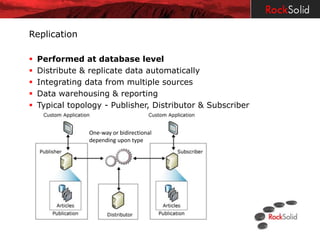
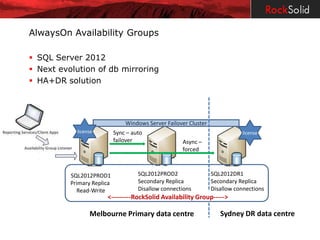
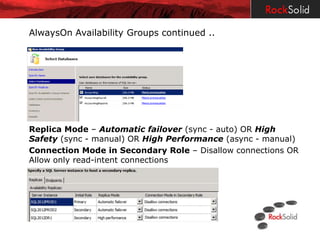
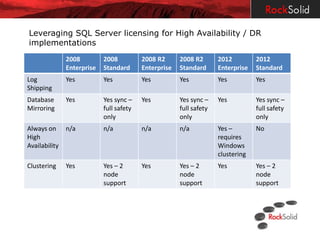
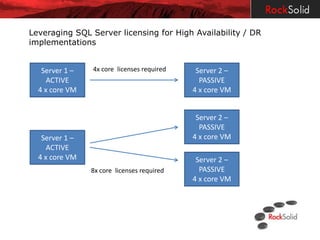
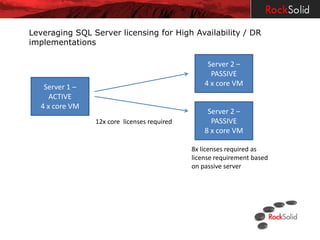
The document provides a detailed overview of disaster recovery (DR) and high availability (HA) technologies for SQL Server, including log shipping, replication, clustering, and Always On availability groups across various SQL Server versions. It outlines the differences between DR and HA solutions, their configurations, advantages, and disadvantages, while emphasizing the importance of seeking professional advice regarding implementation suitability. Licensing considerations for SQL Server in the context of HA and DR are also discussed, highlighting the requirements and limitations for passive instances.