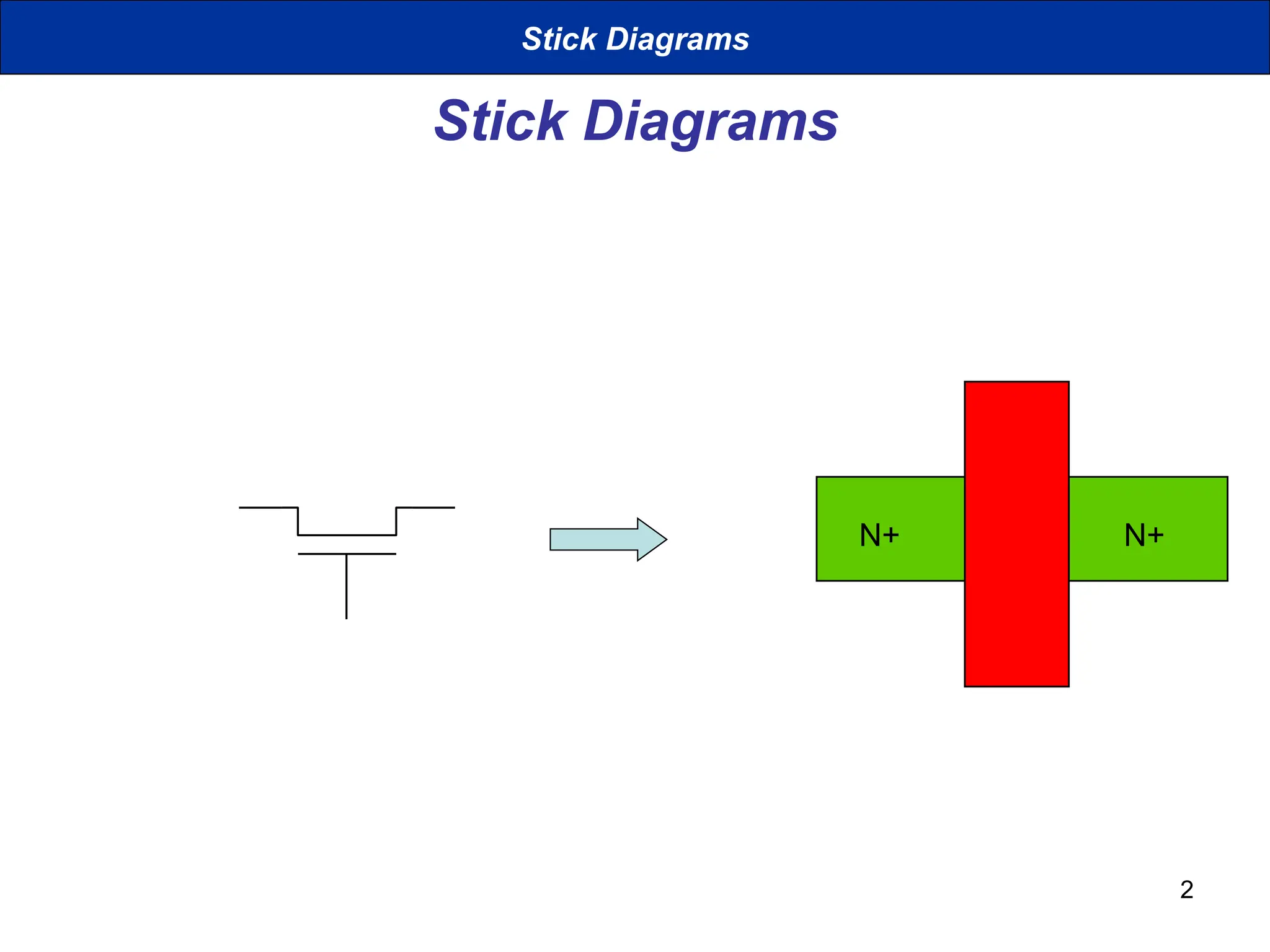
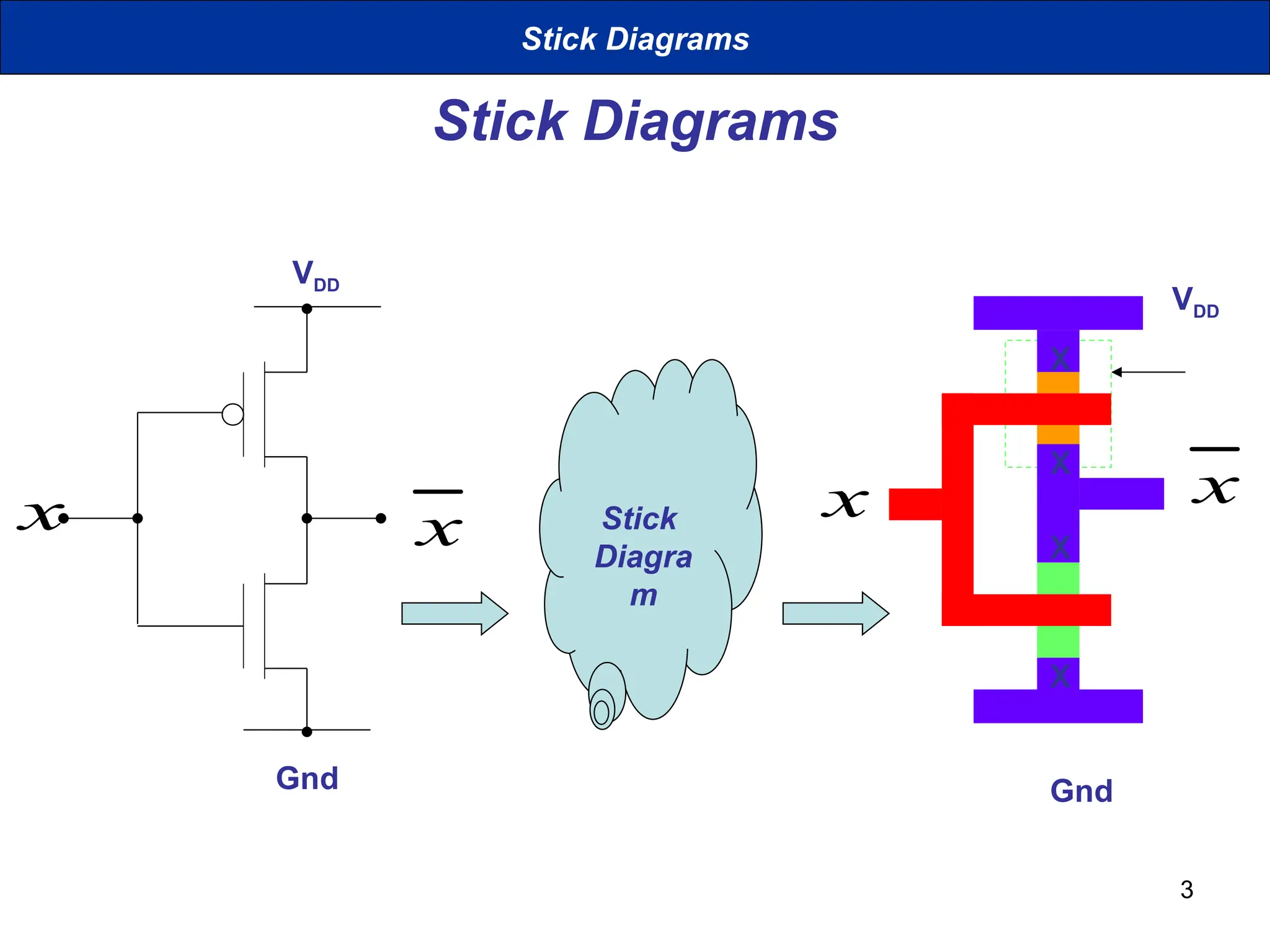
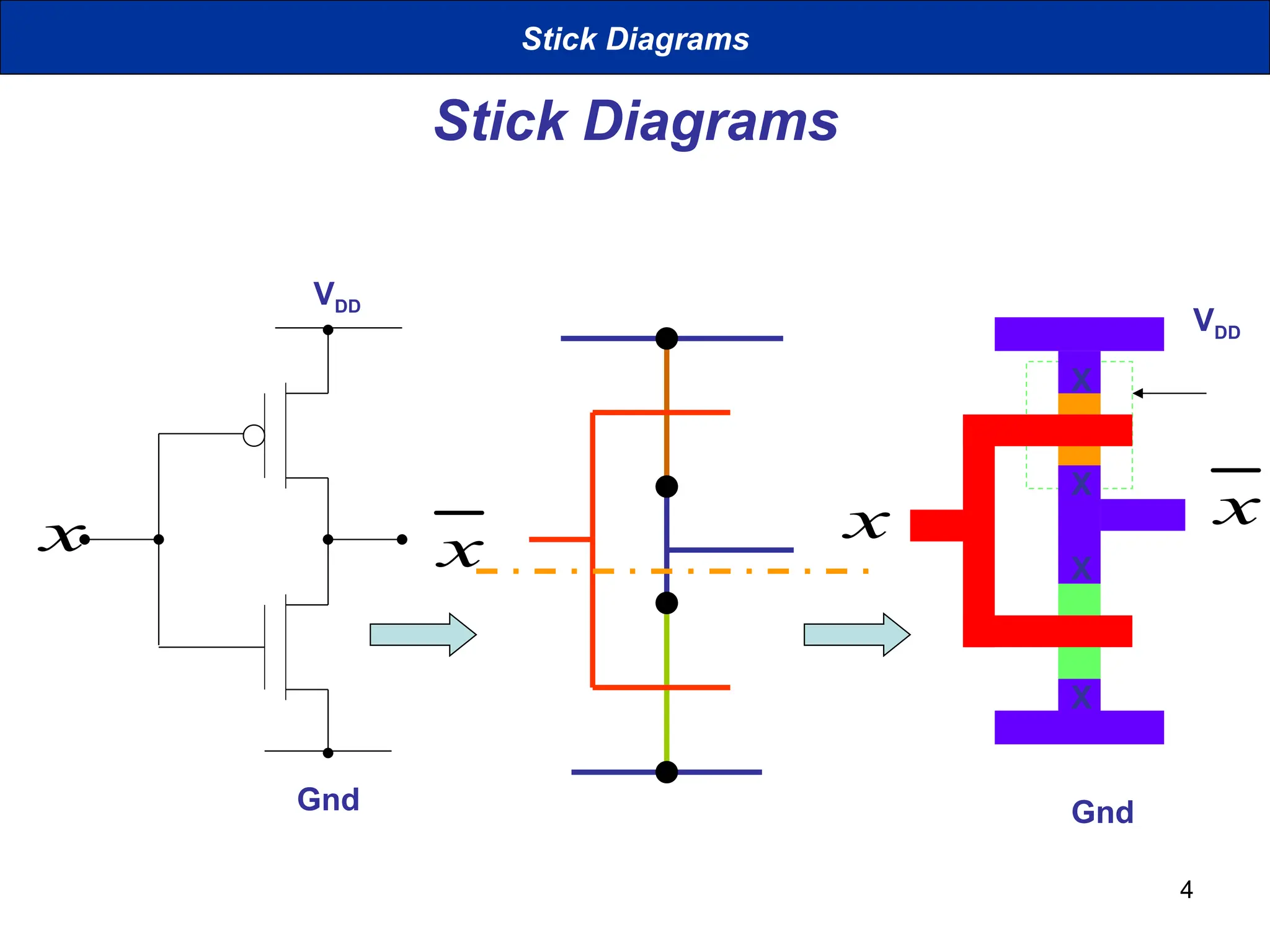
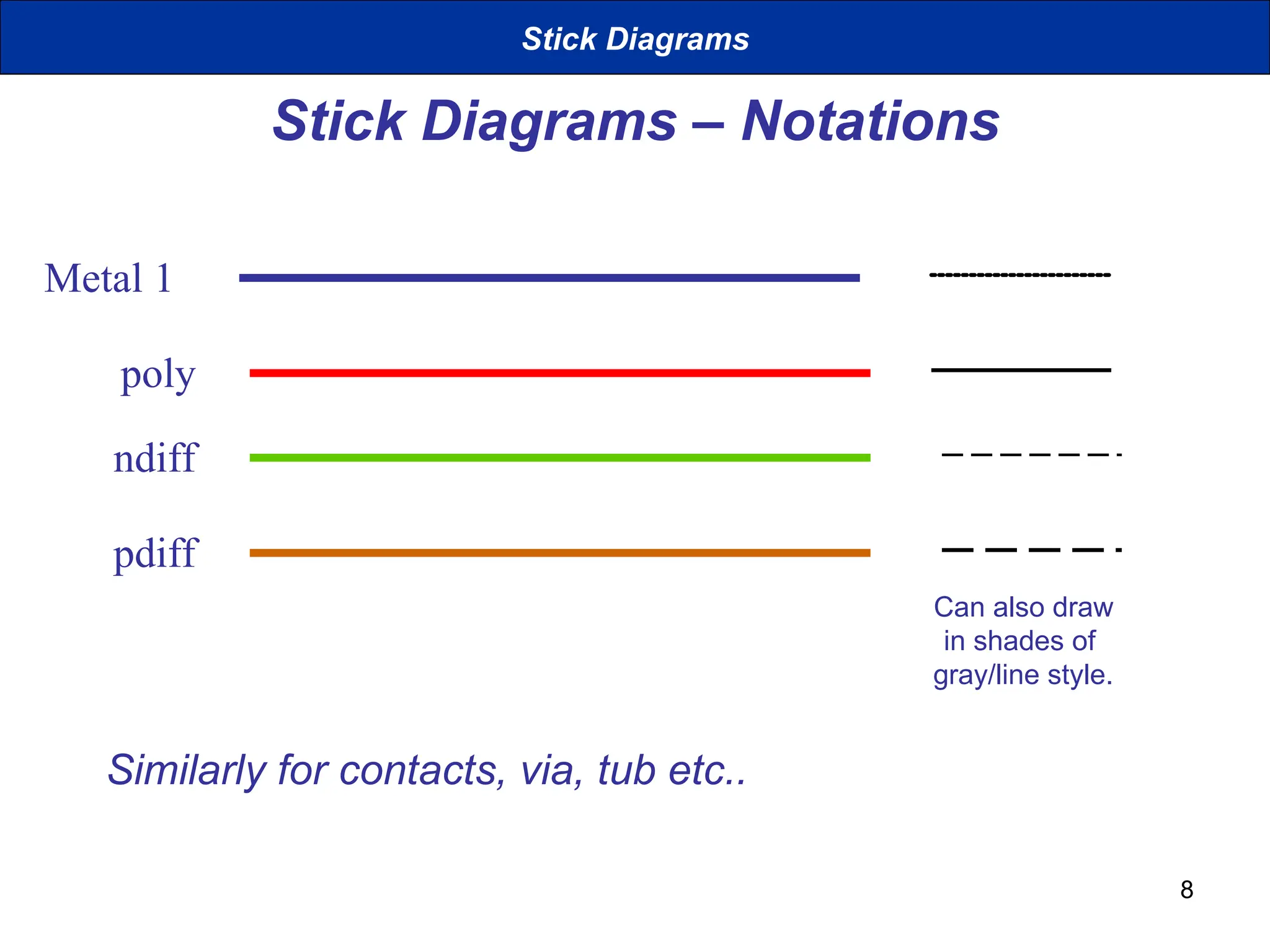
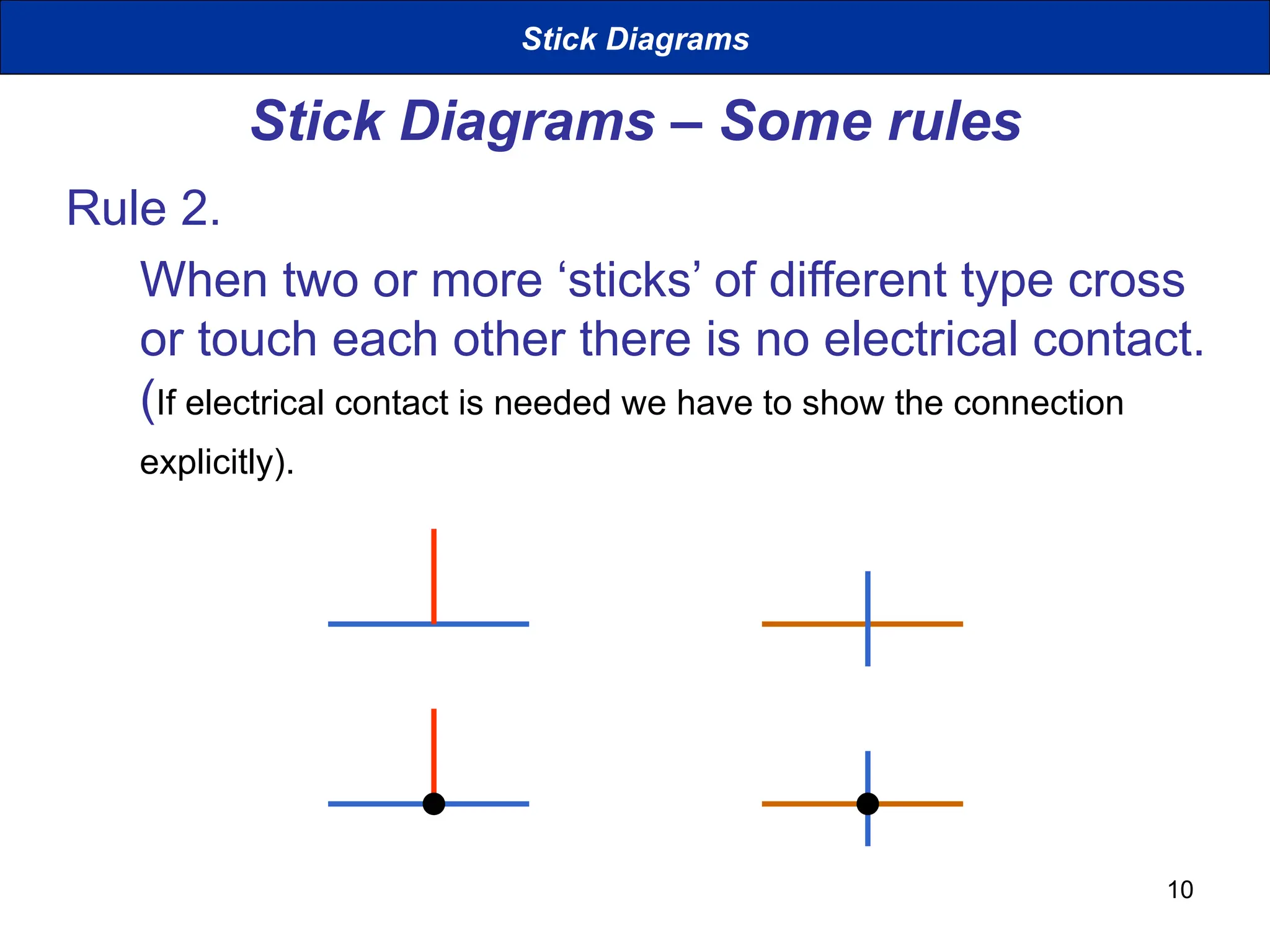
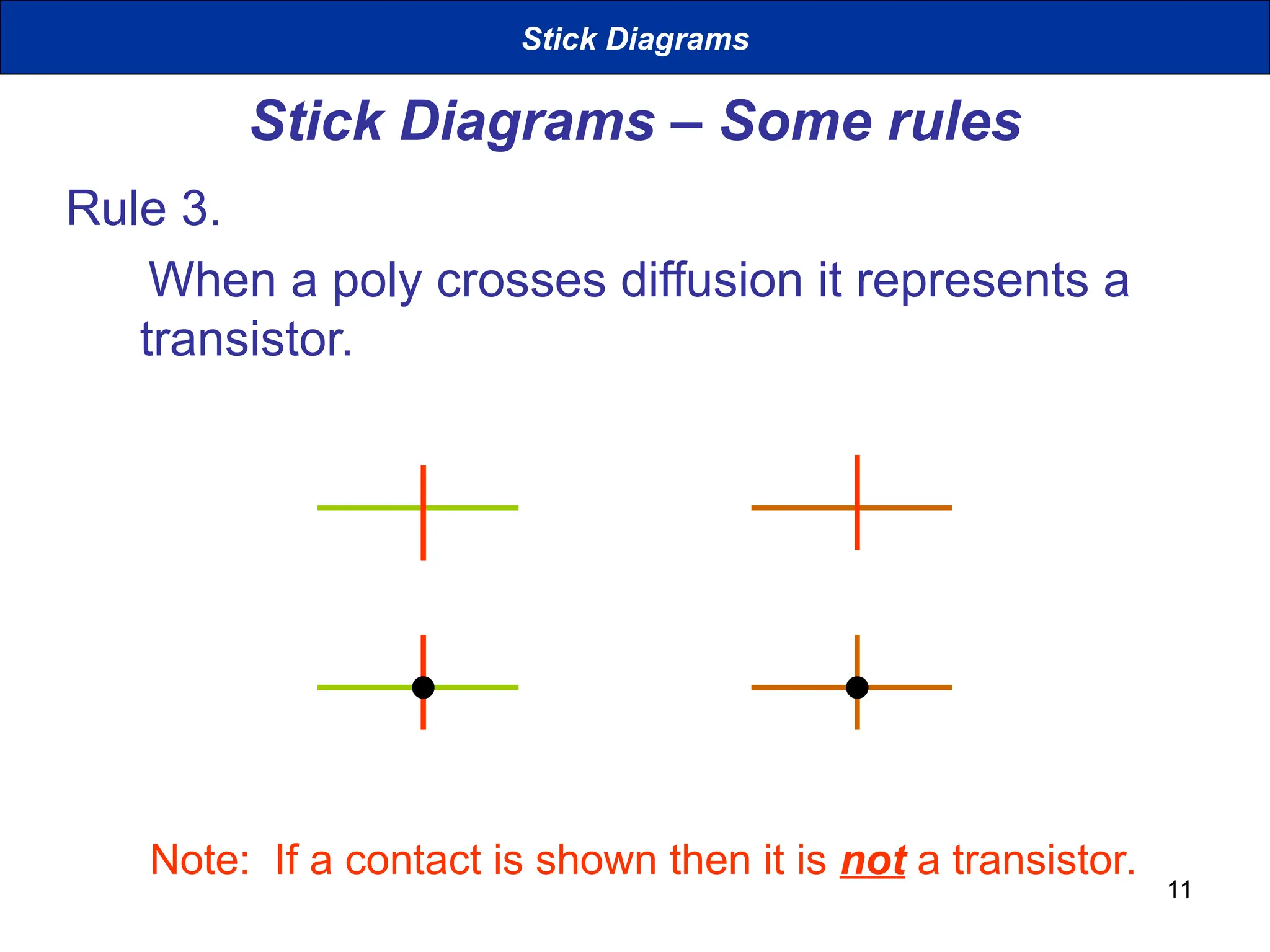
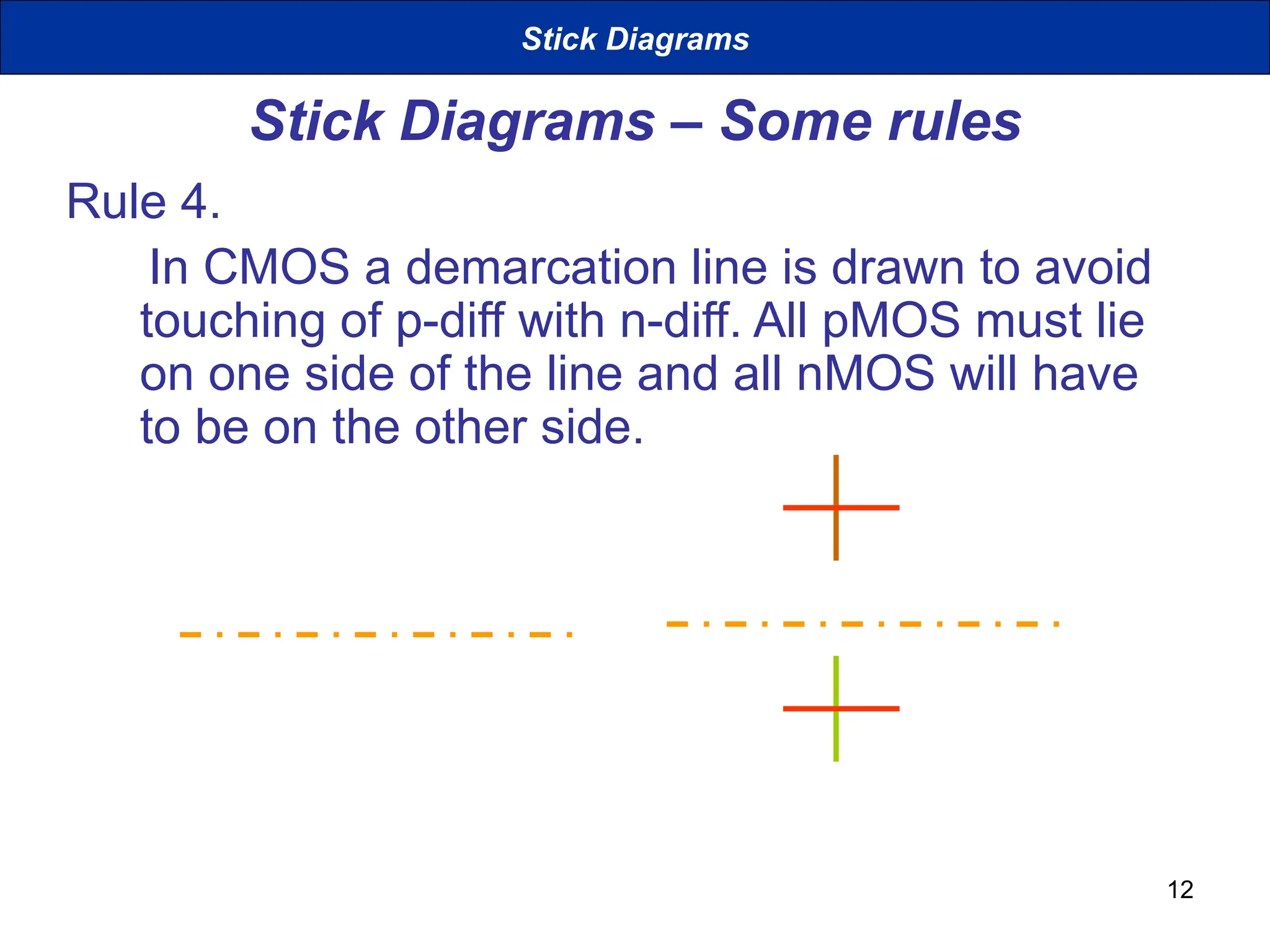
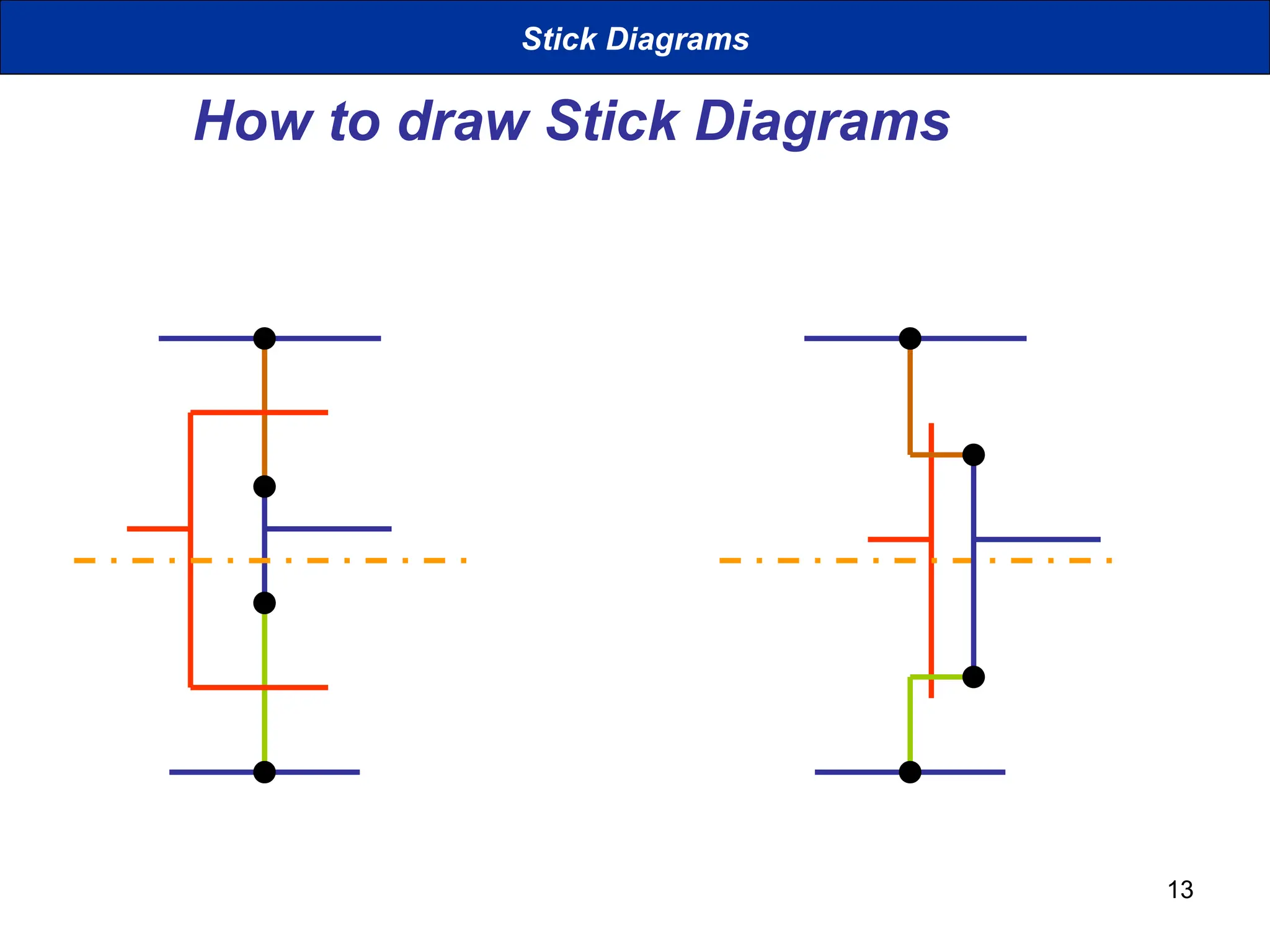
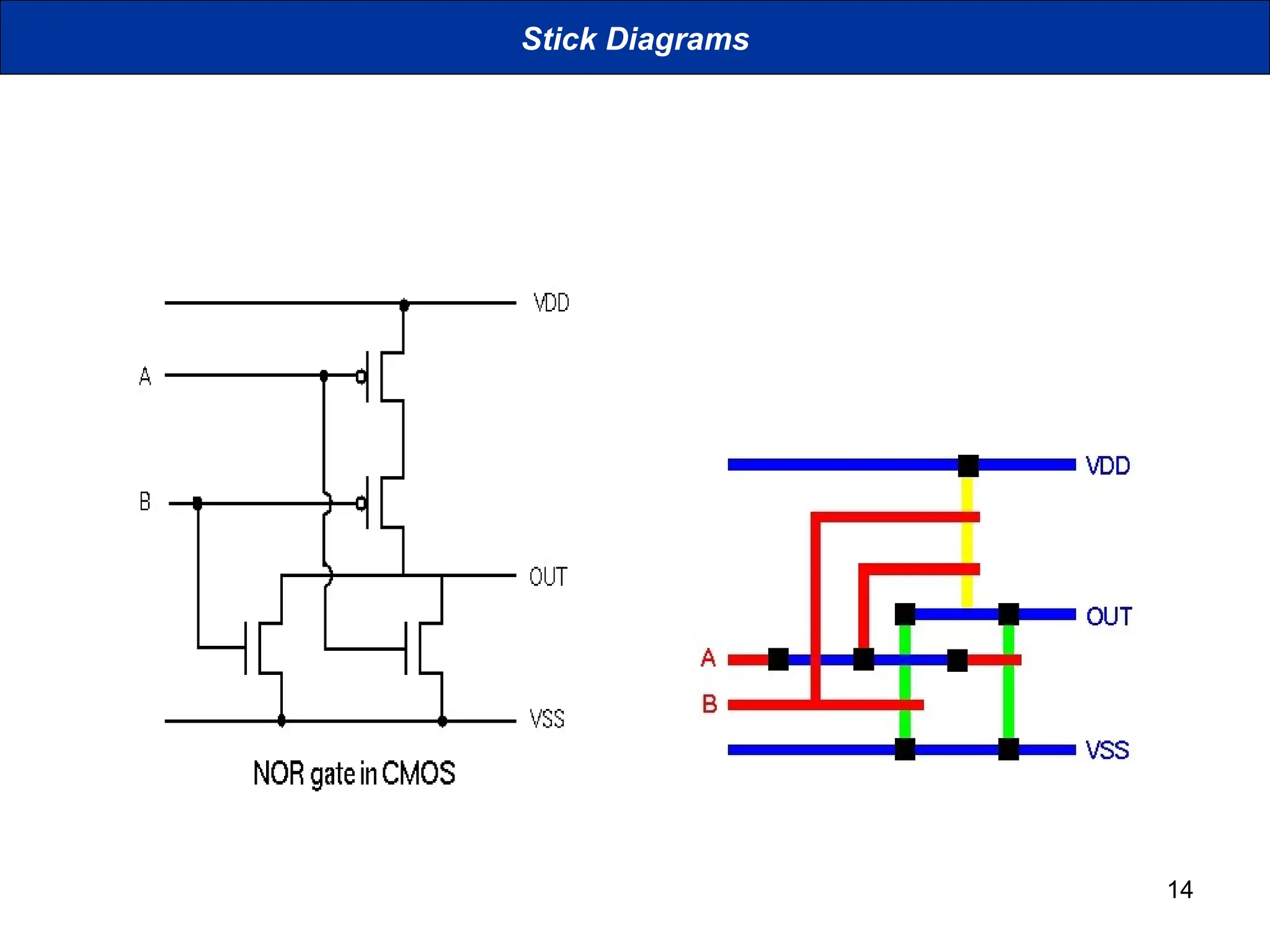
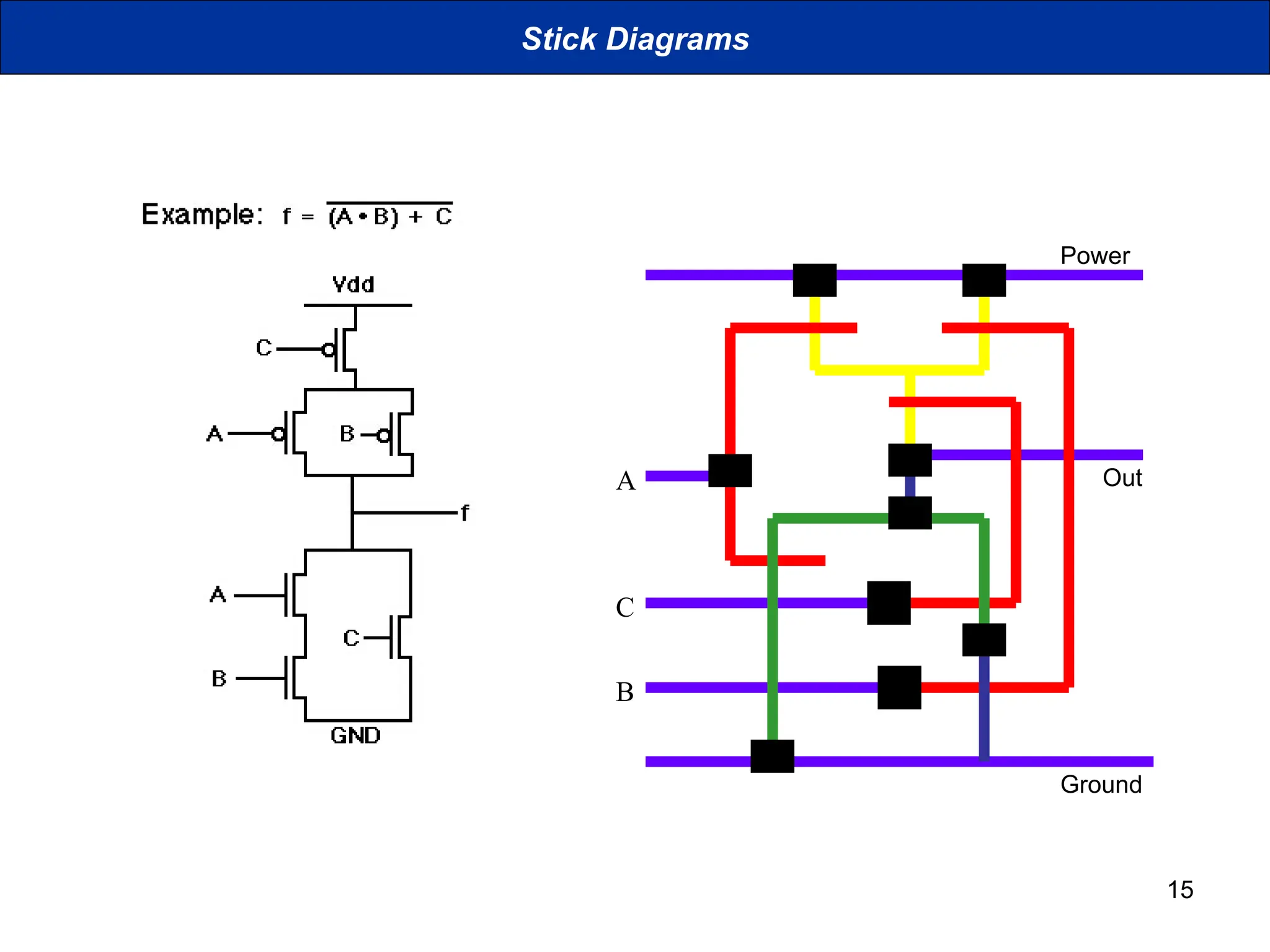
The document discusses stick diagrams used in VLSI design, serving as a simplification of circuit layouts while conveying topographical and layer information. It outlines the basic rules for creating stick diagrams, including how to represent electrical contacts and transistor indications, as well as provides examples of drawings. Stick diagrams play a crucial role in the planning phase of circuit layout and routing.