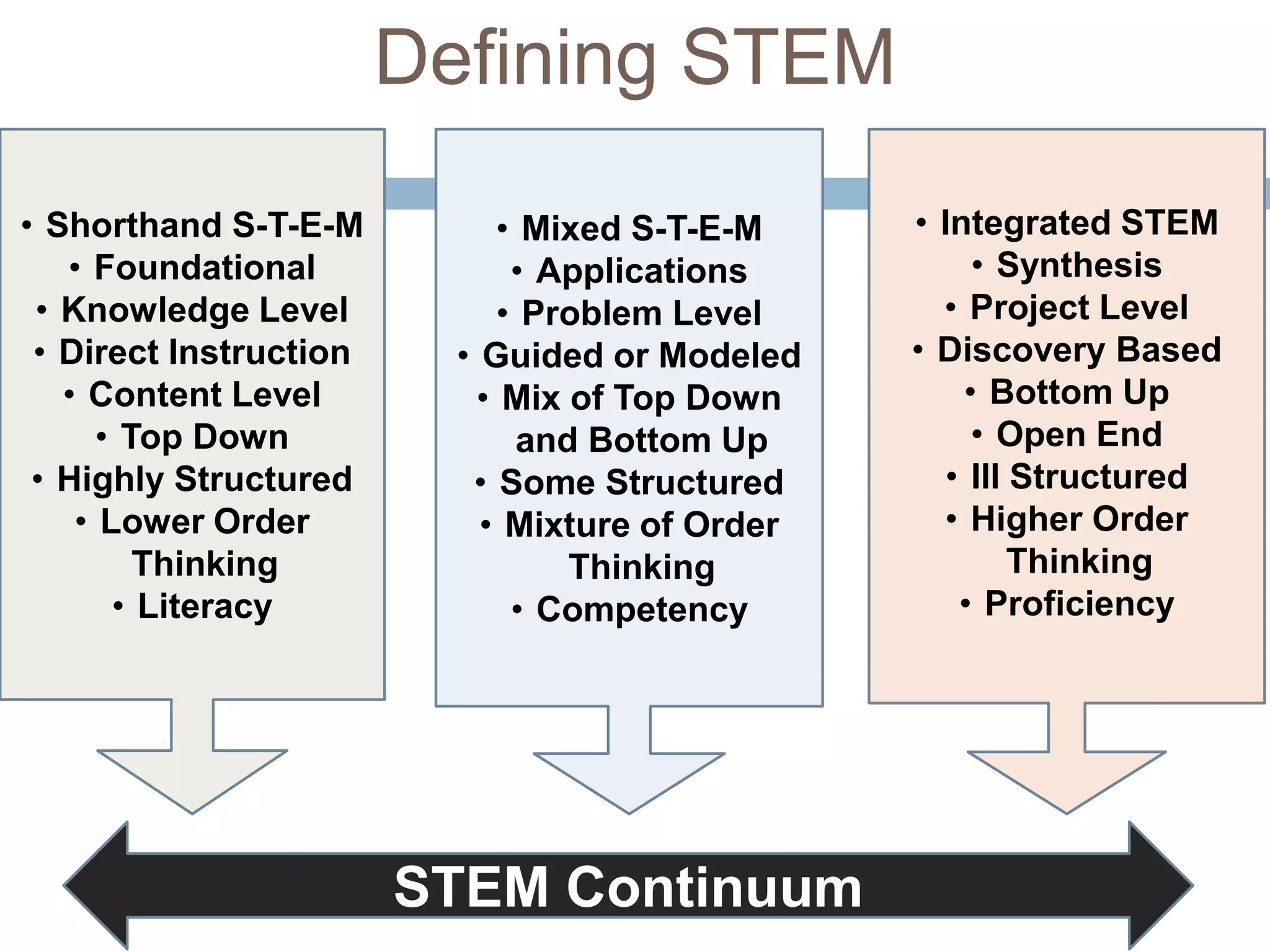
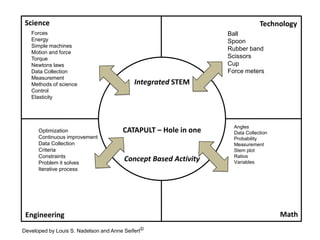
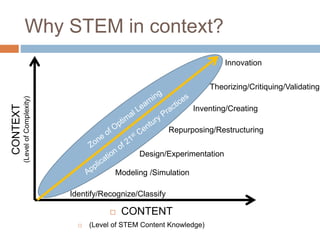
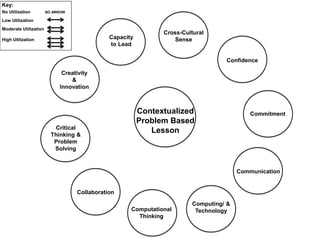
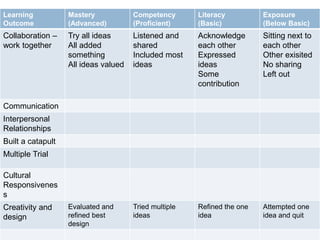
This document outlines a continuum of STEM integration from foundational to highly integrated. It begins with standalone subjects taught through direct instruction and progresses to open-ended, problem-based and discovery learning that synthesizes multiple STEM domains. The highest level involves innovation through theorizing and critiquing integrated STEM applications to real-world problems. Examples are provided of a catapult challenge that integrates science, technology, engineering and math concepts through an iterative design process.