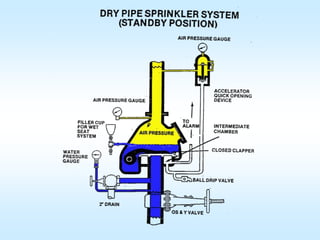
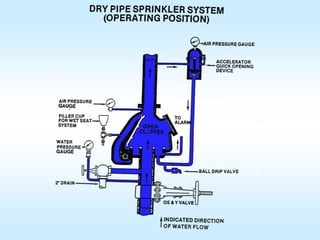
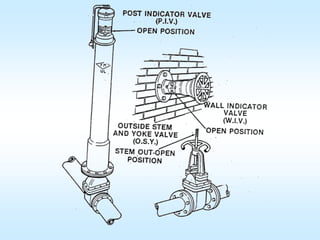
This document discusses automatic sprinkler systems, including their history and components. It describes different types of sprinkler systems like wet pipe, dry pipe, and pre-action systems. The key factors in determining the appropriate sprinkler system are identified as occupancy, commodity classification, storage heights and arrangements. The document provides diagrams of sprinkler system components and outlines the inspection, testing and maintenance requirements.