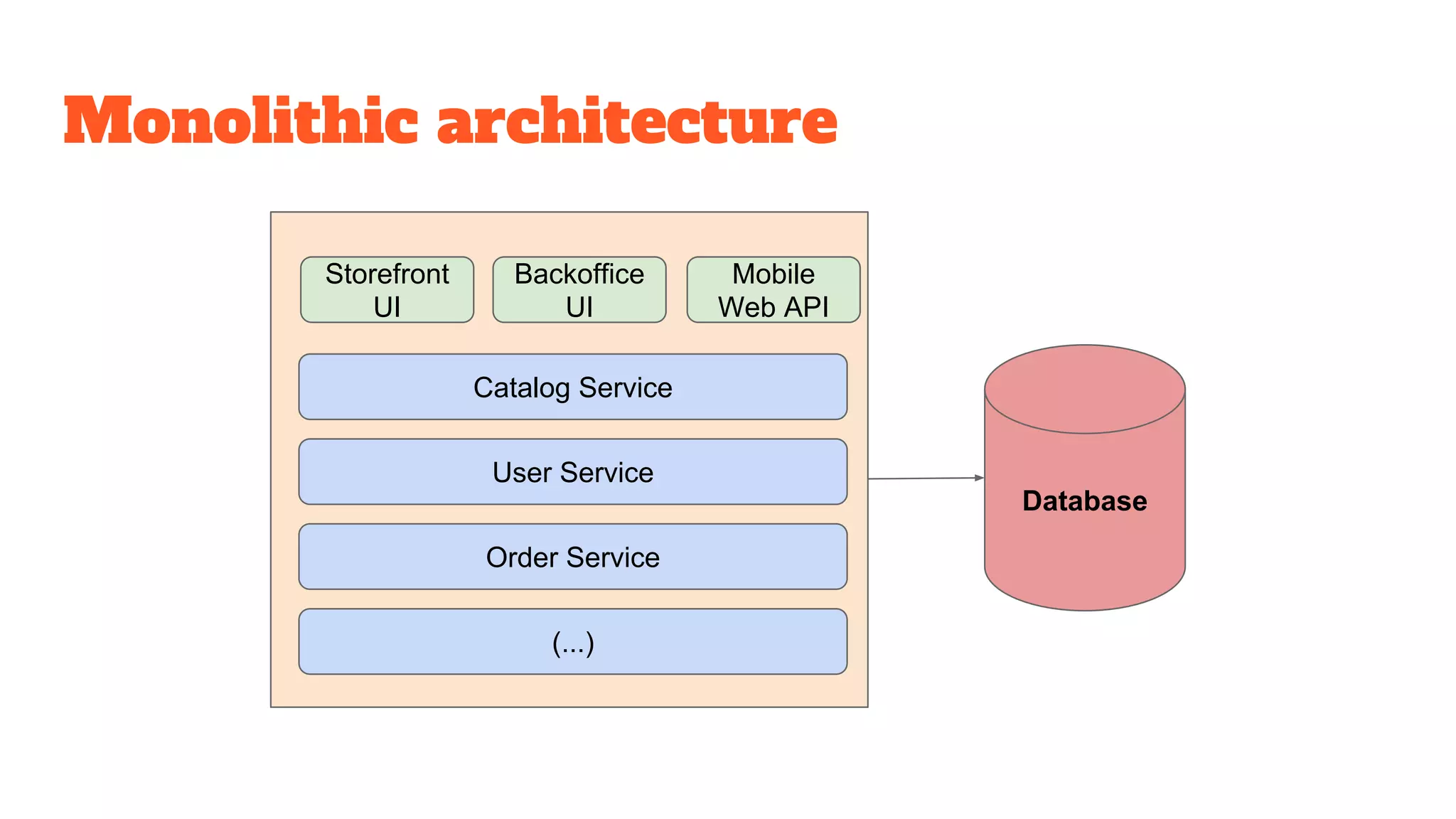
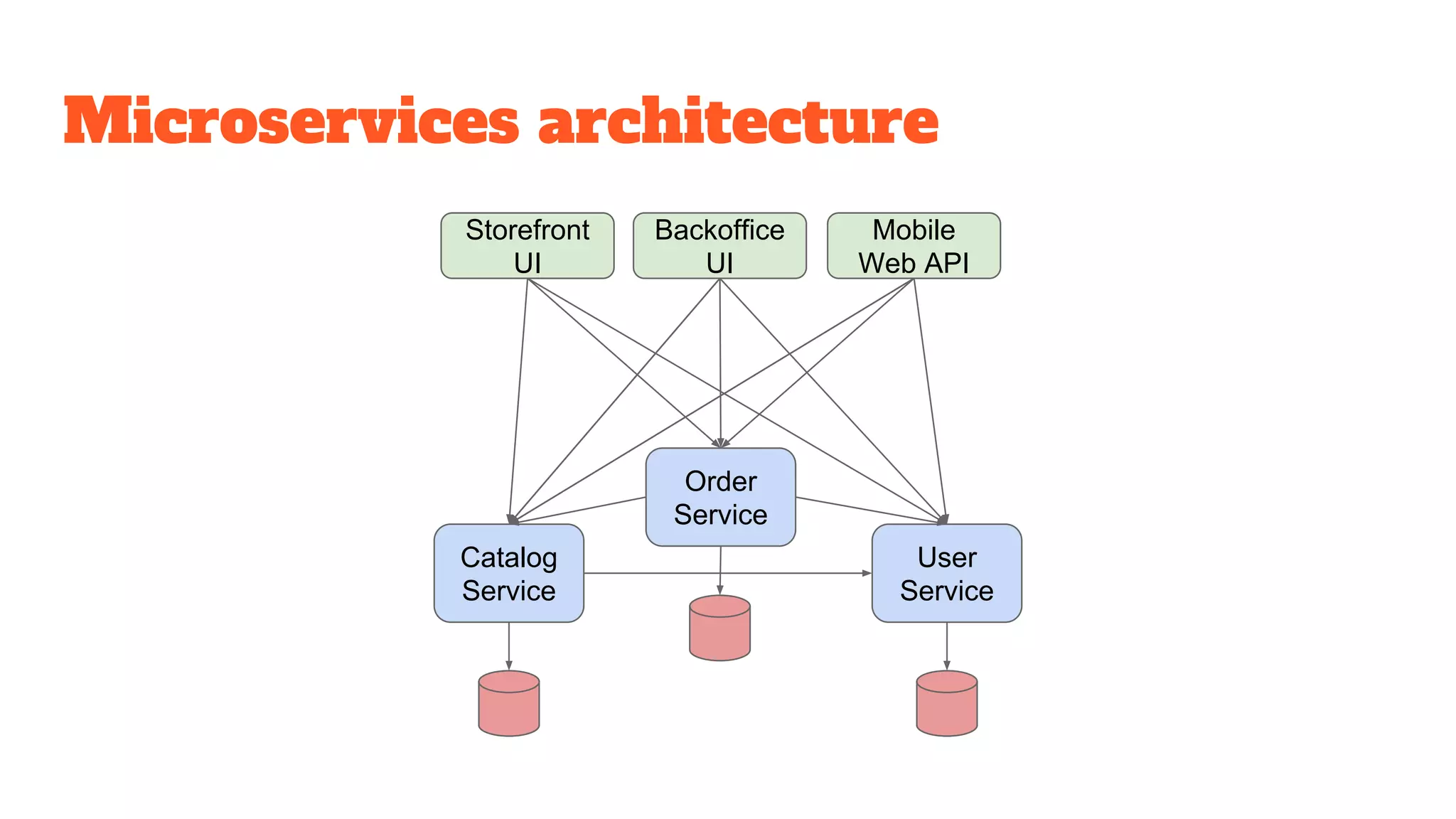
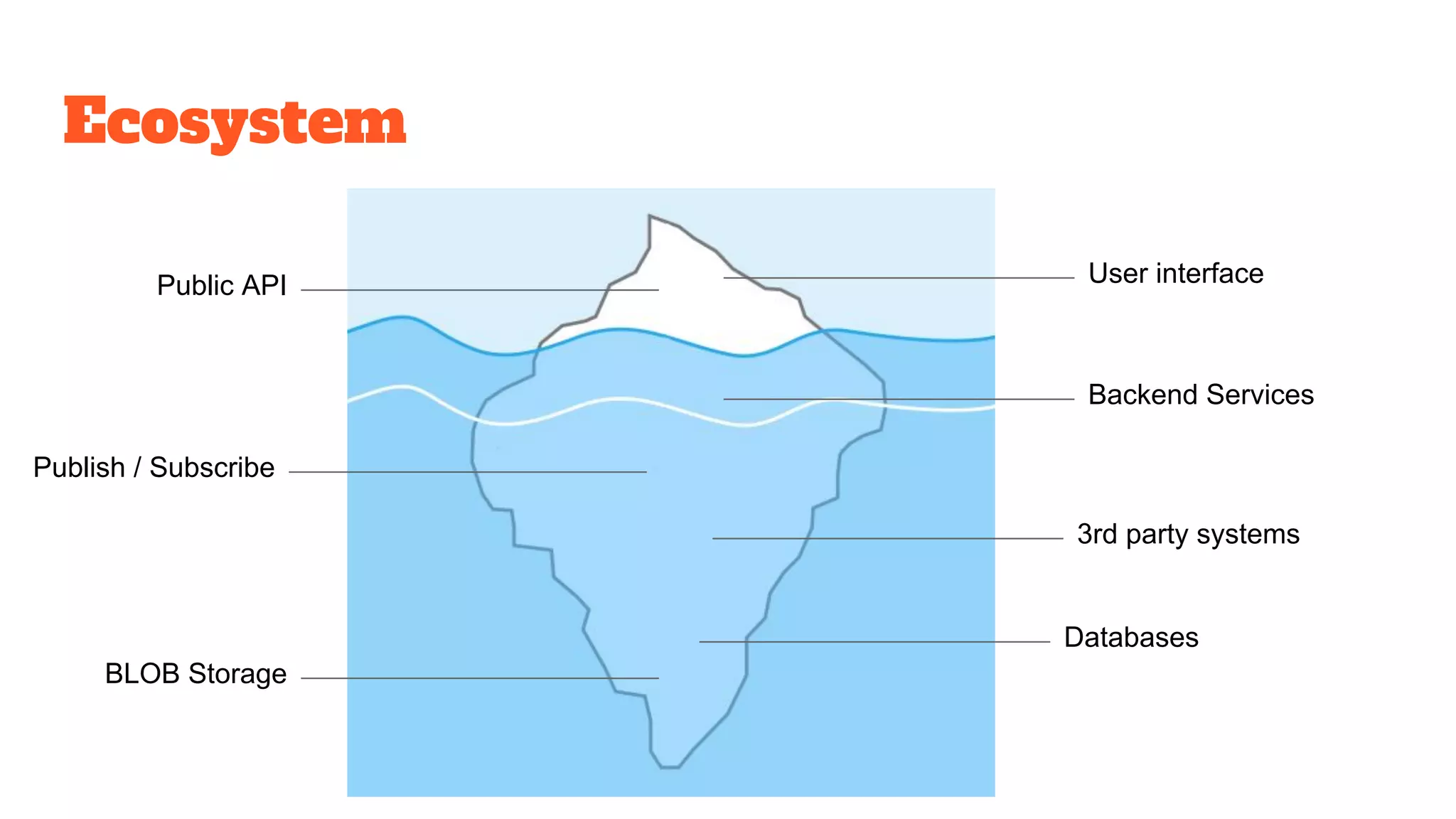
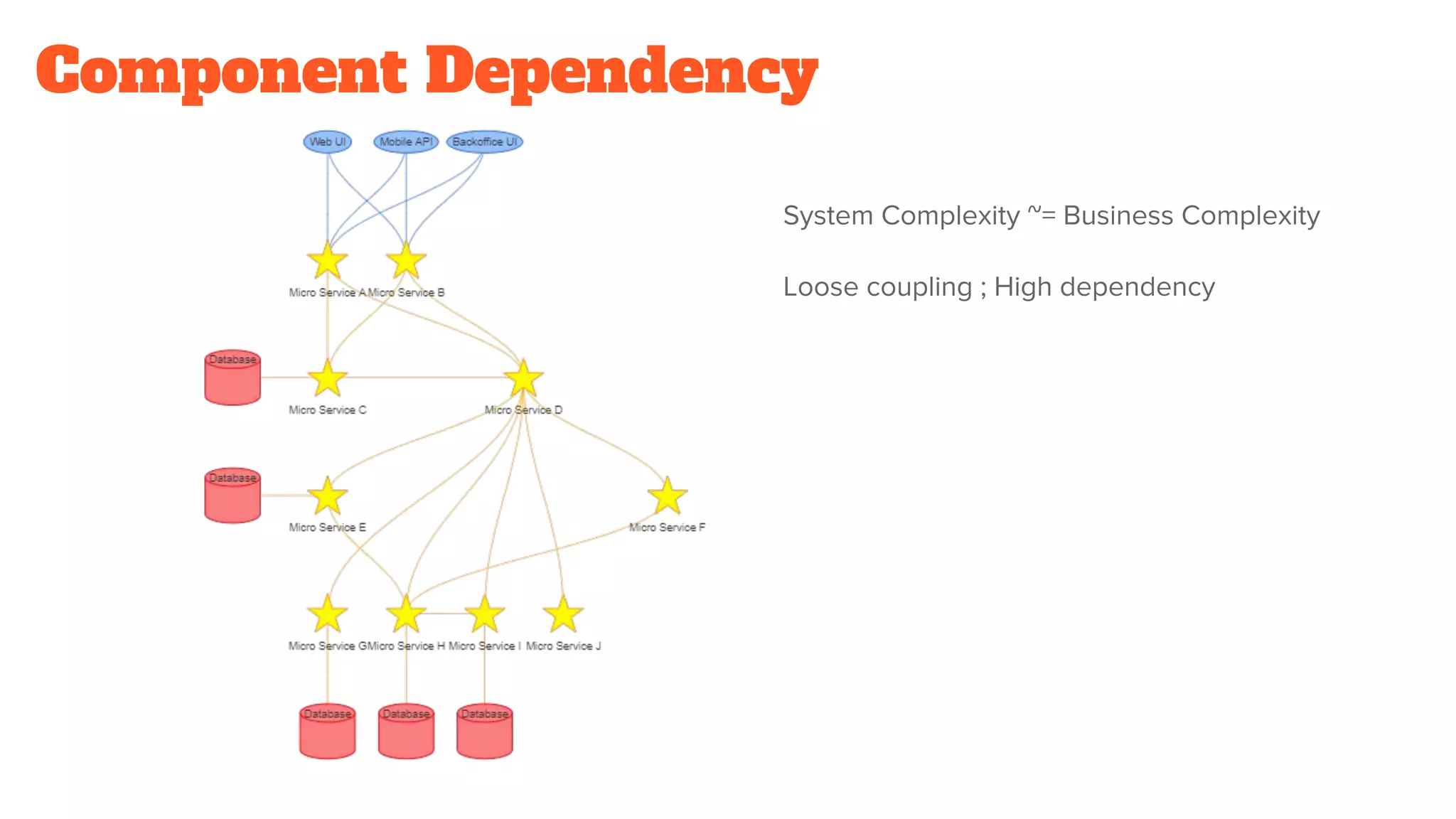
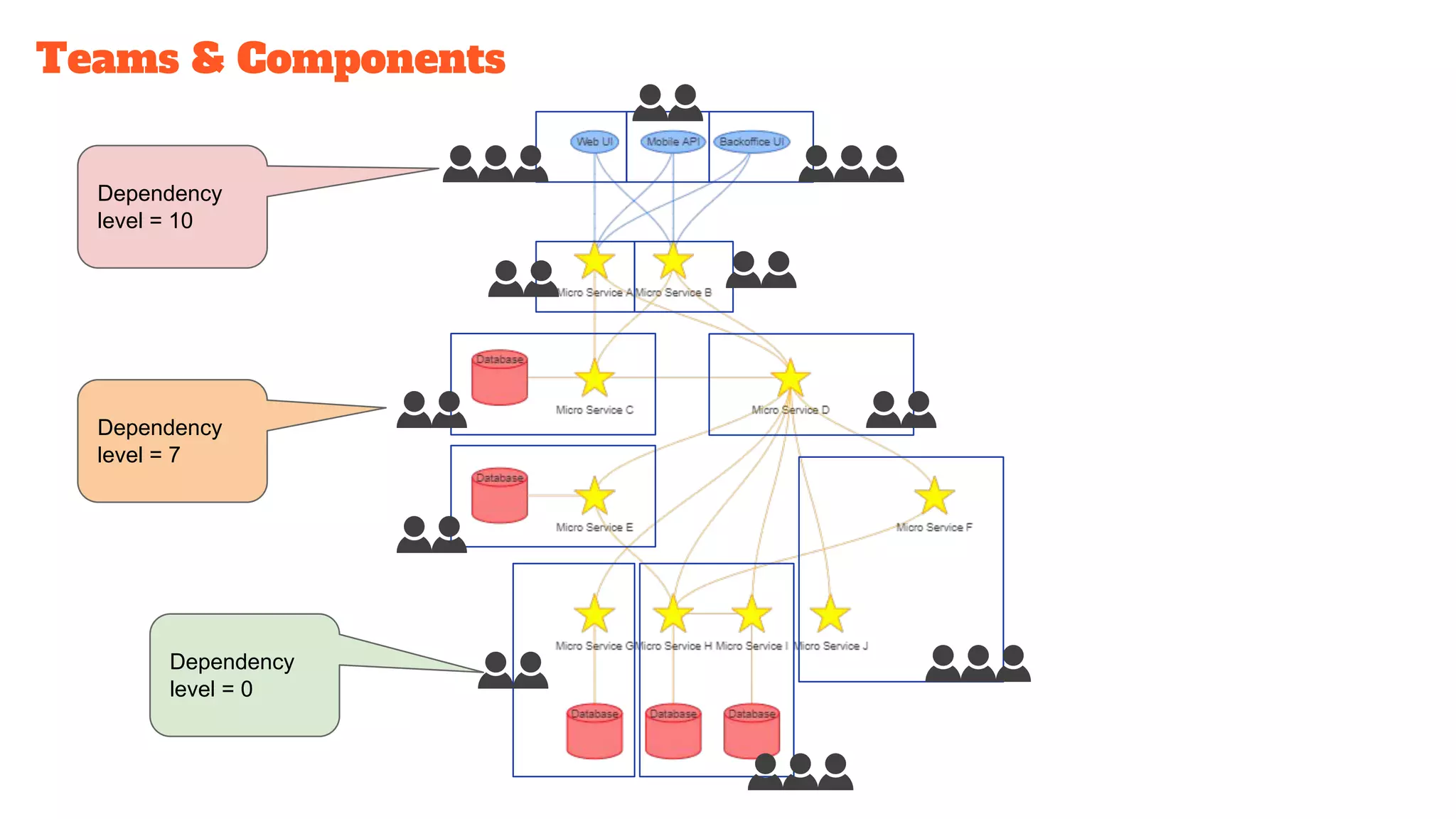
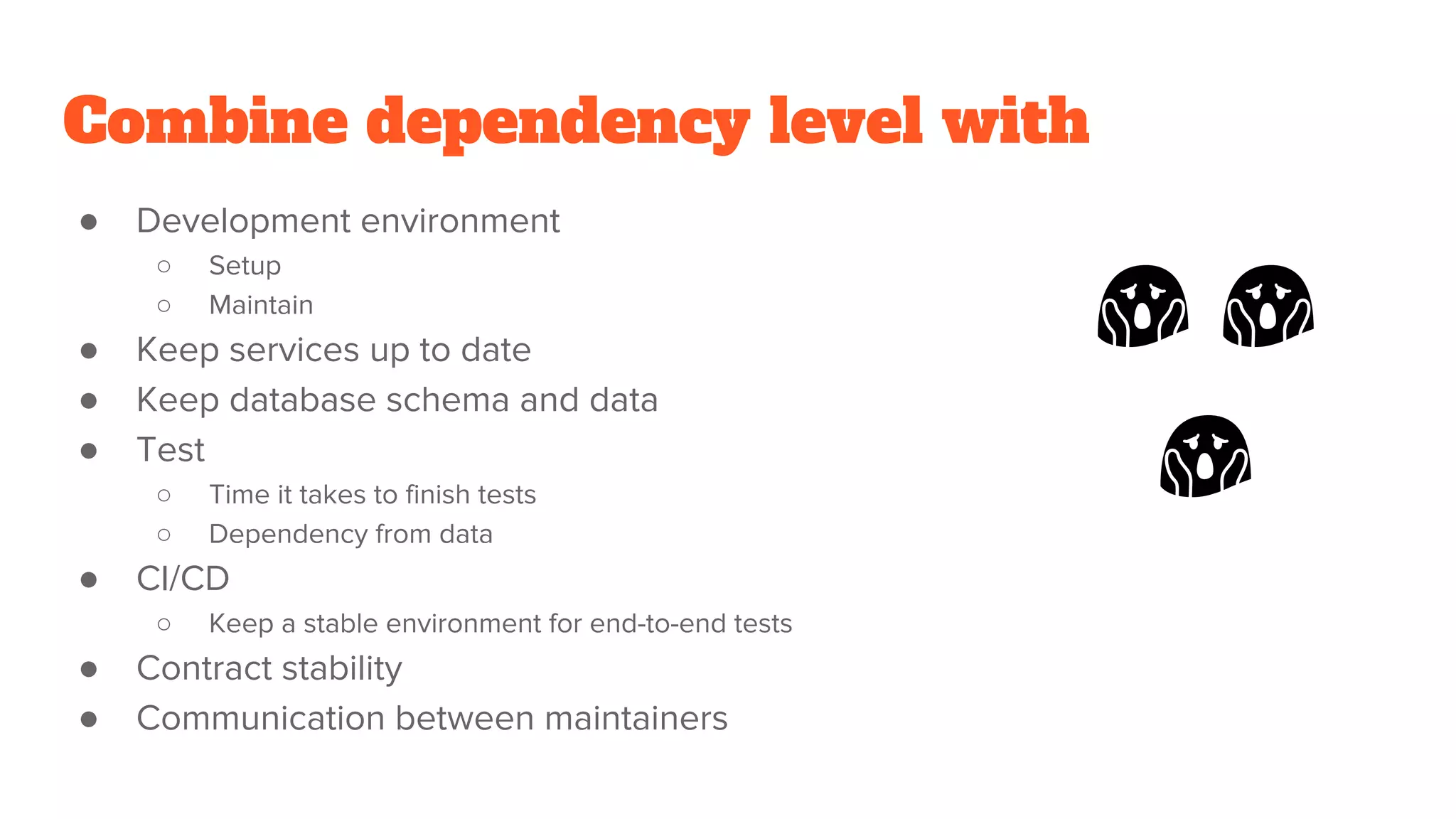
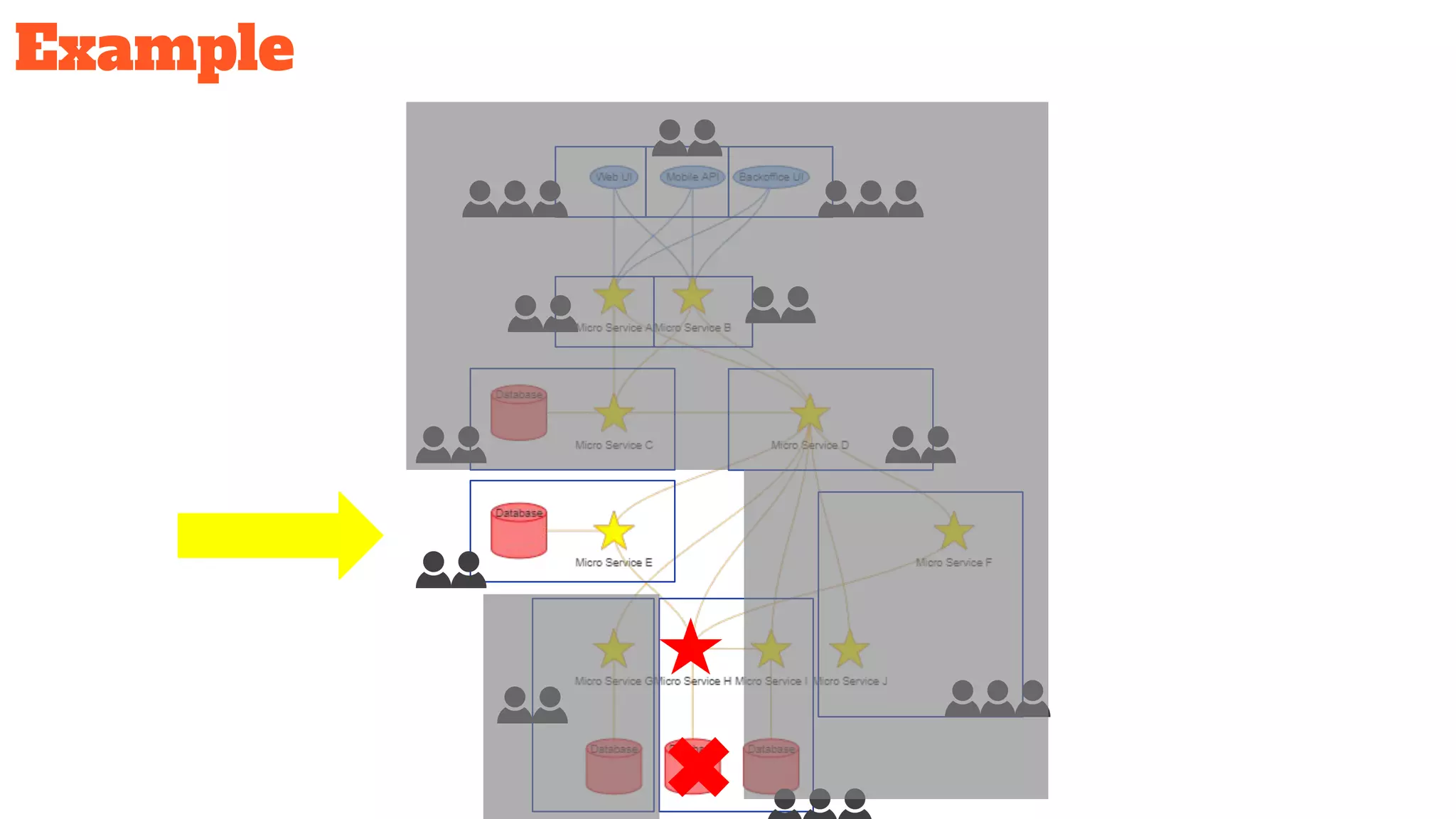
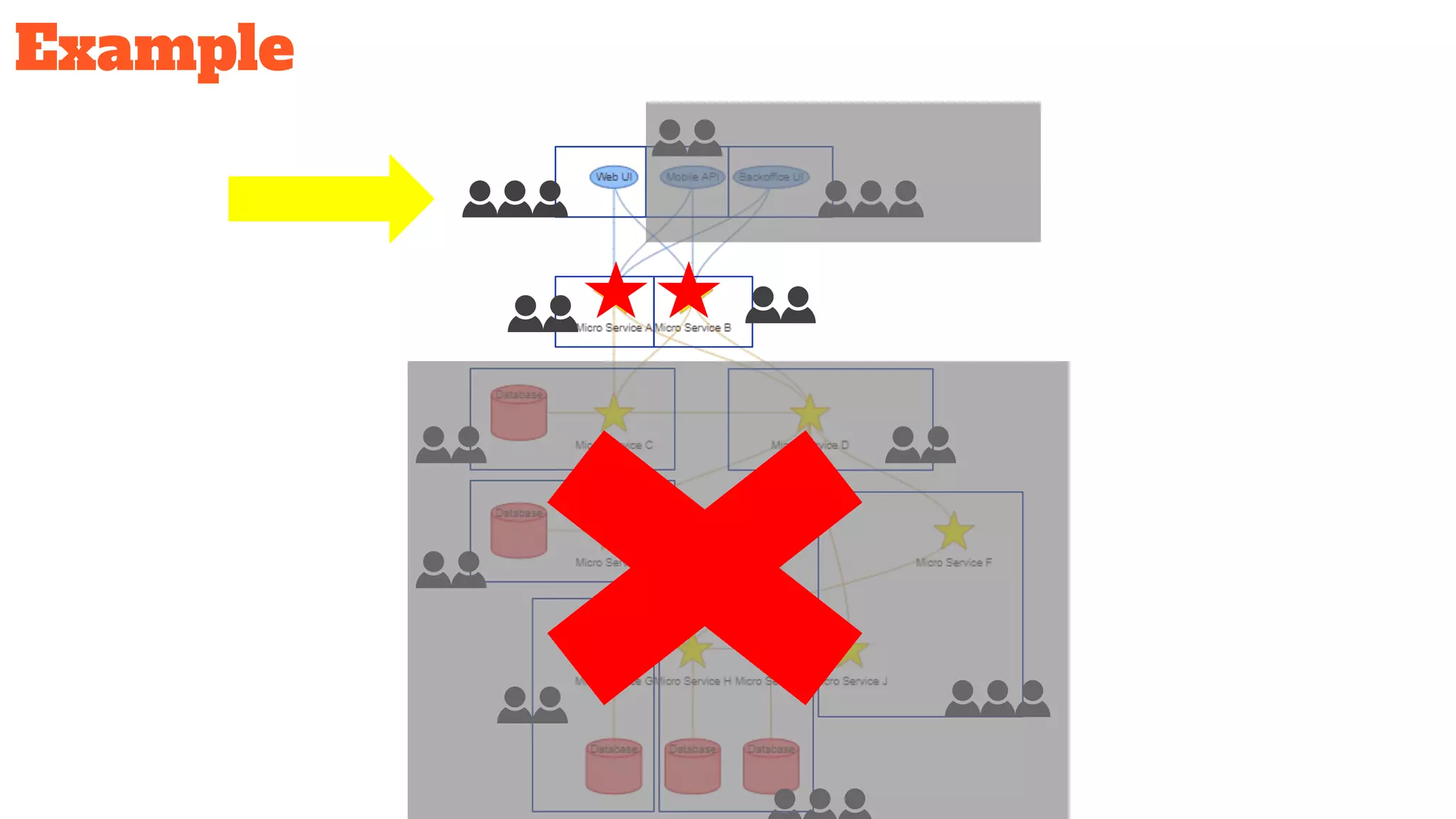
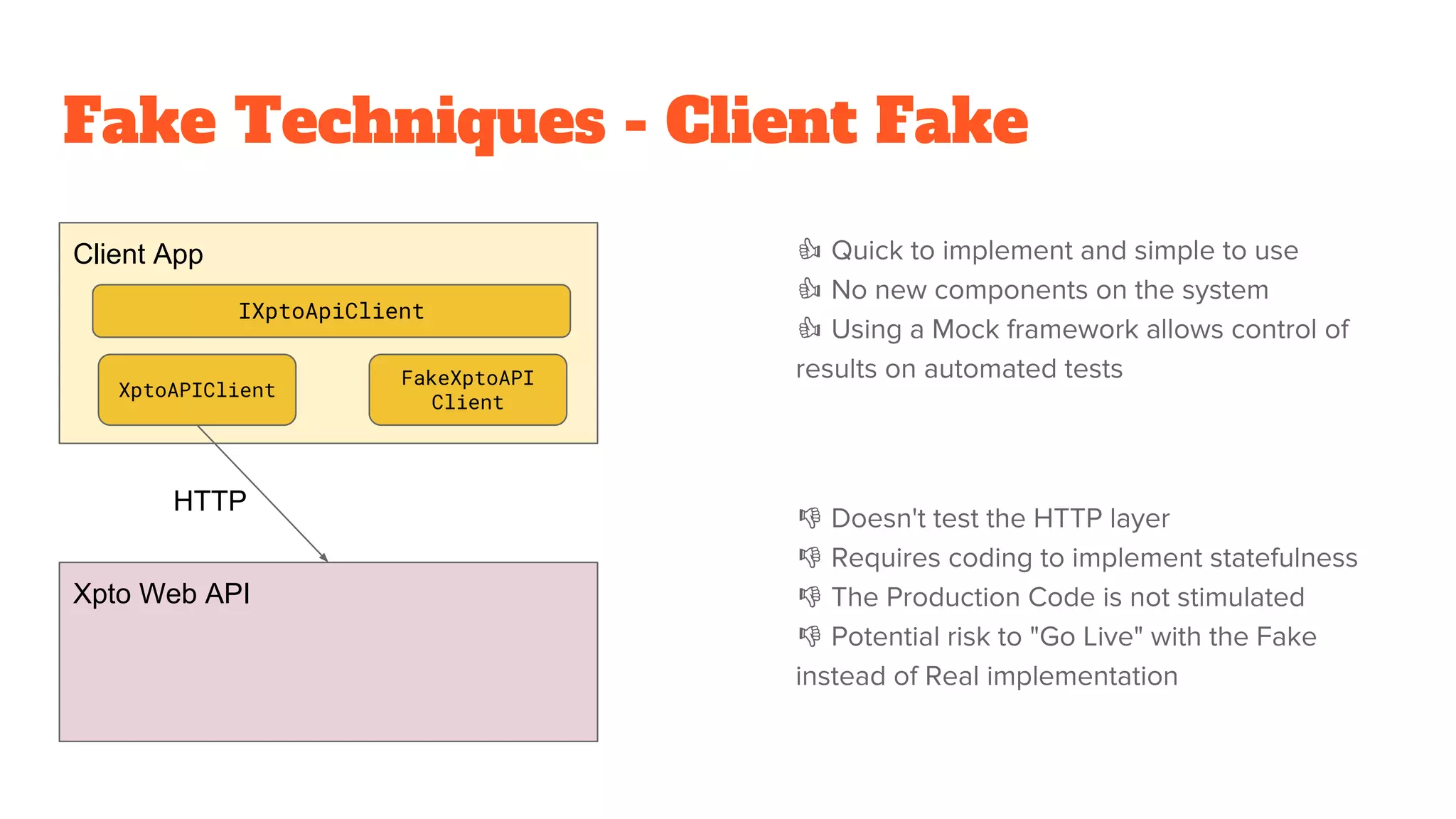
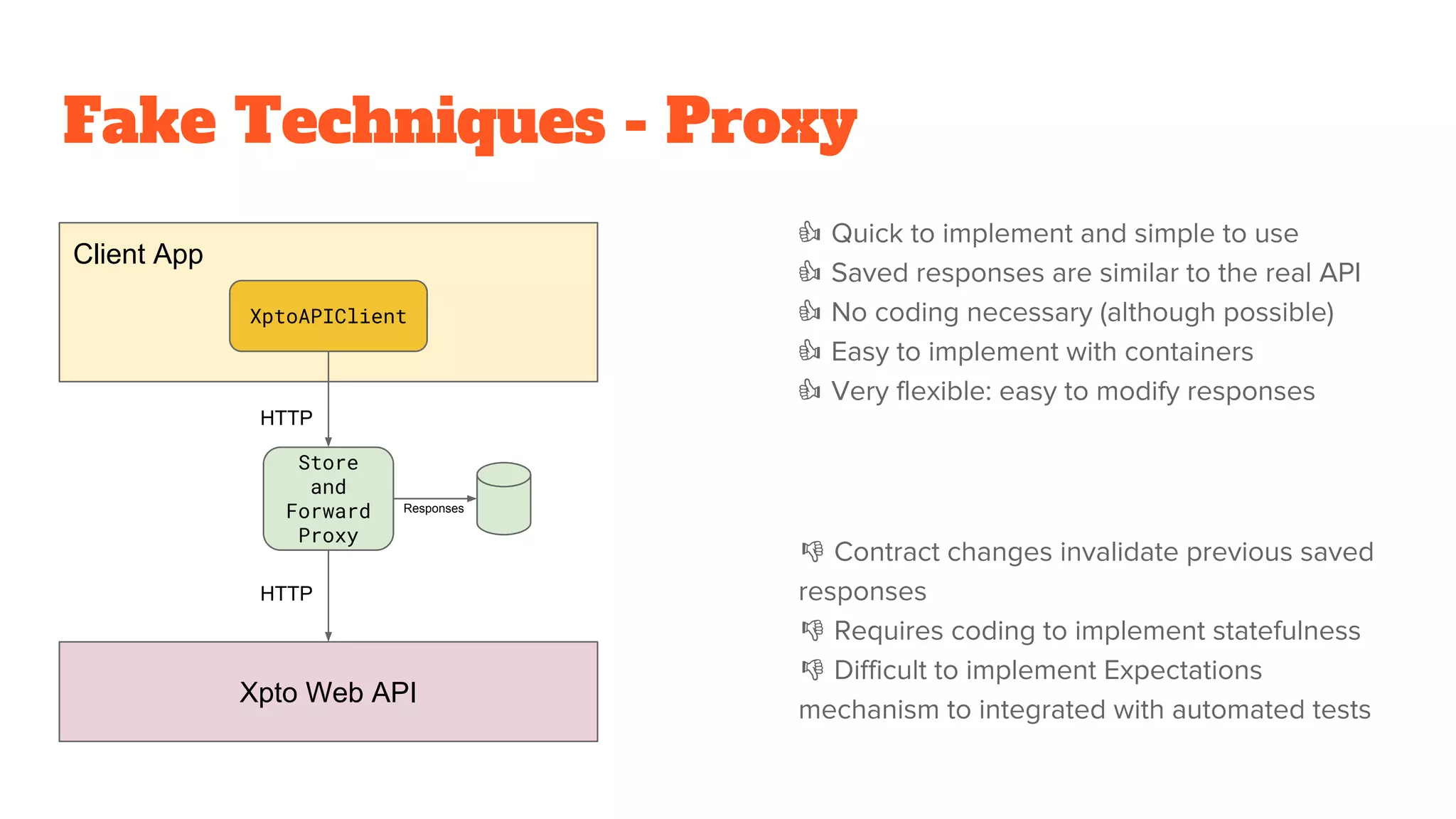
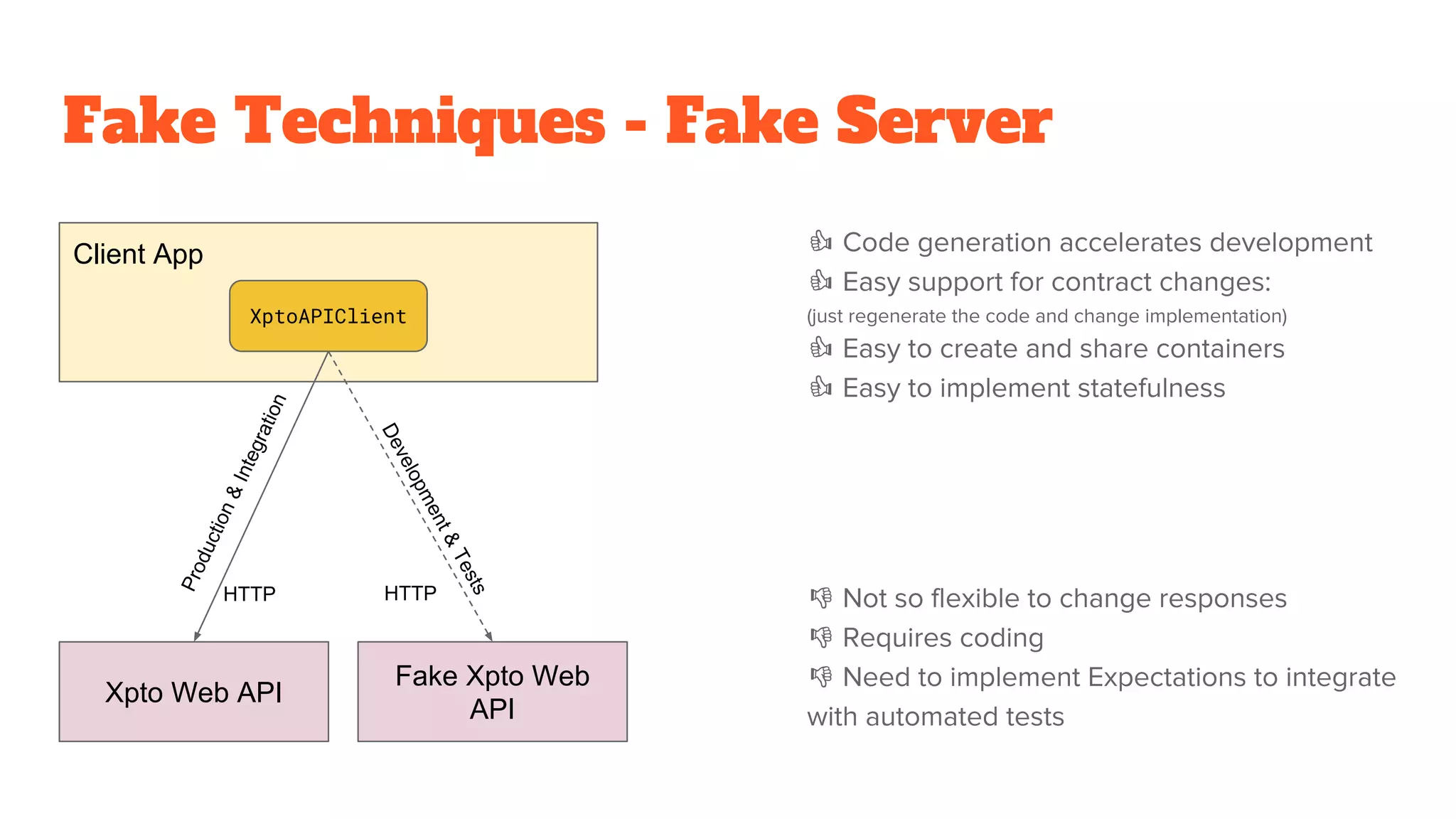
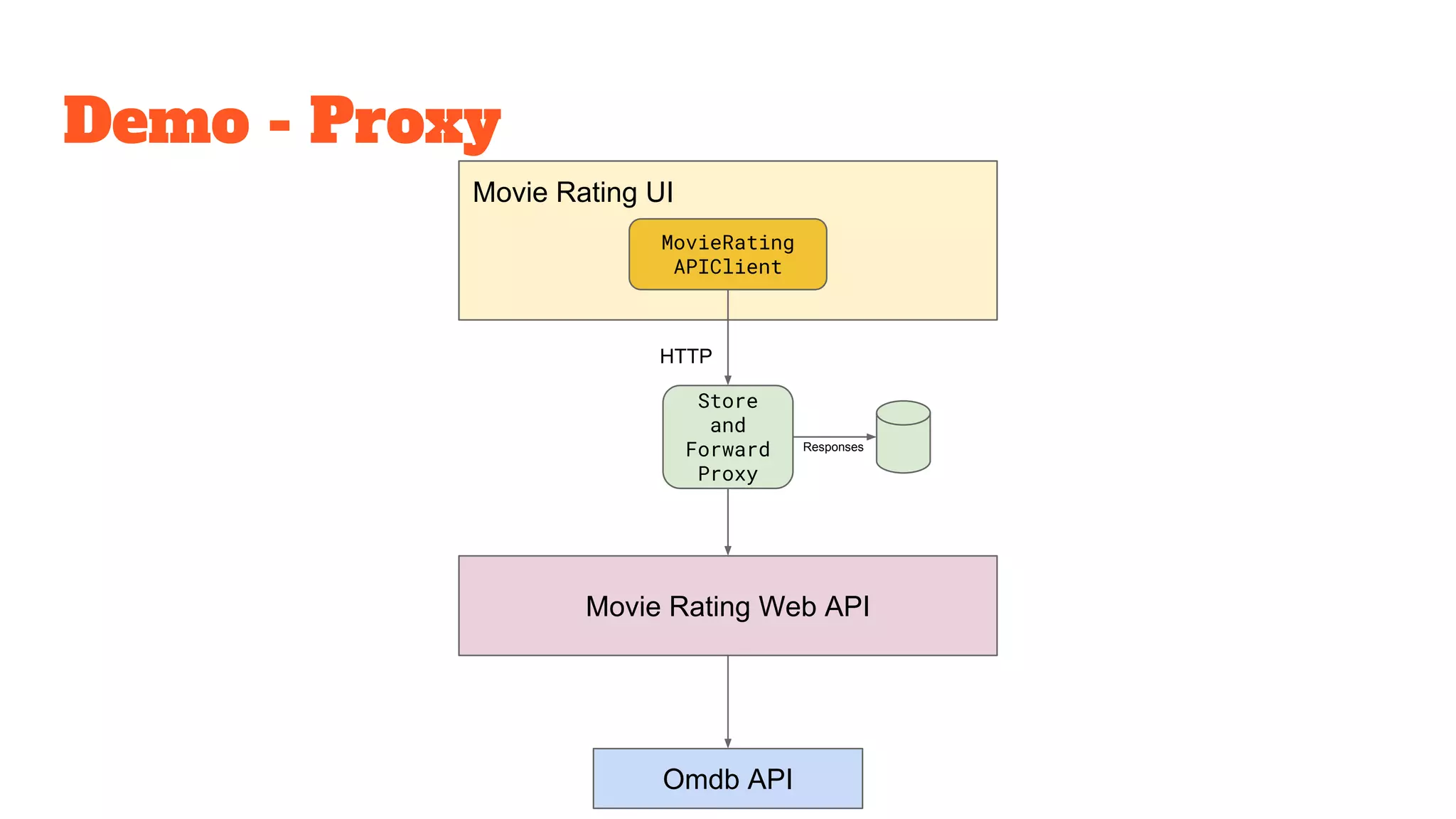
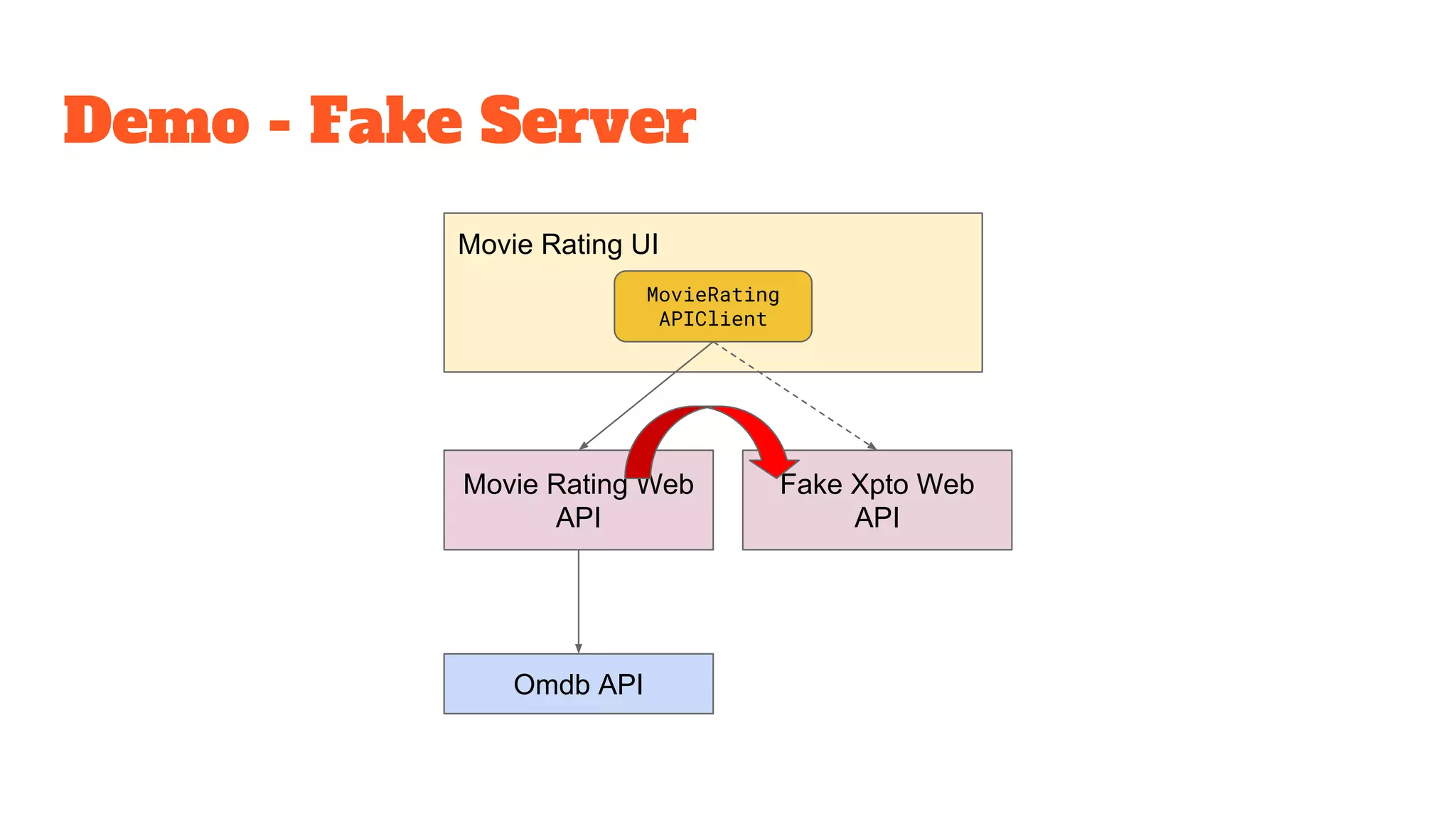
This document discusses the use of stateful mock servers to test REST APIs in microservices architectures. It describes some challenges with testing complex microservices ecosystems, including long test times due to dependencies. Stateful mock servers are proposed as a solution by replacing real dependencies with fake implementations that can be controlled during tests. Examples of different faking techniques like client fakes, proxies, and fake servers are provided. The document emphasizes generating mock server code to reduce development time and easily support contract and integration tests.