This document provides an overview of compilers and their functions. It discusses:
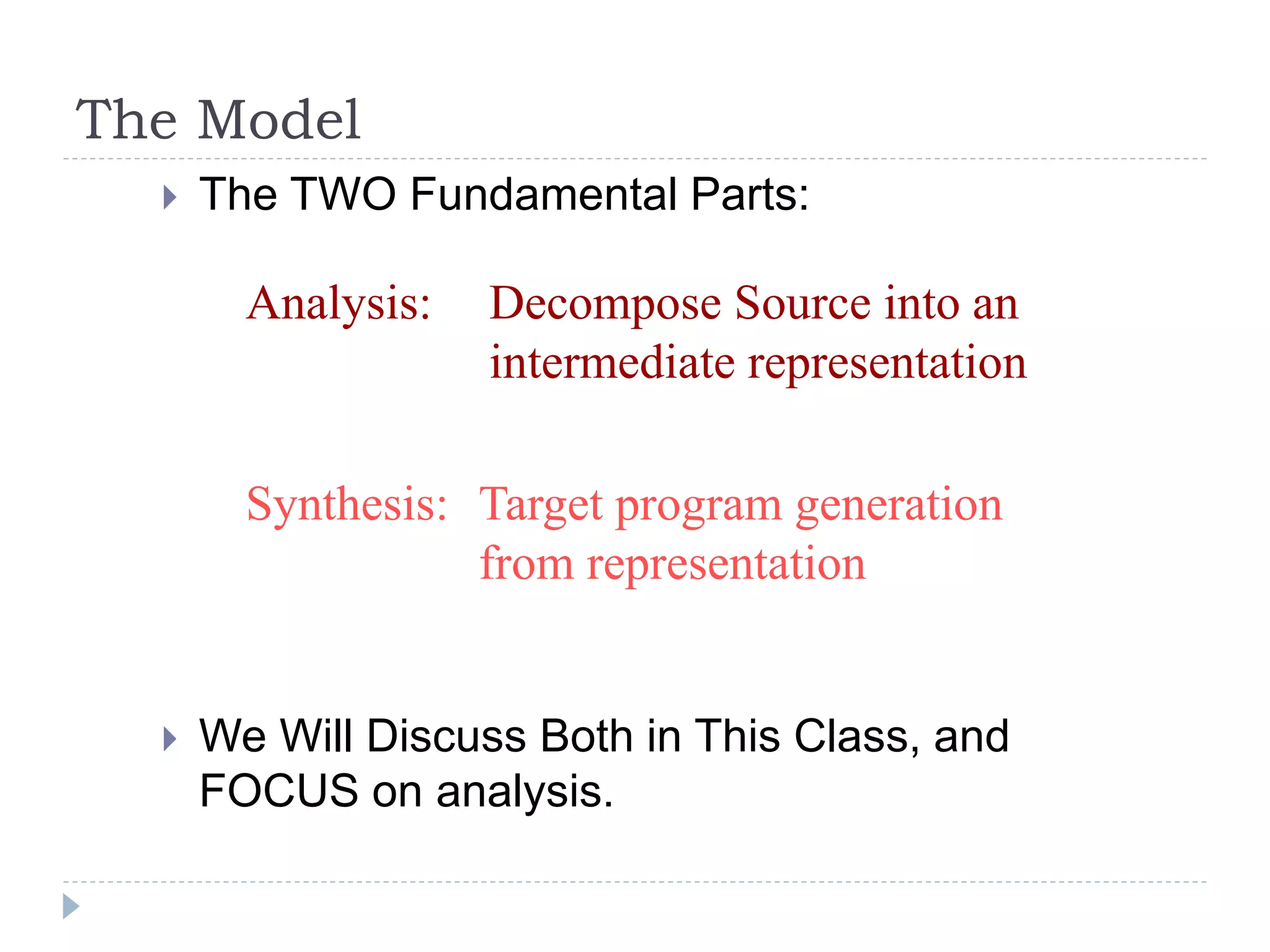
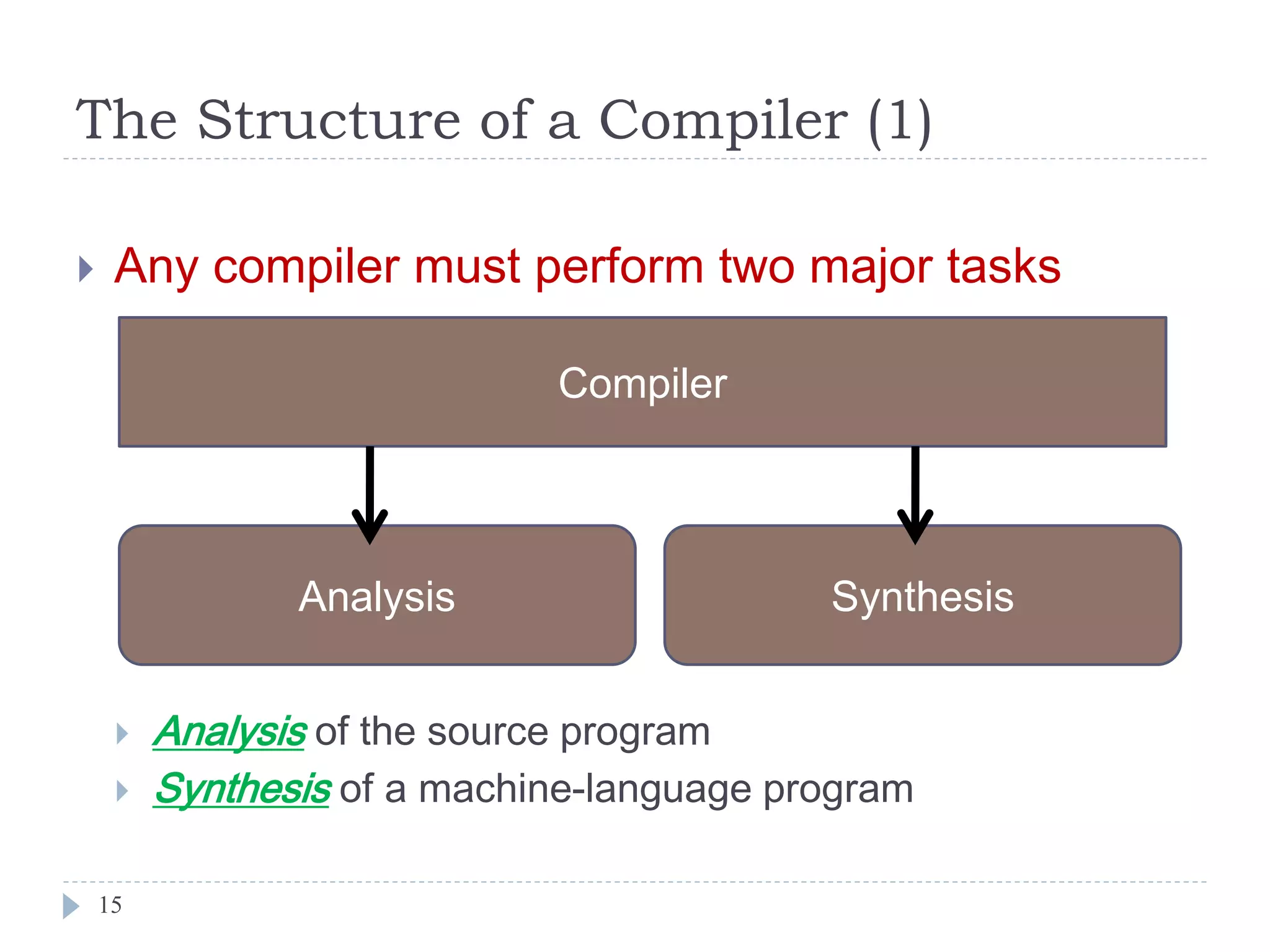
- The main phases of a compiler are analysis and synthesis. Analysis decomposes the source code into an intermediate representation, while synthesis generates the target program from that representation.
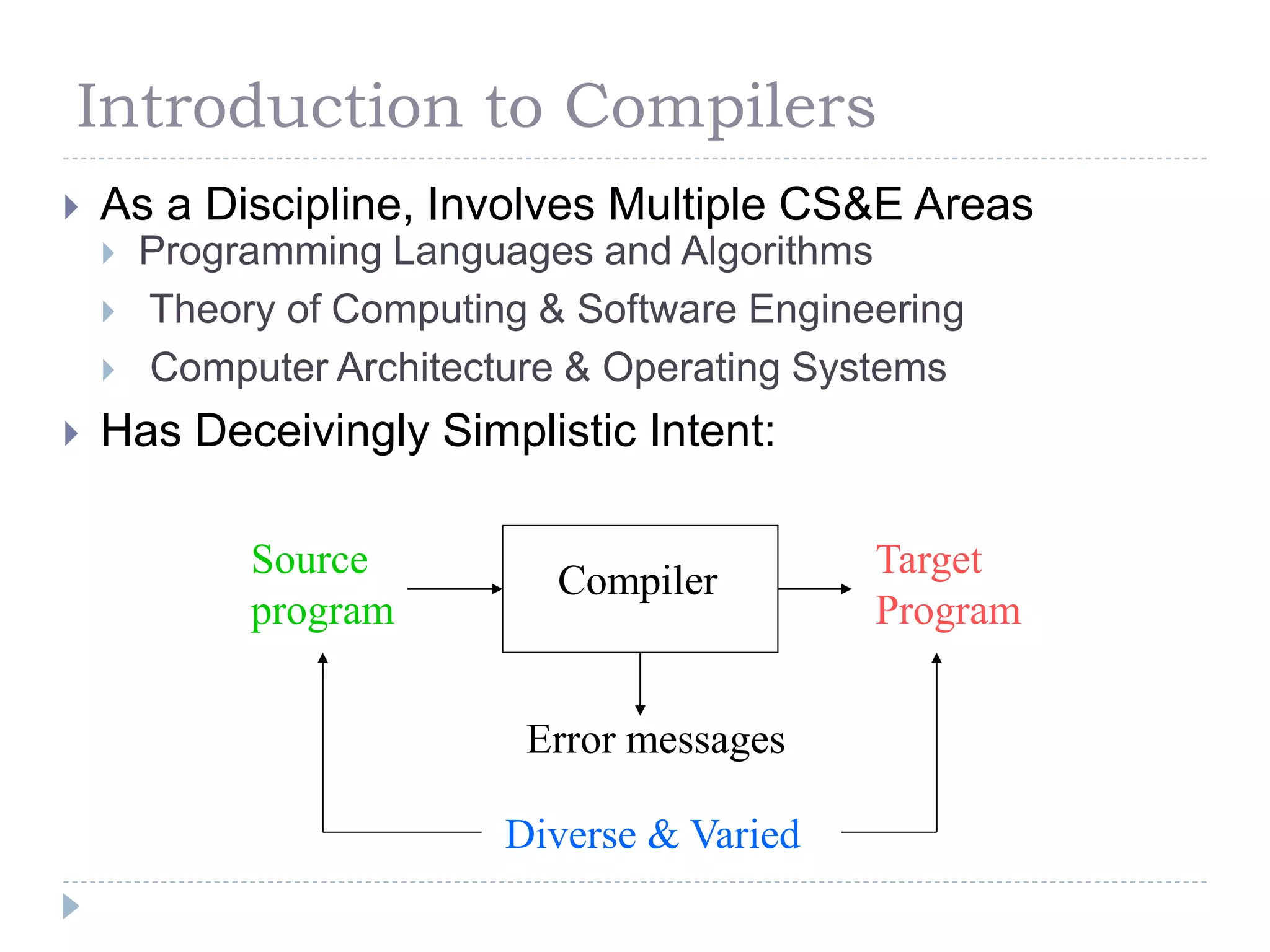
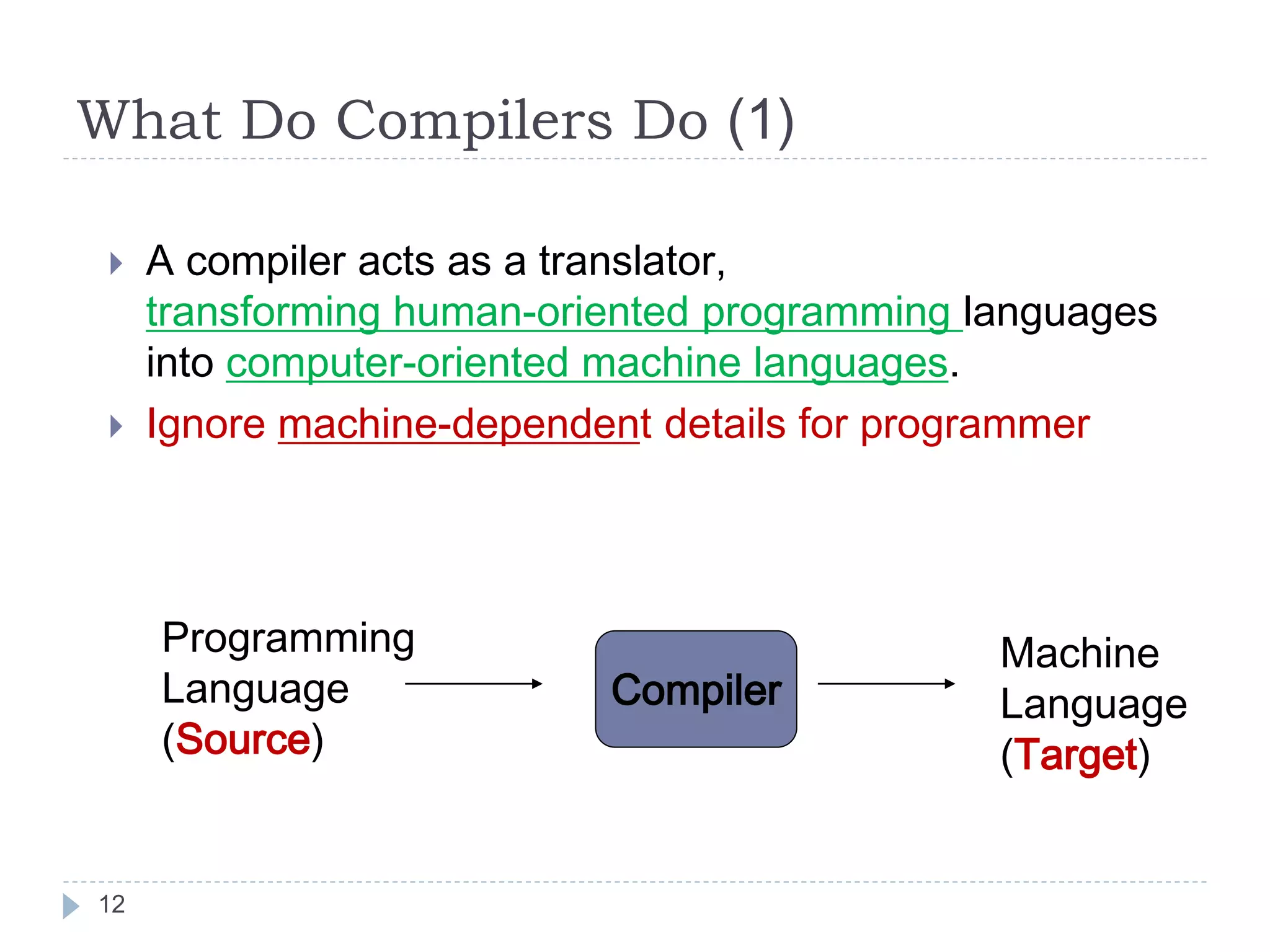
- Compilers translate human-oriented programming languages into machine languages to be executed by computers. They perform analysis of the source program and synthesis of machine-language code.
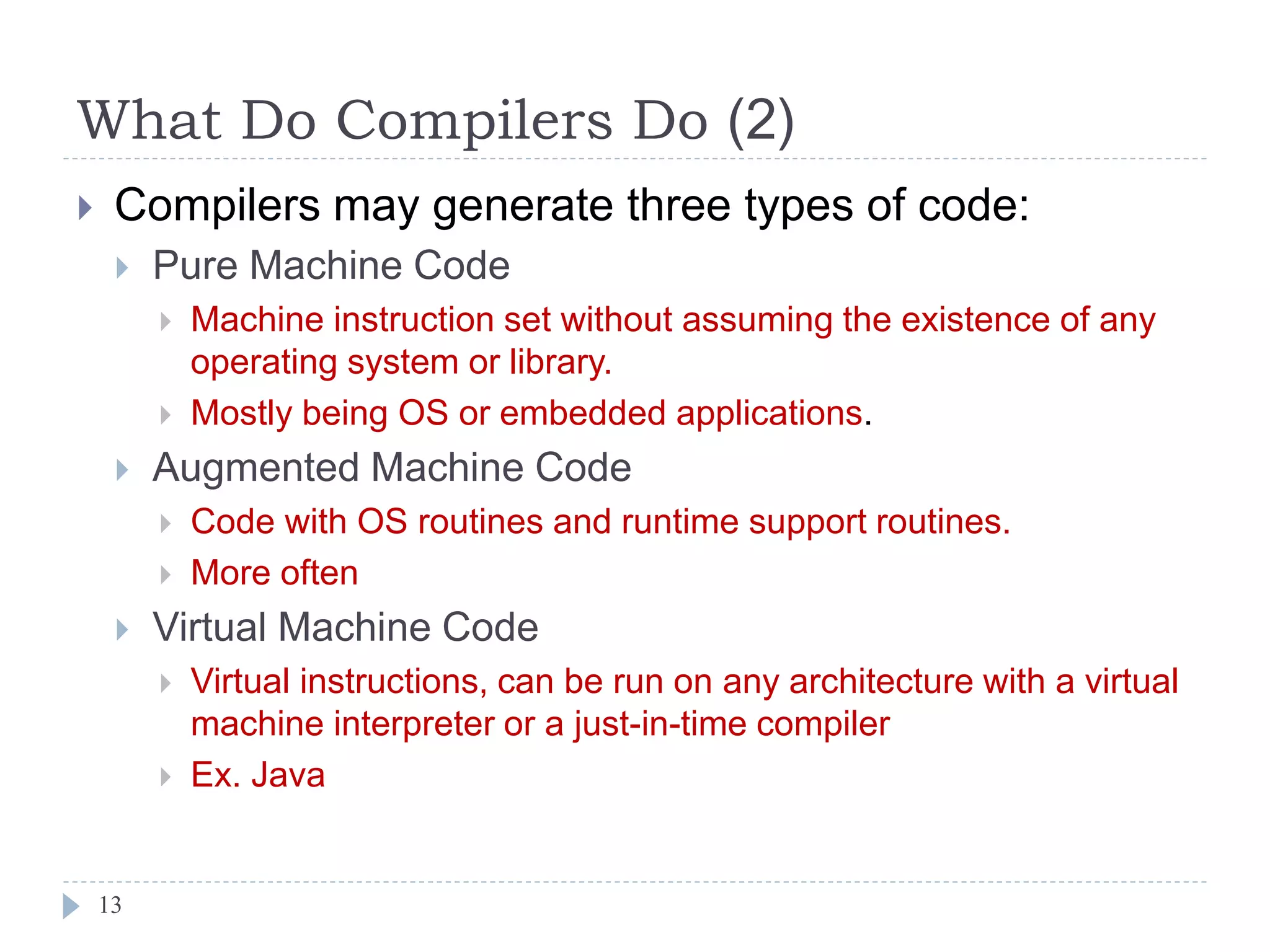
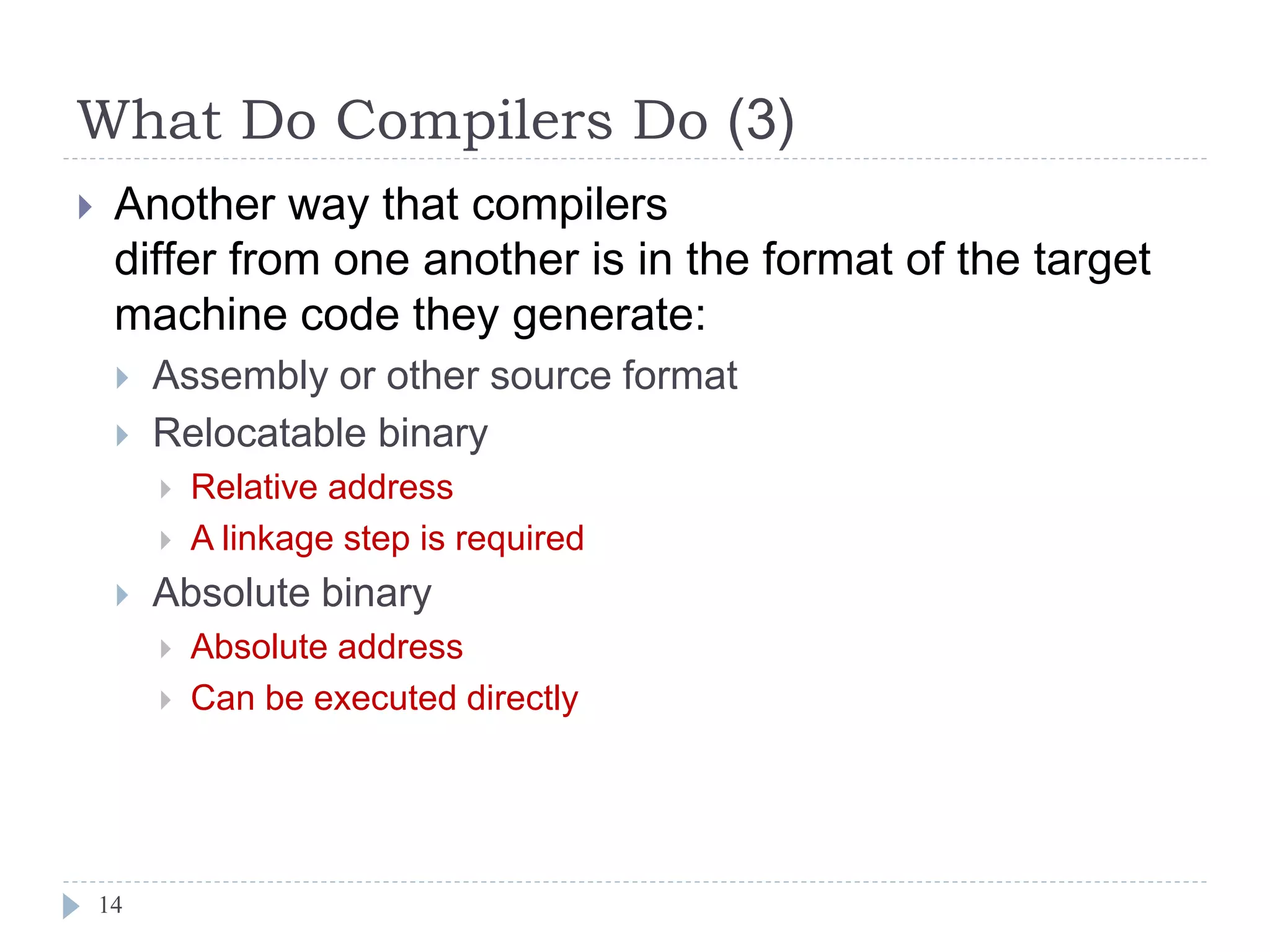
- Compilers generate different types of code like pure machine code, augmented machine code, or virtual machine code. They can also output assembly code or binary formats.