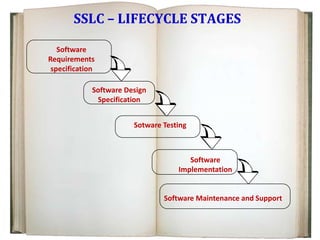
Quality assurance aims to identify and correct errors early in the development process through reviews and testing at each phase. The System Software Lifecycle (SSLC) model aims to ensure quality when developing software. It has five stages: requirements specification, design specification, testing and implementation, and maintenance and support. Testing is an important but difficult part of development that helps eliminate errors by determining what causes failures. Validation and certification ensure the software meets standards through simulated and live testing. Maintenance provides adjustments to comply with specifications and improve quality through problem reporting and resolution.