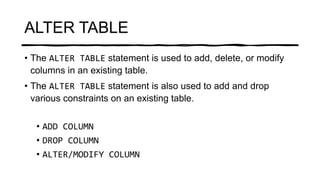
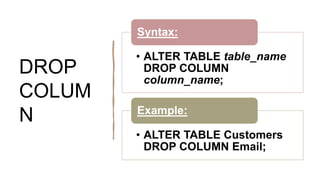
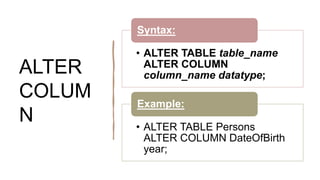
The document explains SQL commands related to altering tables, selecting distinct values, and filtering records using the WHERE clause. It details how to add, drop, and modify columns in a table, as well as how to retrieve unique values and filter results based on conditions. Examples for each command are provided for clarity.