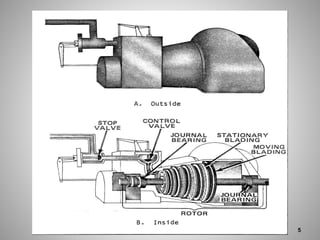
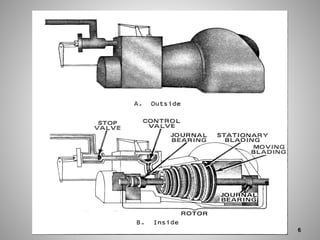
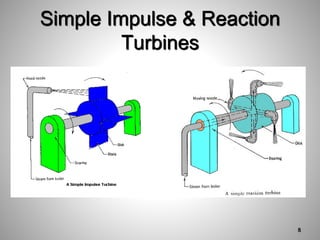
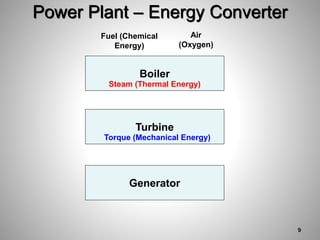
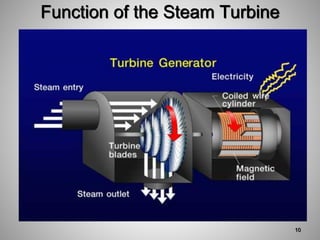
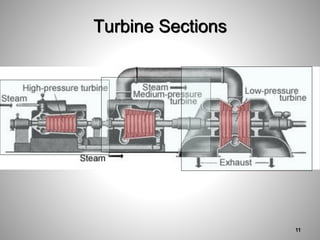
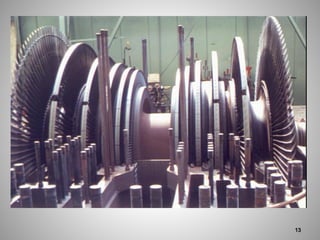
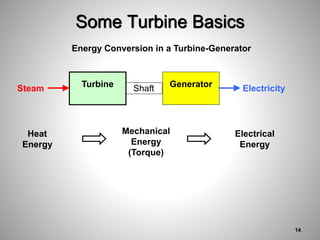
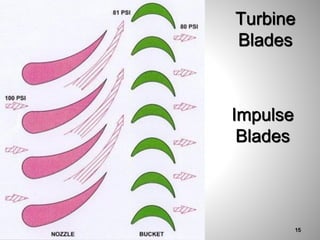
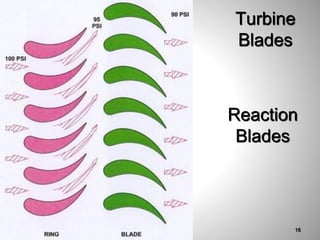
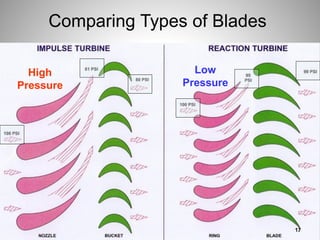
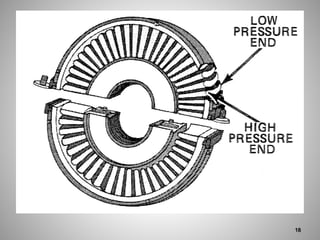
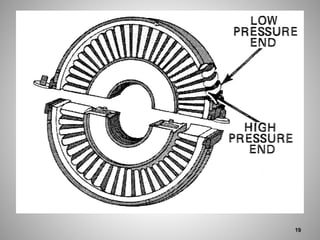
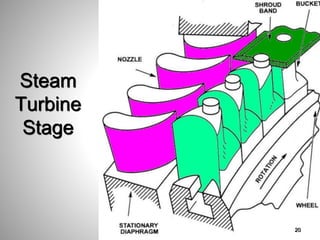
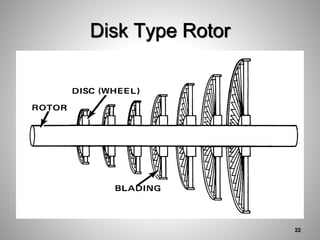
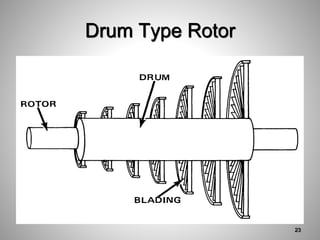
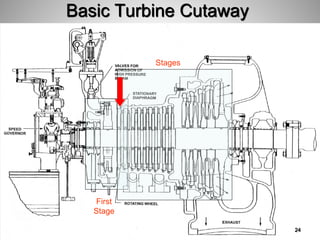
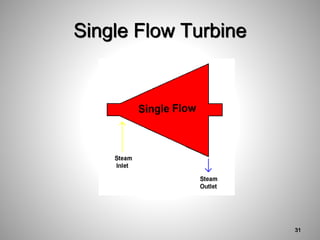
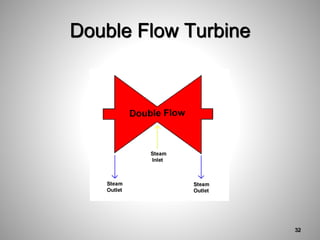
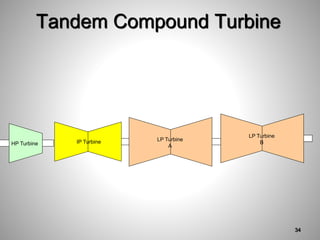
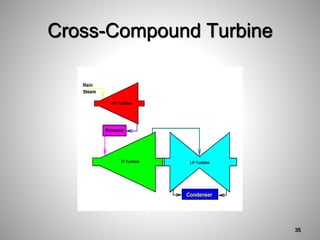
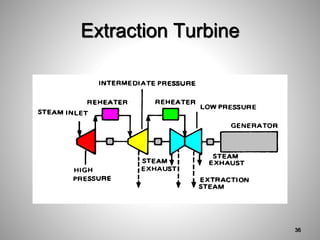
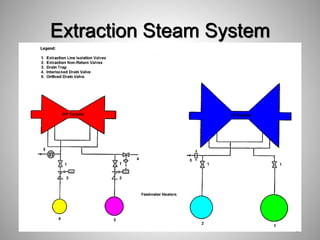
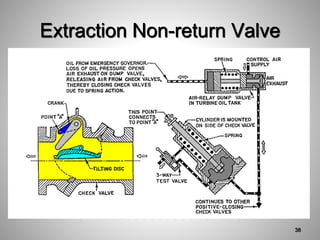
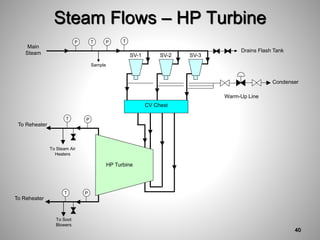
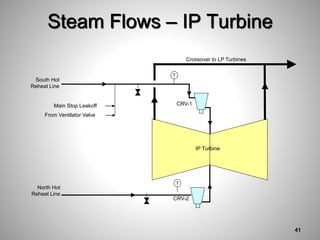
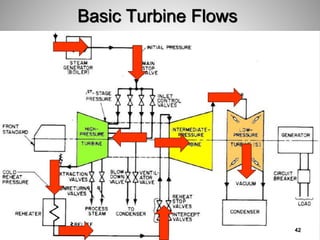
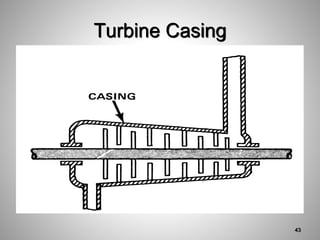
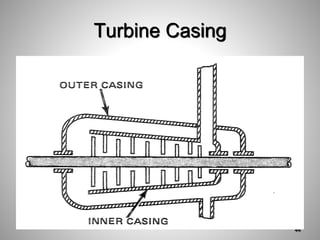
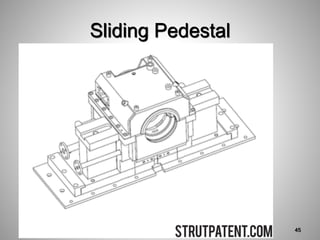
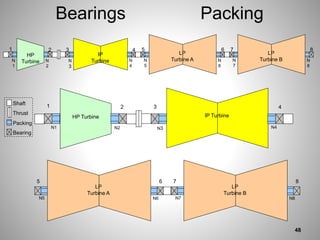
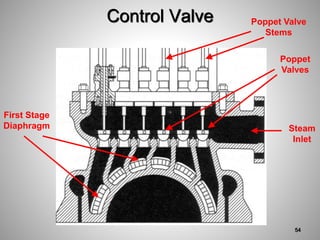
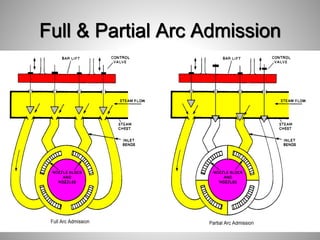
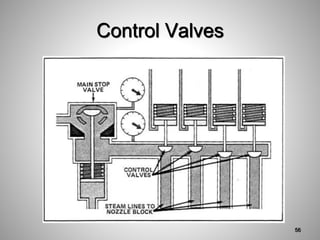
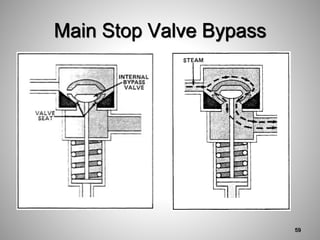
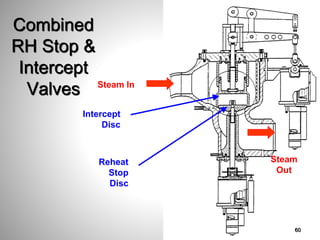
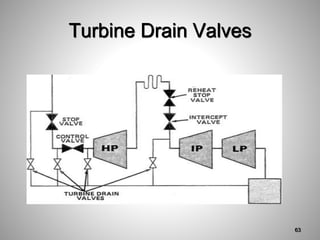
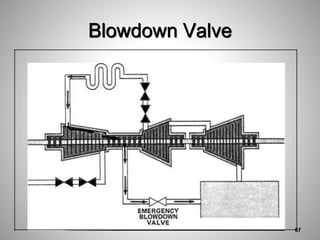
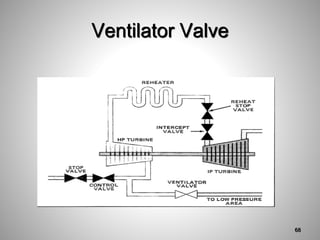
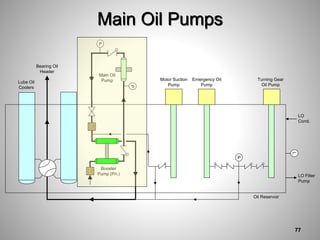
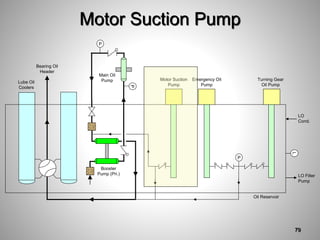
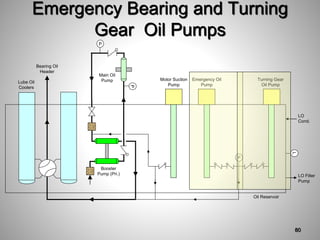
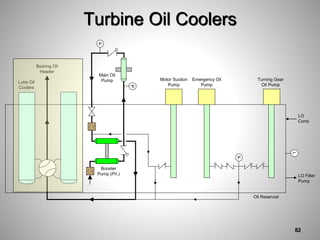
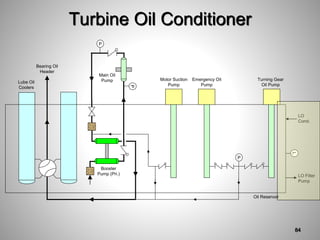
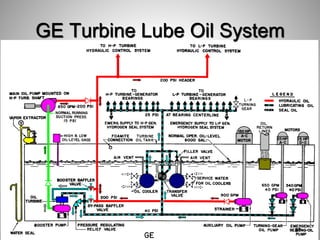
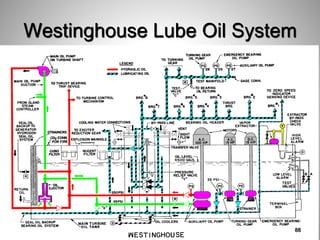
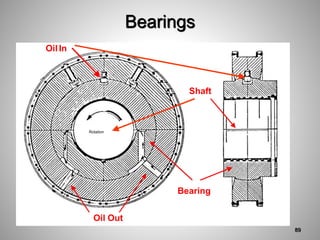
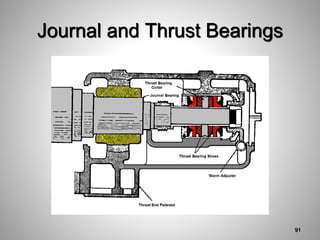
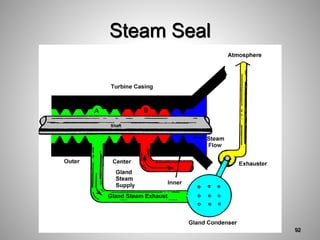
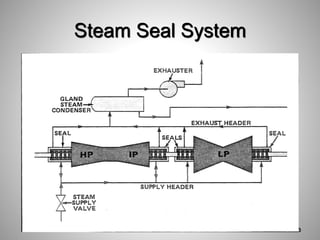
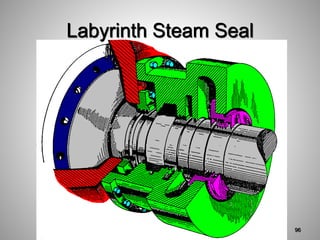
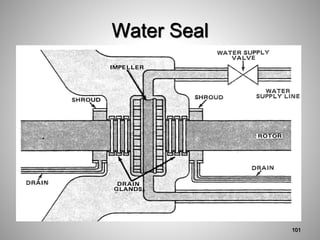
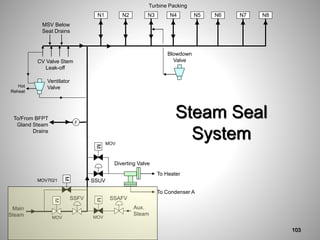
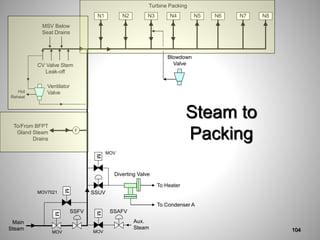
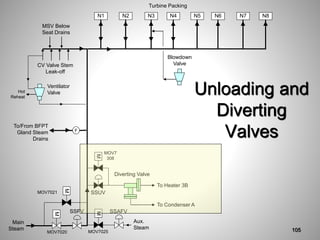
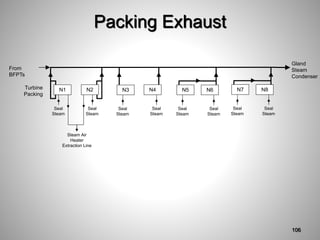
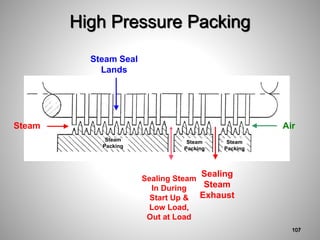
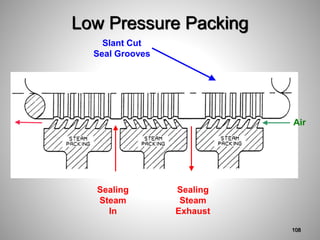
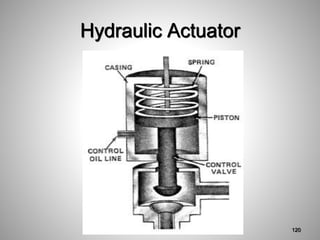
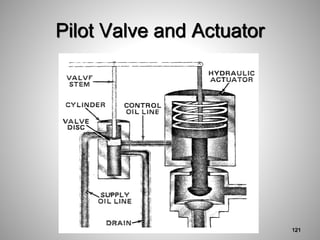
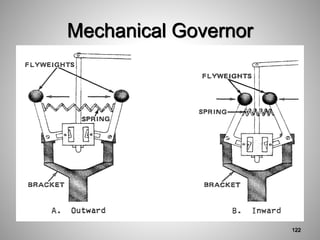
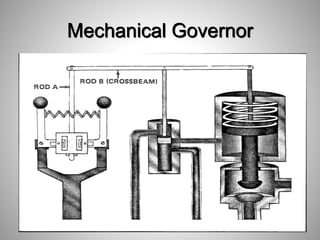
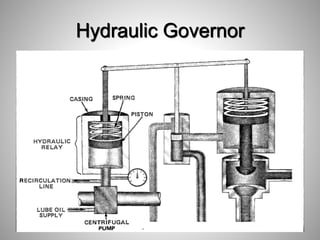
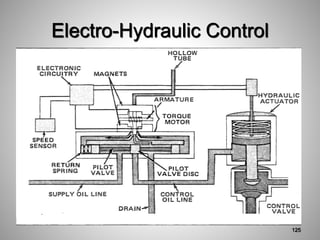
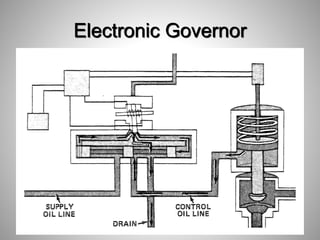
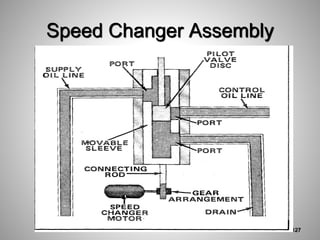
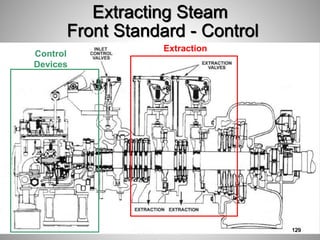
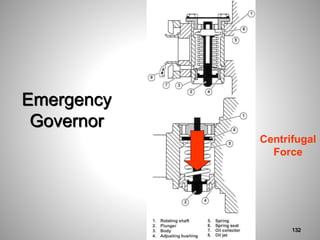
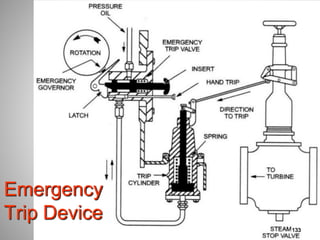
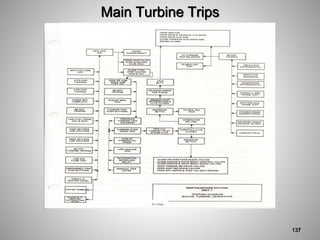
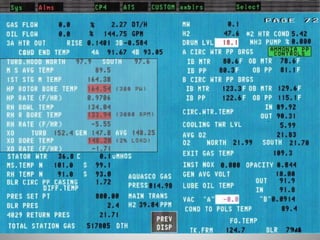
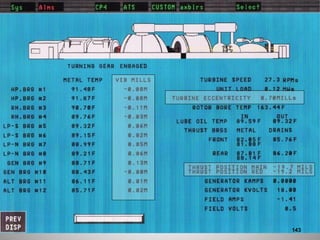
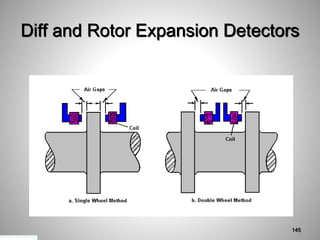
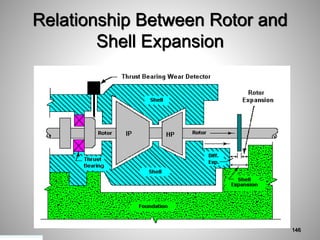
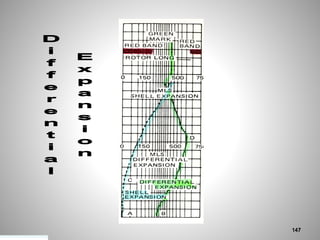
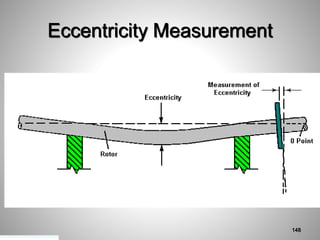
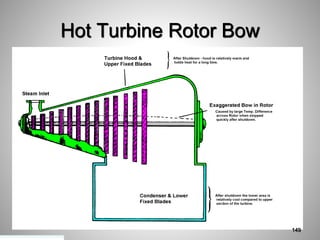
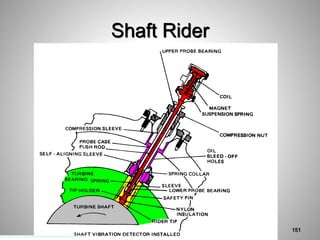
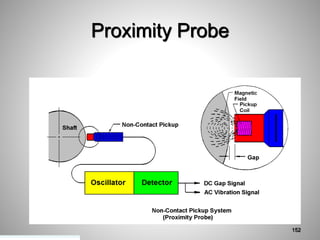
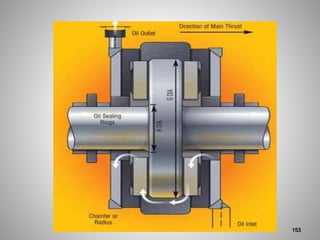
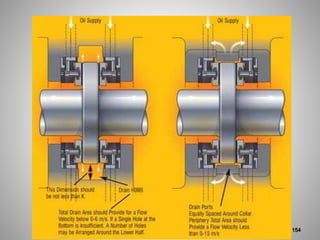
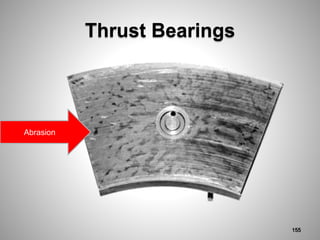
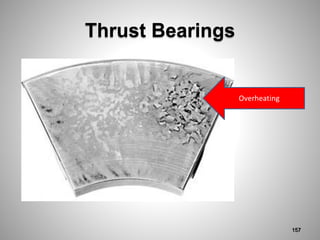
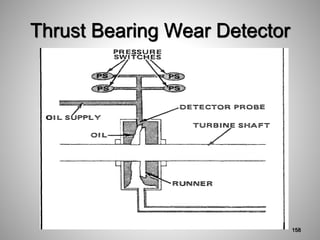
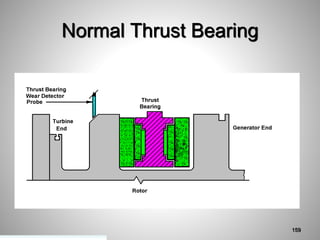
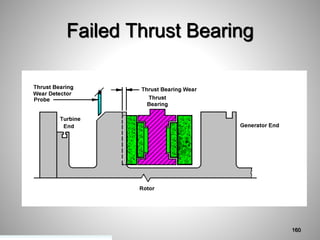
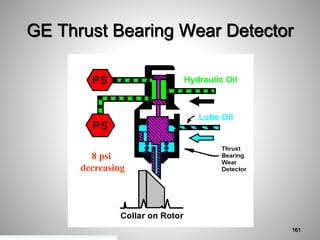
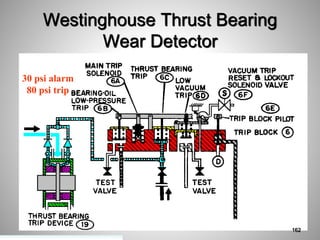
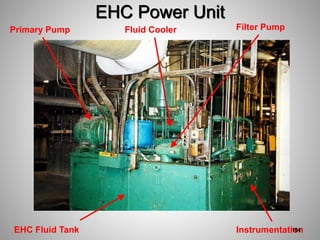
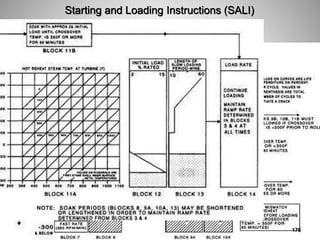
This document provides an overview of a training program on power plant fundamentals and turbines. It covers turbine construction and operation, including the steam cycle, turbine sections and components, valves, support systems, control and instrumentation. The objectives are to demonstrate basic knowledge of the steam cycle and turbine operation, components like blades, casings and rotors, valves and their functions, auxiliary systems, and control of speed and extraction. It uses questions to check understanding of topics like steam flows through different turbine sections and the roles of valves and components like packing glands and turning gears.