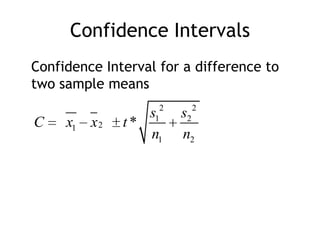
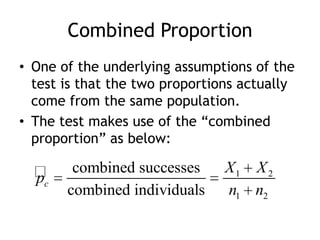
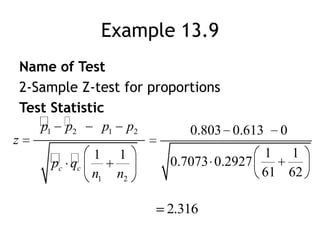
The document discusses comparing two population parameters using sample data. It covers comparing two means using a two-sample t-test or z-test, and comparing two proportions using a two-sample z-test. Key assumptions for these tests include independent random samples from each population and sample sizes large enough for the sampling distributions to be approximately normal. An example compares systolic blood pressure for two groups, one taking calcium and one placebo, and finds no significant difference. A second example finds preschool significantly reduces the proportion needing later social services.


















![CalculatorsThe tests we are using are located in the [STAT] -> “TESTS” menu2-SampZTest = two sample z-test for means2-SampTTest = two sample t-test for mean2-SampZInt = two sample z Confidence Interval for difference of means2-SampTInt = two sample t Confidence Interval for difference of means](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/statschapter13-110406112754-phpapp02/85/Stats-chapter-13-24-320.jpg)
















![Calculators The tests we are using are located in the [STAT] -> “TESTS” menu2-PropZTest = 2 proportion z-test2-PropZInt = 2 proportion confidence interval](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/statschapter13-110406112754-phpapp02/85/Stats-chapter-13-43-320.jpg)