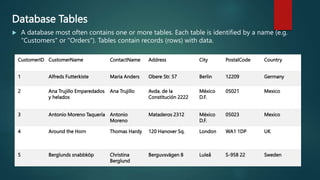
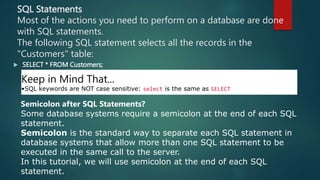
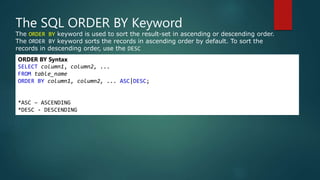
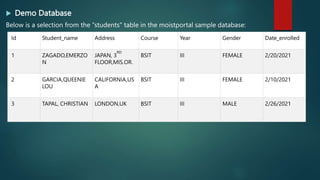
This document provides an introduction to SQL and relational database concepts. It explains that SQL is used to manipulate and retrieve data from relational databases. It then defines key SQL commands like SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, and INSERT which allow users to query, modify, and manage data. The document also introduces SQL clauses and syntax like WHERE, ORDER BY, AND, OR to filter and sort query results. It provides examples of these commands using sample database tables.