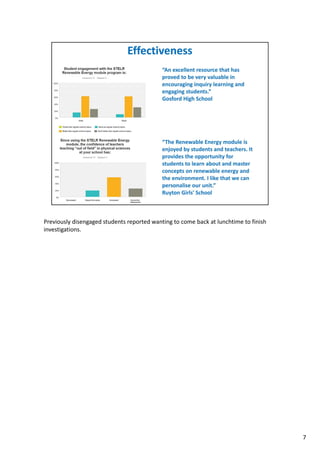
STELR is a national education initiative run by the Australian Academy of Technology and Engineering that involves over 500 schools and benefits over 130,000 students each year. The STELR Project uses inquiry-based, hands-on learning with relevant themes like sustainability to engage over 50,000 students and 1,500 teachers annually in STEM education. It was created by Alan Finkel, the current Chief Scientist of Australia, to improve science and math education in Australian schools.