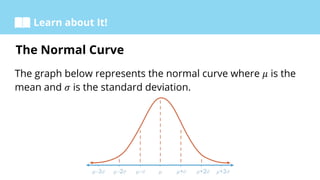
The document discusses the normal curve and its key properties. It defines the normal curve and explains that it represents a normal probability distribution. It presents the empirical rule, which states that approximately 68%, 95%, and 99% of the data lies within 1, 2, and 3 standard deviations of the mean, respectively. Examples are provided to illustrate how to construct a normal curve, find the area under the curve, and solve problems involving the normal distribution.