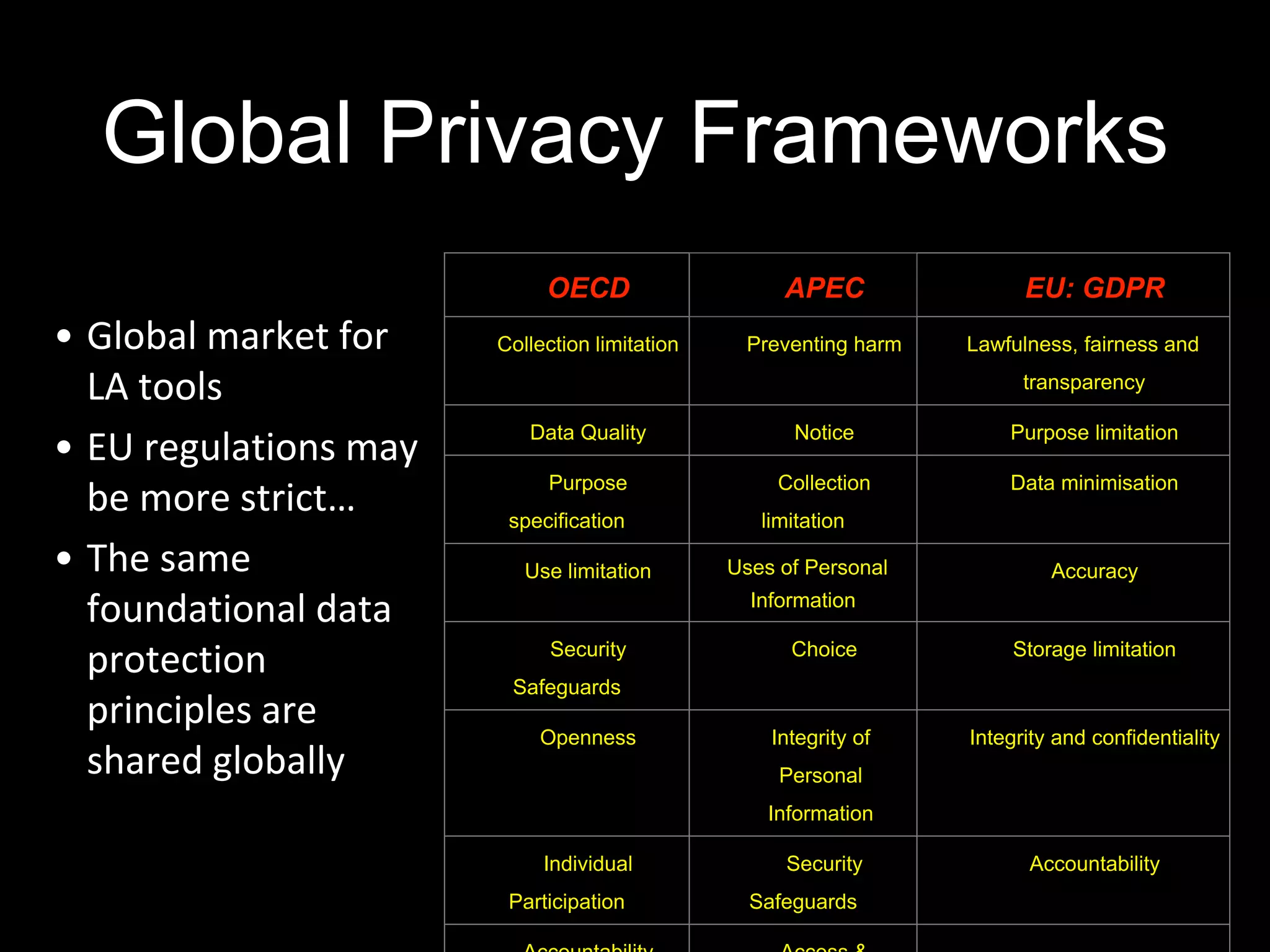
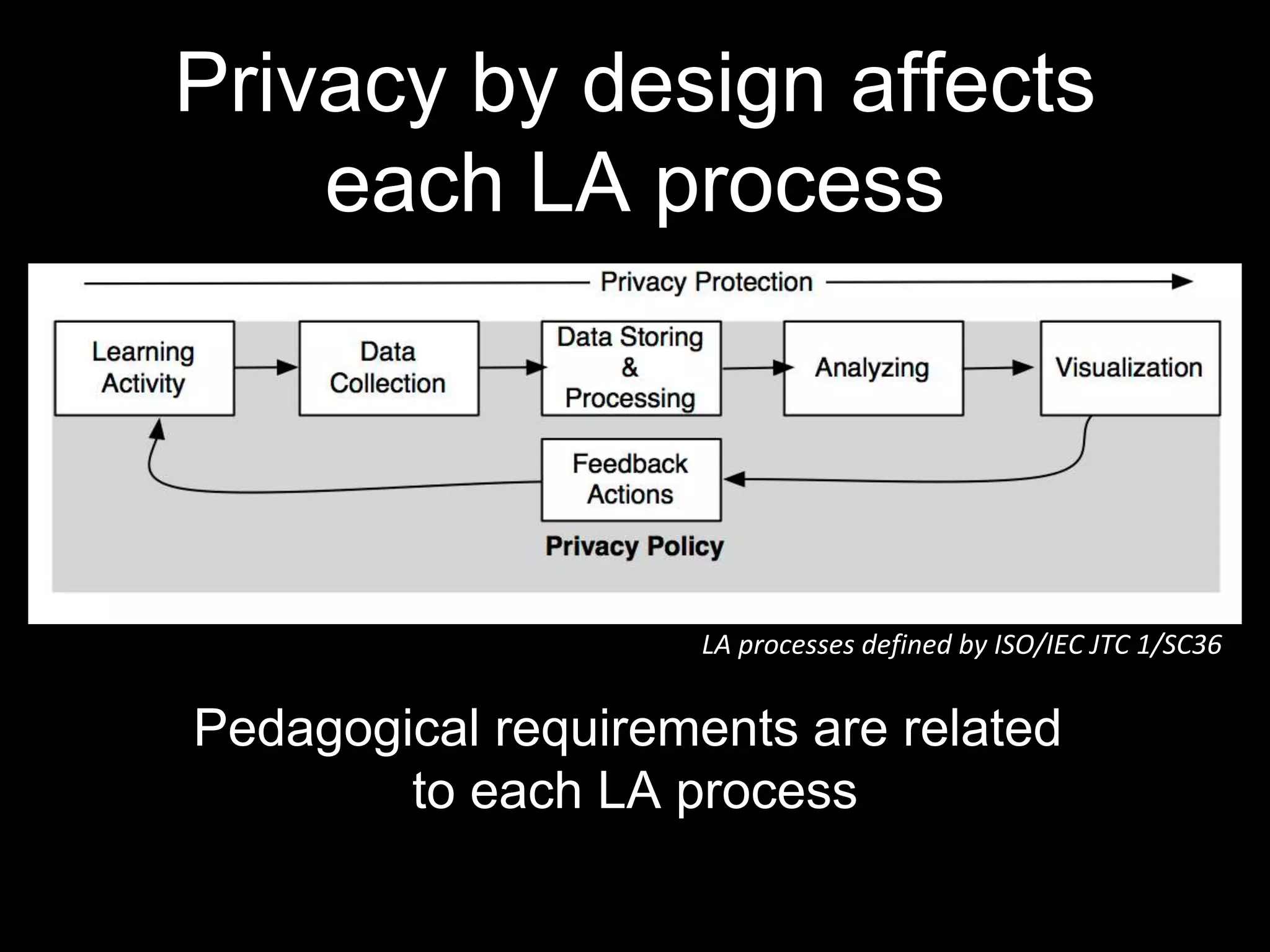
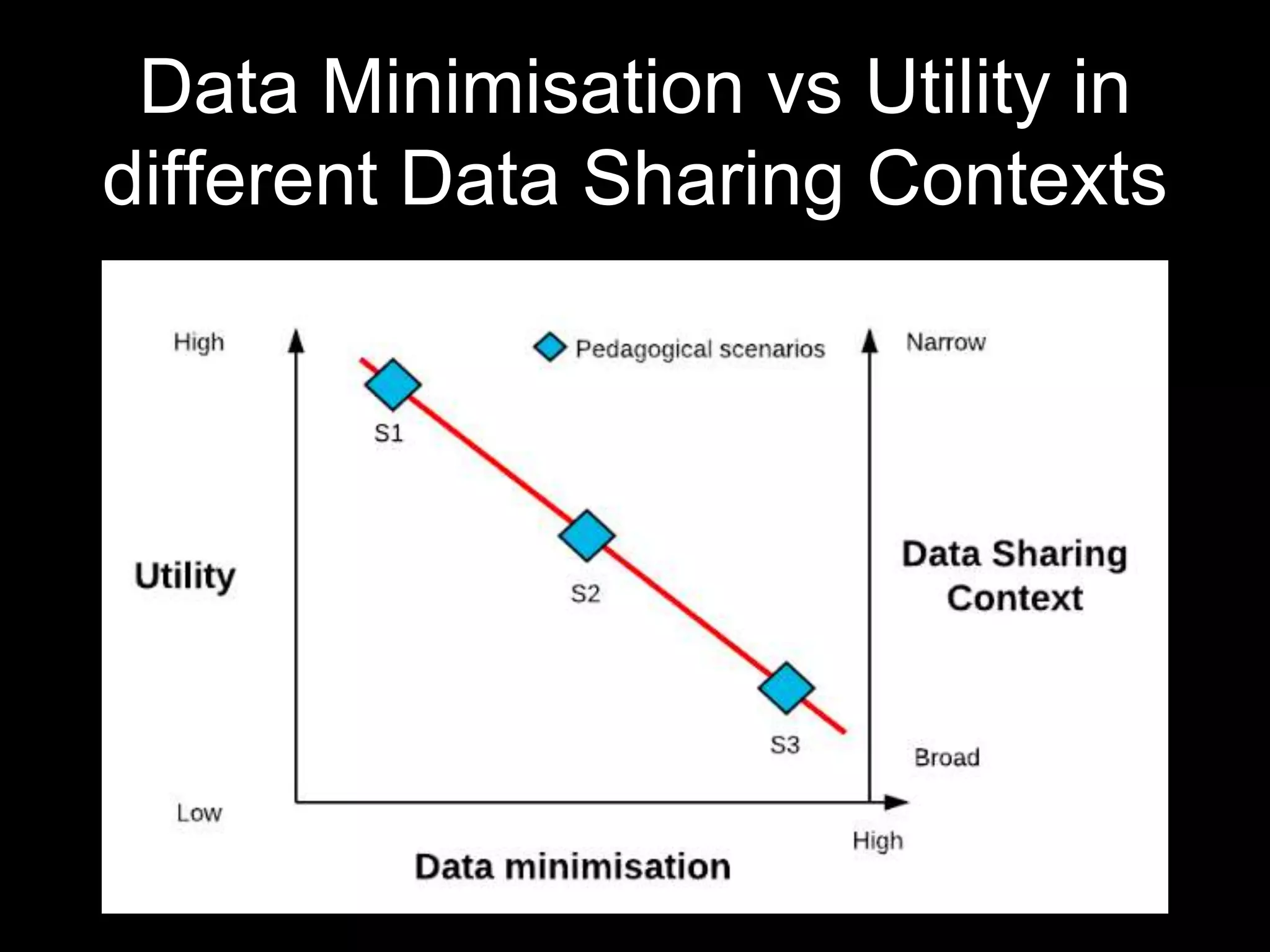
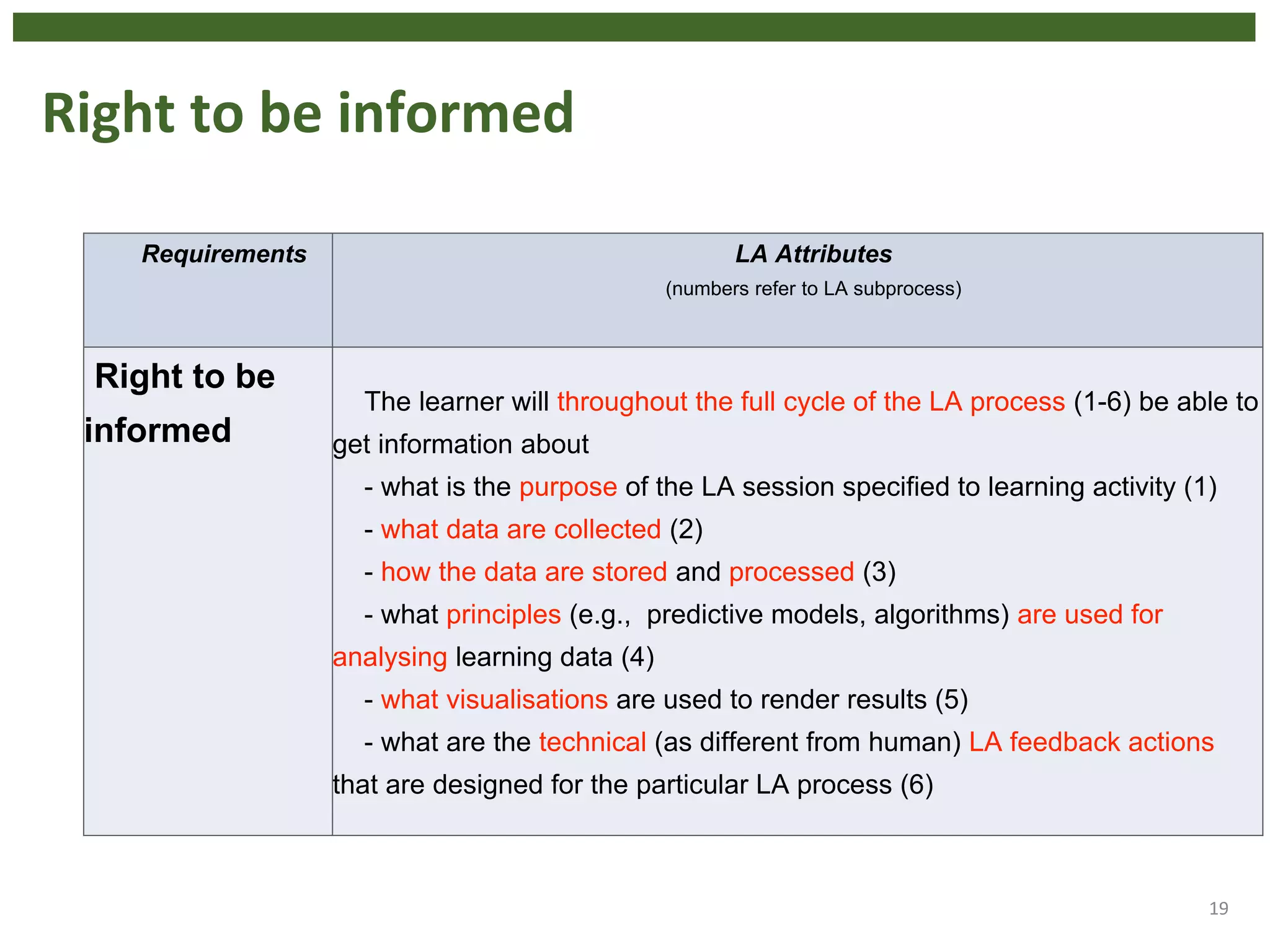
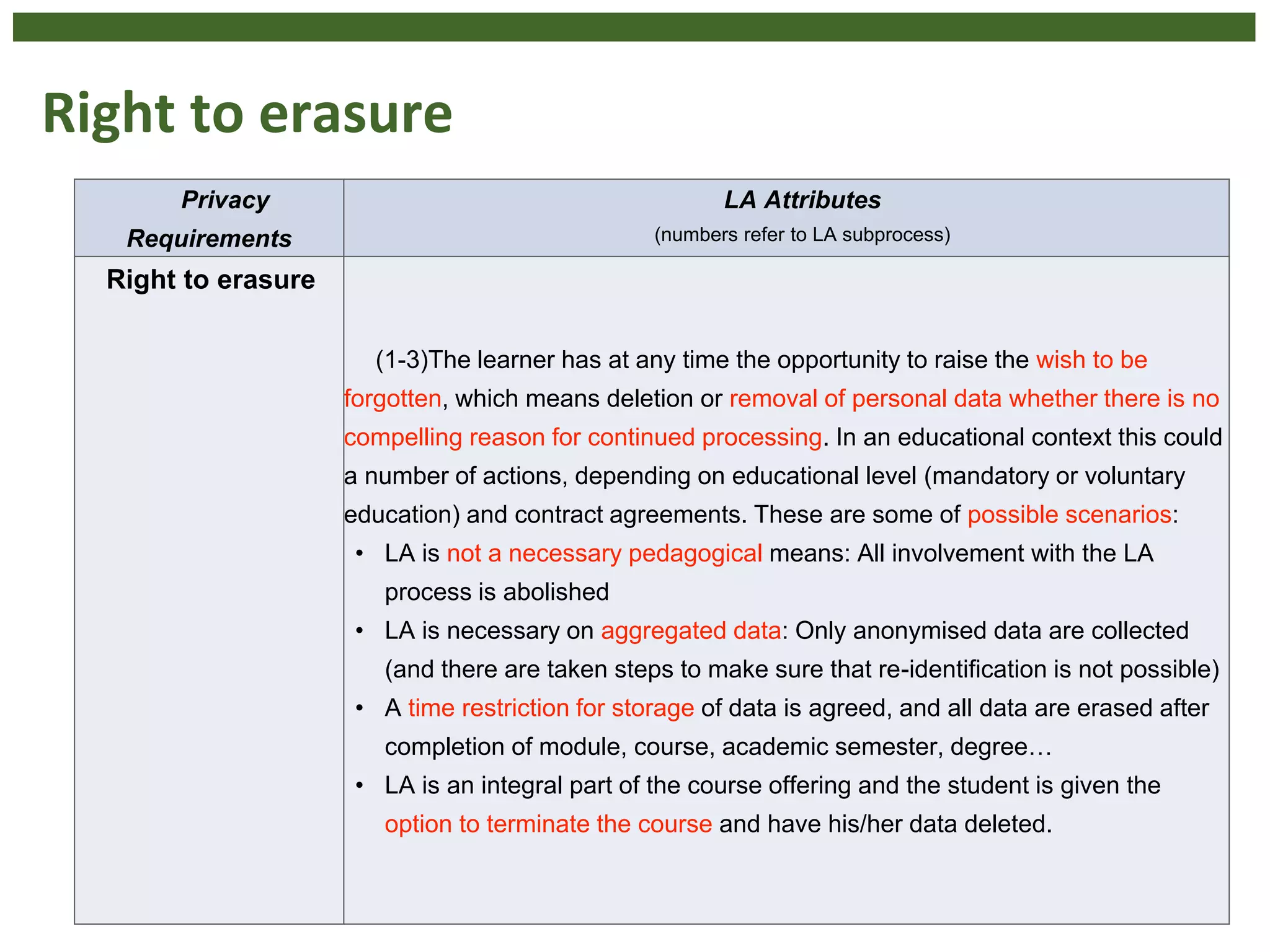
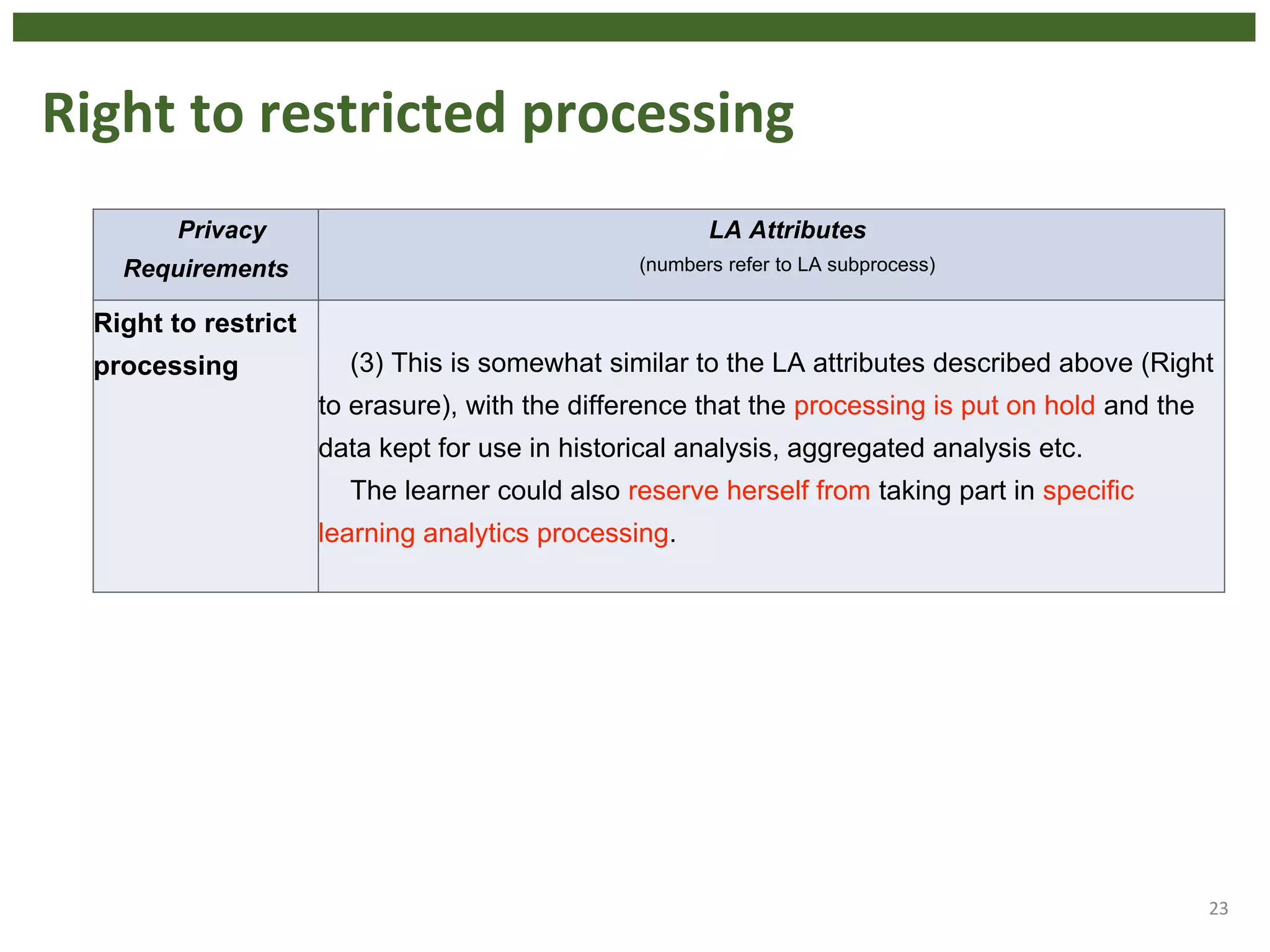
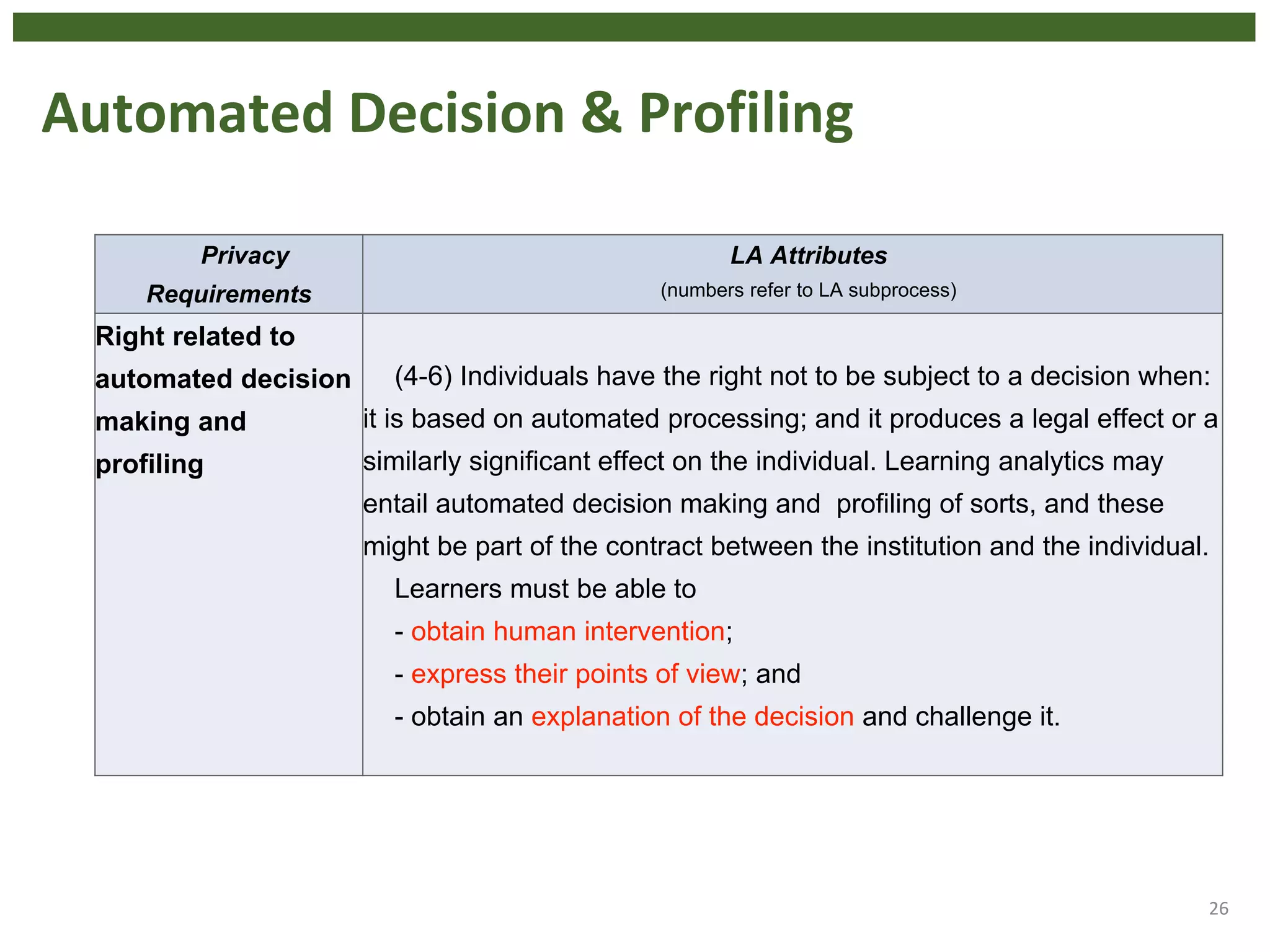
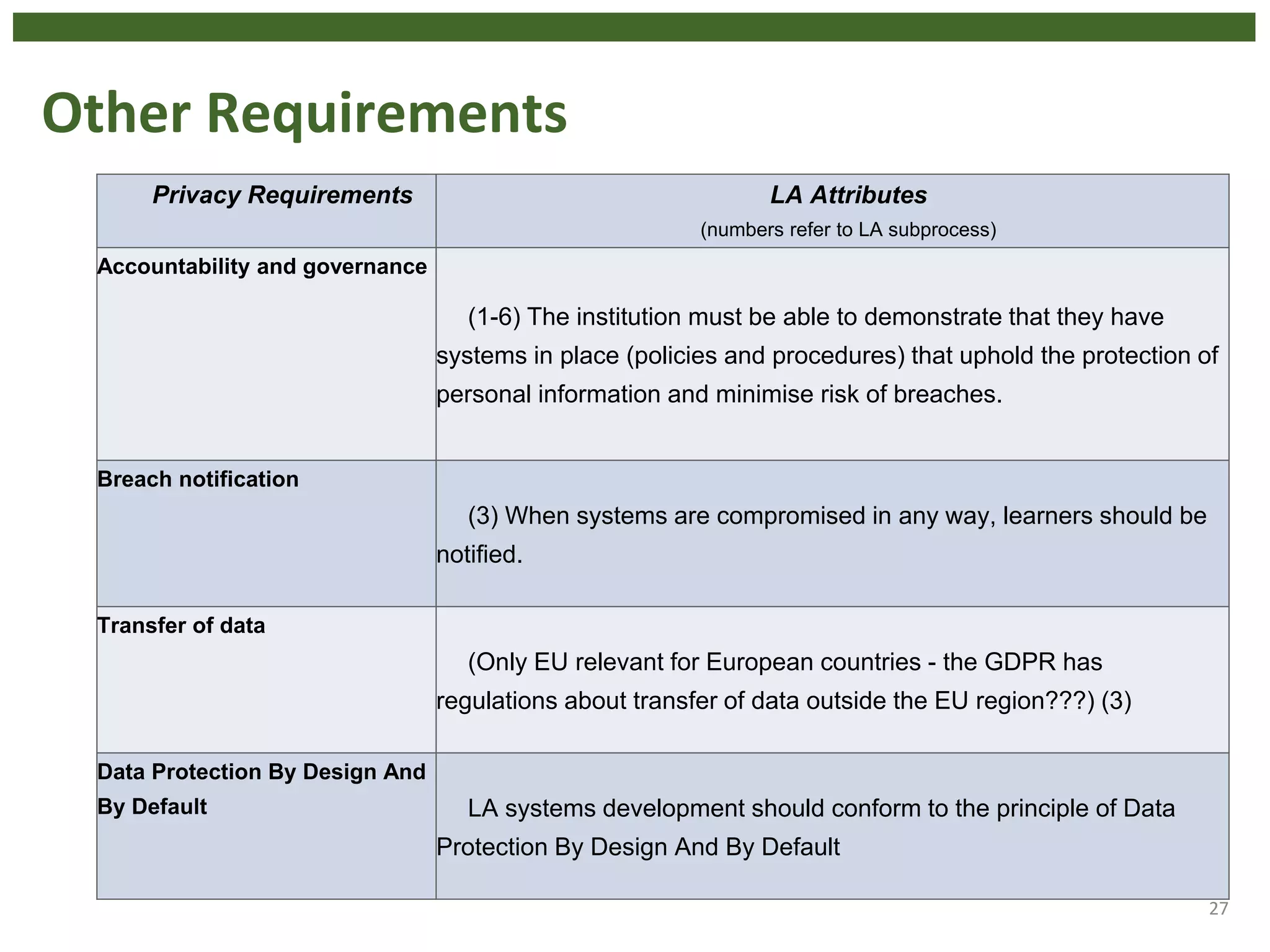
The document discusses the principle of data protection by design and default in the context of learning analytics, highlighting its role in integrating pedagogical approaches into data collection and usage. It emphasizes the necessity of aligning learning analytics applications with privacy regulations, notably the EU's GDPR, to enhance learner agency and trust. Various privacy rights for learners are outlined, including data access, rectification, erasure, and portability, underscoring the importance of robust governance and accountability in educational settings.