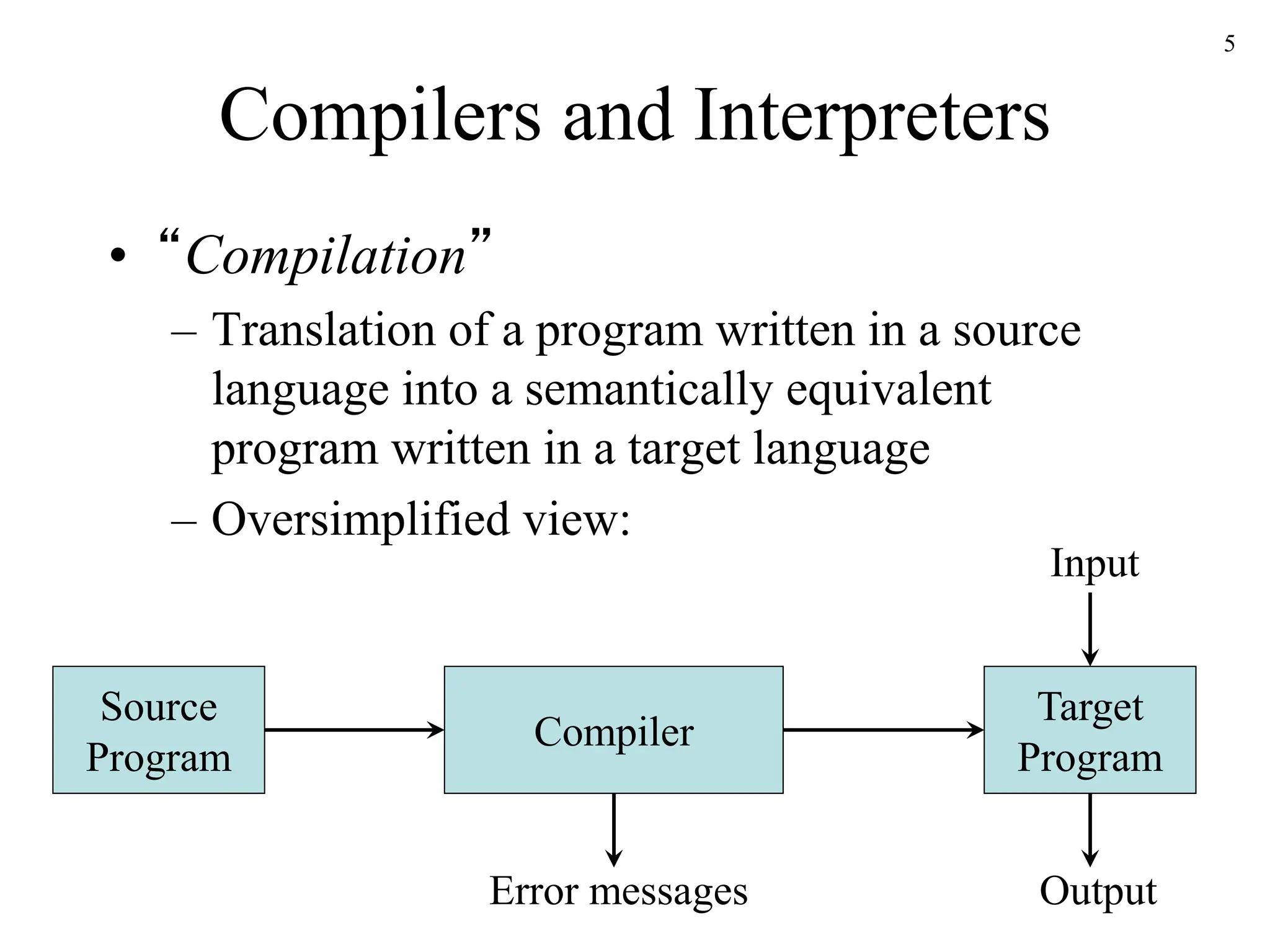
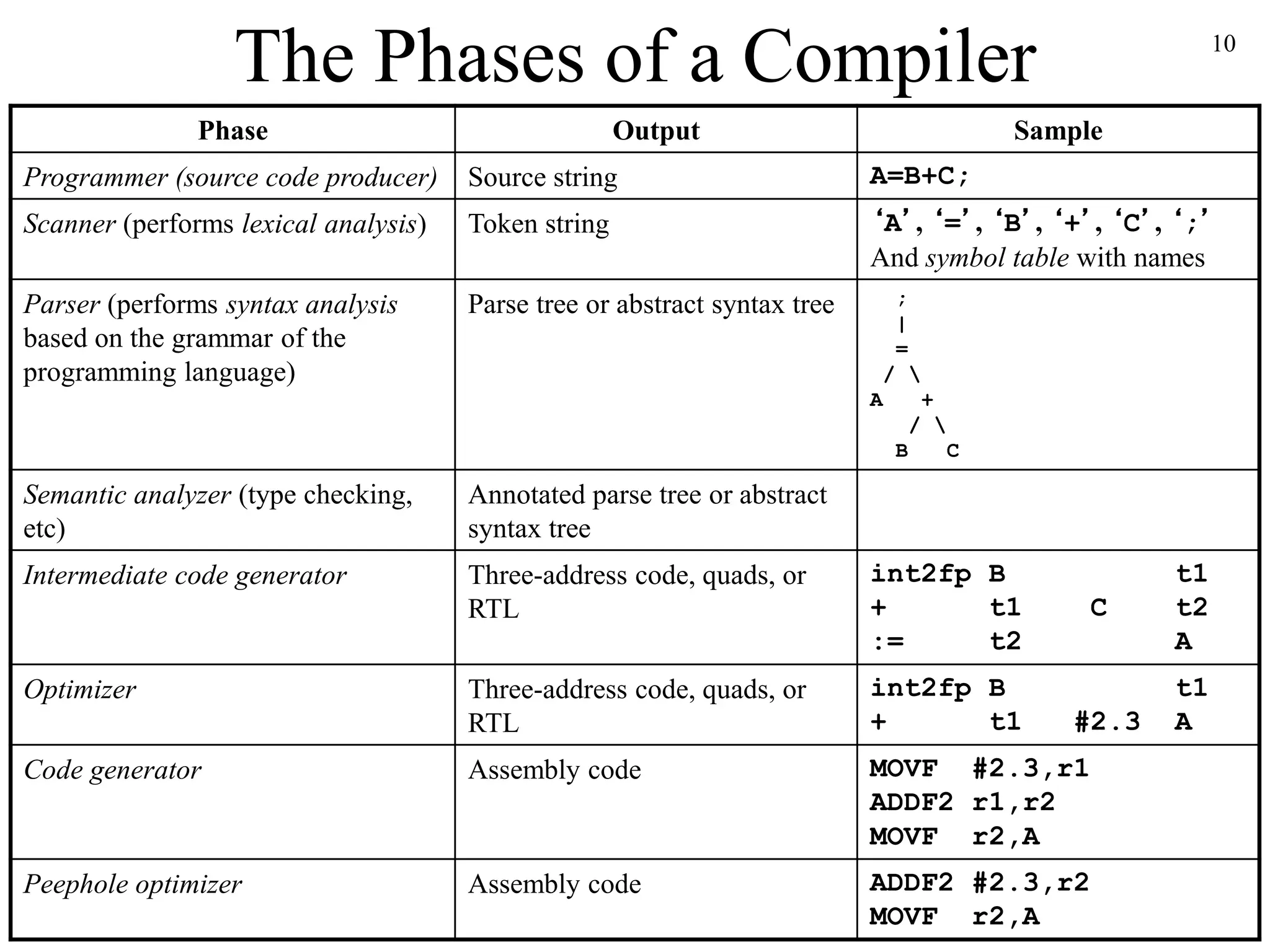
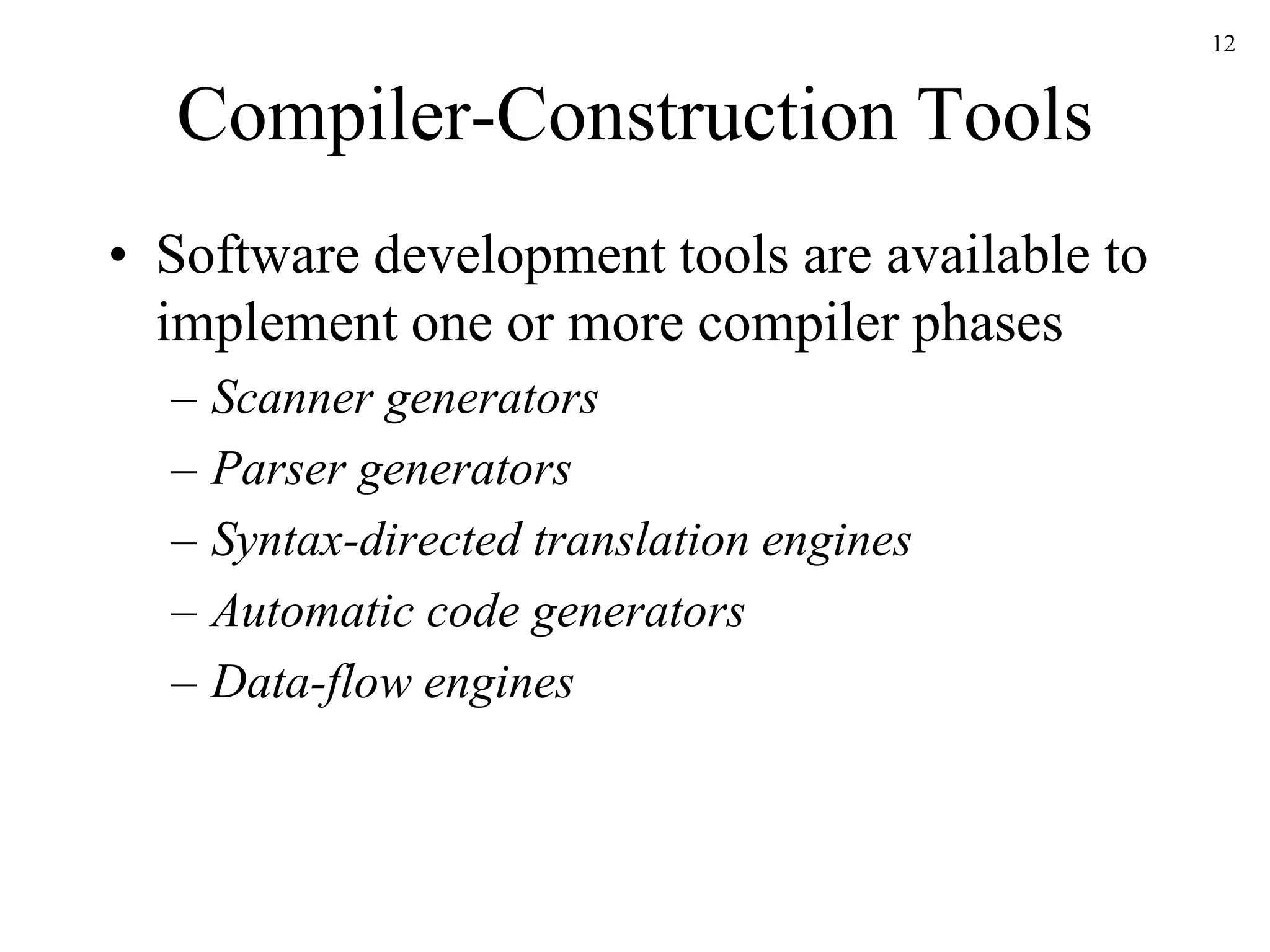
This document provides an introduction and syllabus for a compiler construction course. It will cover the principles, techniques, and tools for building compilers, including defining grammars, compiler analysis and optimization, and working on software projects. Students will learn how to build a compiler for a simplified programming language and become familiar with compiler construction tools, virtual machines like the JVM, and bytecode. The grade breakdown includes exams, projects, and optional homework.