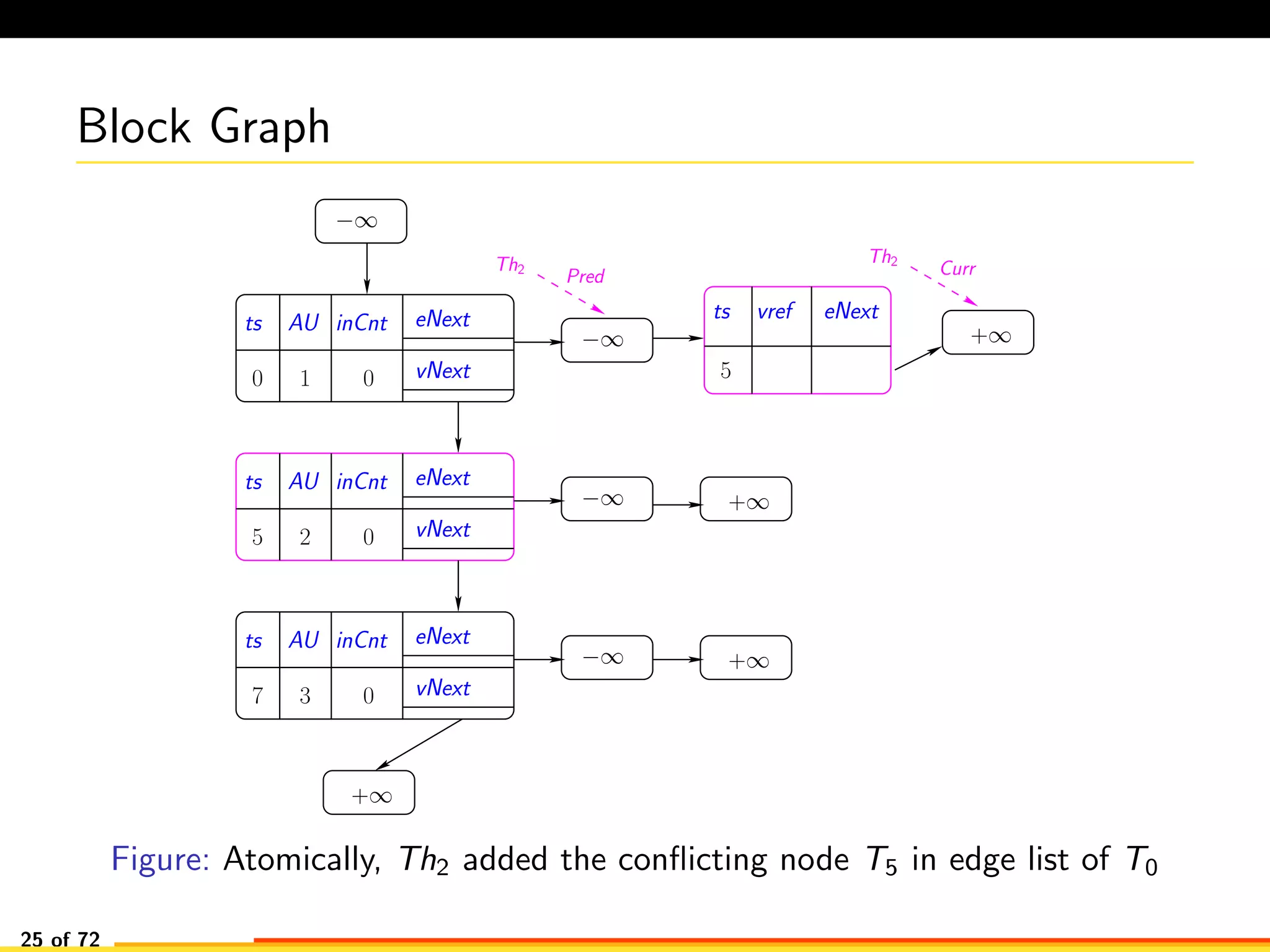
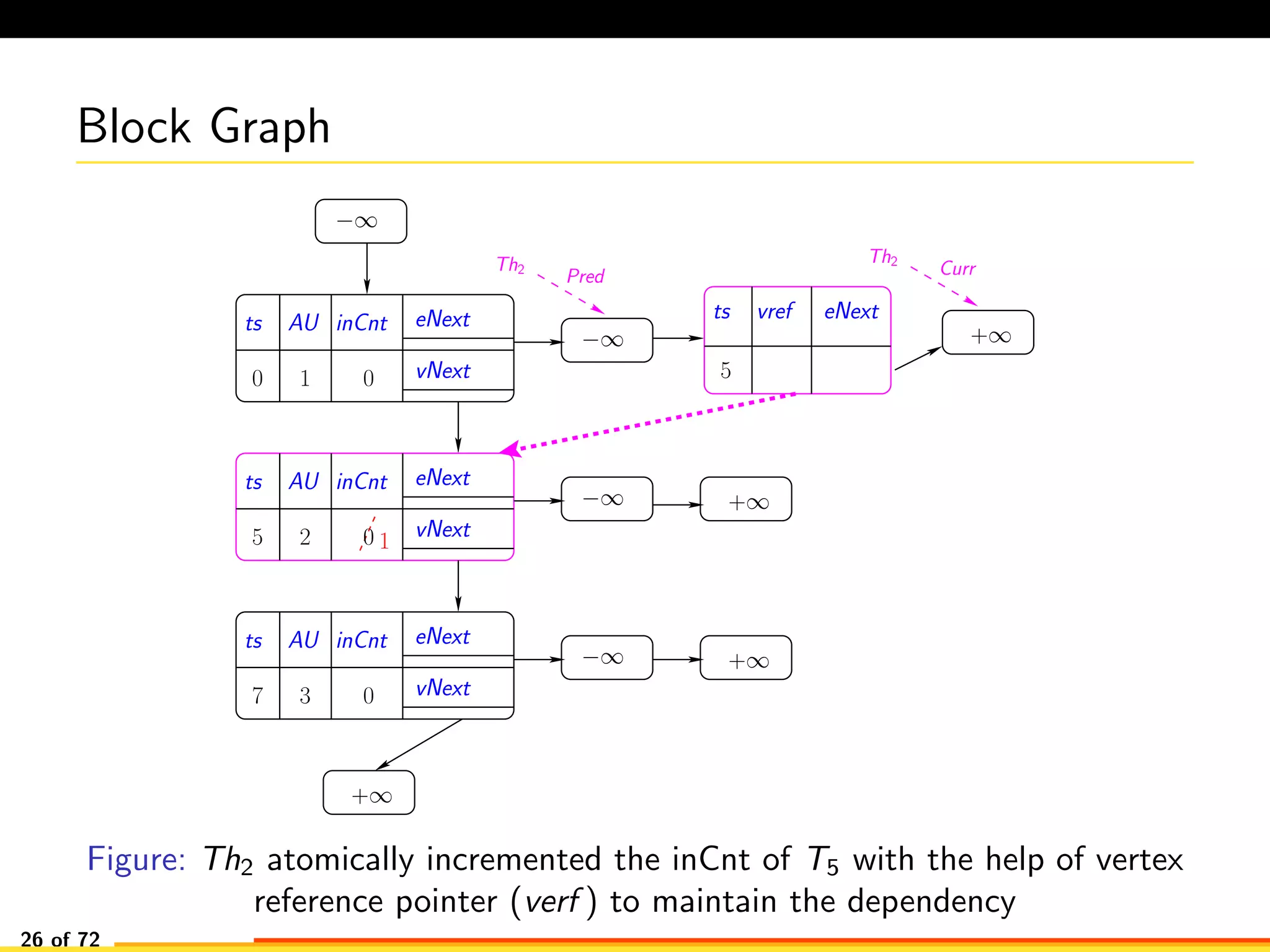
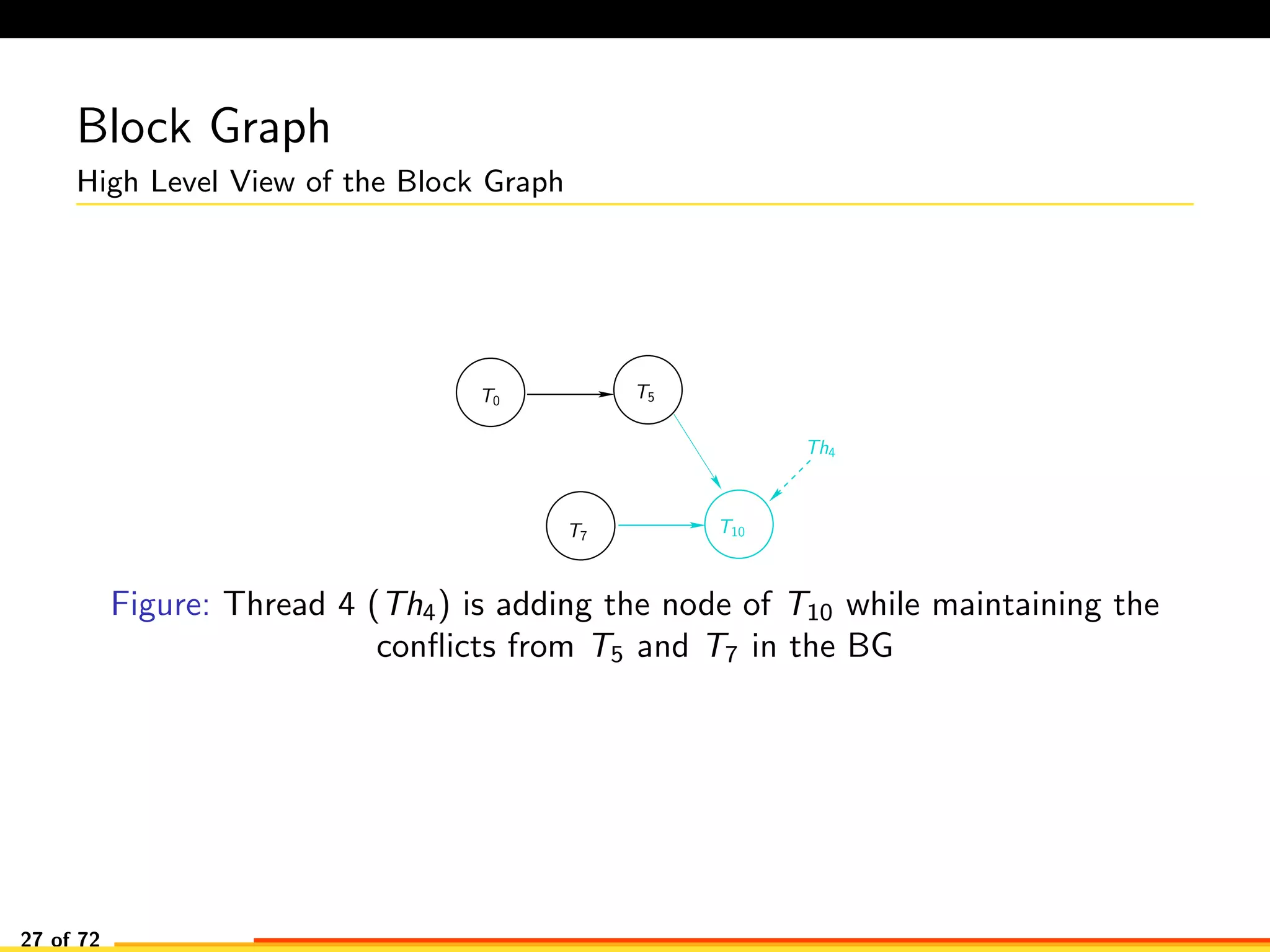
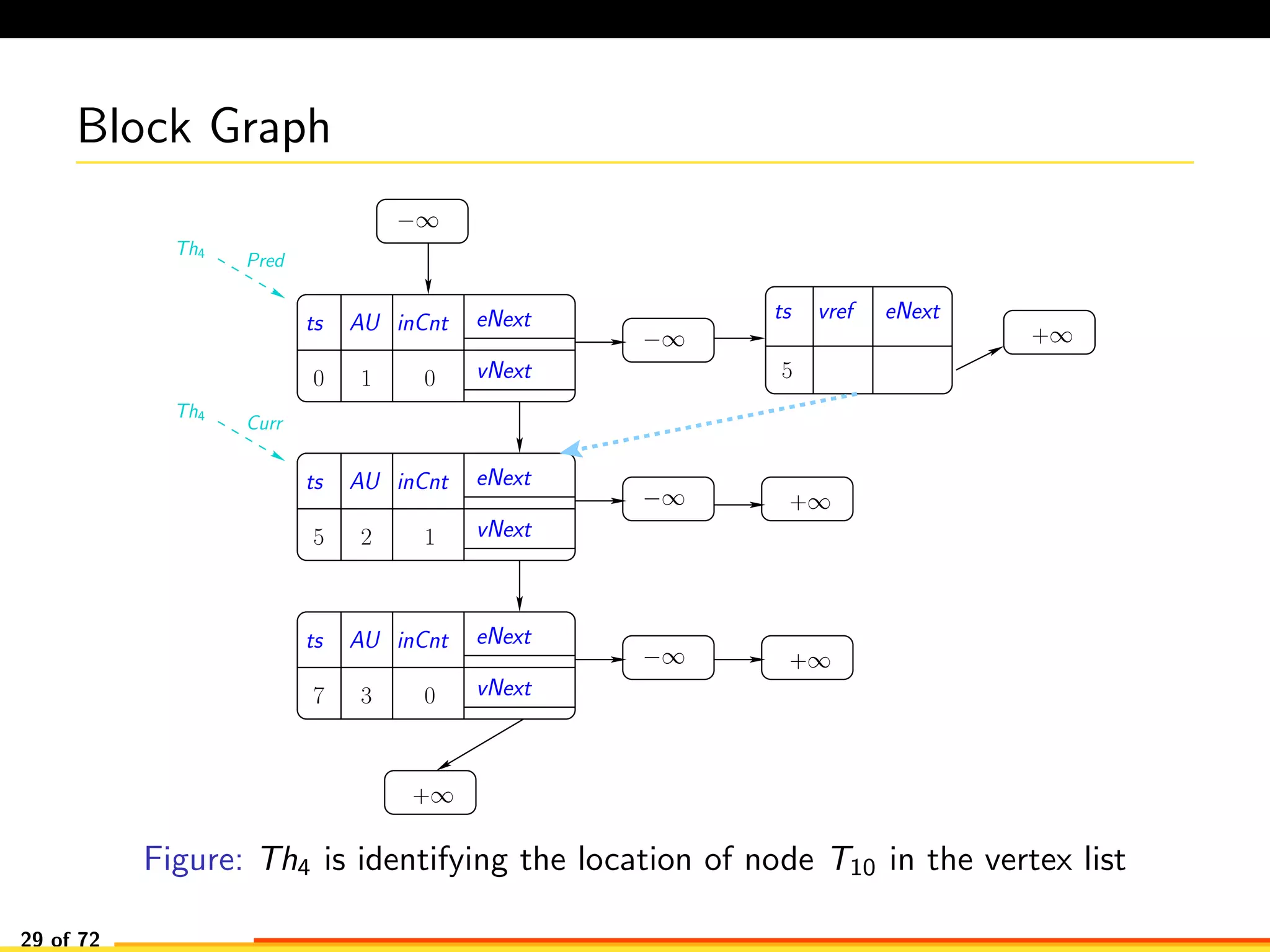
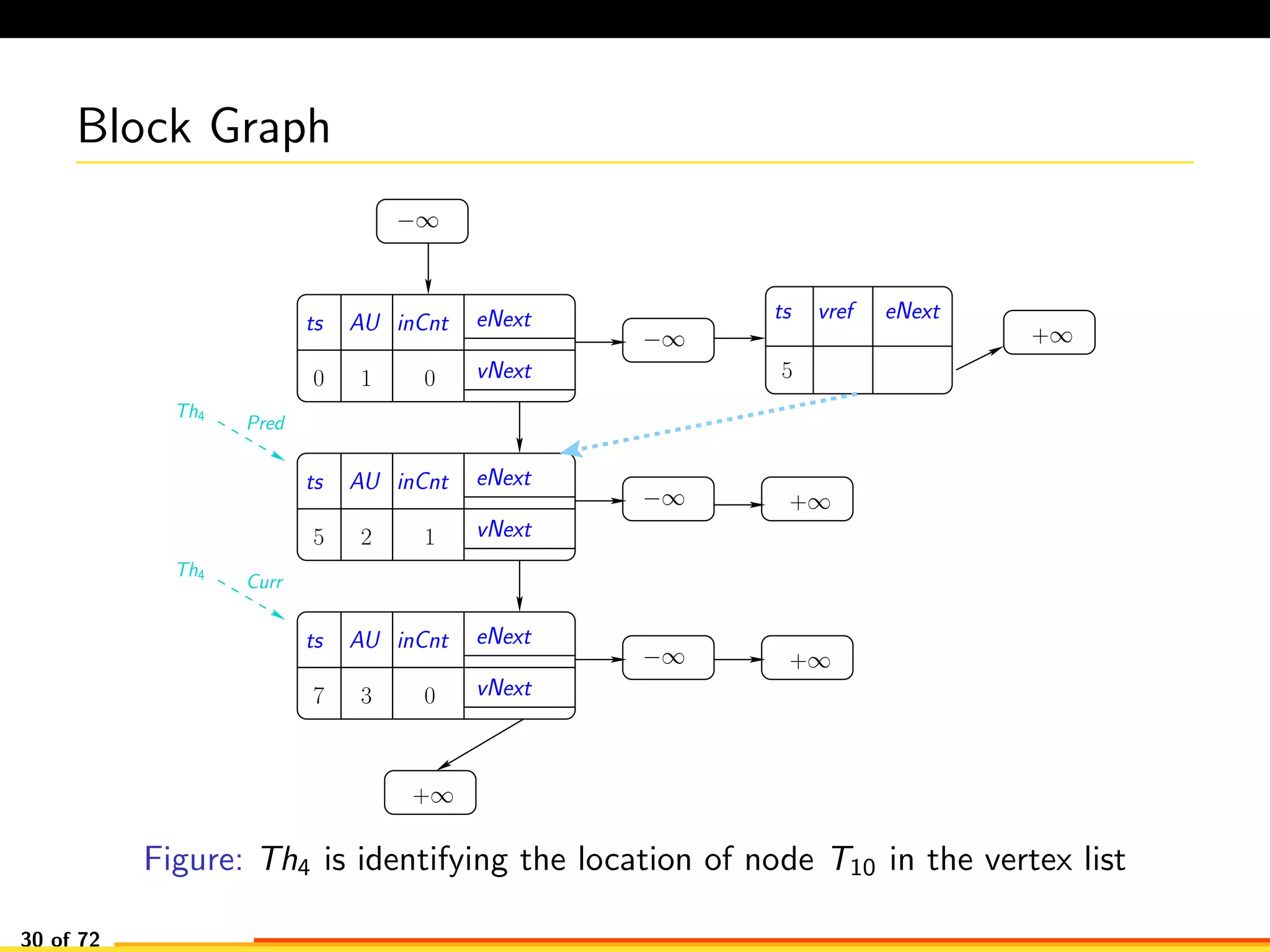
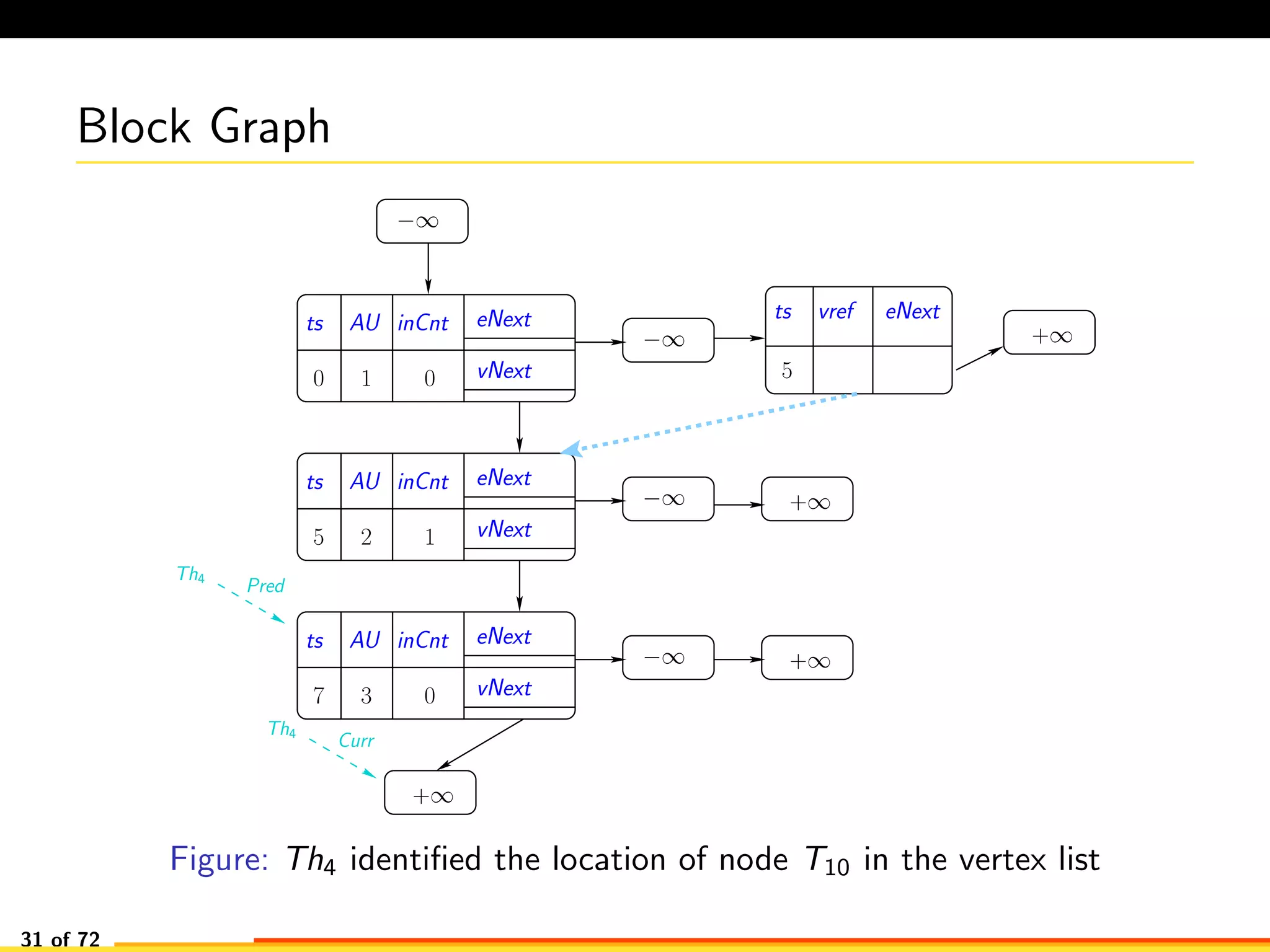
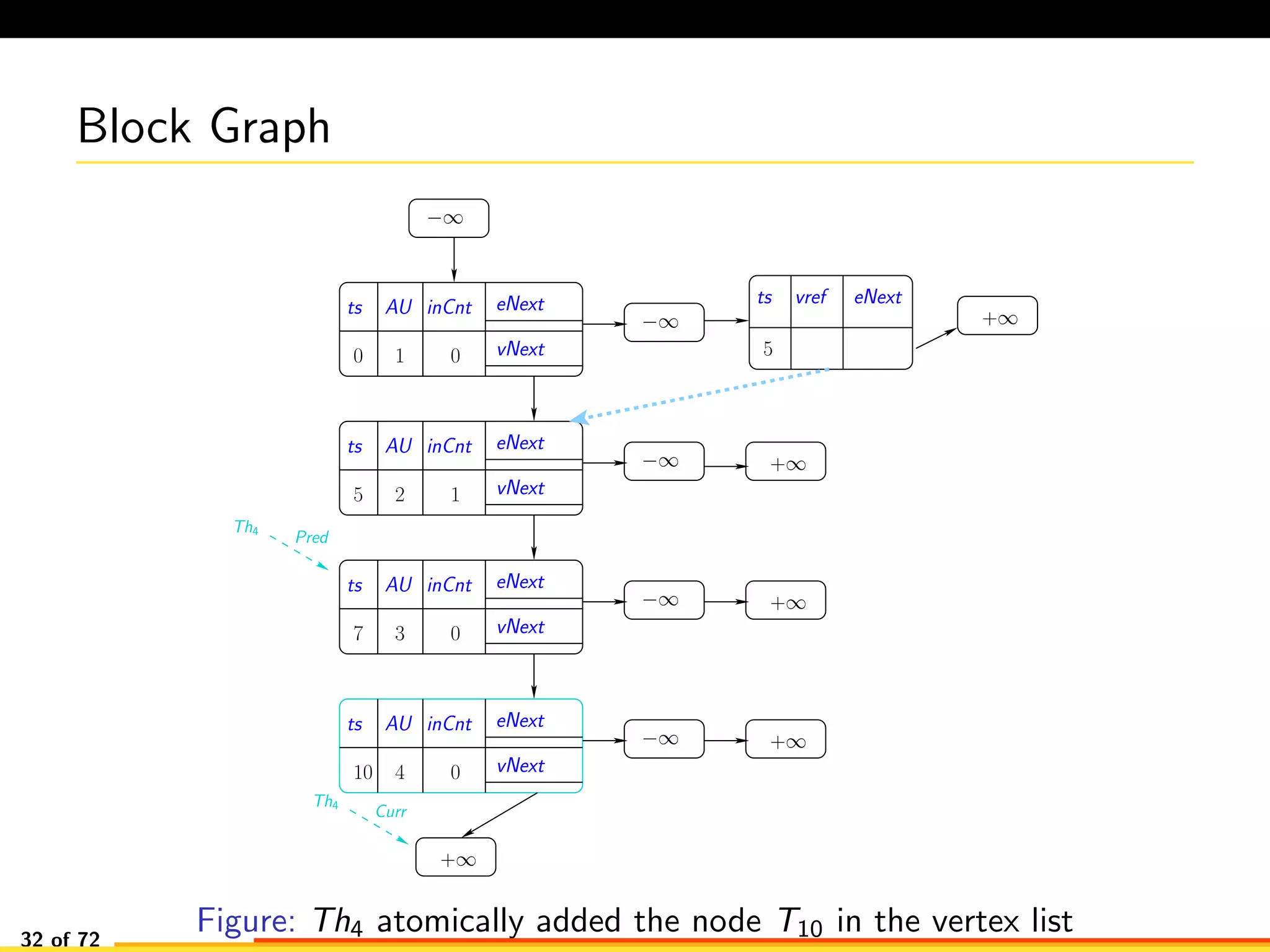
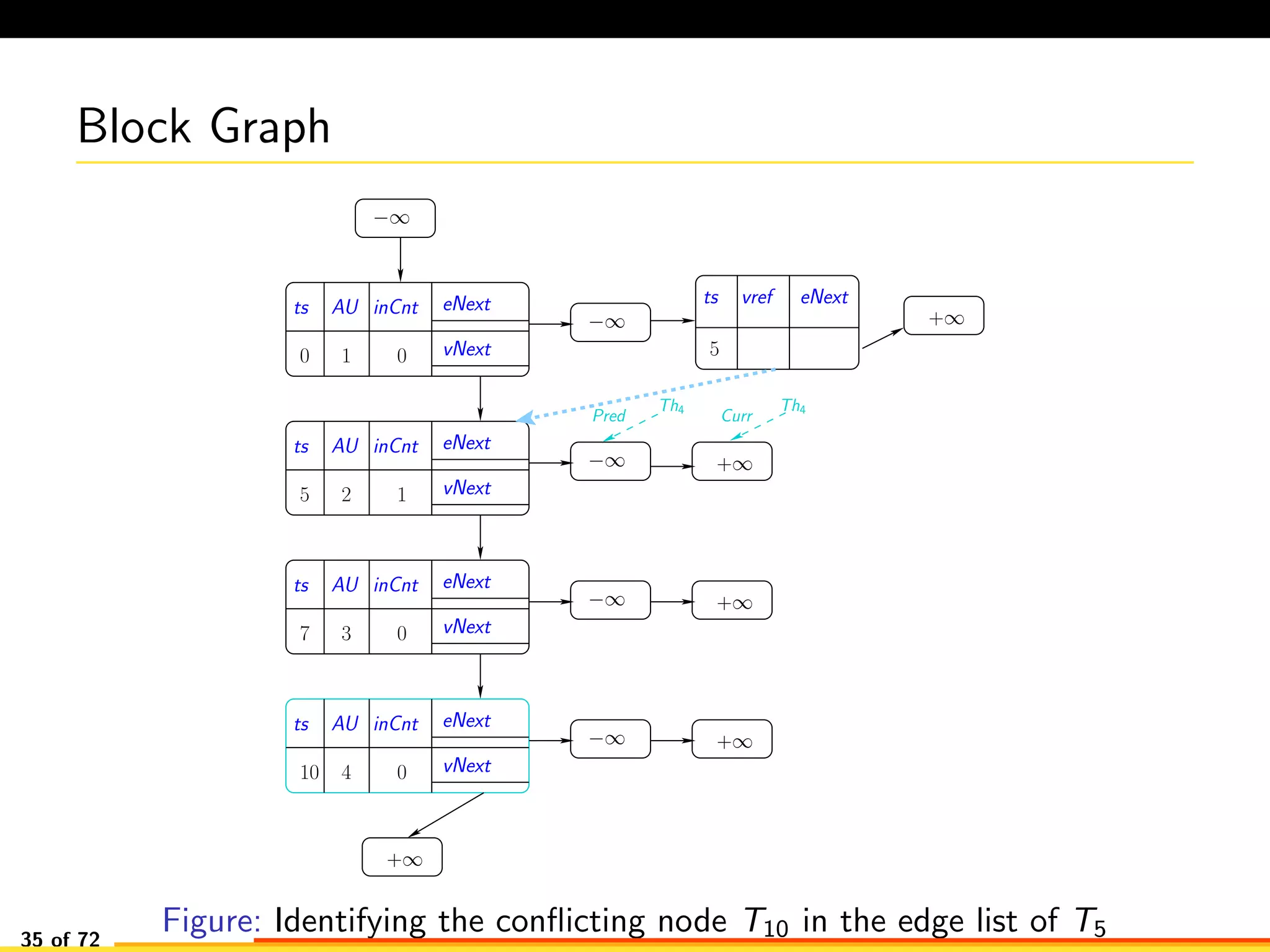
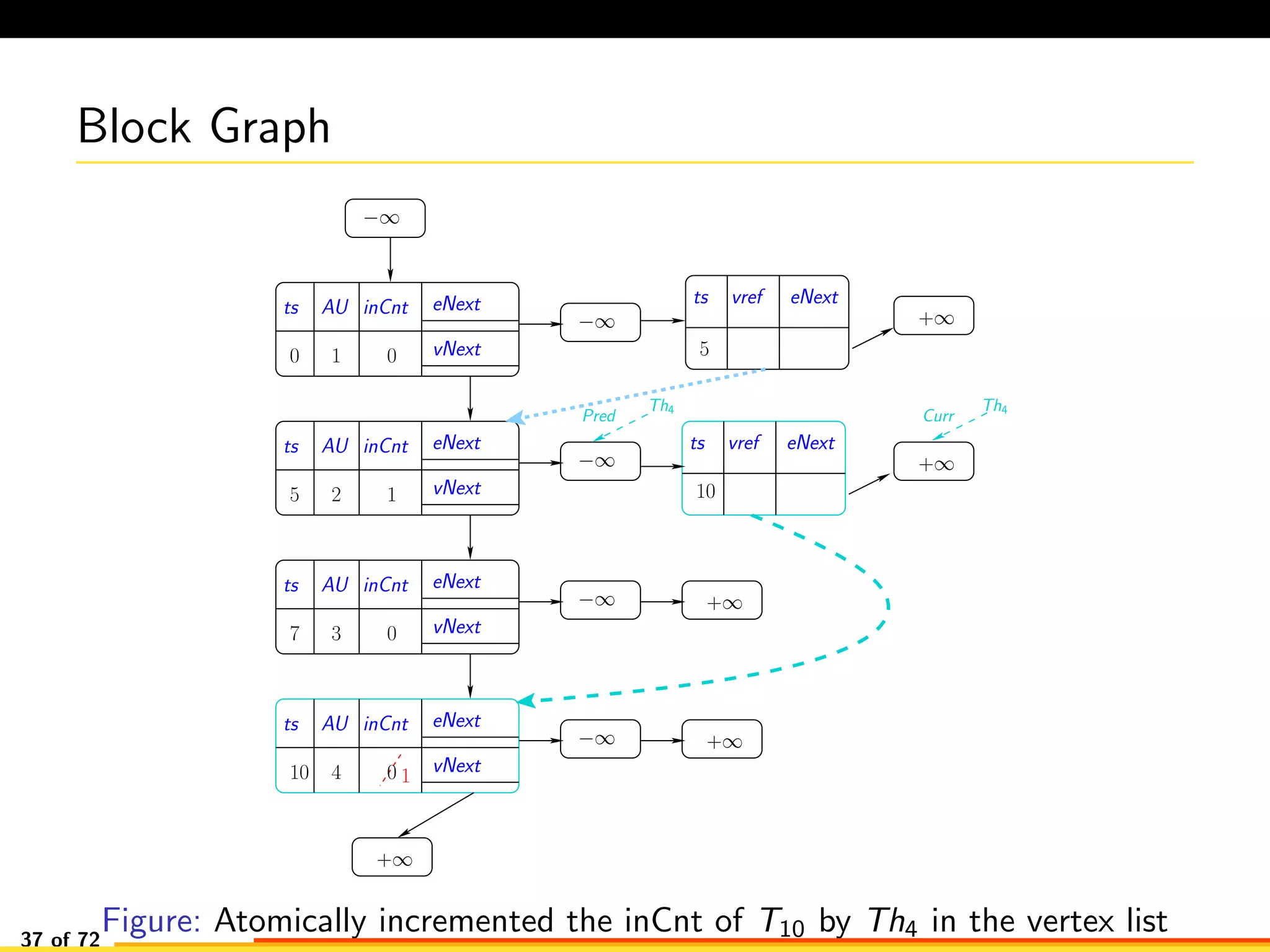
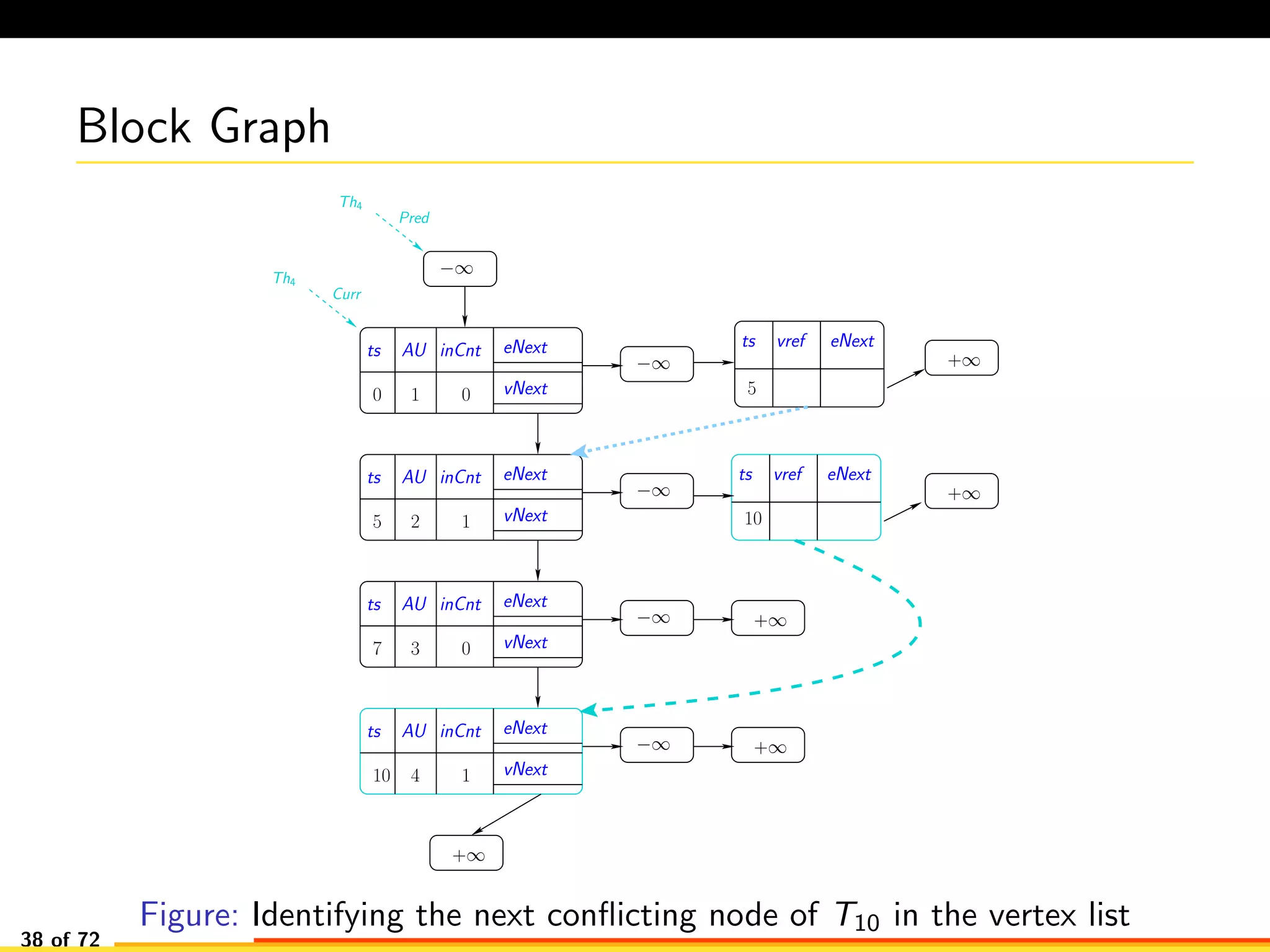
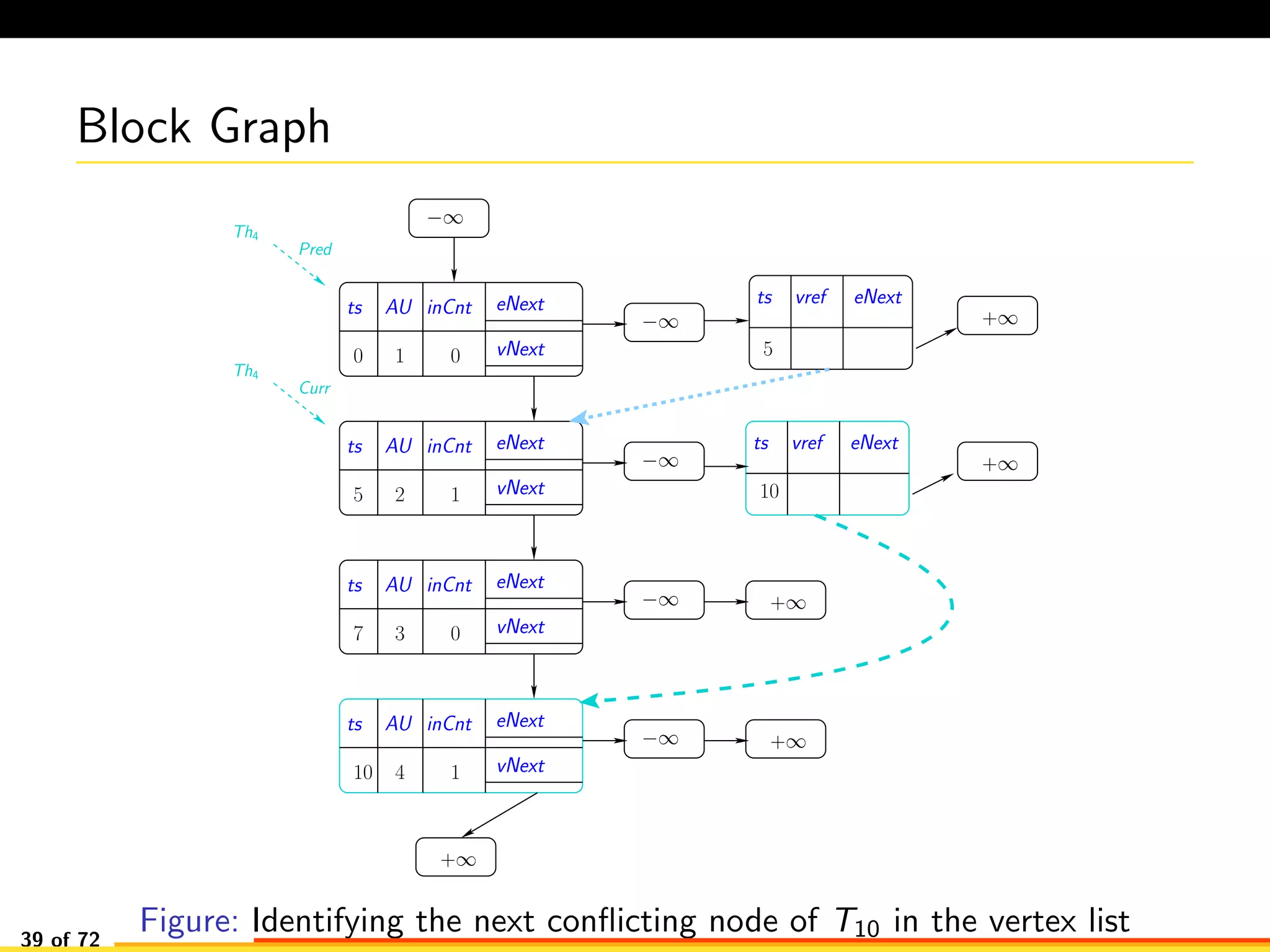
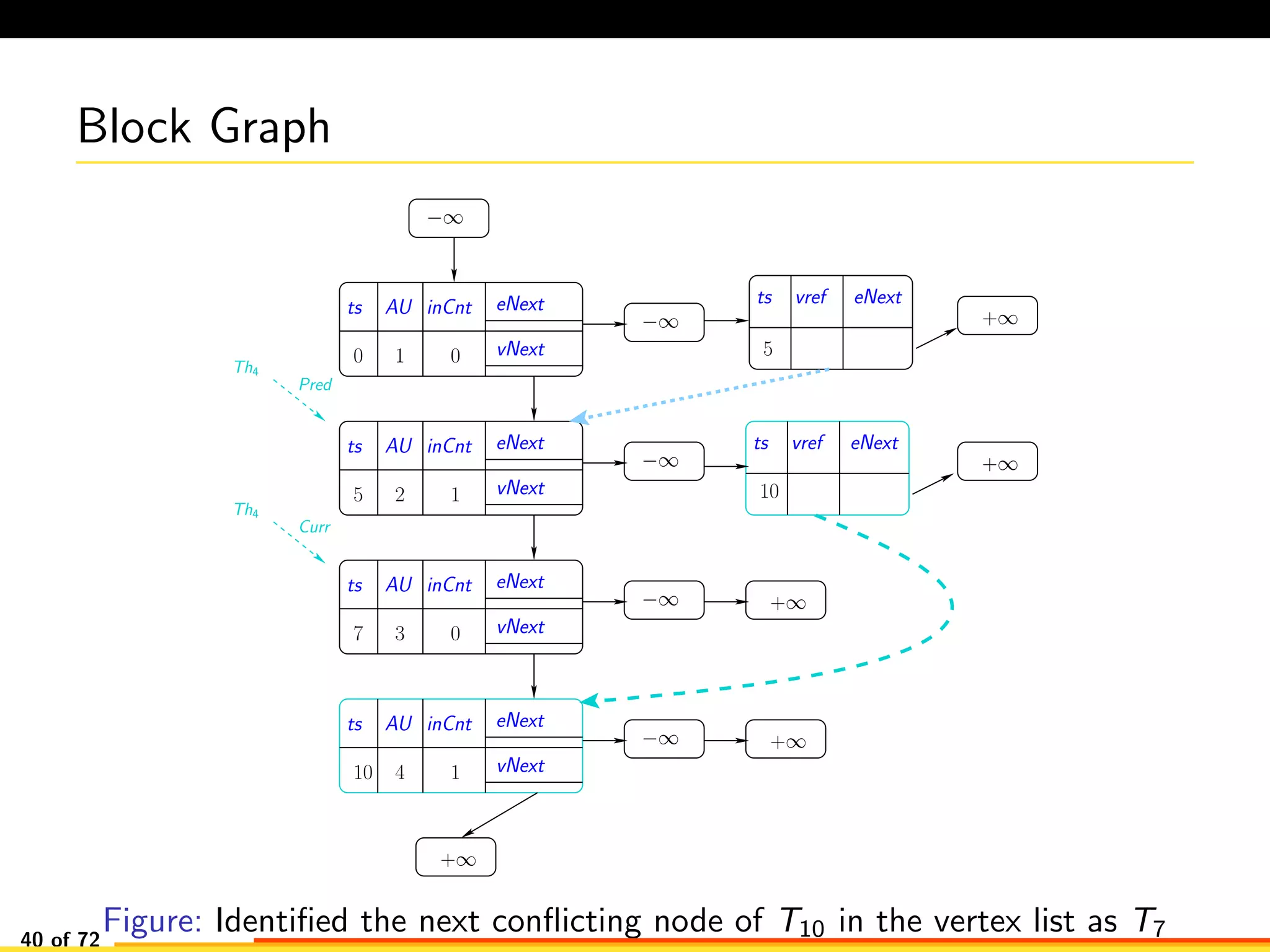
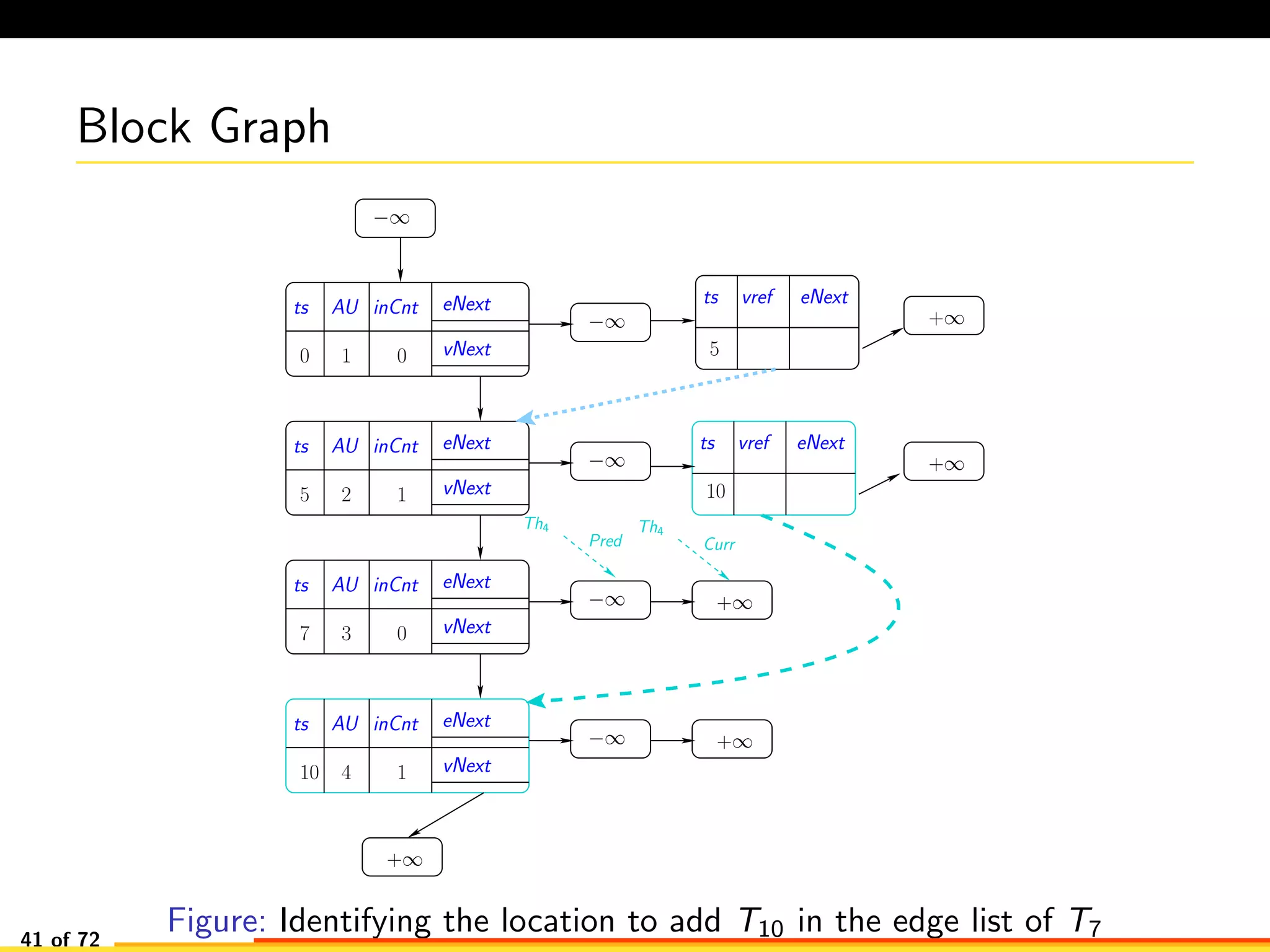
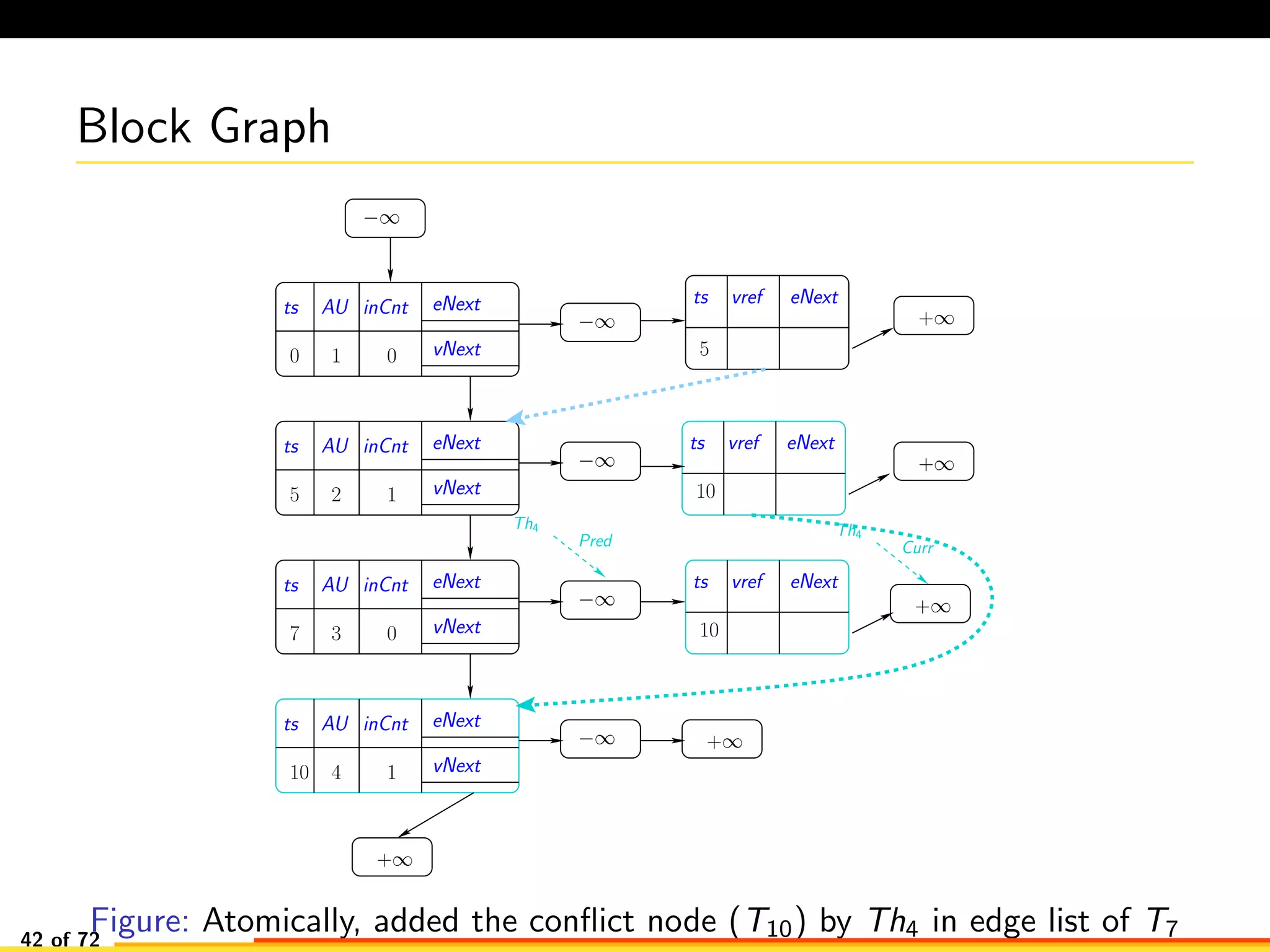
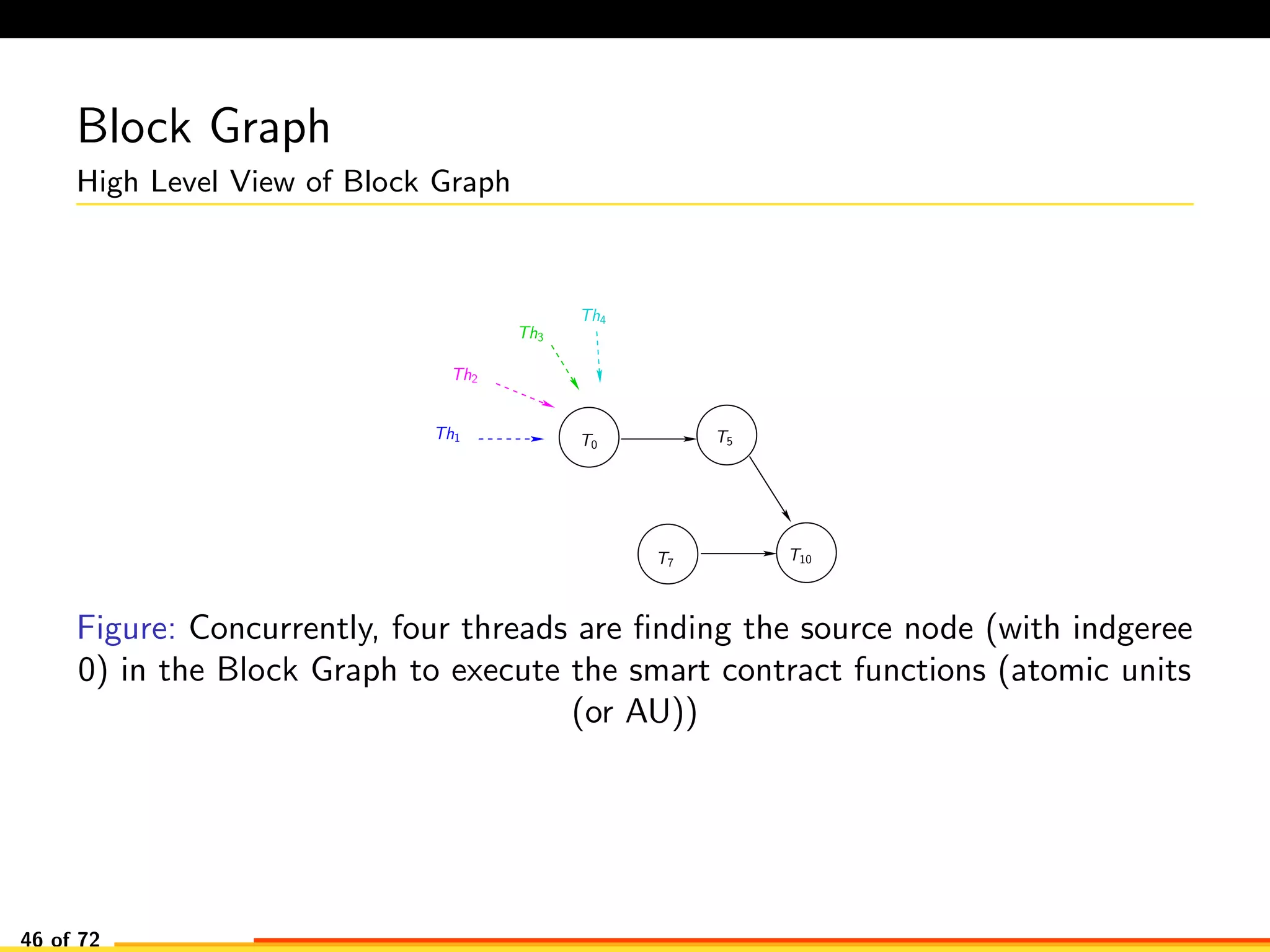
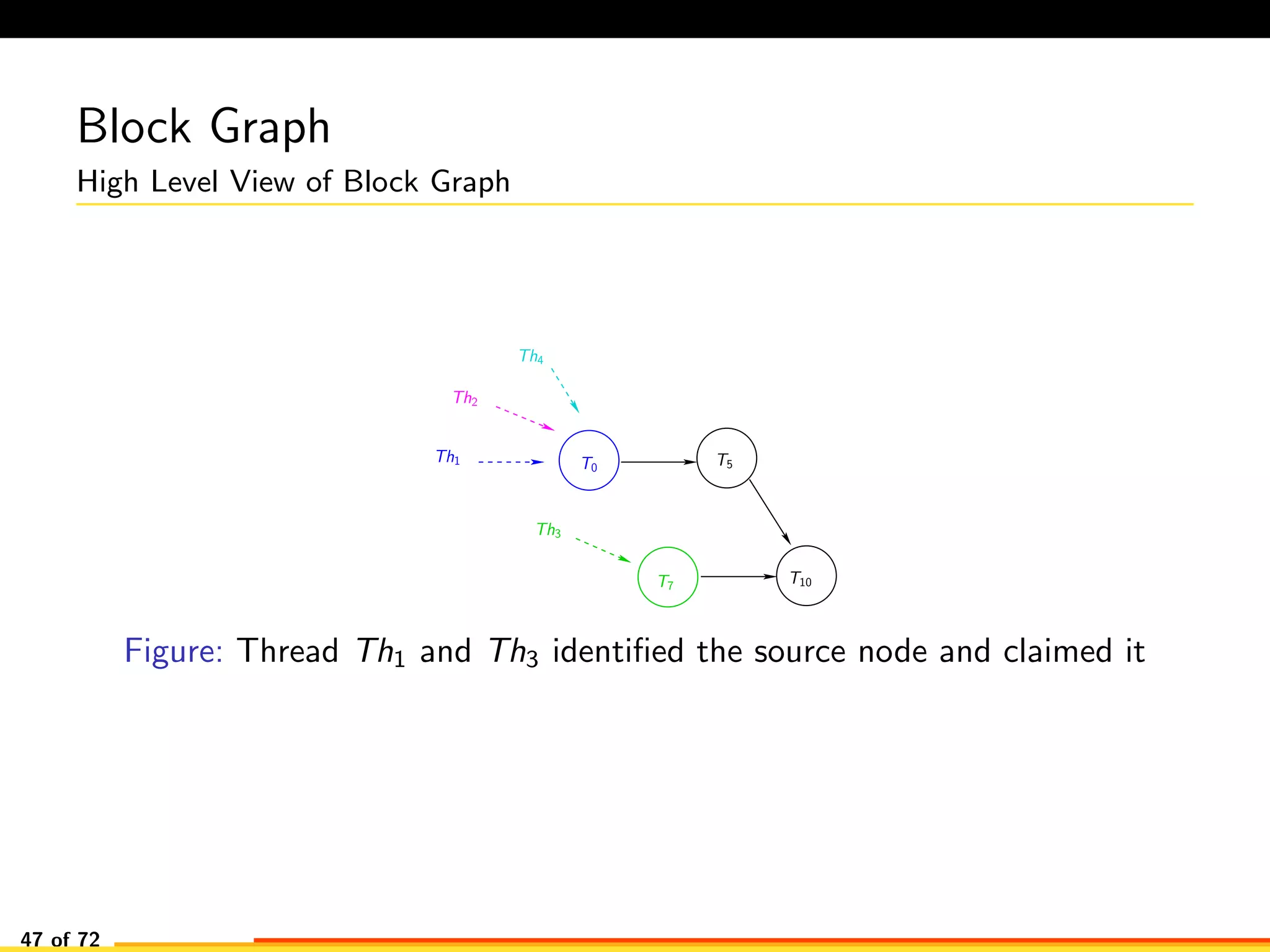
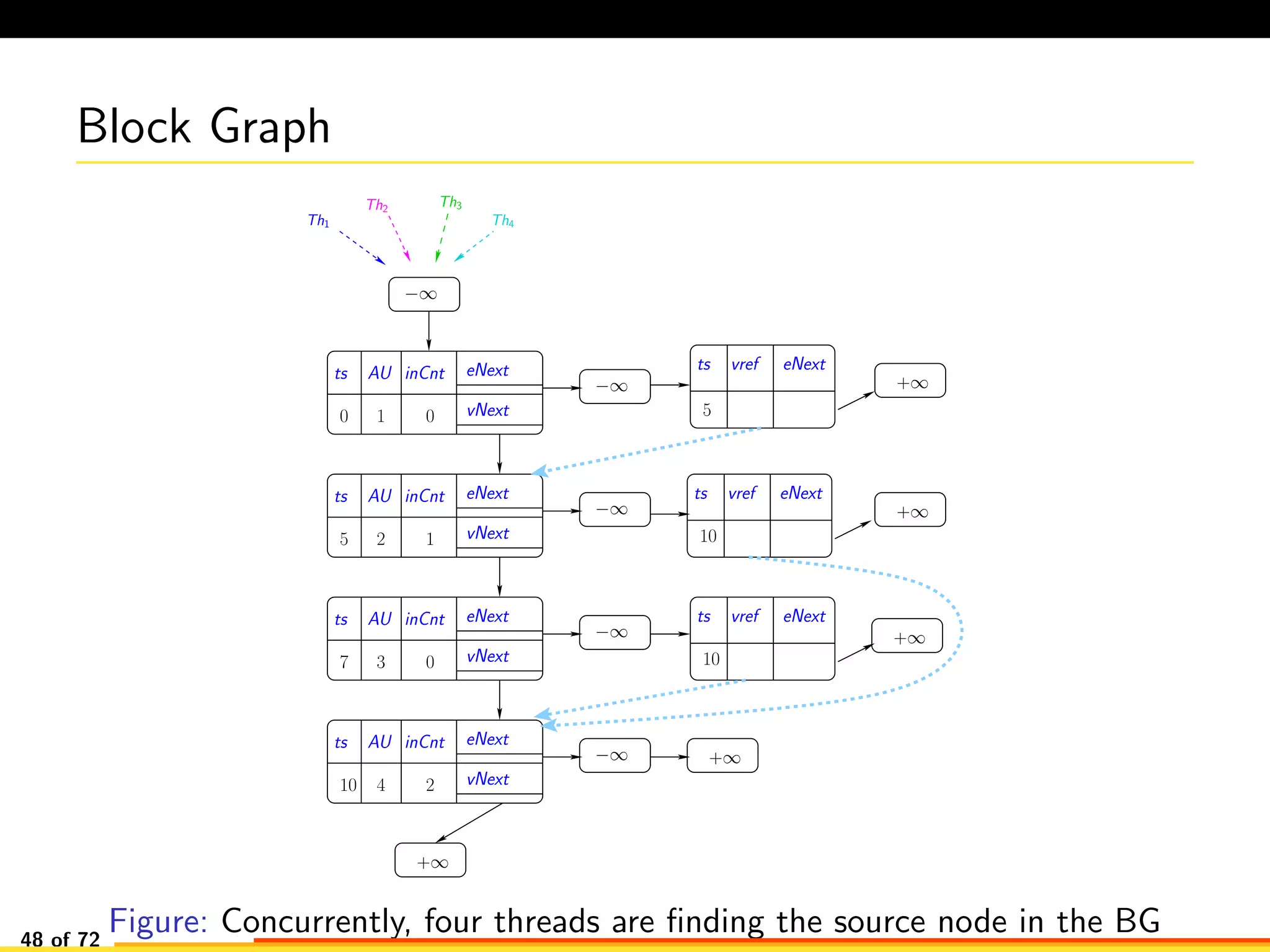
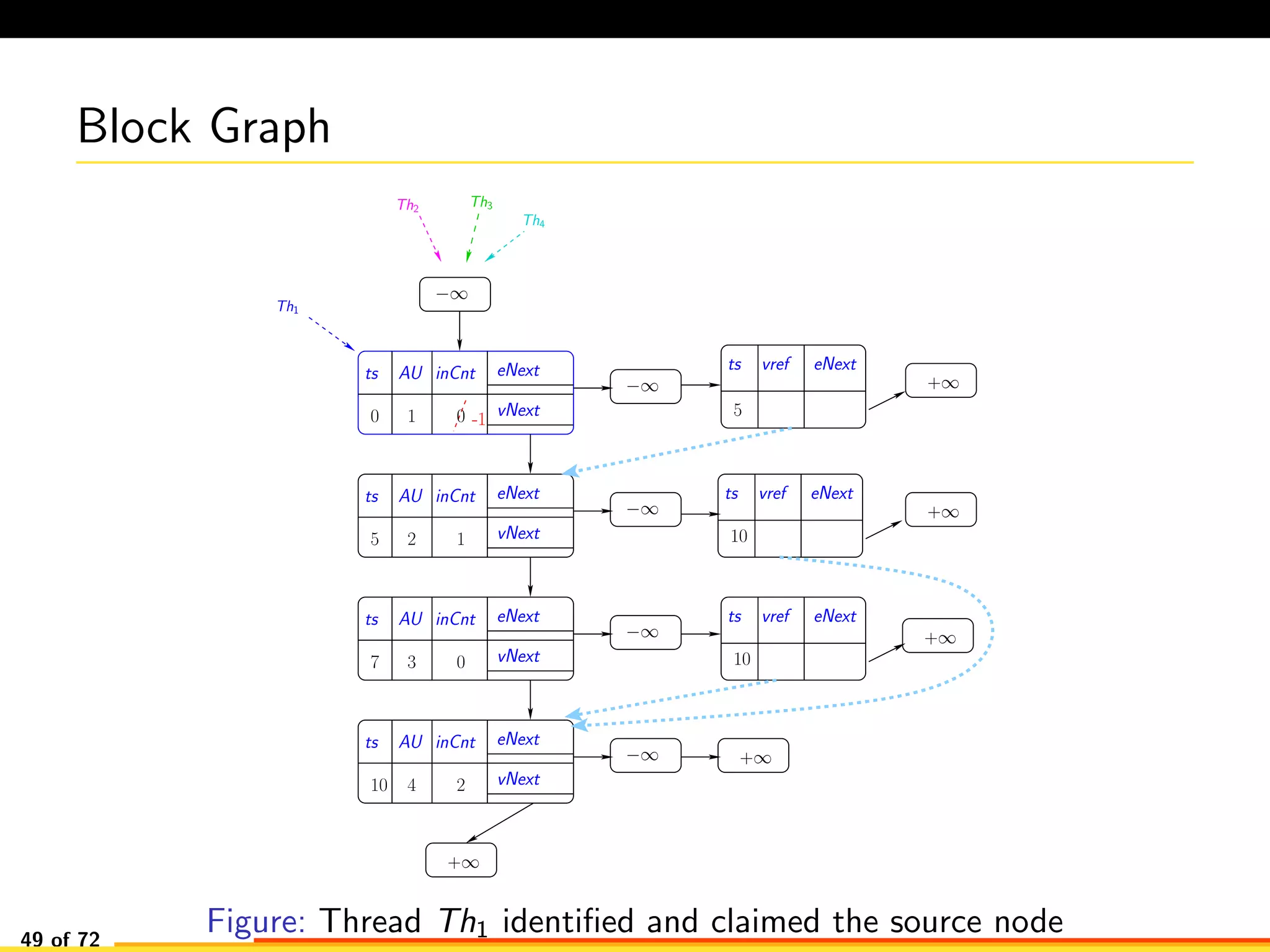
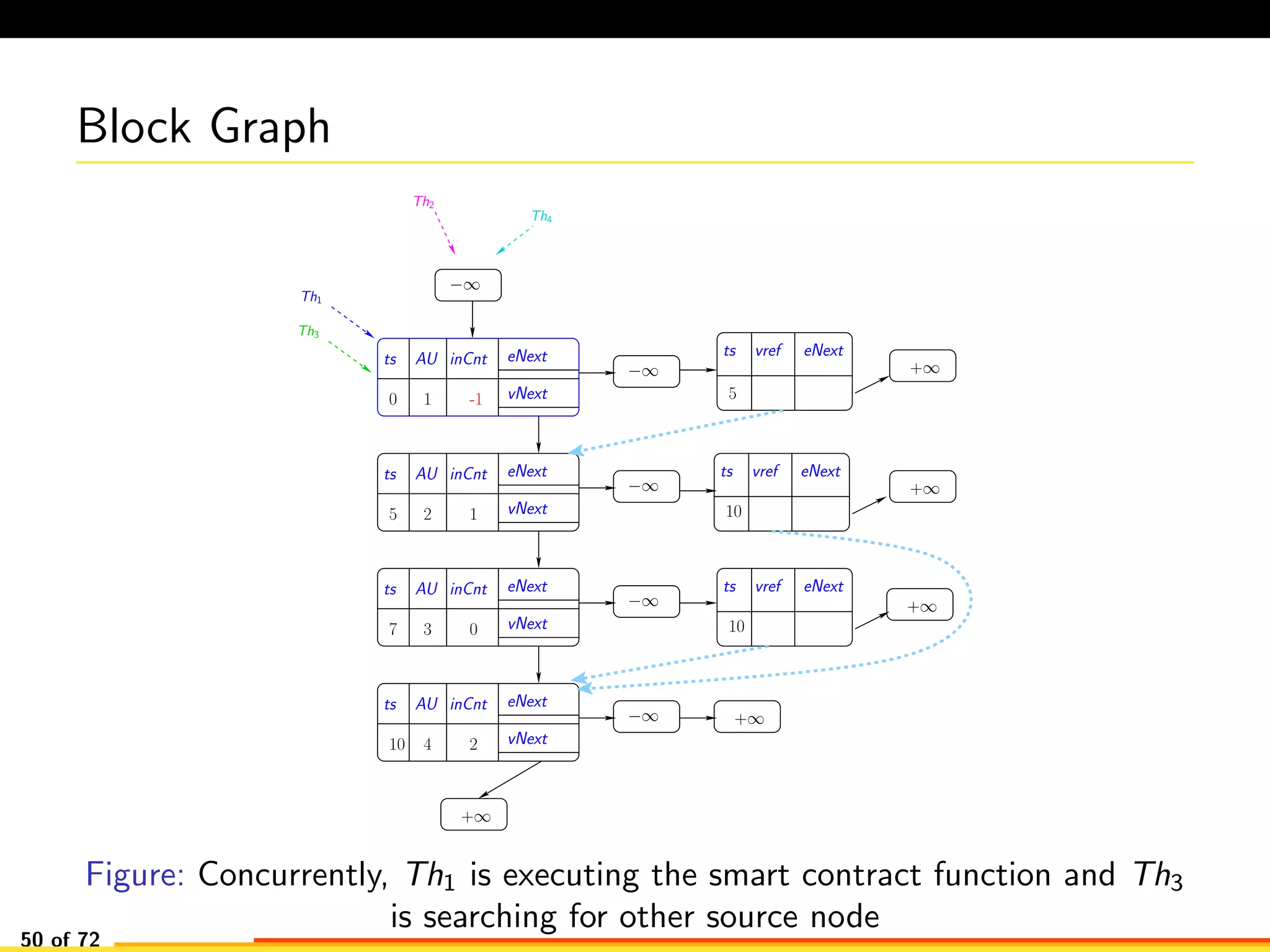
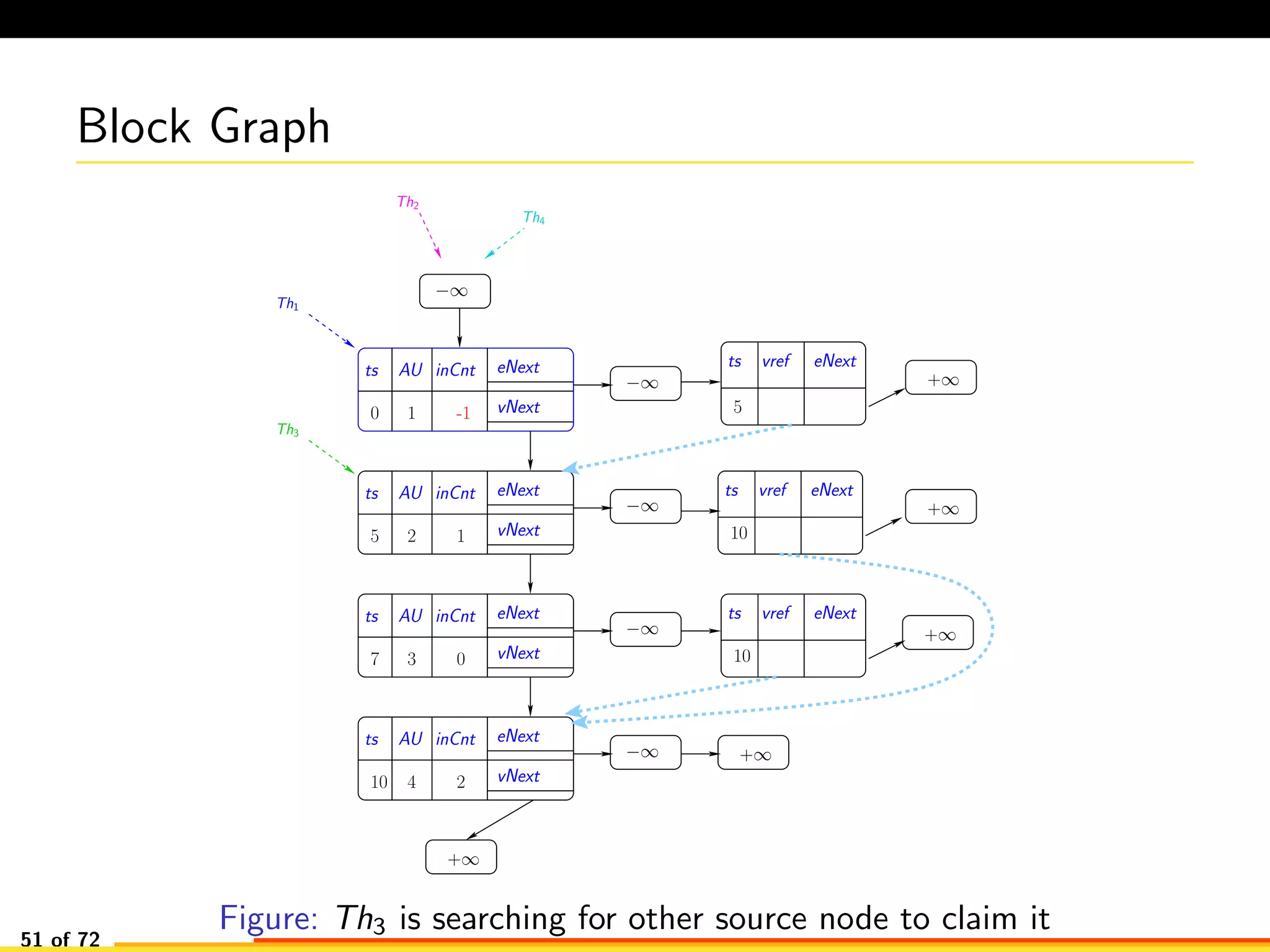
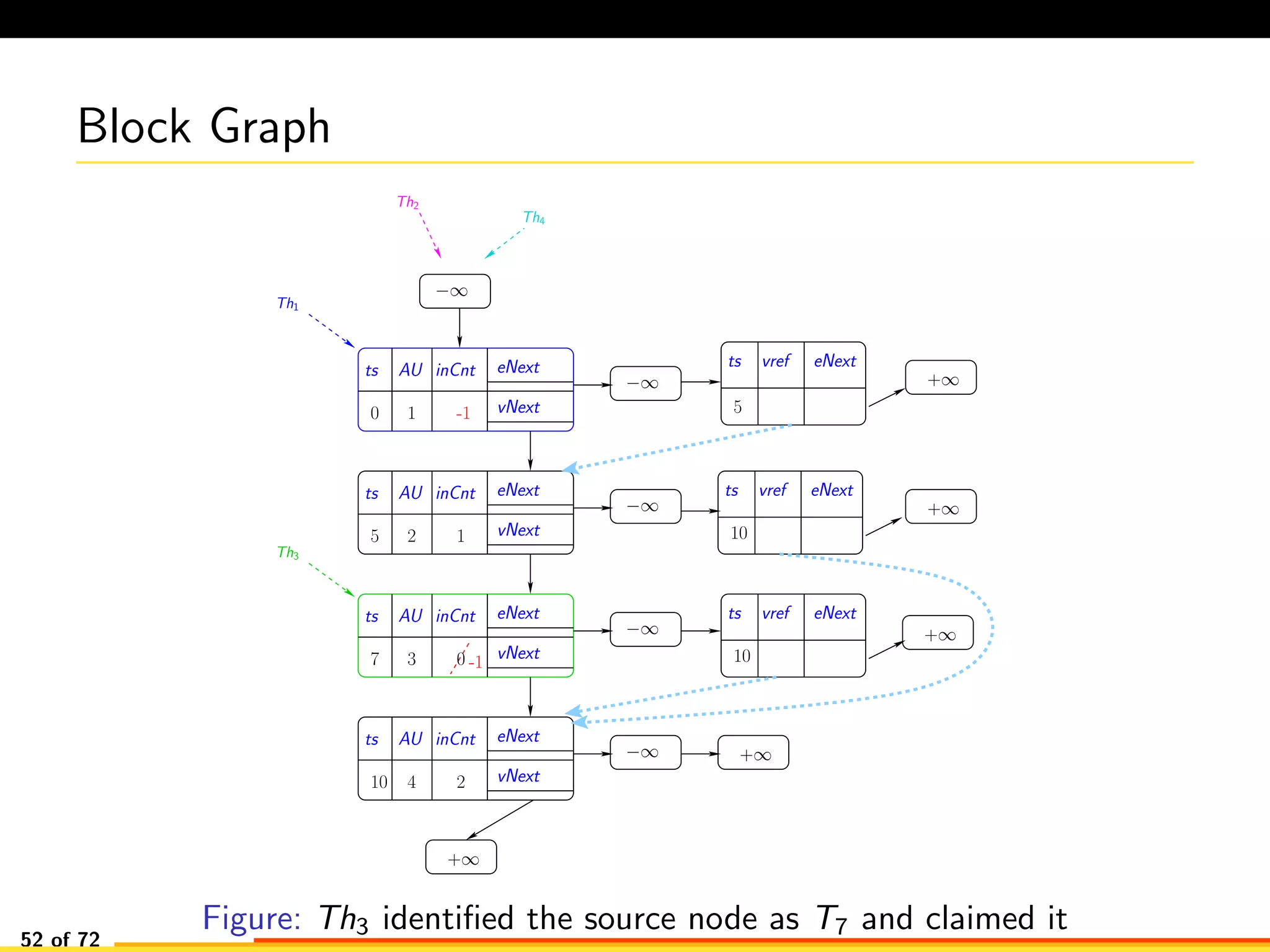
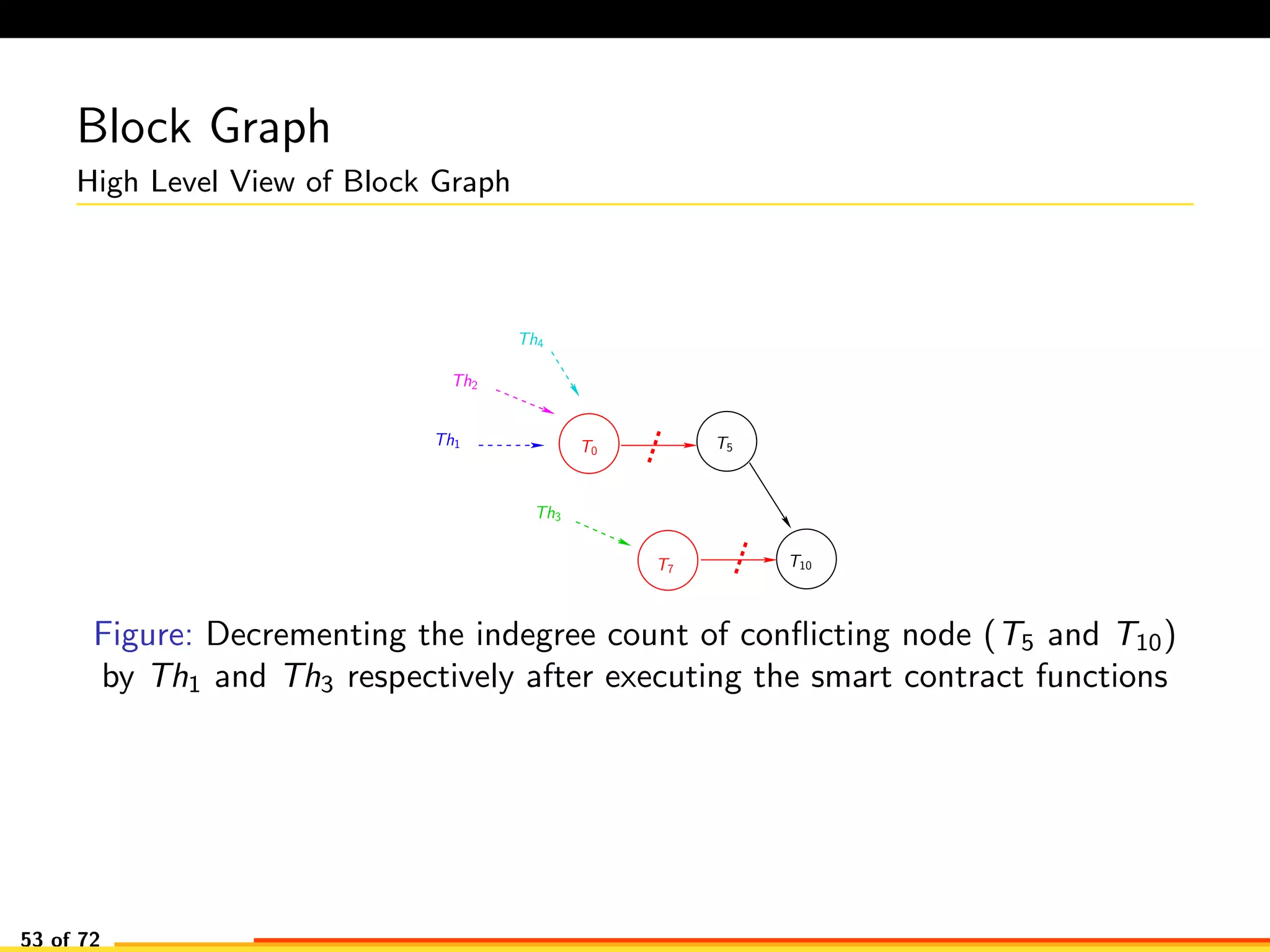
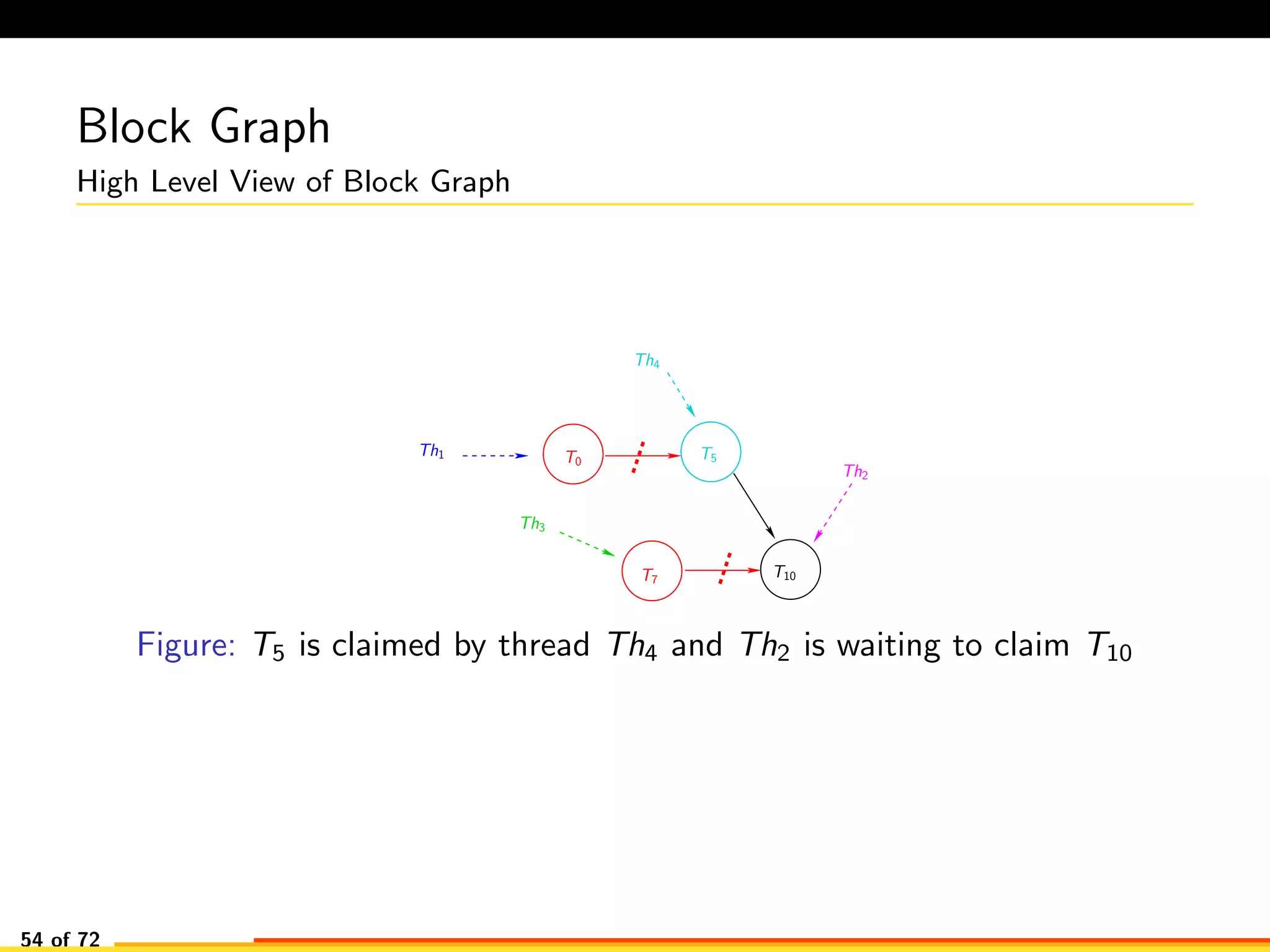
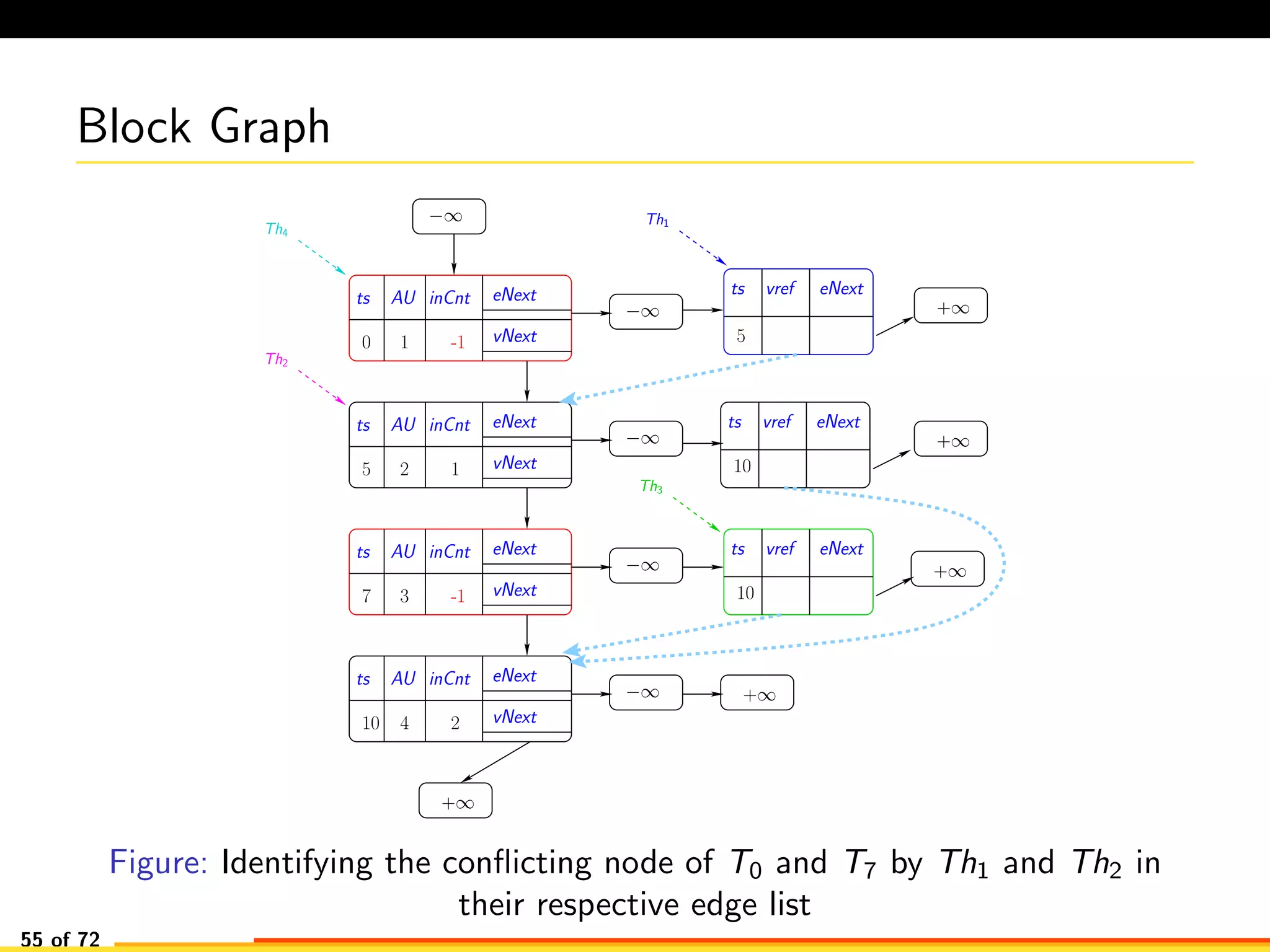
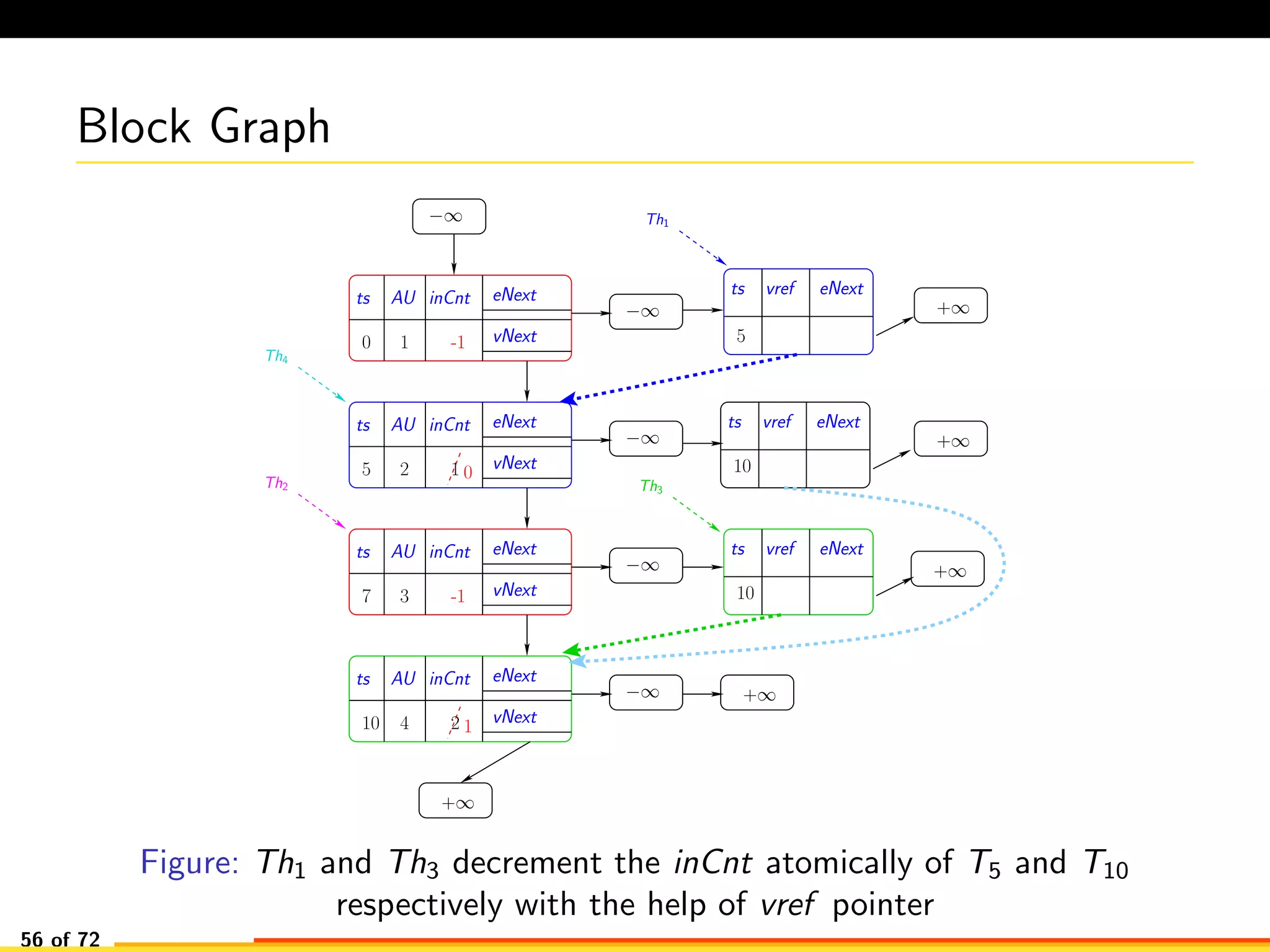
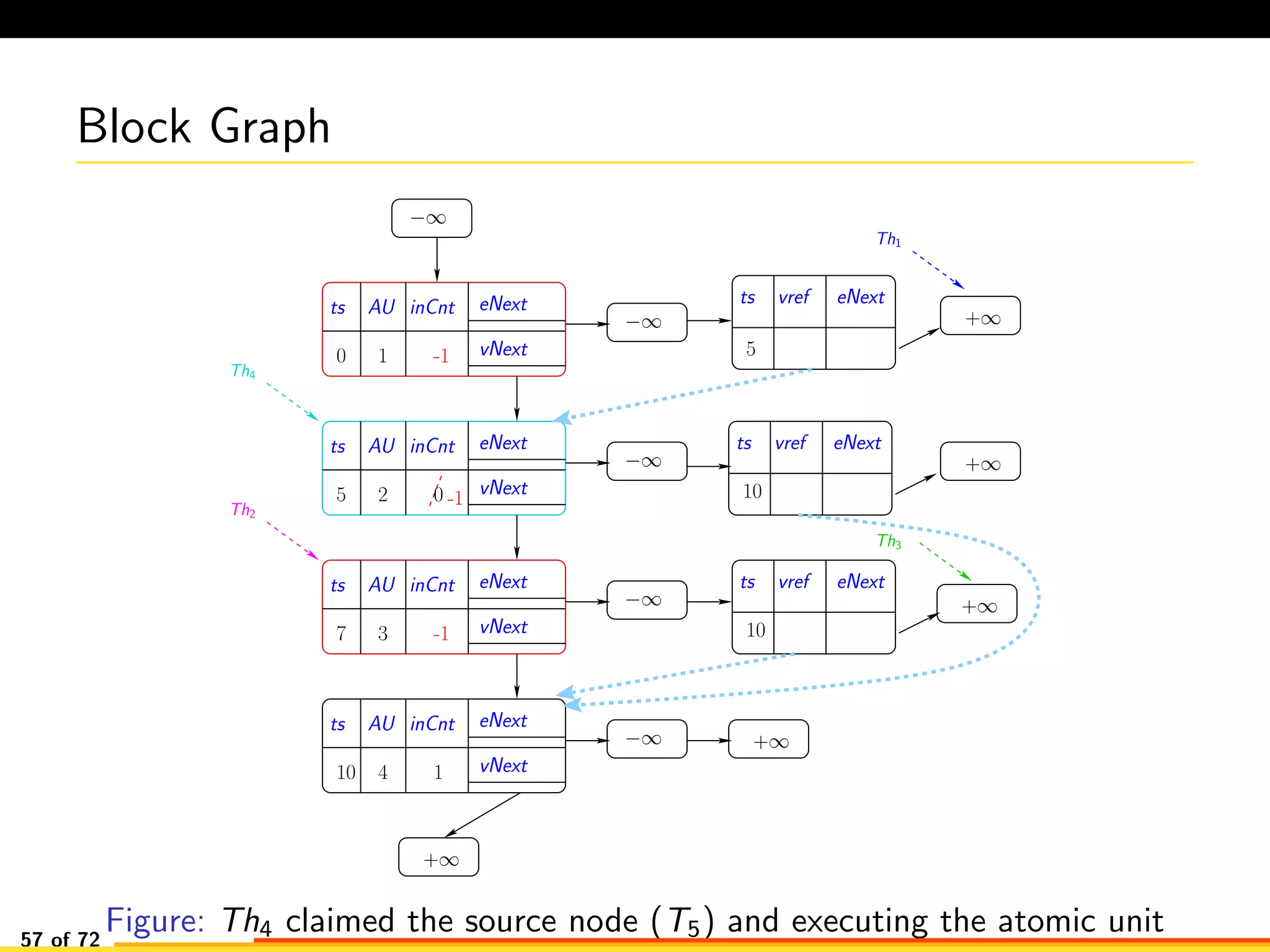
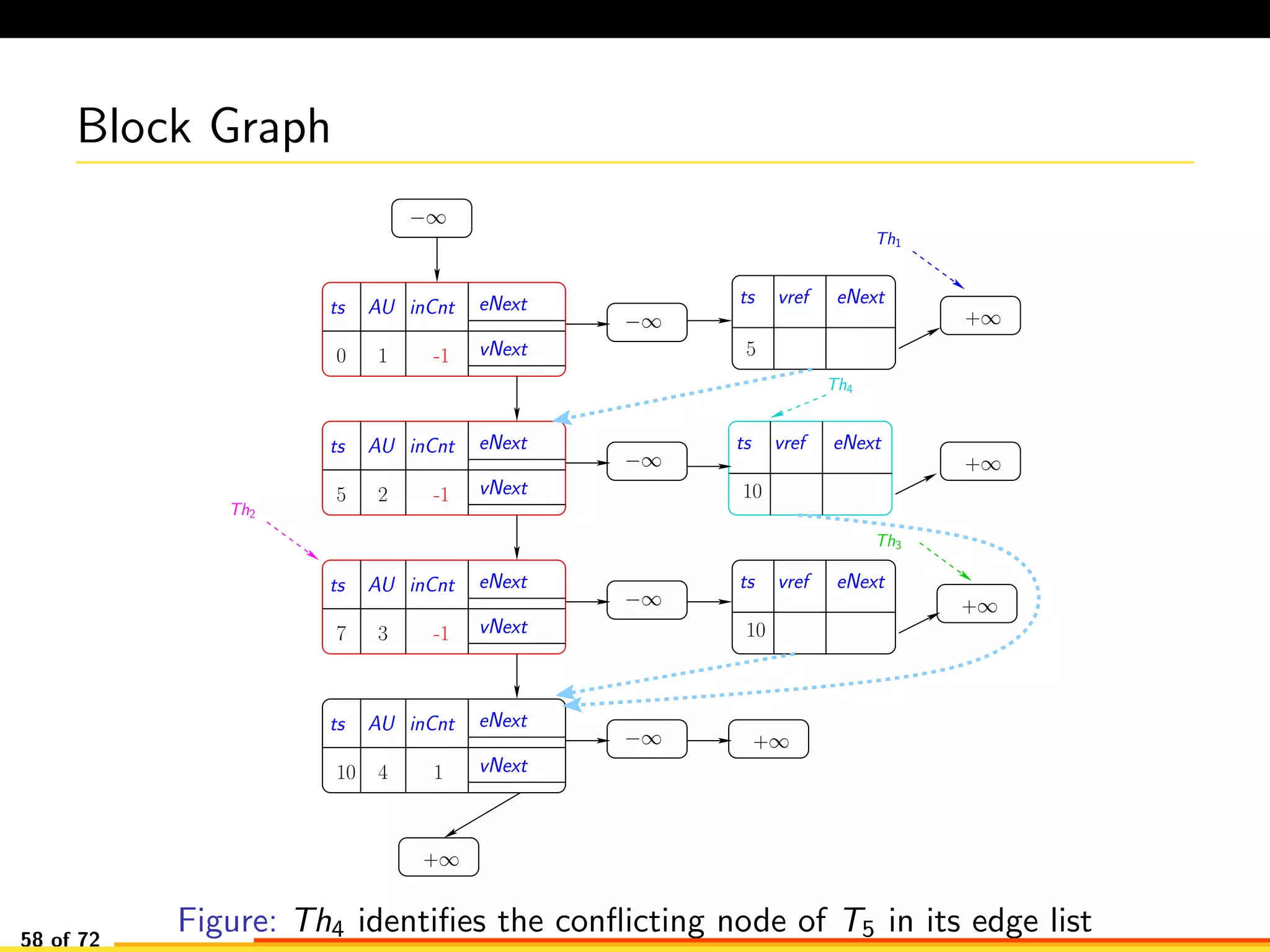
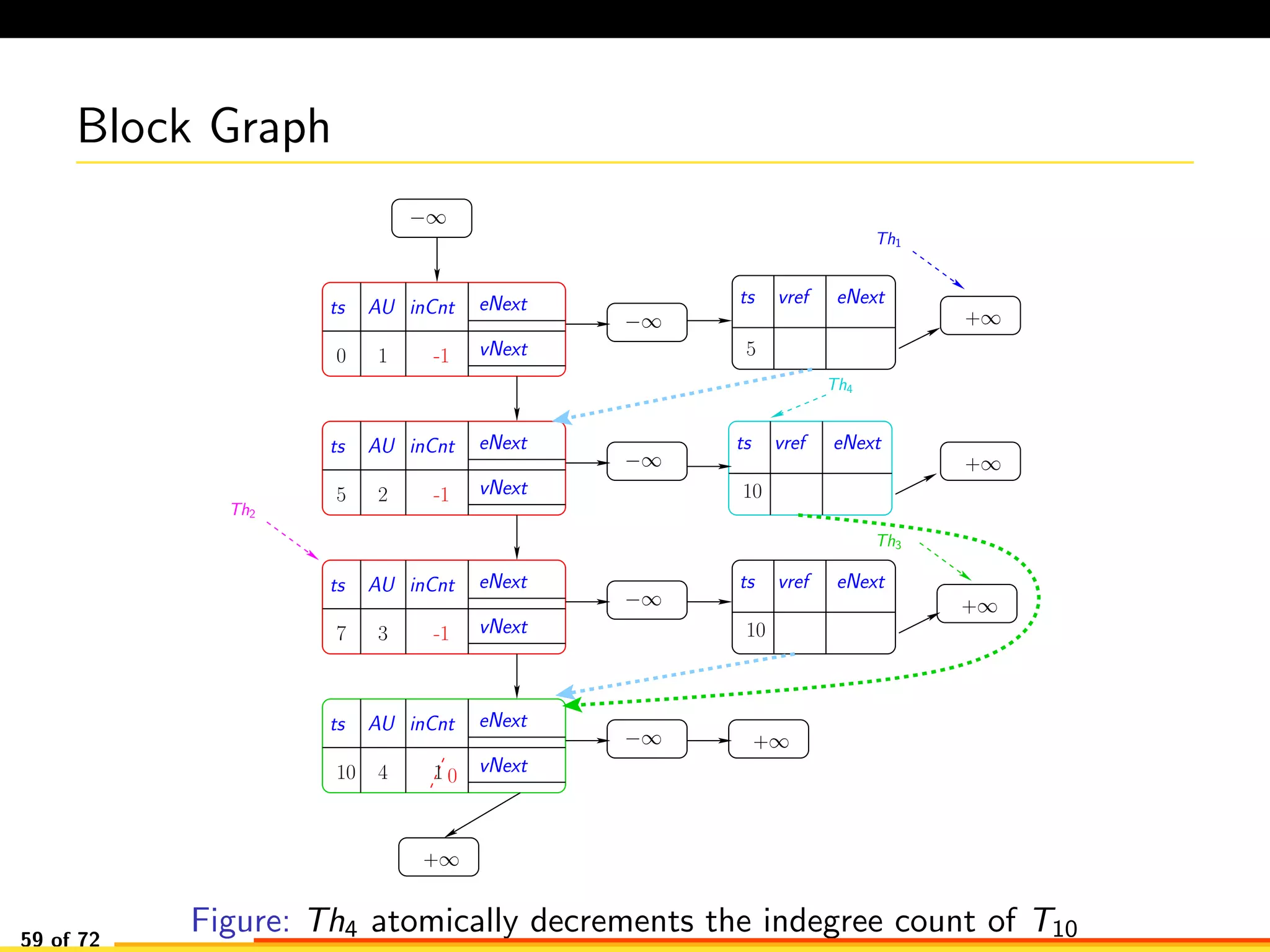
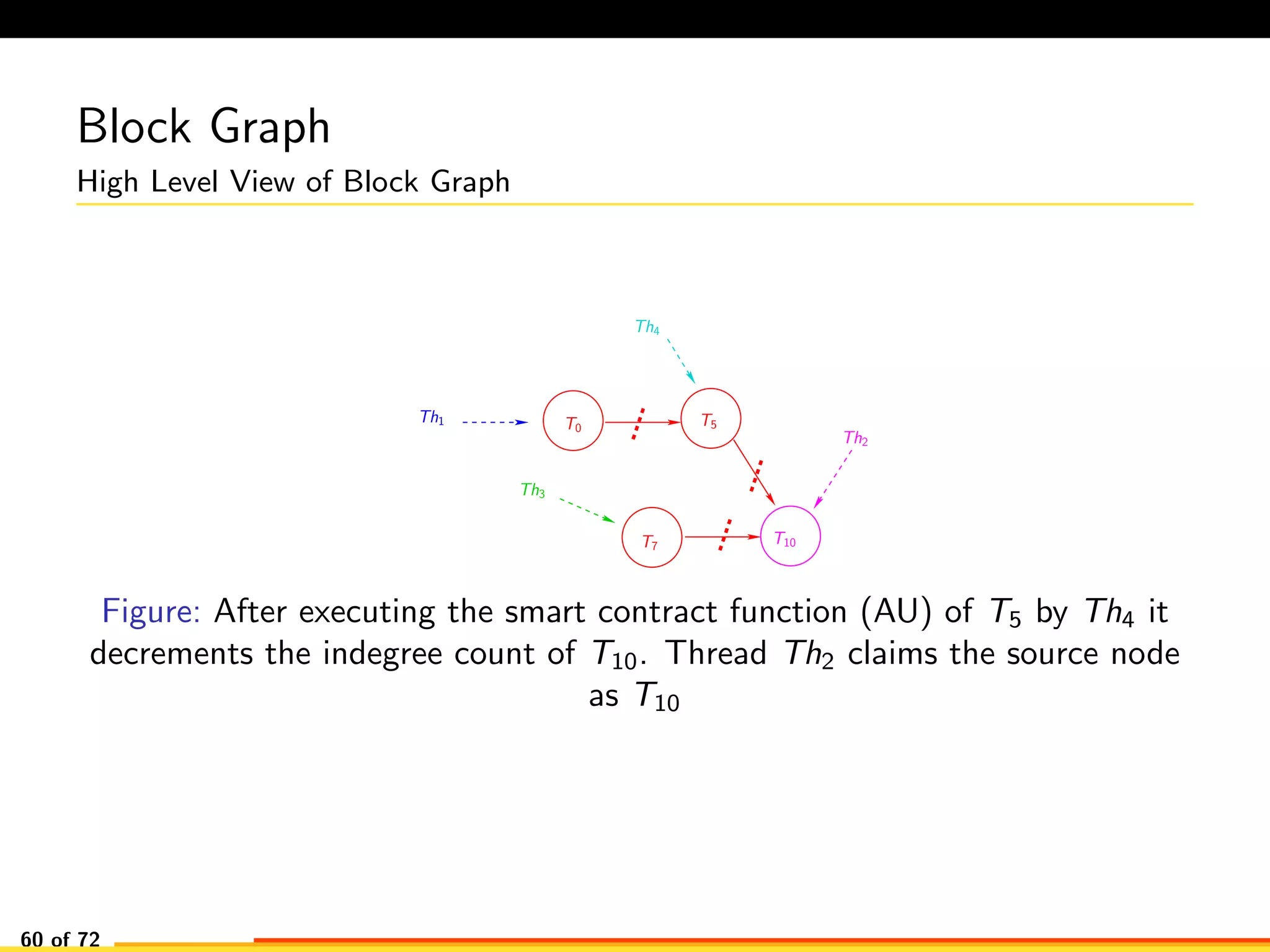
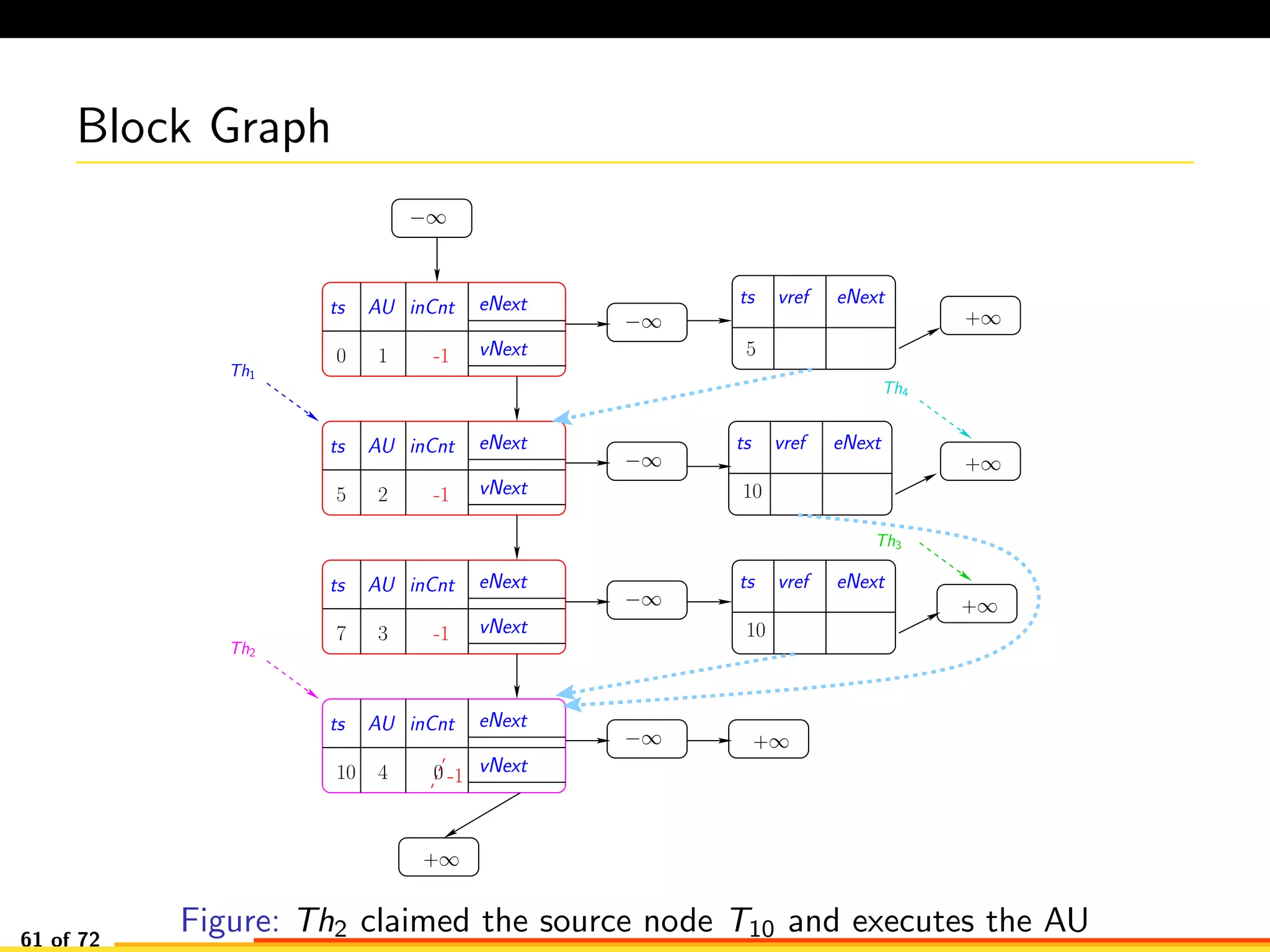
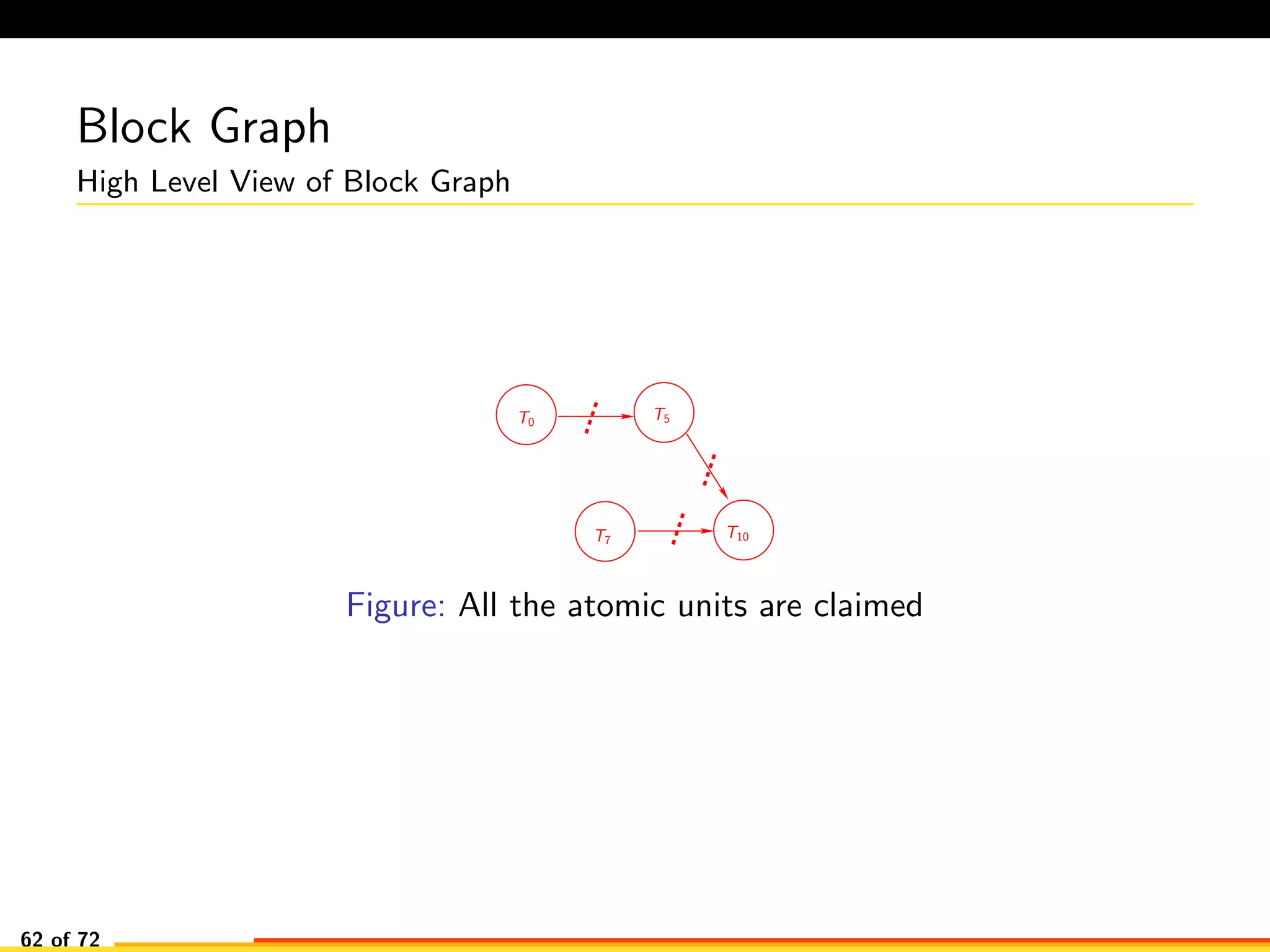
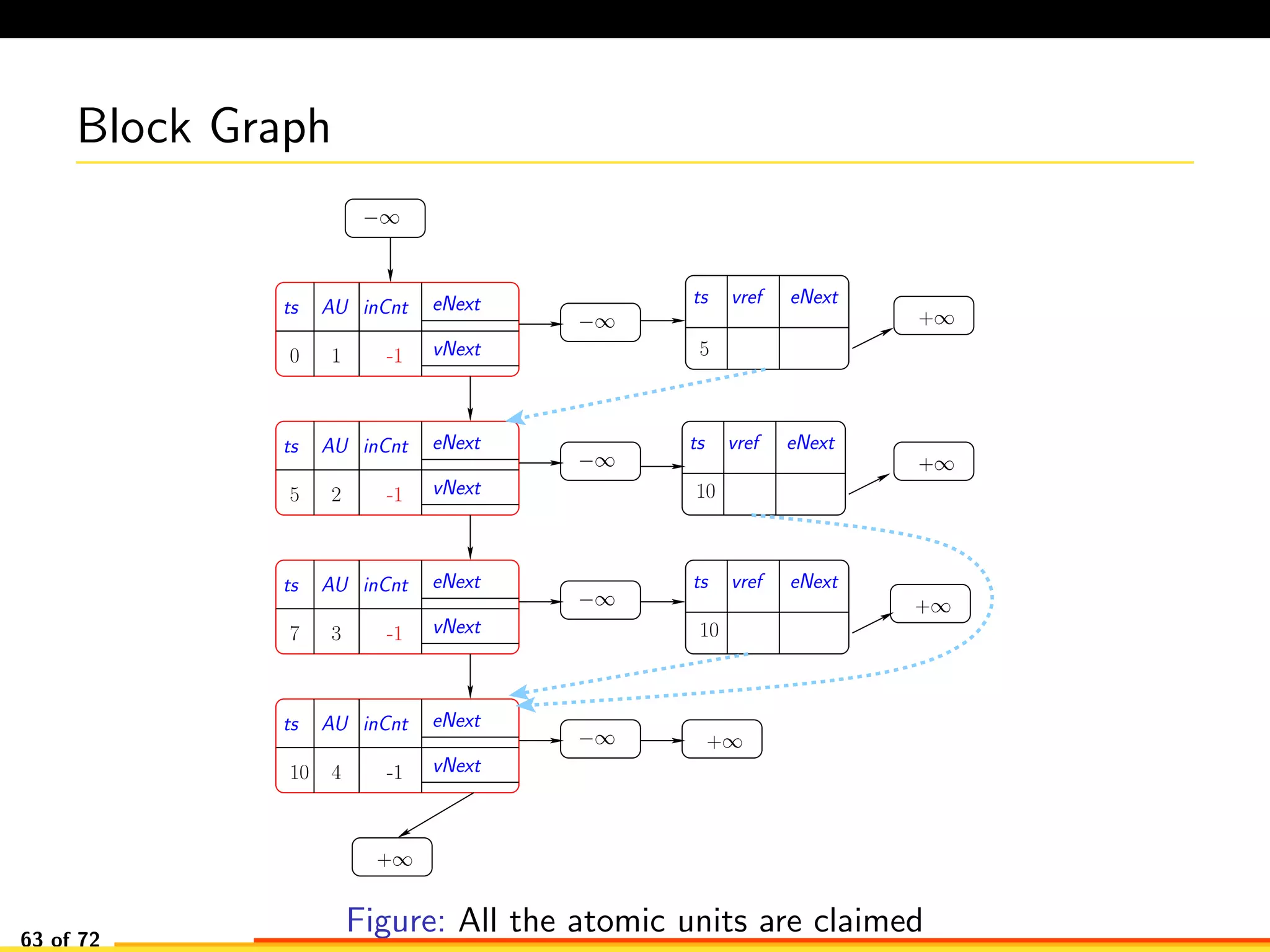
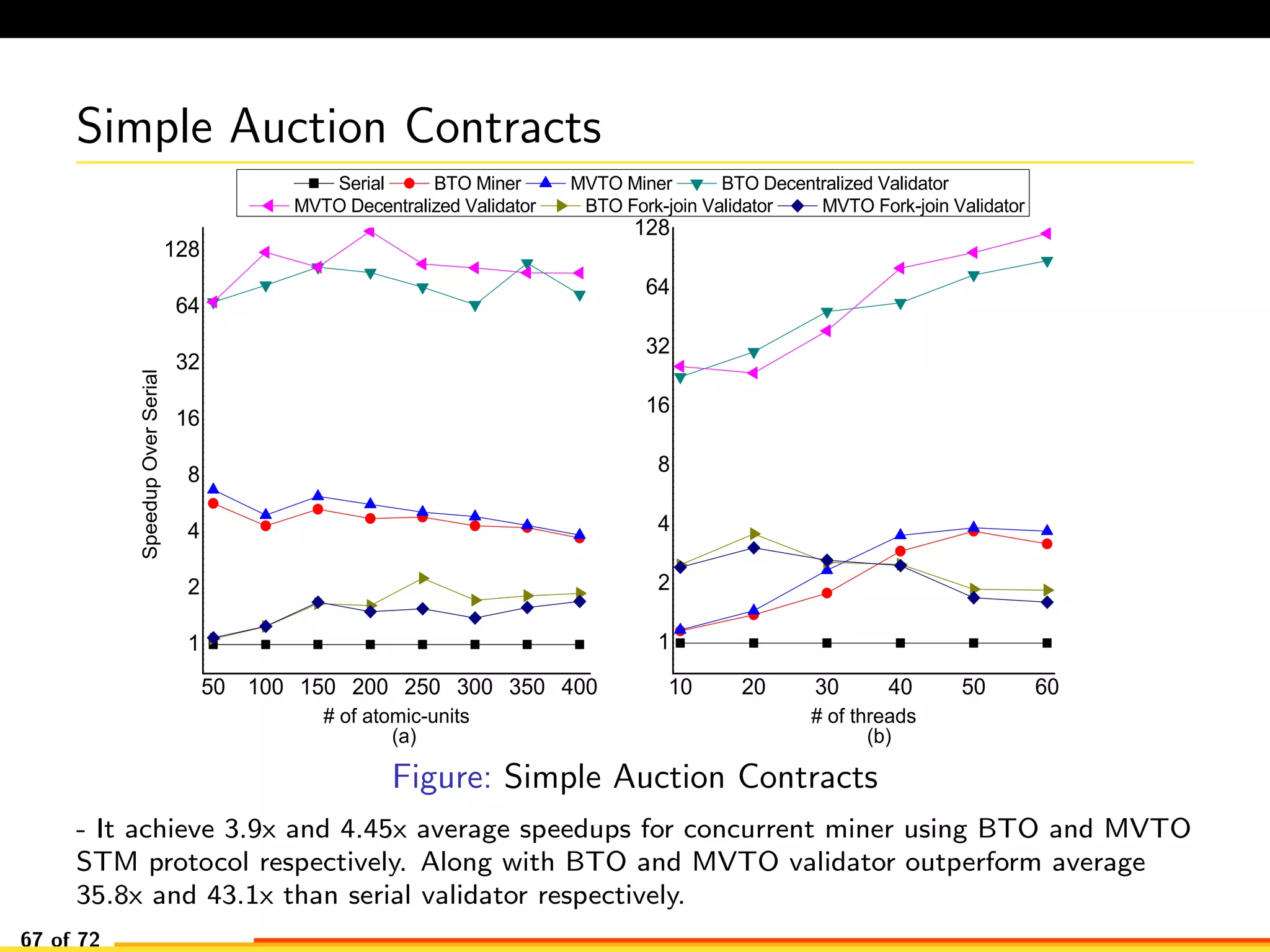
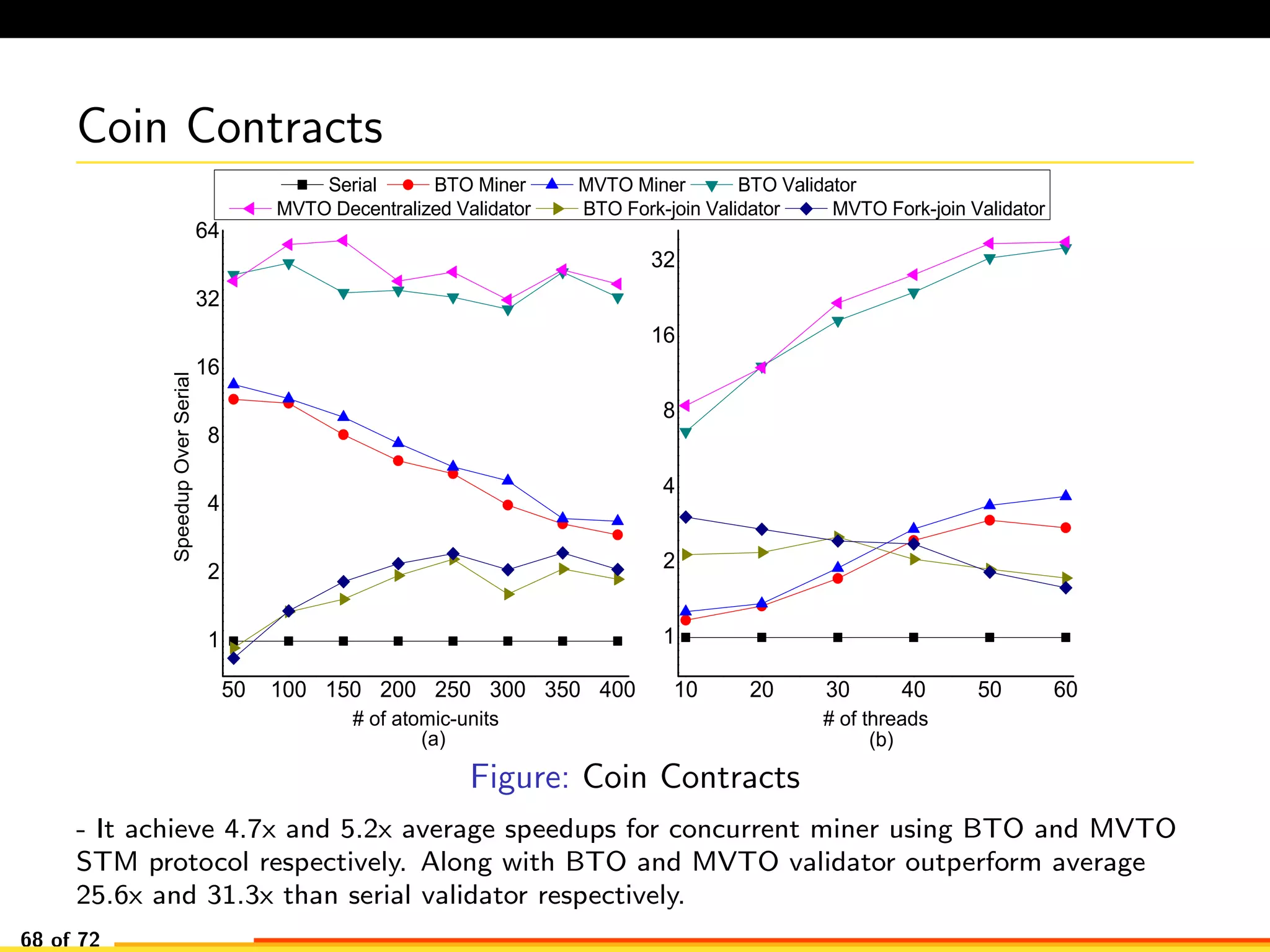
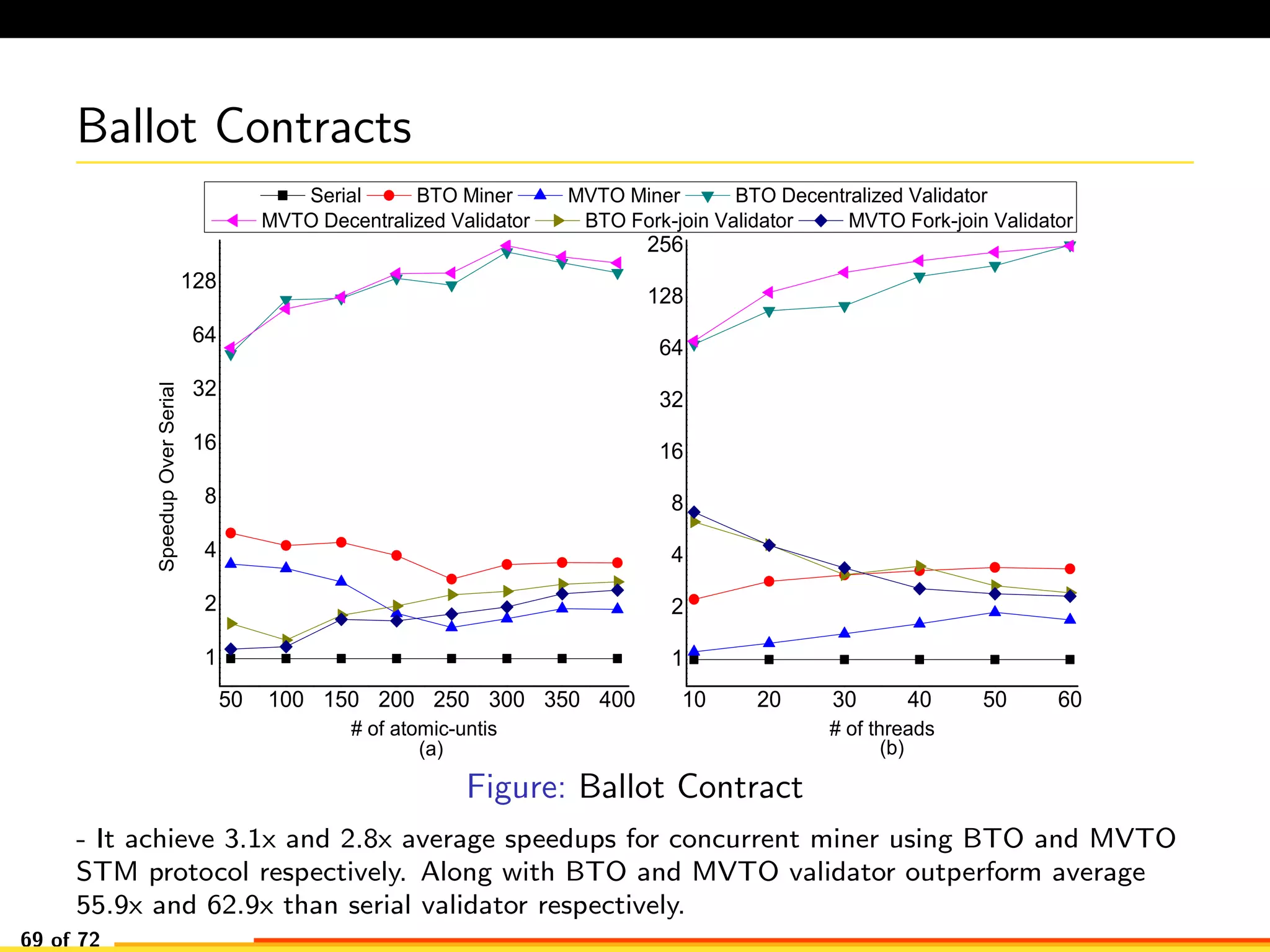
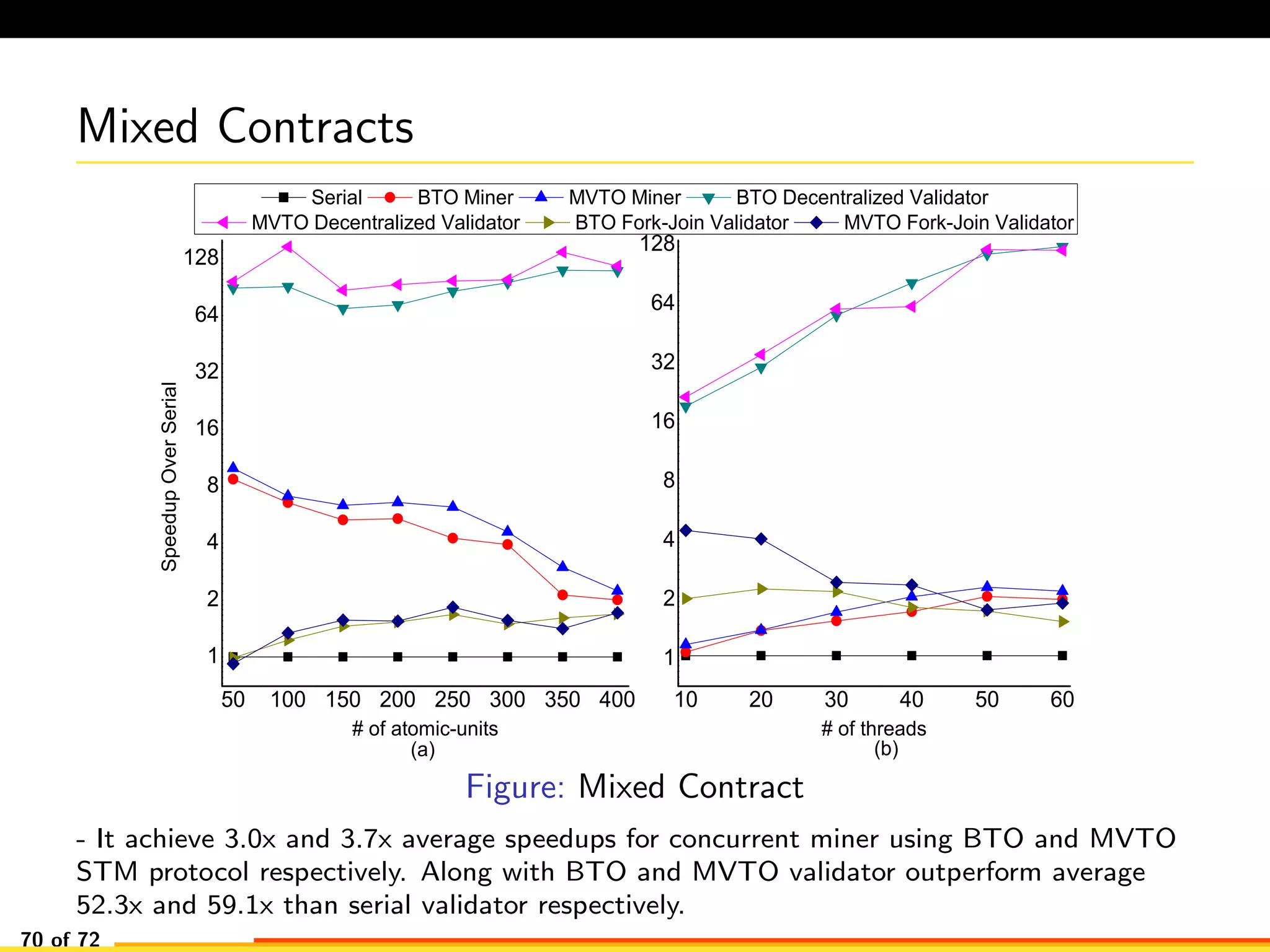
The document discusses efficient smart contract design for blockchains. It begins with an introduction to blockchains and smart contracts. It then describes the current Ethereum blockchain design, which executes smart contract transactions sequentially. This results in poor throughput due to underutilization of multi-core processors. The document proposes a new concurrent methodology using software transactional memory systems to allow miners to execute smart contract transactions concurrently. This aims to improve efficiency and throughput. However, concurrent execution presents challenges such as identifying and resolving data conflicts between transactions. The document discusses protocols to enable concurrent transaction execution while maintaining equivalent results to the serial execution model.