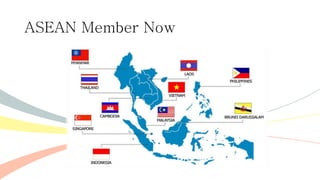
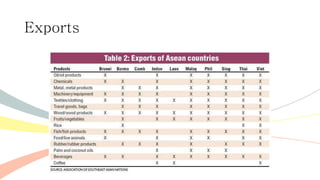
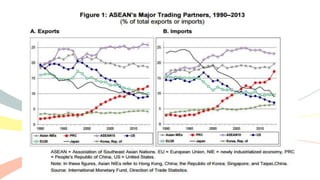
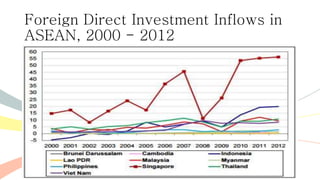
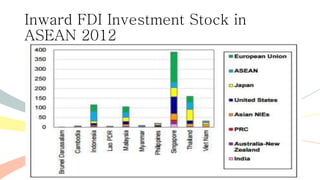
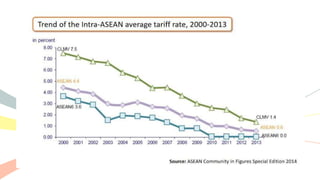
The document outlines the history and purposes of the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) and ASEAN's regional integration agenda, emphasizing cooperation among Southeast Asian nations to achieve economic growth and stability. It highlights the benefits of integration, such as increased trade and market size, as well as ASEAN's various agreements and collaborations with external partners. The document also discusses AFTA's goals of eliminating tariffs and attracting foreign direct investment while enhancing local manufacturing and supporting small businesses.