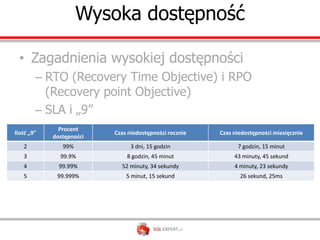
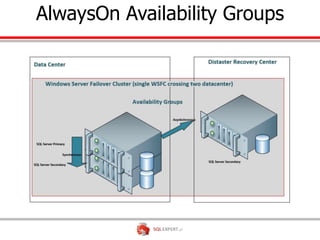
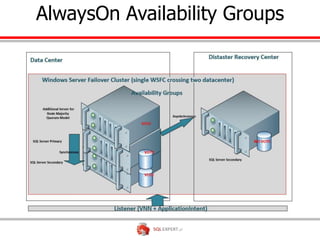
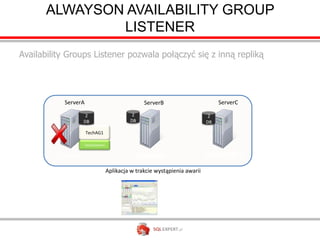
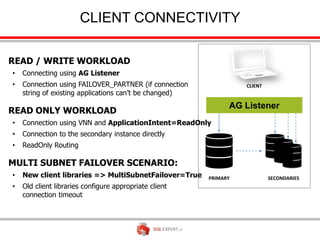
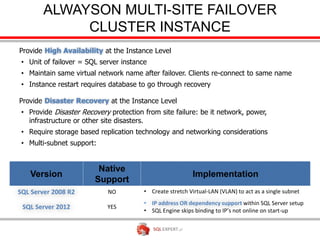
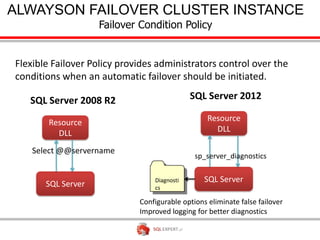
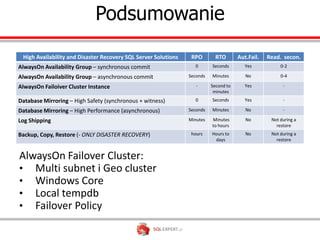
The document outlines high availability and disaster recovery solutions in SQL Server, focusing on AlwaysOn technology. It details architecture requirements, monitoring, management, and various solutions like Windows failover clusters, mirroring, and log shipping. Key metrics such as recovery time objectives and availability percentages are also discussed, along with best practices for utilizing active secondaries and multi-subnet configurations.