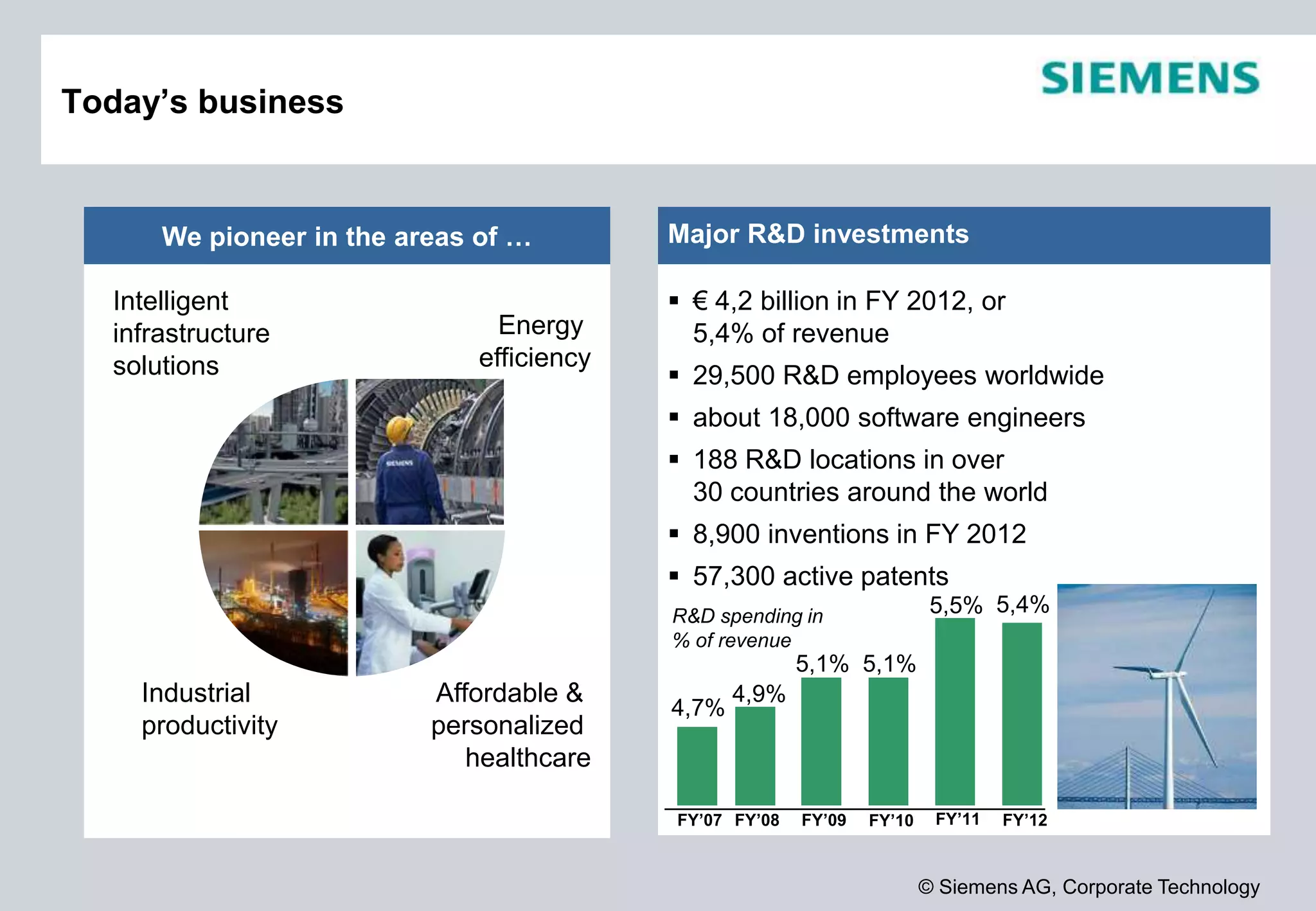
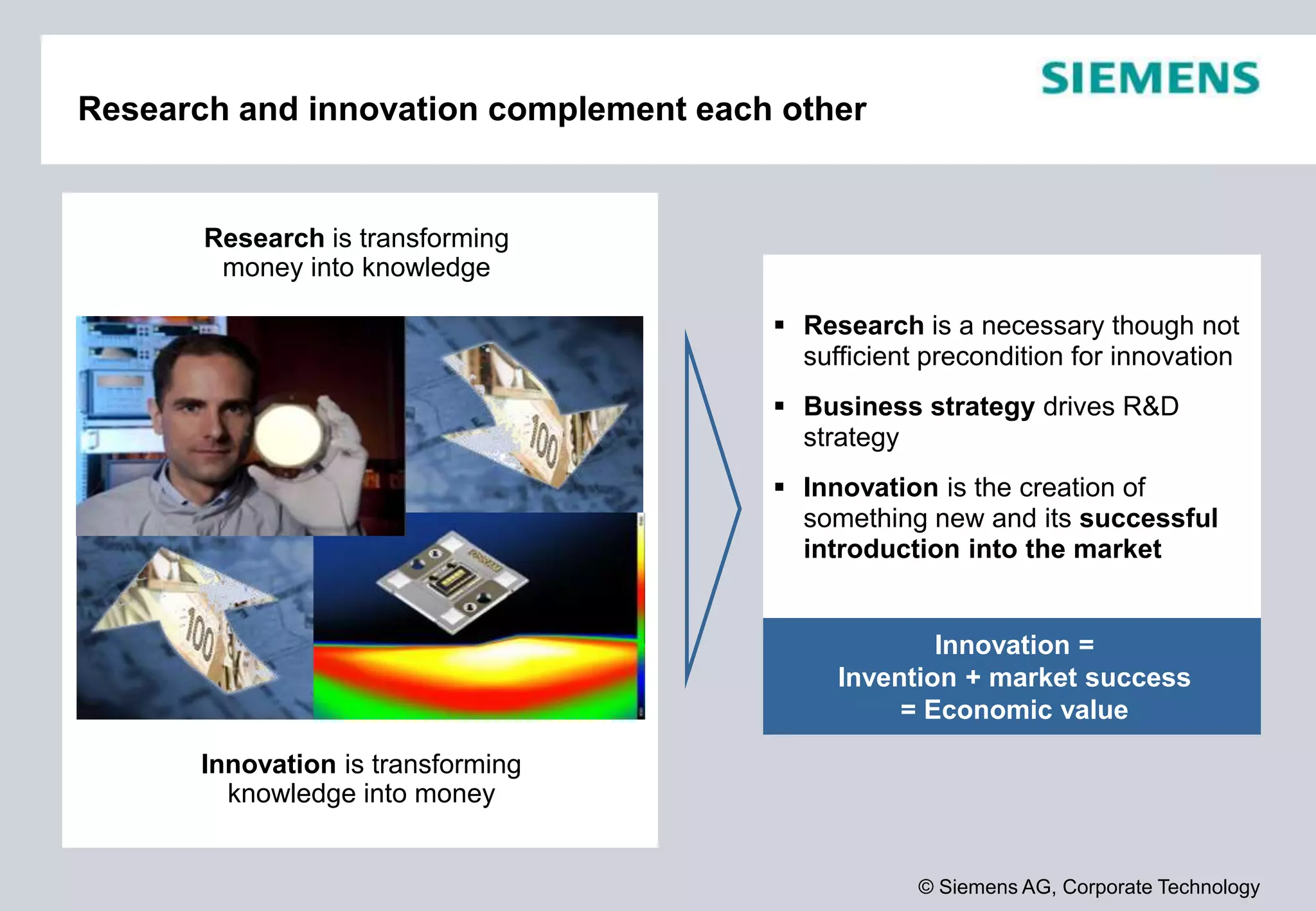
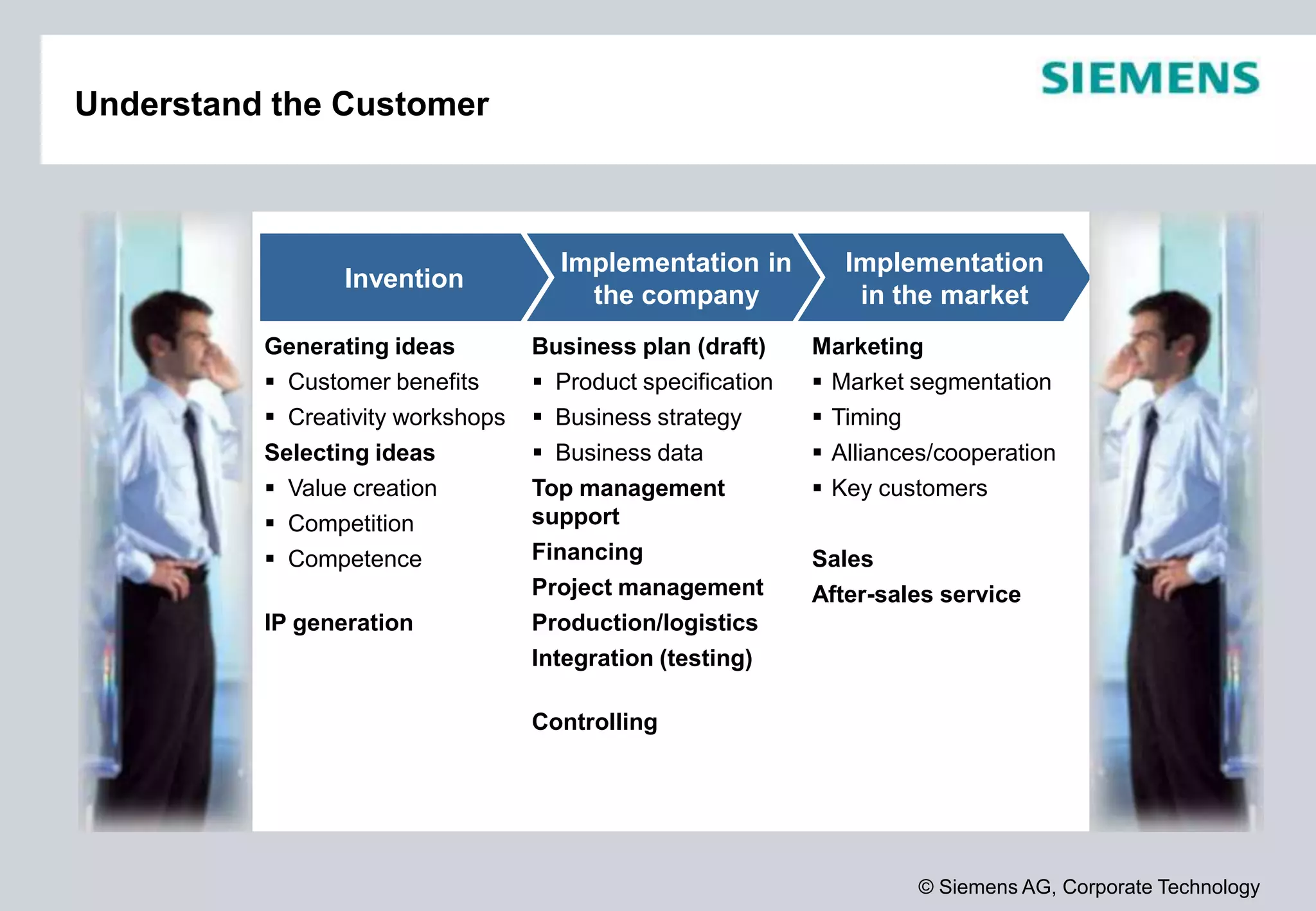
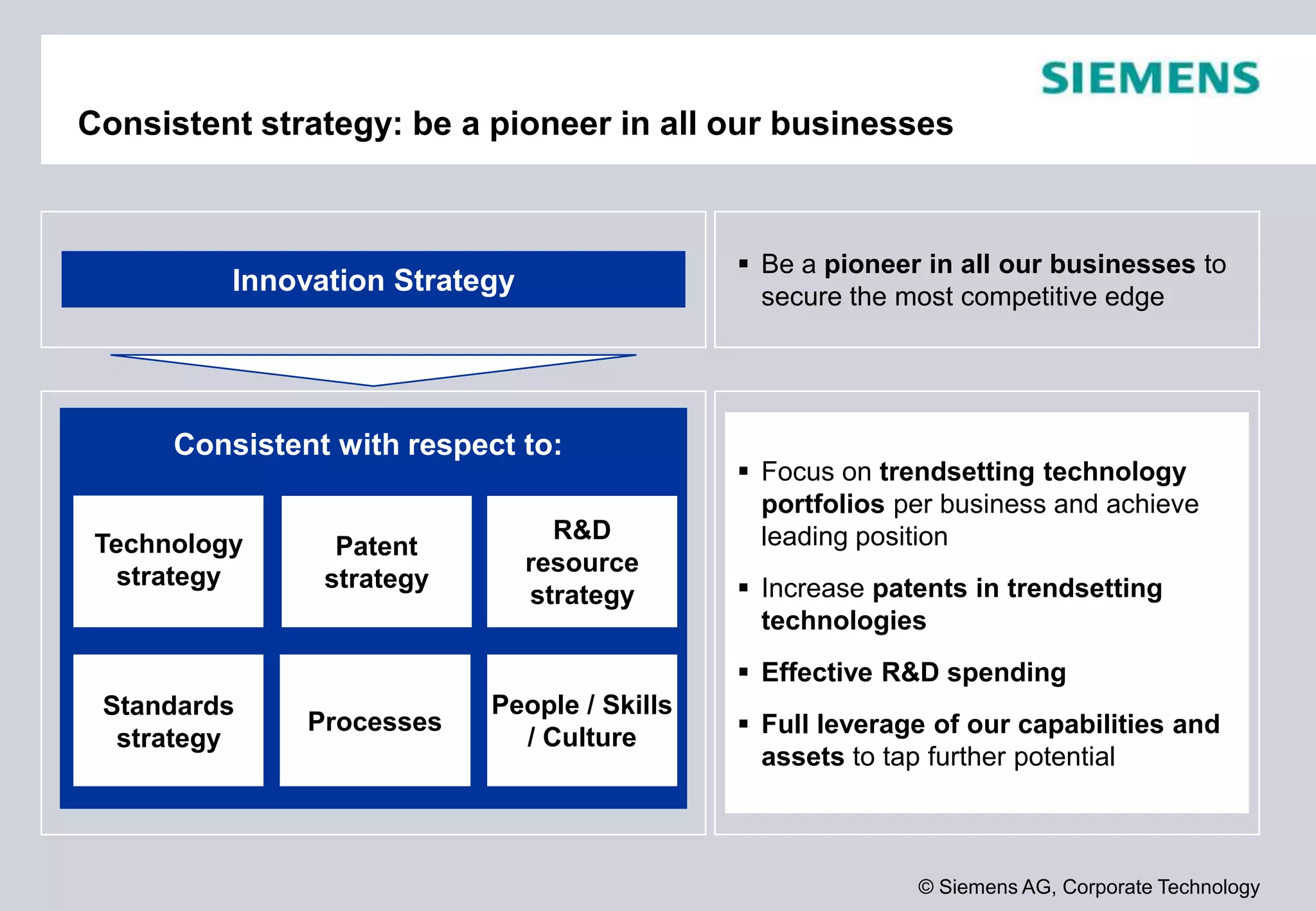
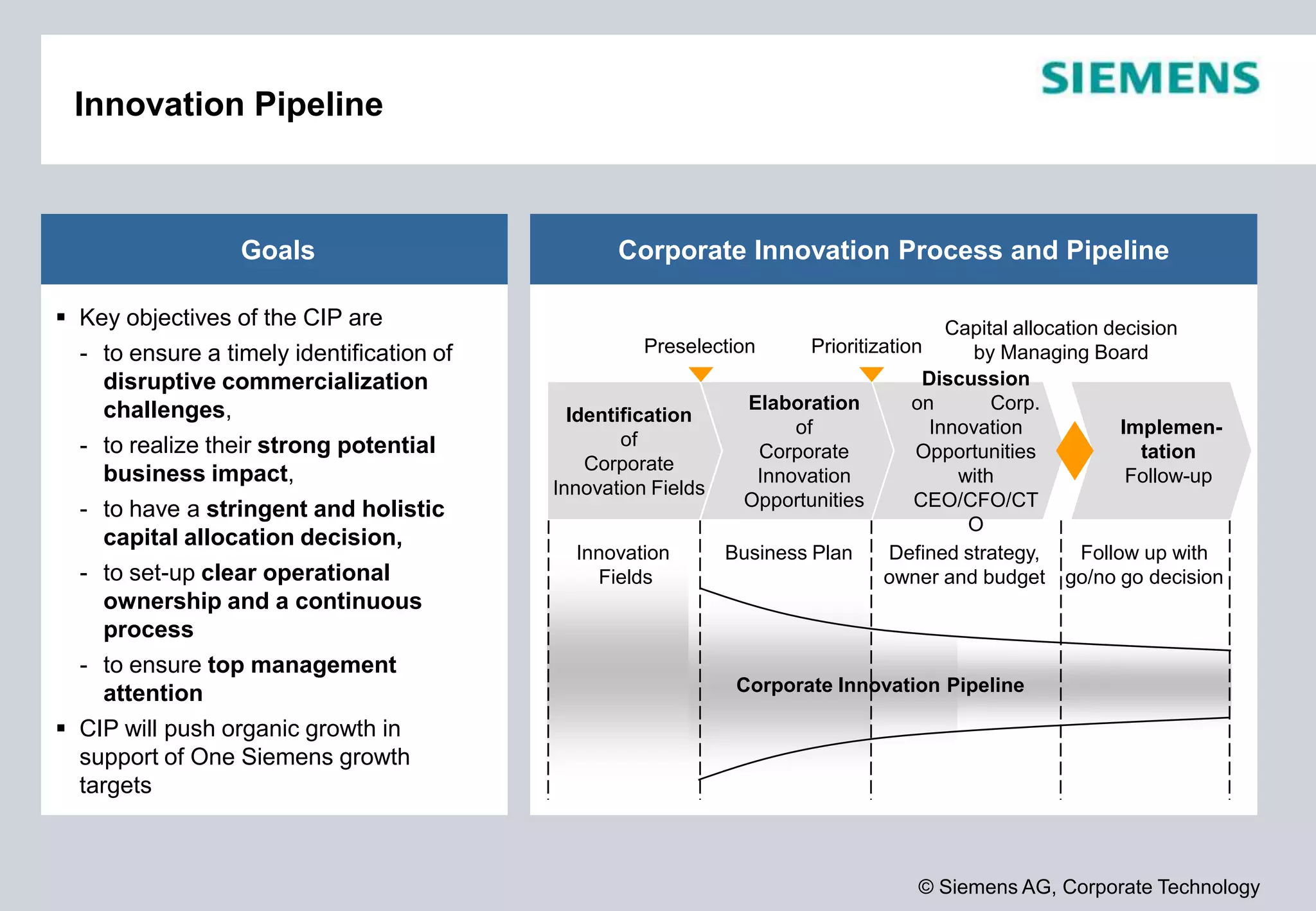
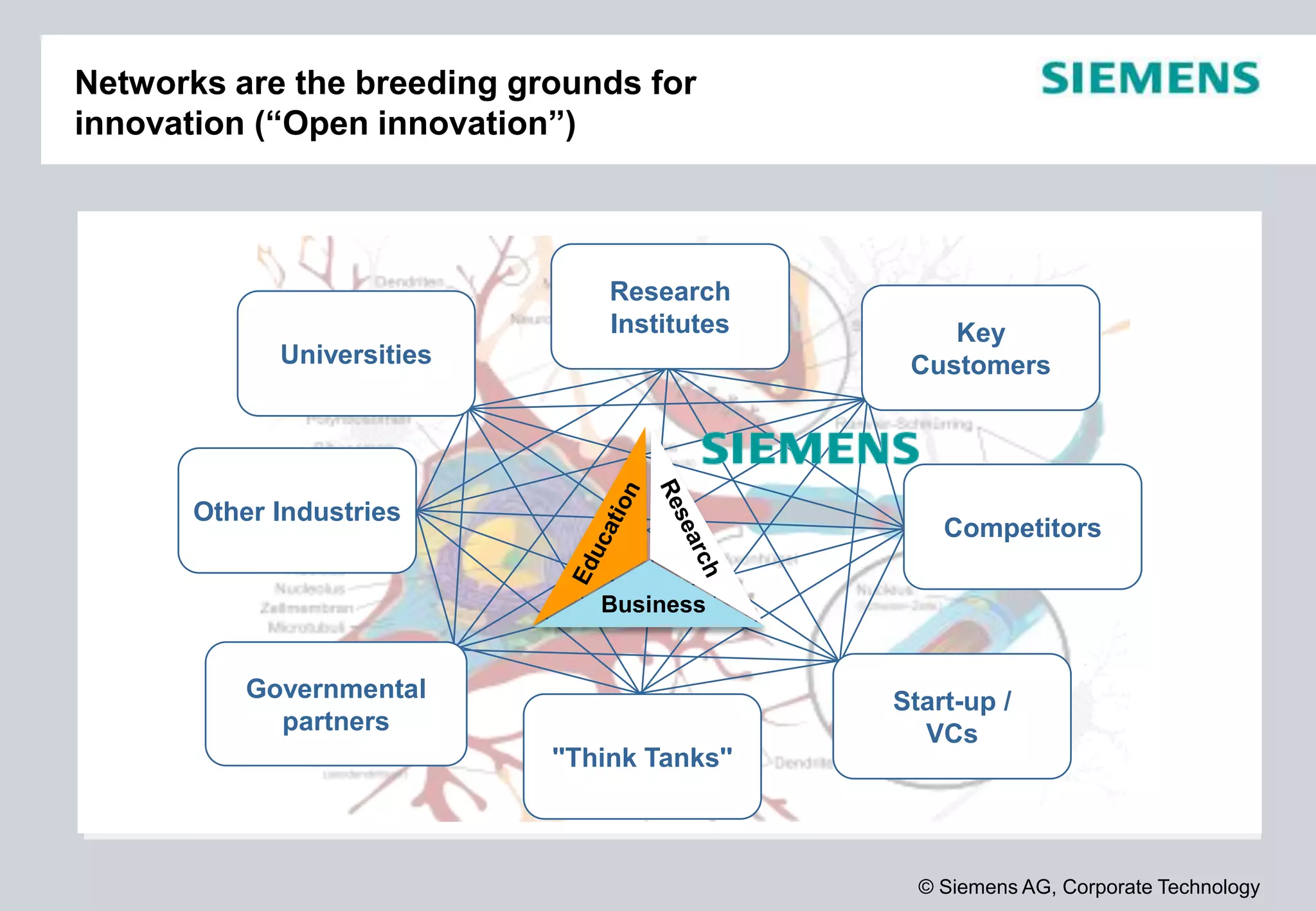
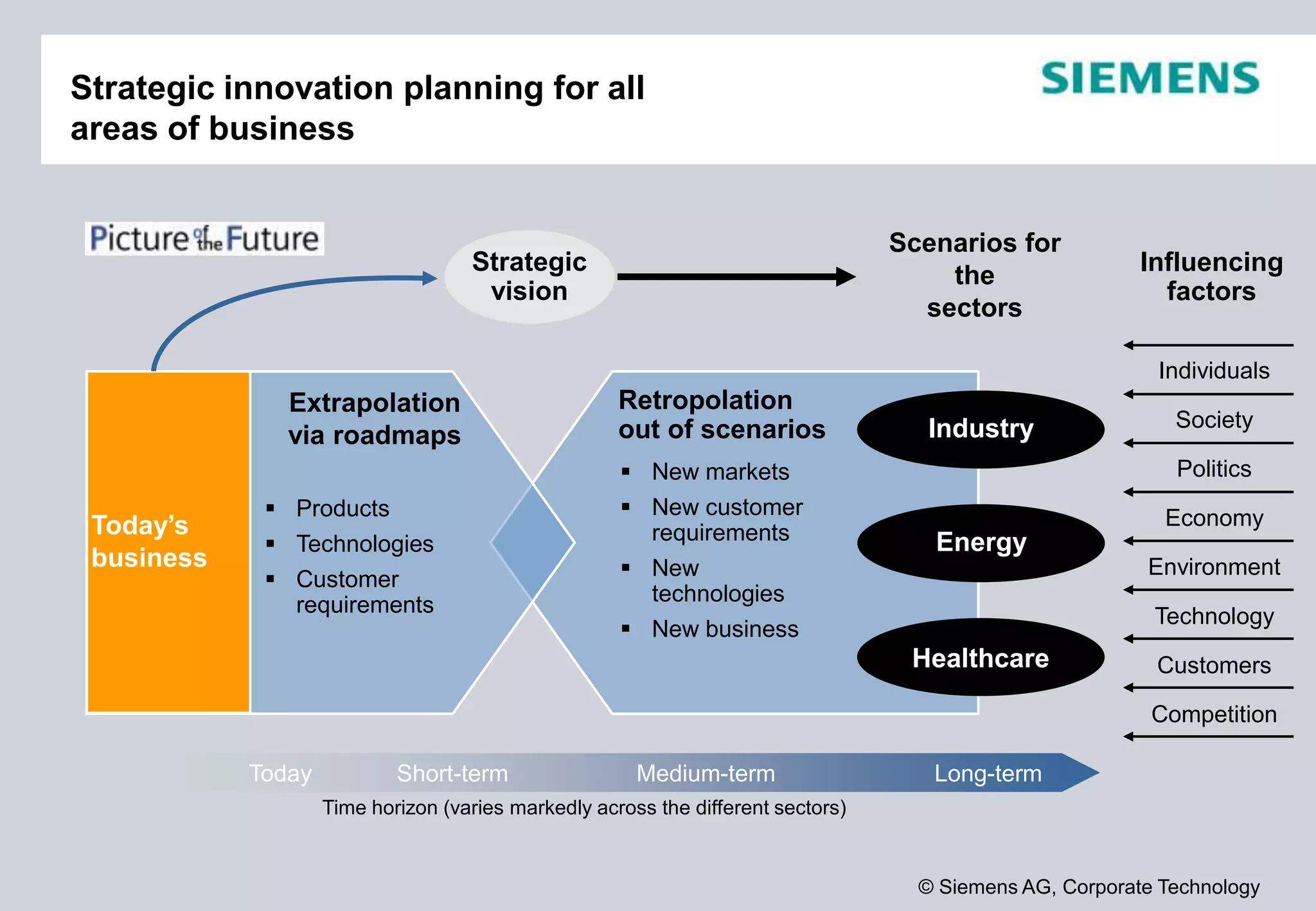
Siemens is a global technology company that operates in more than 190 countries with over 370,000 employees. In fiscal year 2012, Siemens reported sales of €78.3 billion and a profit of €4.59 billion. Siemens invests heavily in research and development, spending €4.2 billion or 5.4% of revenue in fiscal year 2012. The company focuses its innovation strategy on developing technologies with the highest customer value and profit potential by understanding customer needs, trends, and cross-divisional opportunities to fill its innovation pipeline.