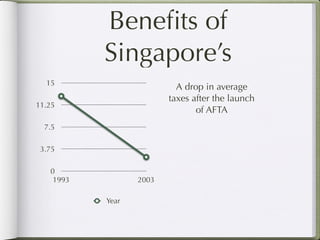
The document discusses regional relations and ASEAN. It provides background on ASEAN's formation in 1967 with 5 countries to promote economic and social development, protect peace and stability, and allow peaceful dispute resolution. It now has 10 members. It discusses Singapore's participation in ASEAN, including the ASEAN Free Trade Area, ASEAN Regional Forum, and ASEAN Scholarship program. Regional relations are emphasized as being important for strength in numbers and for smaller countries to have their voices heard.