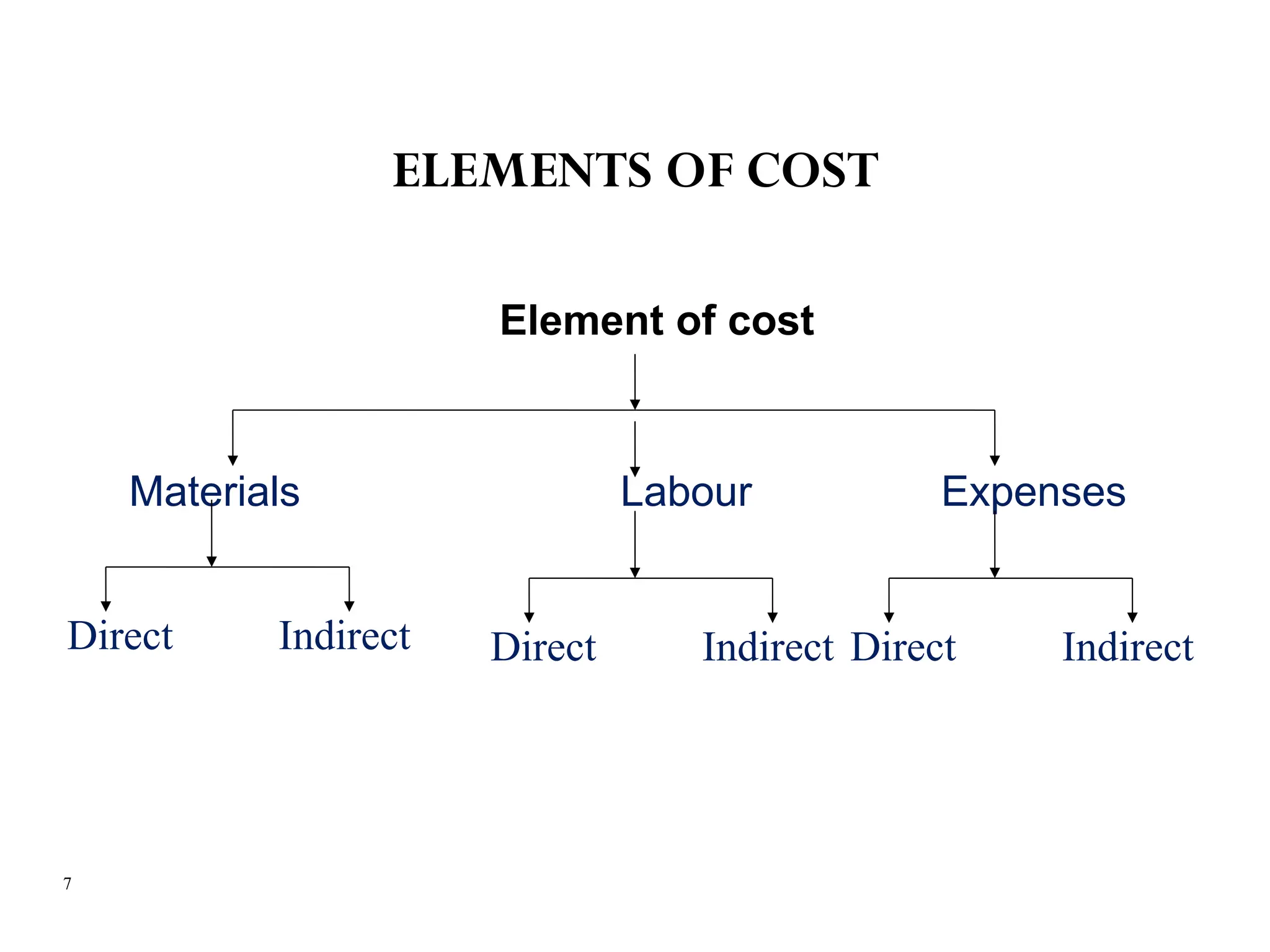
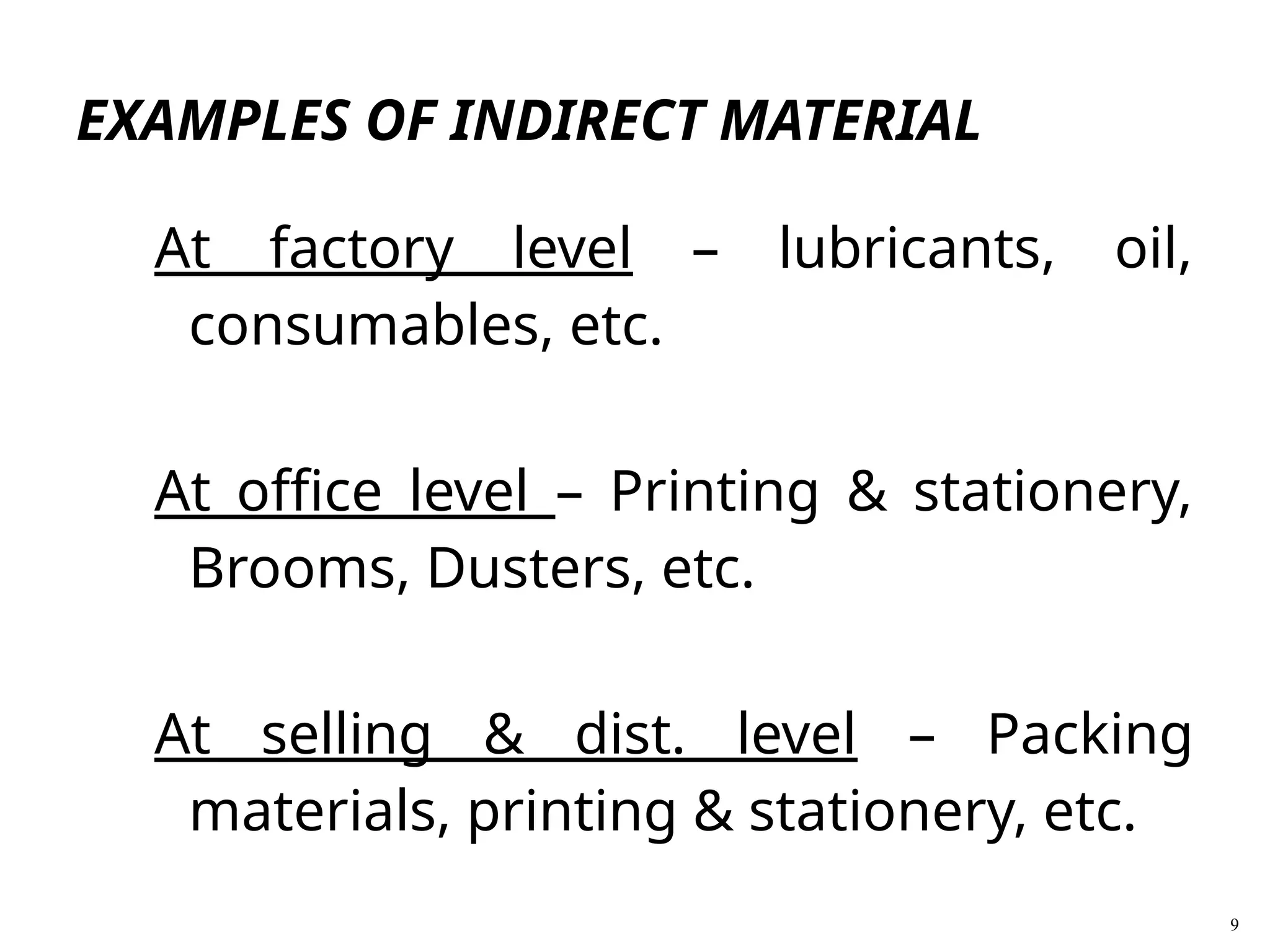
The document outlines the fundamentals of cost accounting, defining cost as the expenditure associated with products or services, and emphasizing the processes of recording, classifying, and summarizing costs for management decision-making. It elaborates on various objectives, cost terminologies, and classifications, including direct and indirect costs relating to materials, labor, and expenses. Key aspects of cost control and different costing methods, such as job and batch costing, are also discussed.