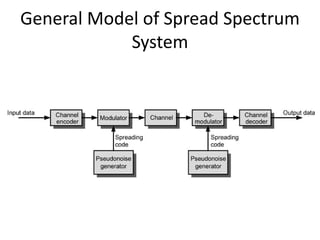
The document discusses spread spectrum techniques which spread signals over a wide bandwidth to make them more resistant to interference and interception. It describes how a normal audio signal can be expanded to cover many megahertz. There are two main types of spread spectrum - frequency hopping, where the signal broadcasts over random frequencies, and direct sequence, where each bit is represented by multiple bits in the transmitted signal using a chipping code. The spread spectrum concept involves using a channel encoder to produce a narrow bandwidth signal, then modulating it using a spreading code to significantly increase the bandwidth and spread the spectrum before transmission.