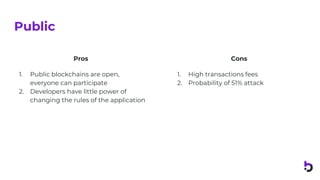
This document provides an introduction to Hyperledger Fabric, a permissioned blockchain platform developed by the Hyperledger project. It outlines the key components of Hyperledger Fabric including nodes, transactions, channels, chaincode, and membership services. It also discusses the differences between public and private blockchains as well as examples use cases for Hyperledger Fabric such as global supply chain management and city management.