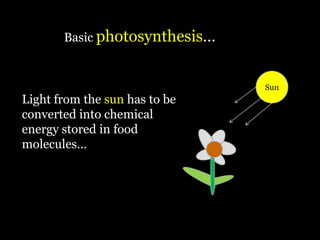
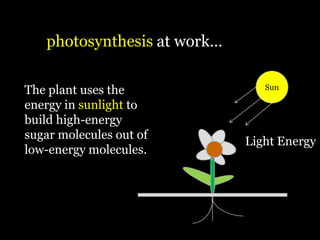
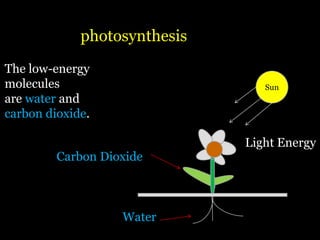
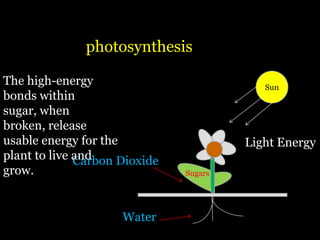
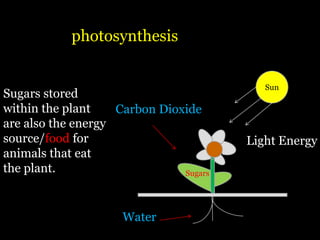
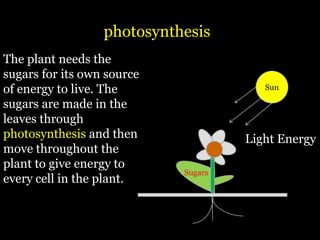
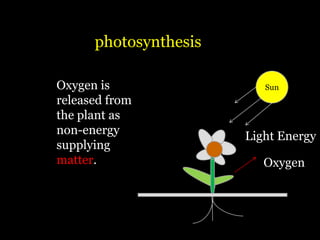
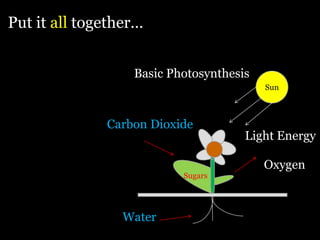
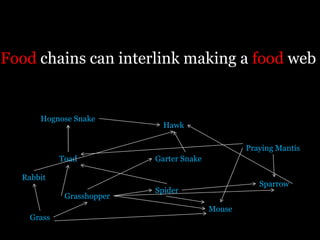
Food is defined scientifically as matter and energy that provides living things with the materials and fuel they need to live, grow, and reproduce. Matter provides the physical building blocks and energy powers all of the functions within cells and organisms. Living things get energy and matter by consuming other organisms within a food web - producers like plants get energy from the sun through photosynthesis, consumers obtain energy by eating other organisms, and decomposers get energy from breaking down waste and dead matter. All organisms depend on each other for the transfer of energy and matter throughout the food web.