1) Unlike established companies, startups are constrained by limited cash and must keep a low cash burn rate until validating their business model through paying customers.
2) To control costs, startups can use the OODA (Observe, Orient, Decide, Act) loop to regularly question assumptions and learn through iterative experimentation.
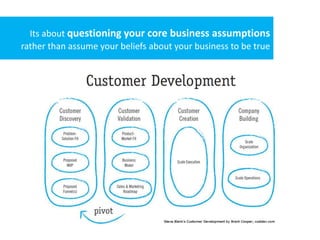
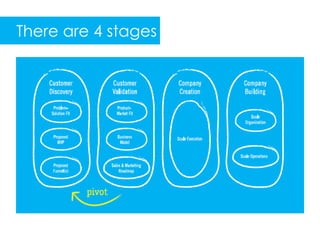
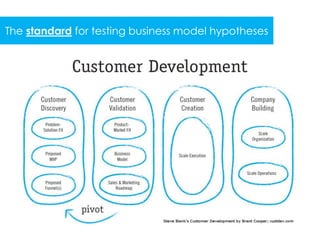
3) The customer development process focuses a startup on deeply understanding customer needs through stages of customer discovery, validation, creation and building to develop a repeatable sales process and transition to profitability.