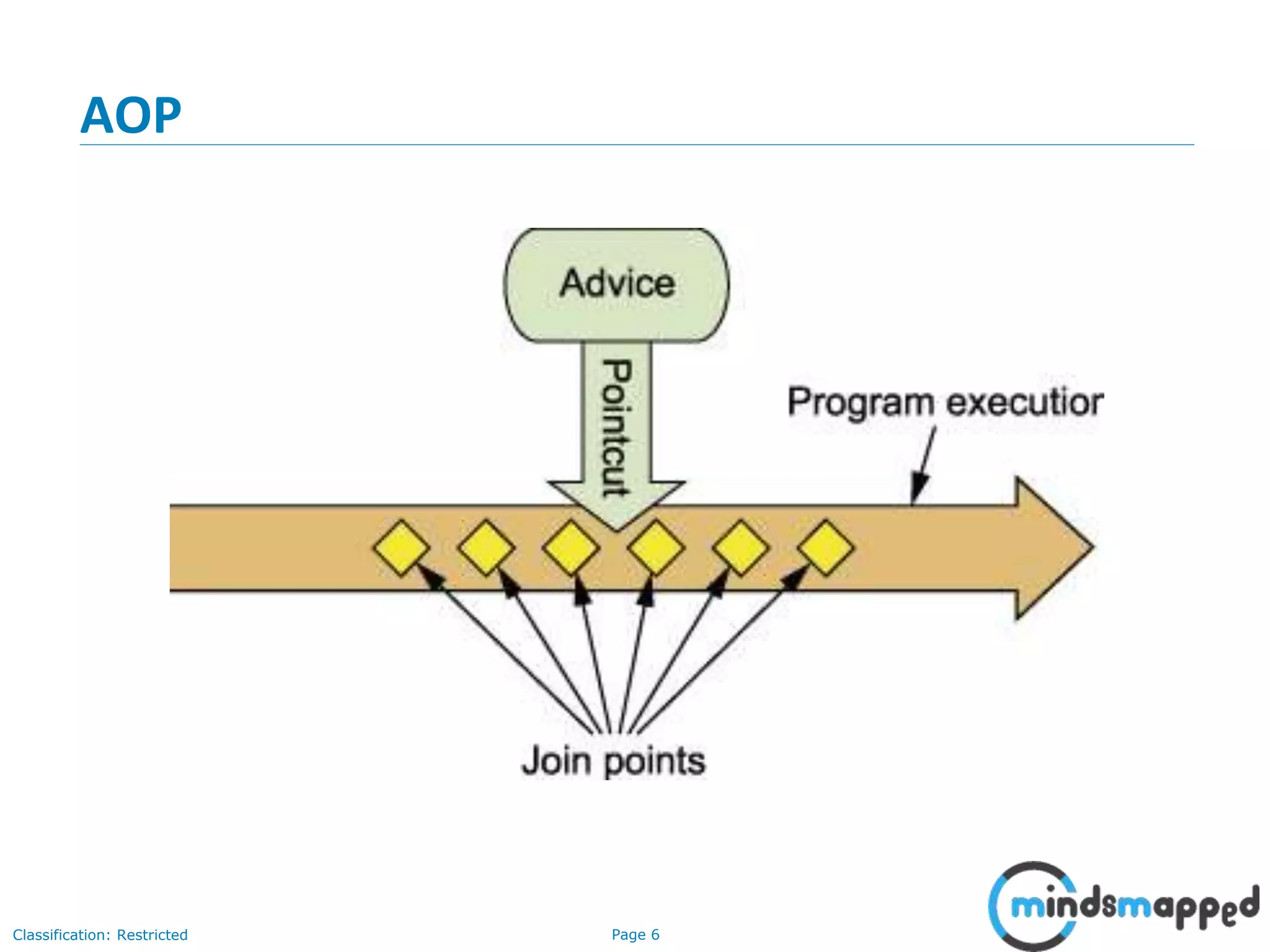
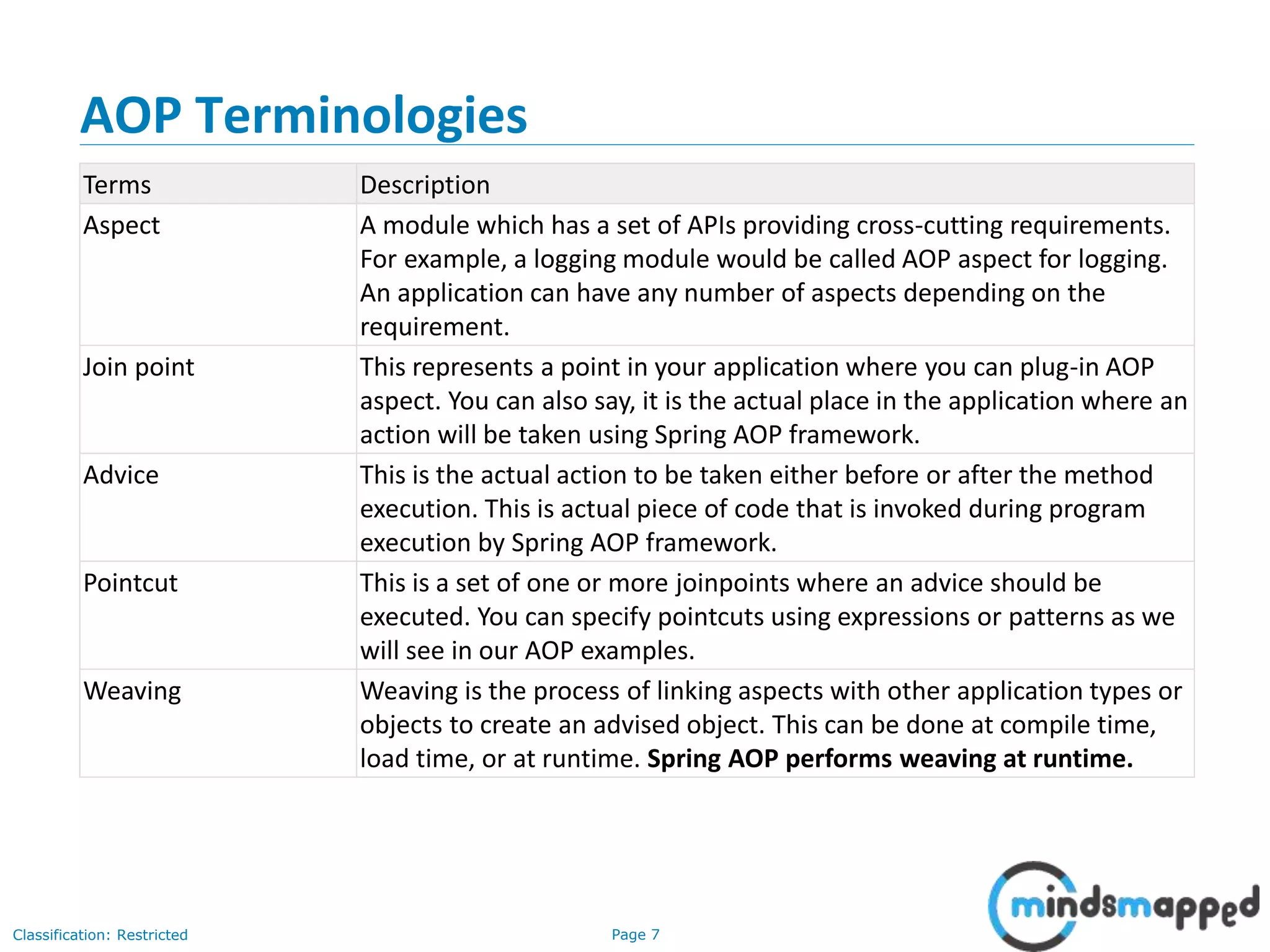
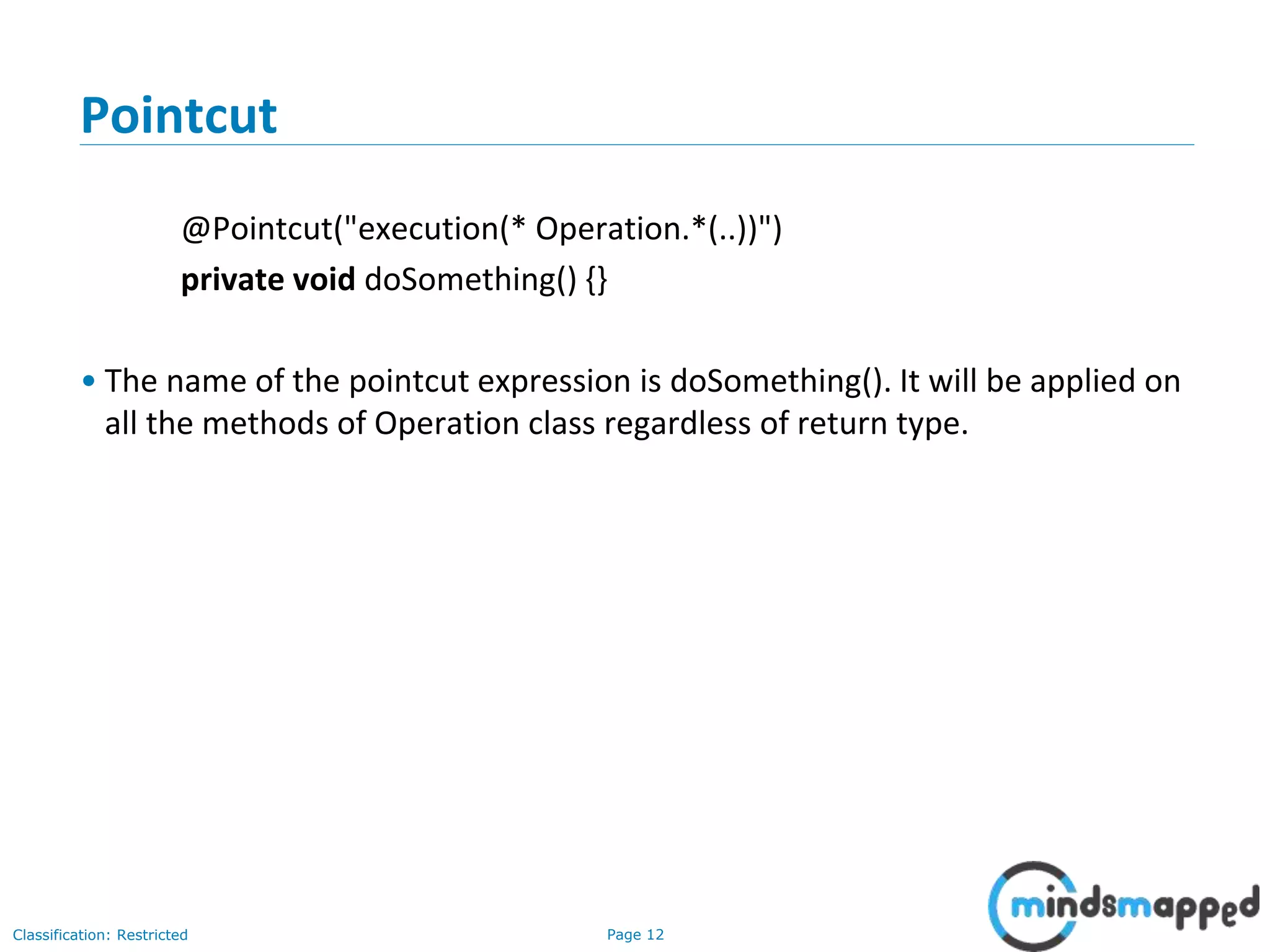
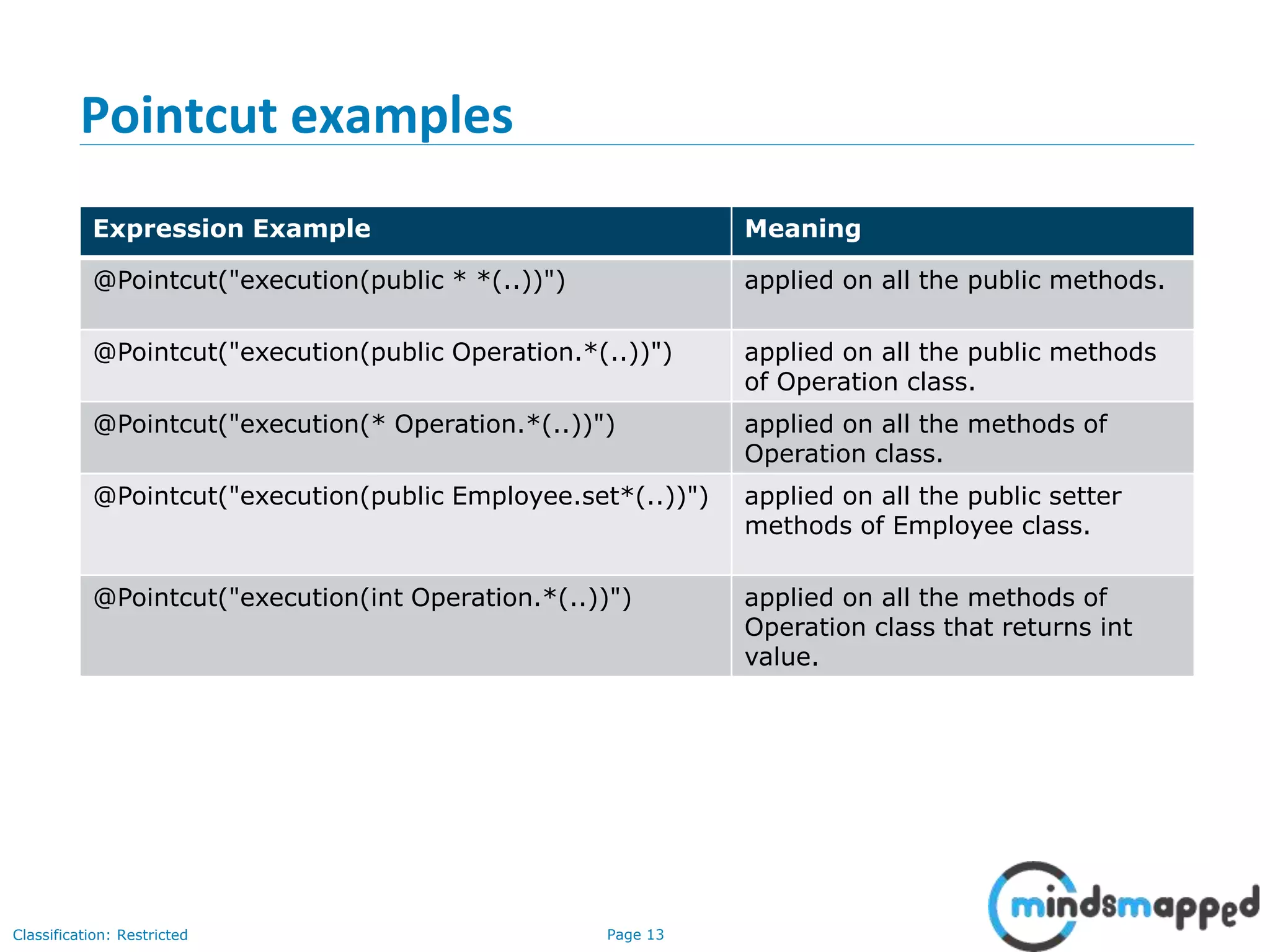
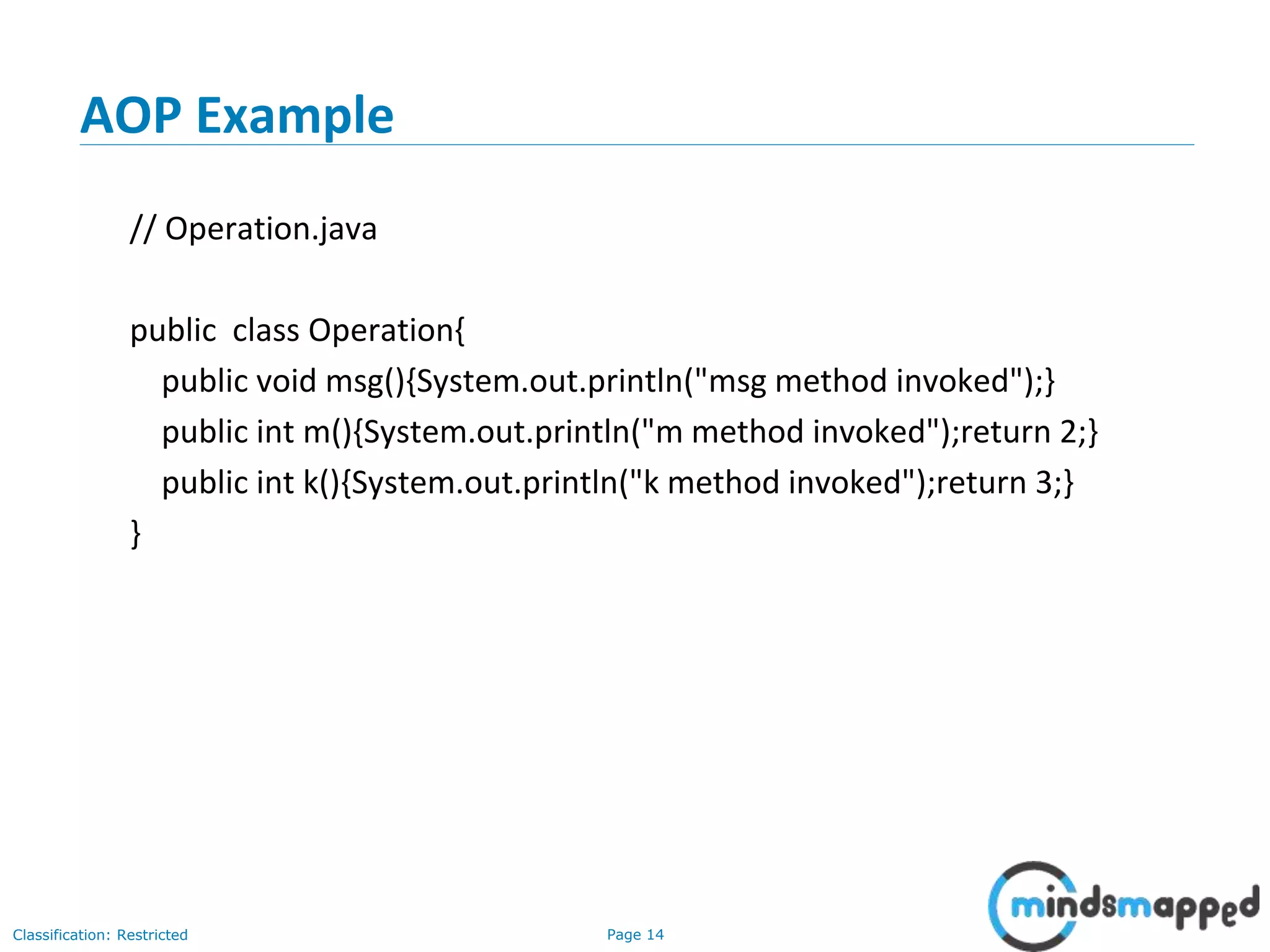
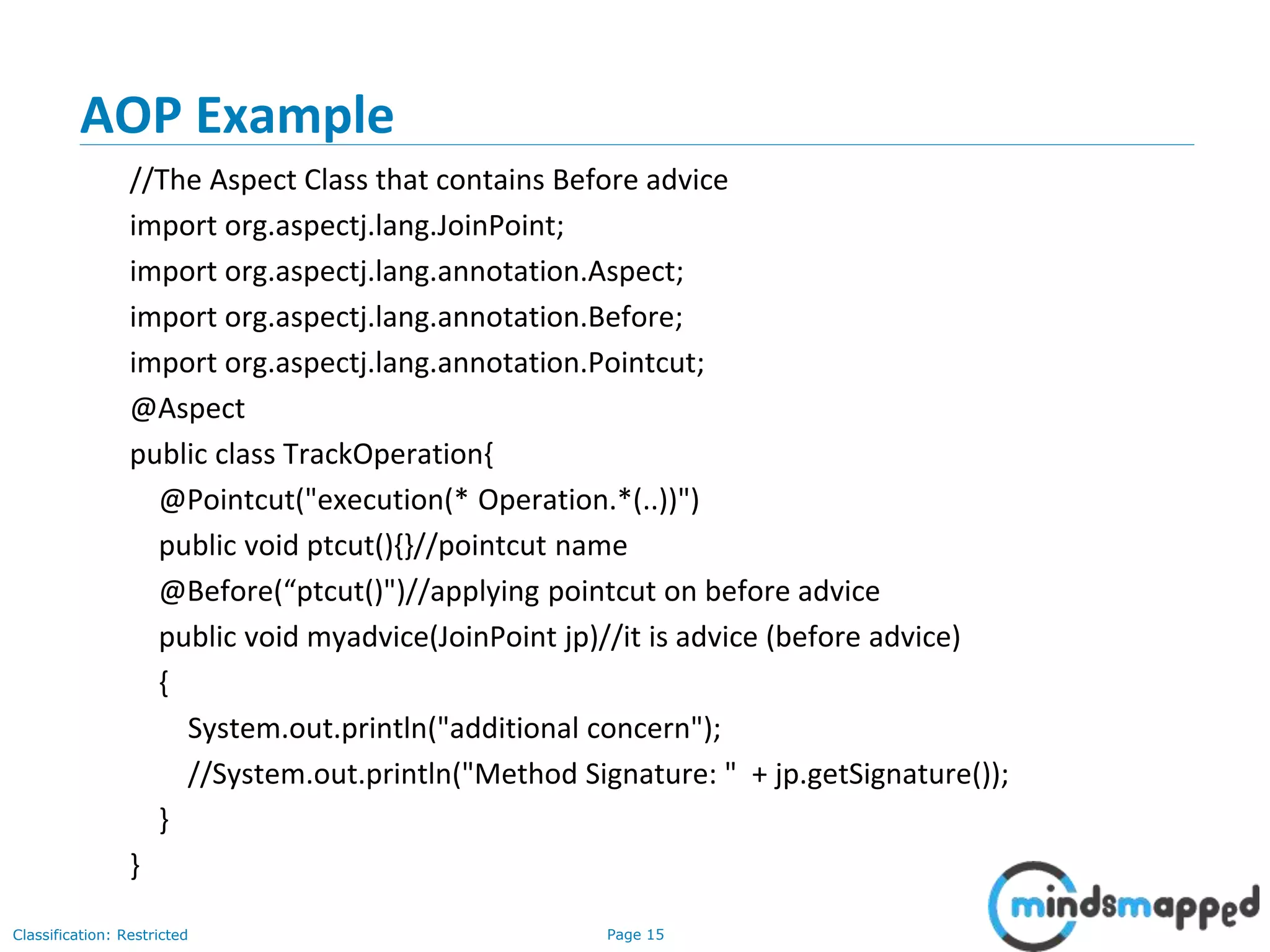
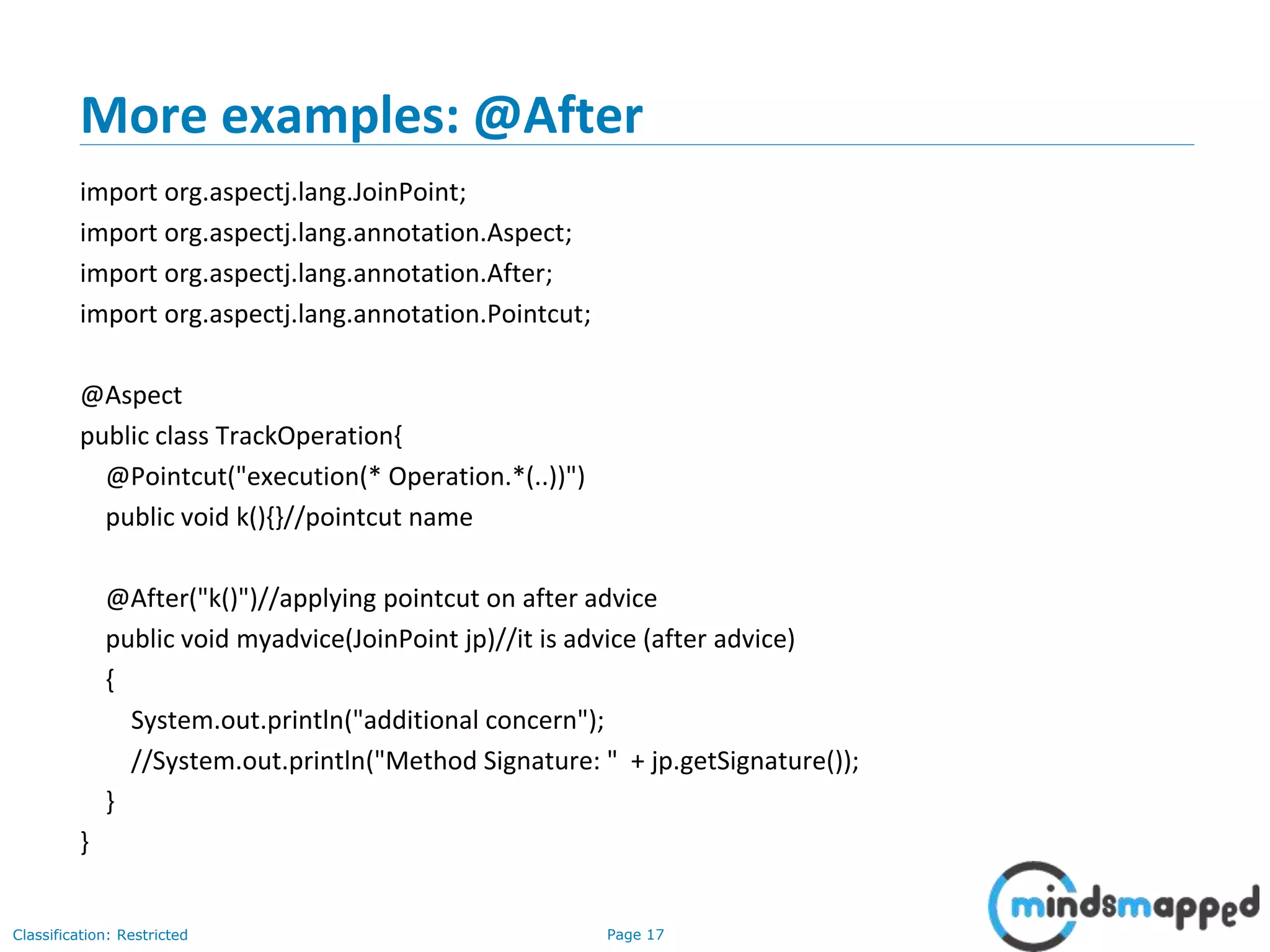
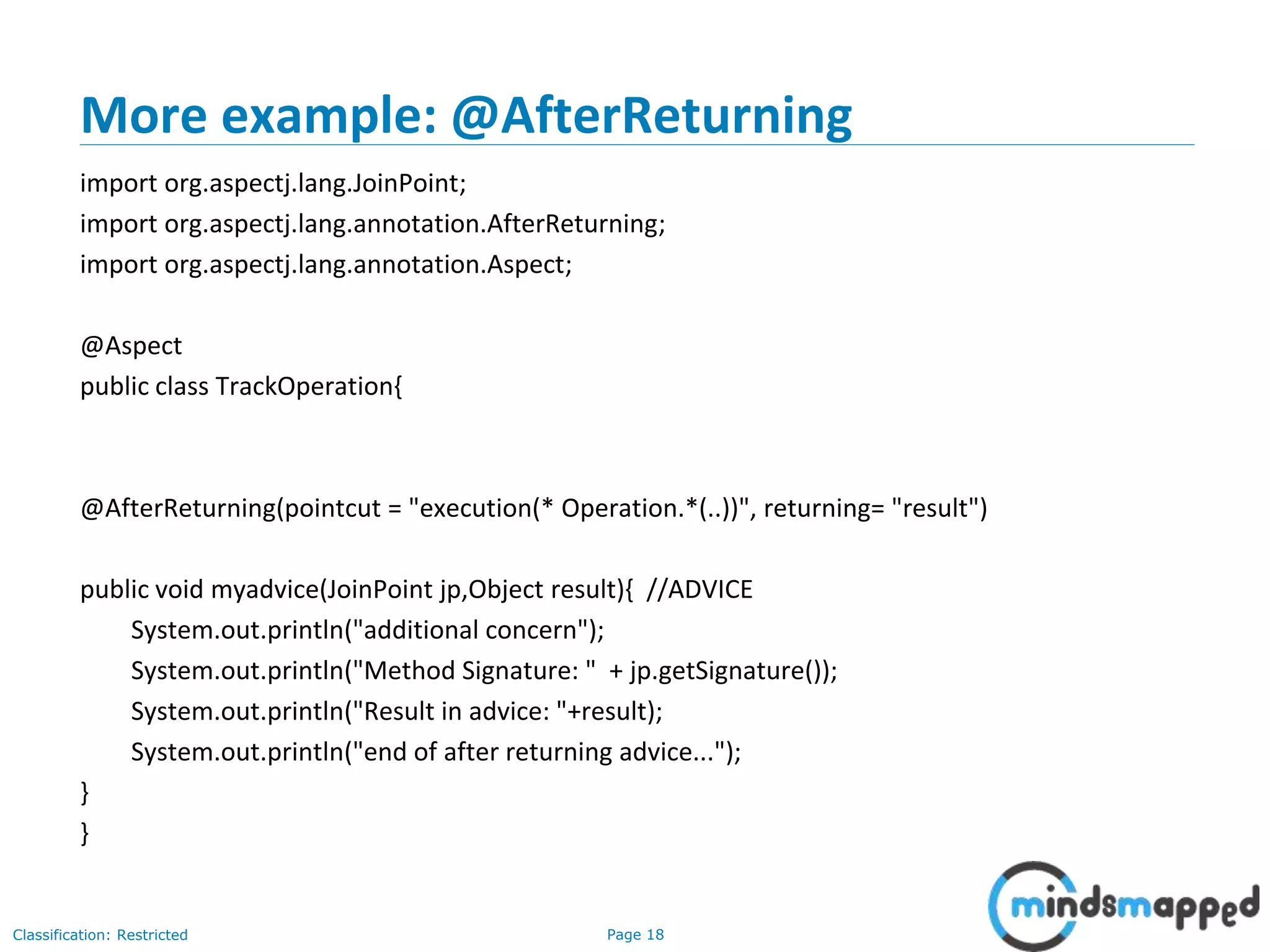
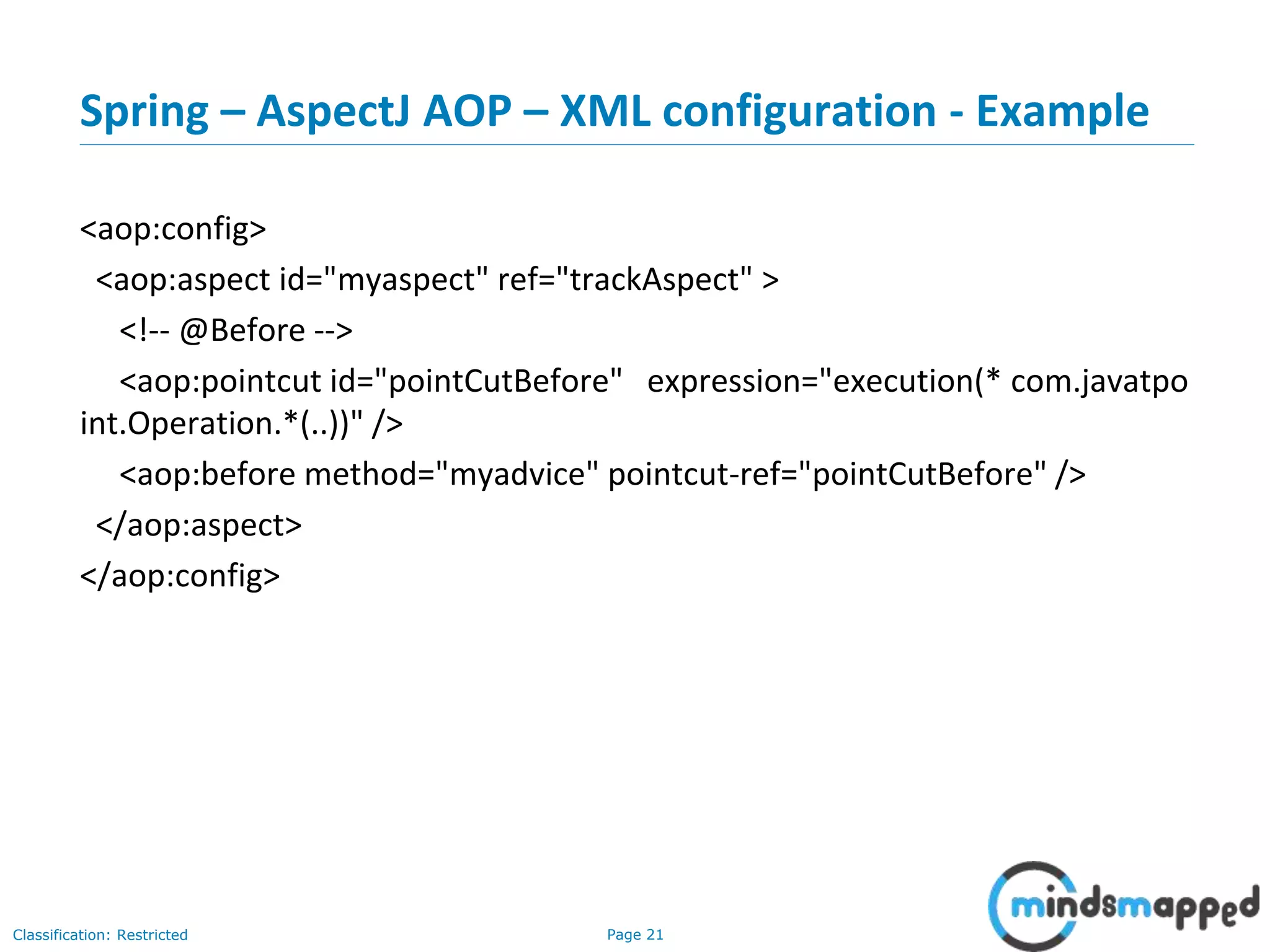
The document provides an overview of Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP) within the Spring framework, detailing its concepts like aspects, join points, advice, and pointcuts. It discusses how AOP enhances Object-Oriented Programming by decoupling cross-cutting concerns and covers various AOP implementations, configurations, and examples using AspectJ annotations. The document also includes XML configuration examples and highlights the necessary libraries for AspectJ integration.