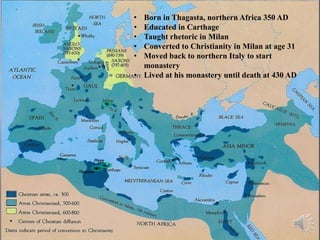
Augustine of Hippo was a philosopher, teacher, and bishop born in 350 AD in Thagasta, northern Africa. He was educated in Carthage and later taught rhetoric in Milan, where he converted to Christianity at age 31. He then moved back to northern Italy to start a monastery in Hippo where he lived until his death in 430 AD. He was one of the most prolific Latin authors and wrote extensively on theology, philosophy and pedagogy. He advocated for the value of community in learning and believed that knowledge is a journey.