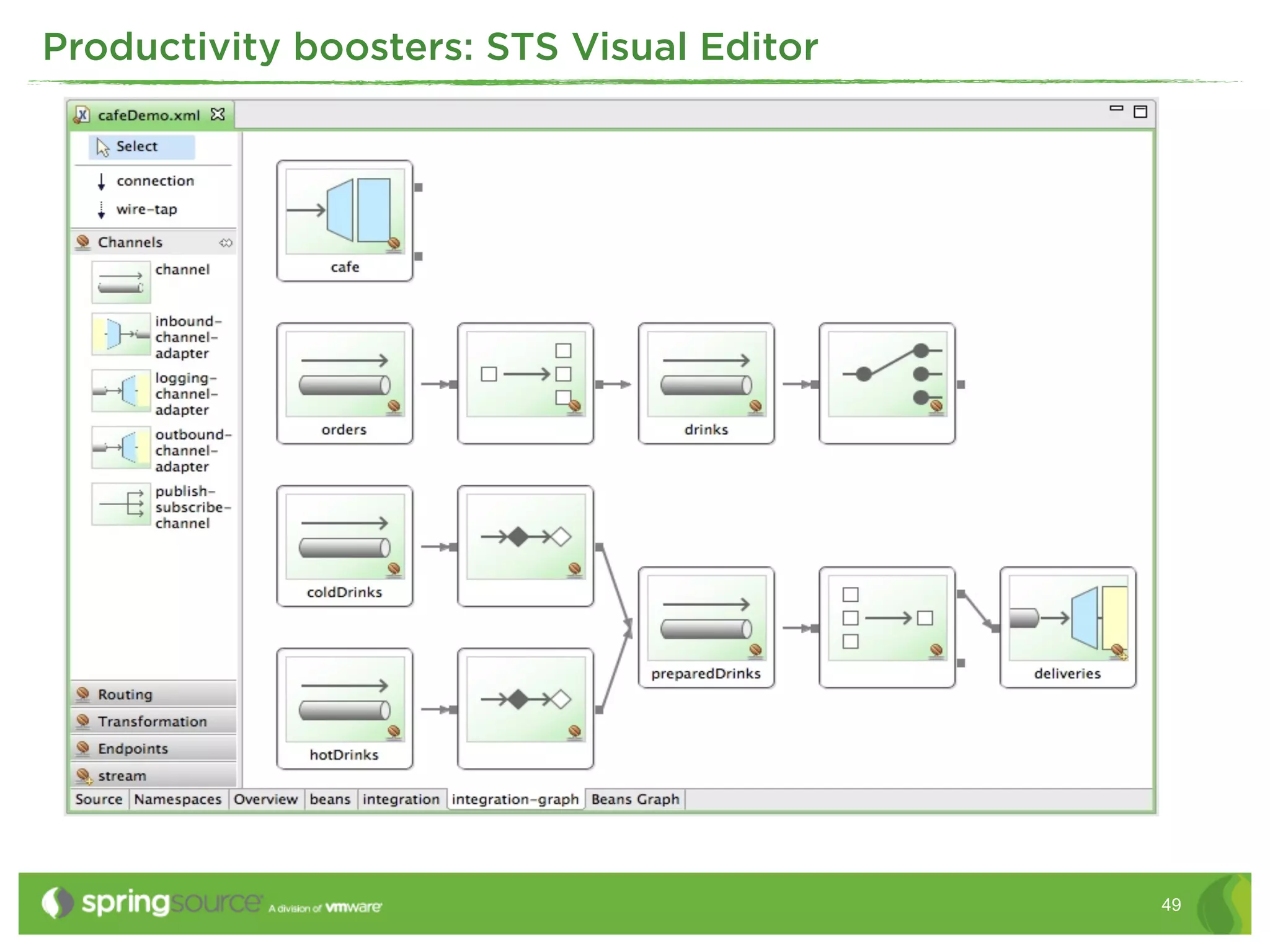
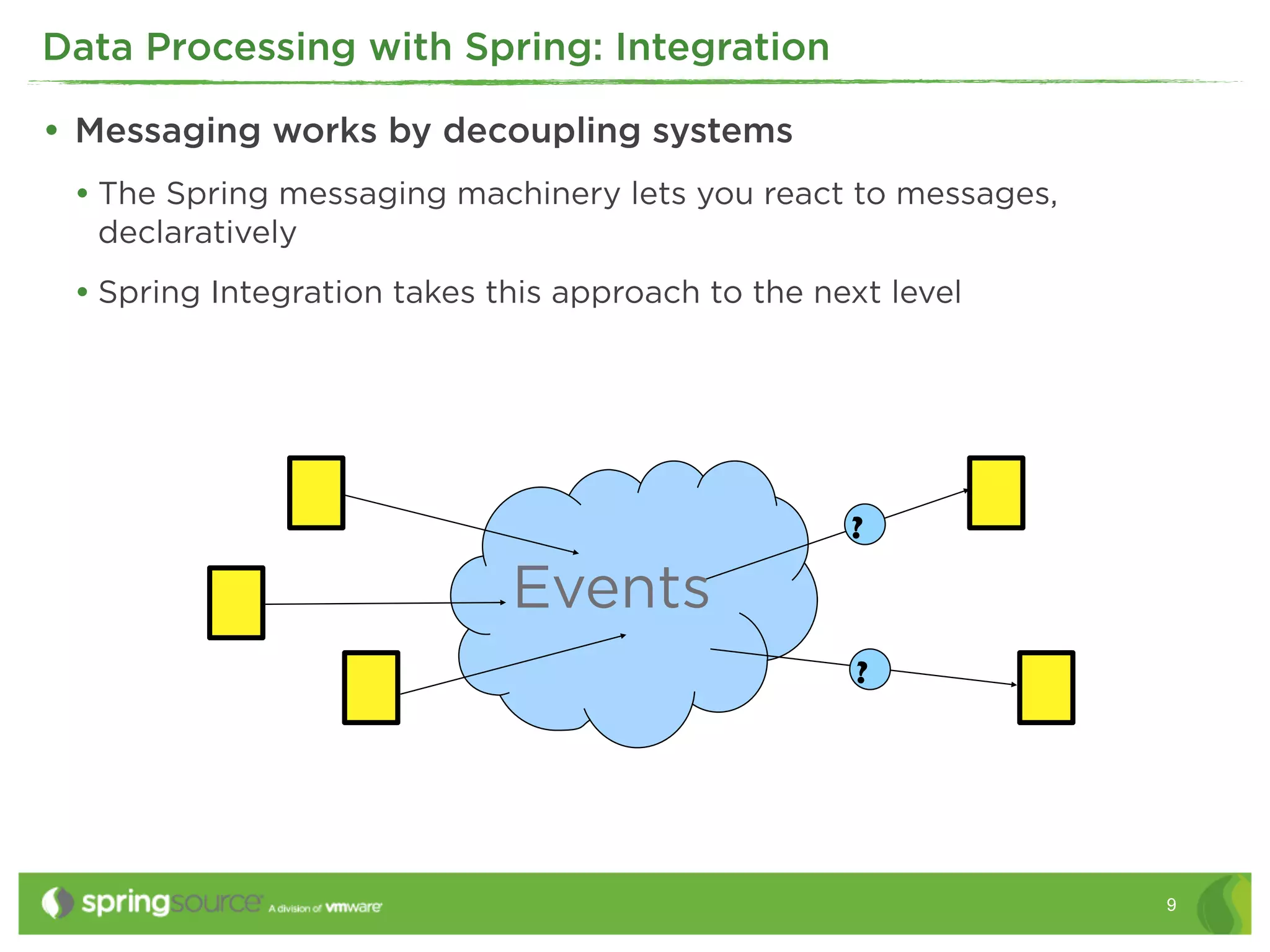
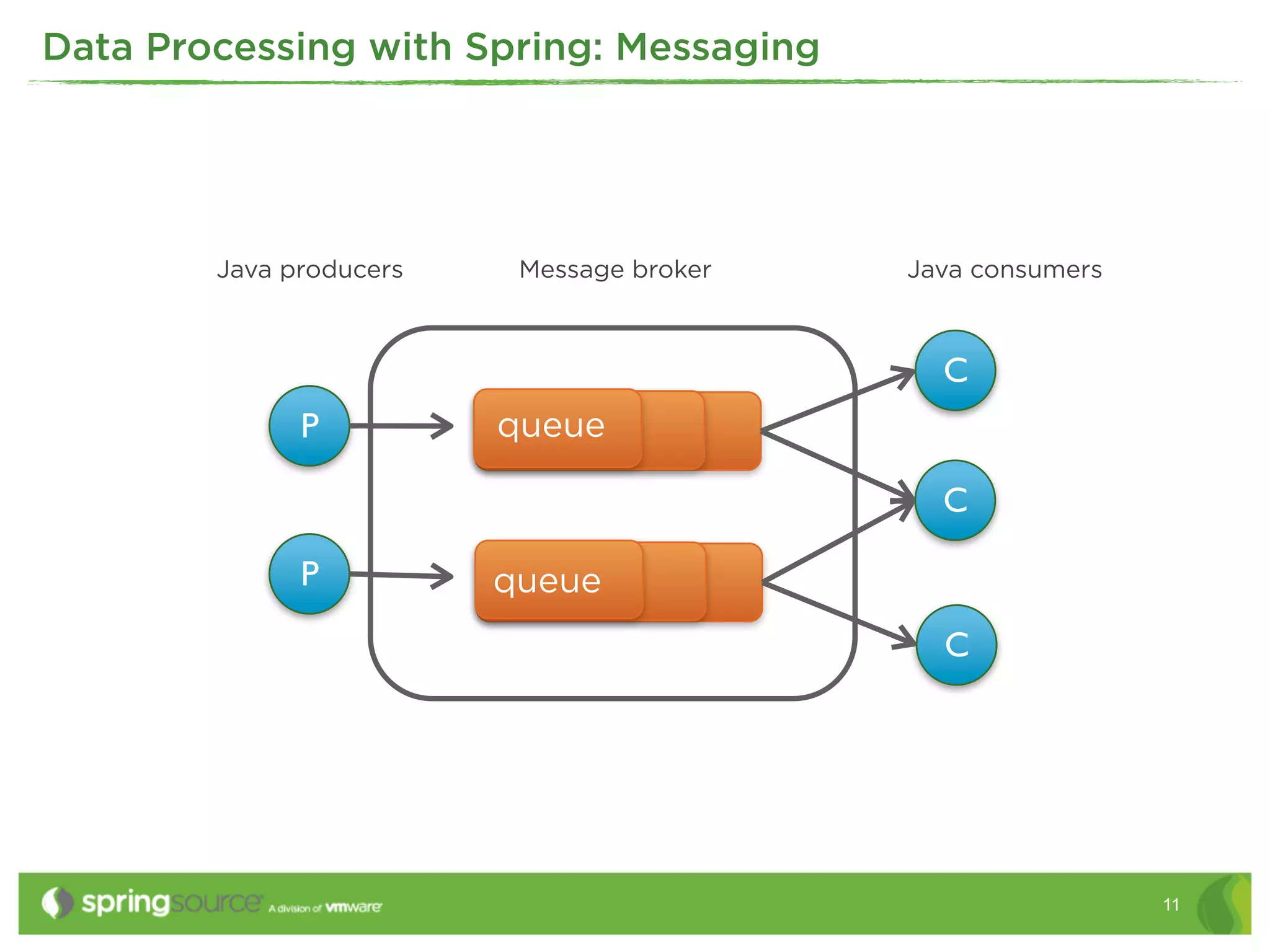
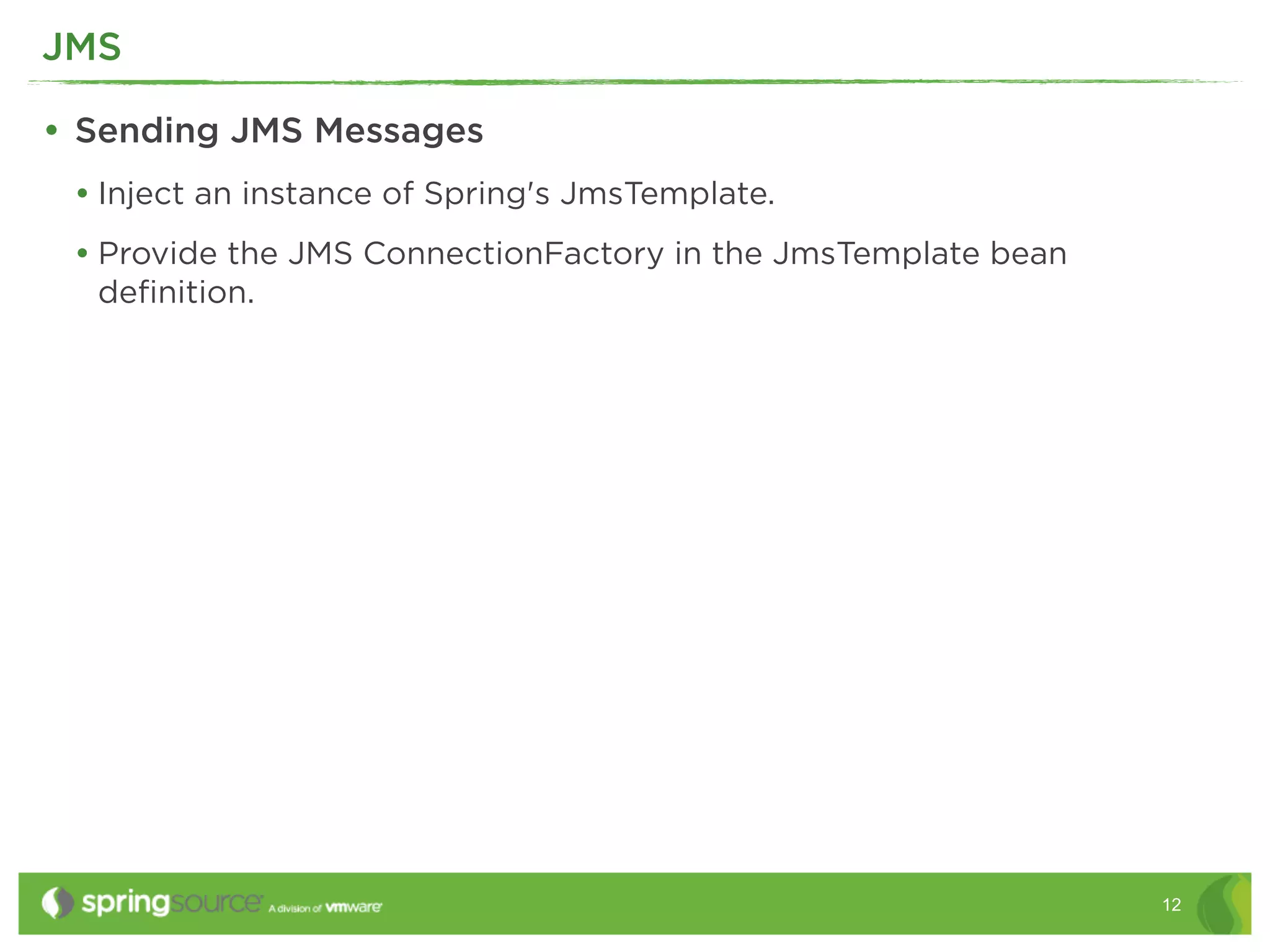
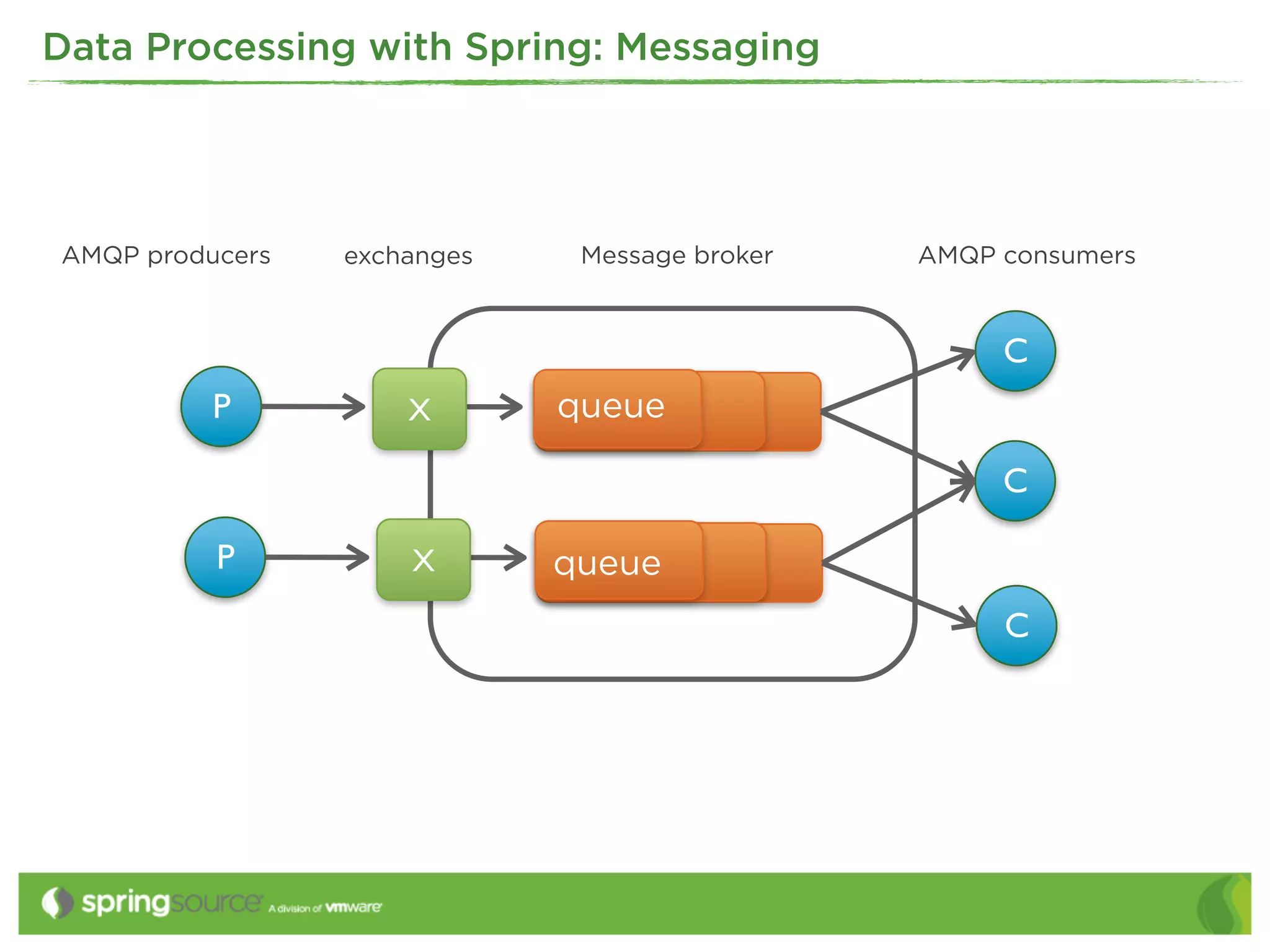
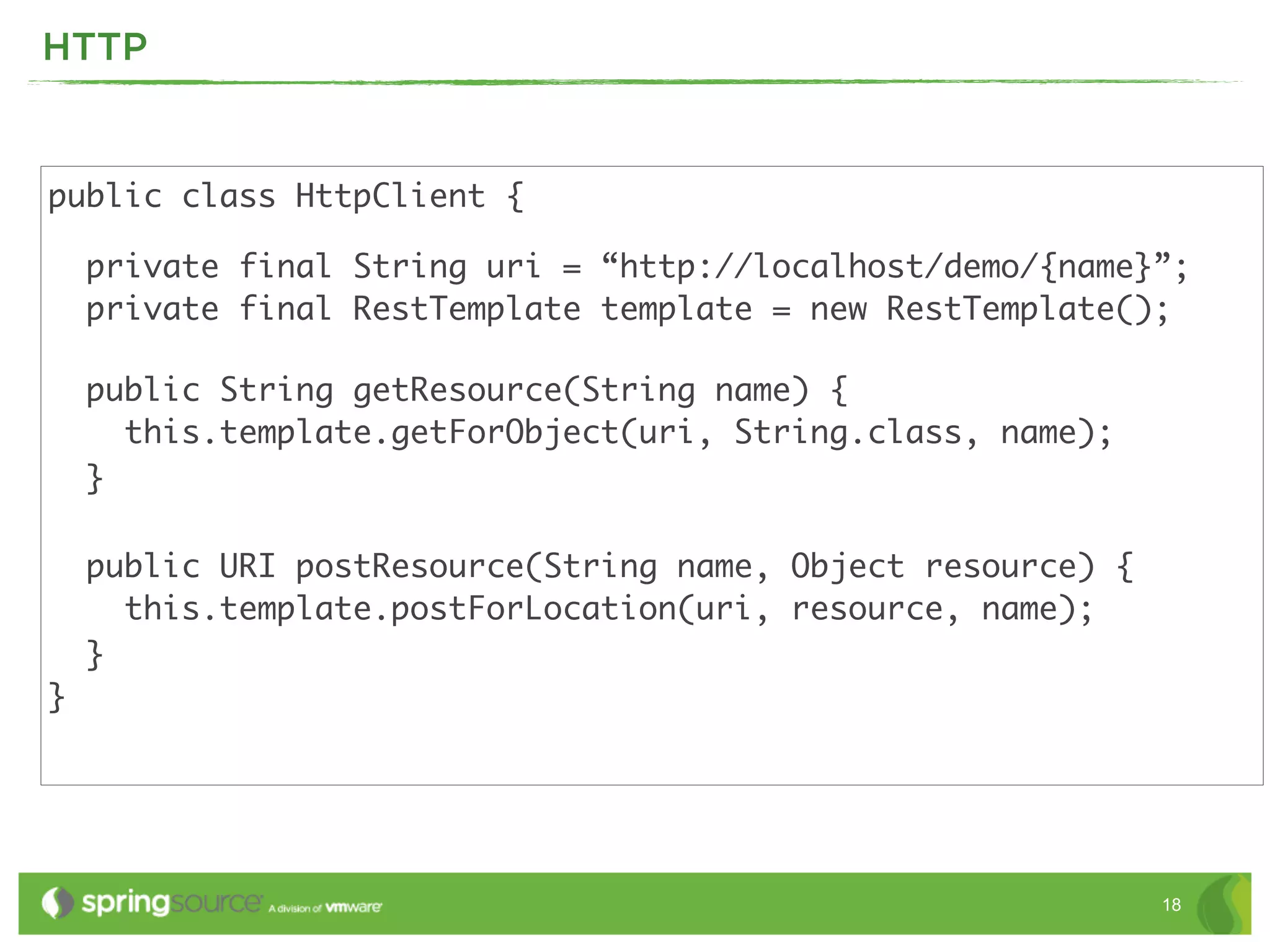
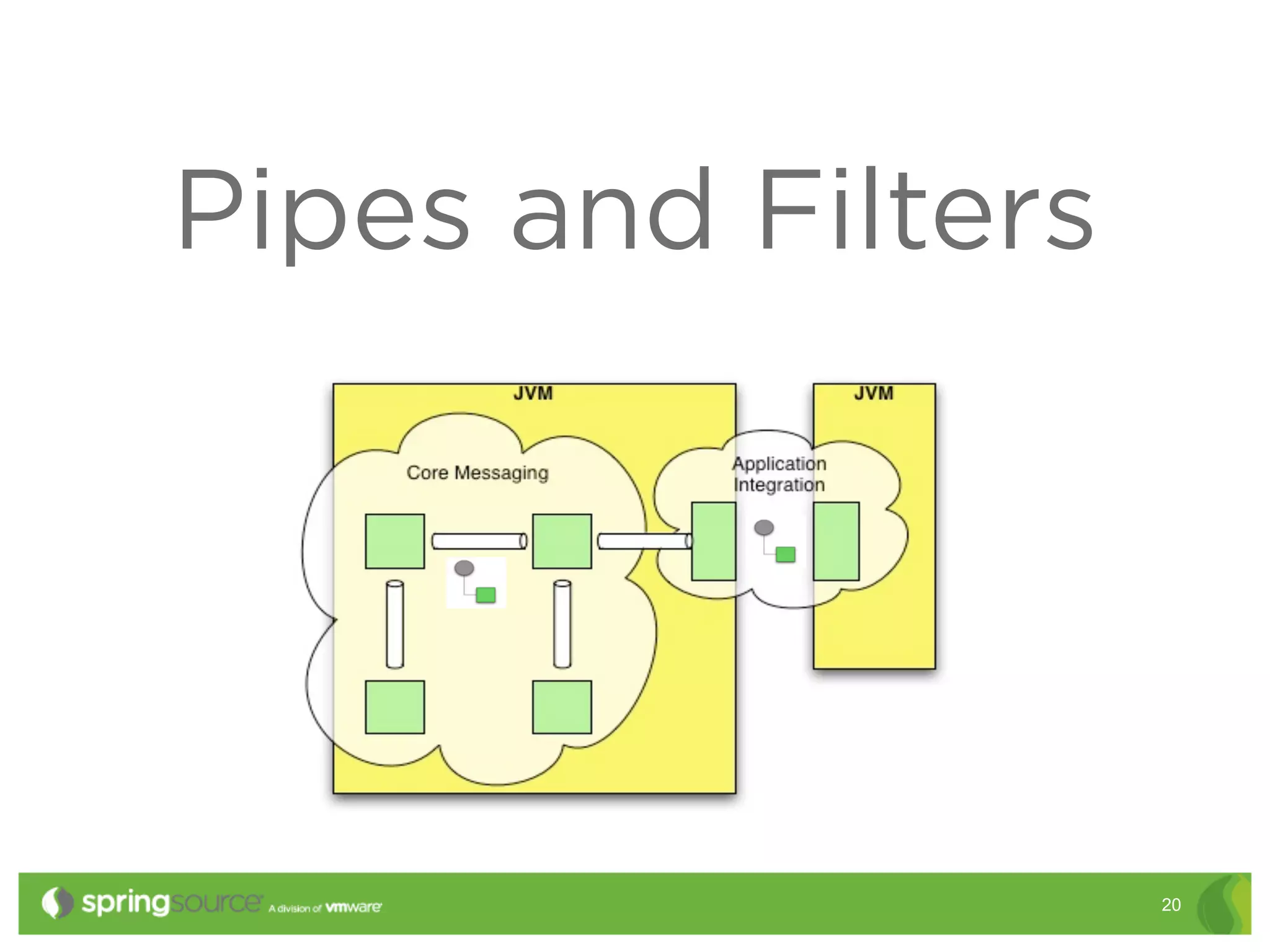
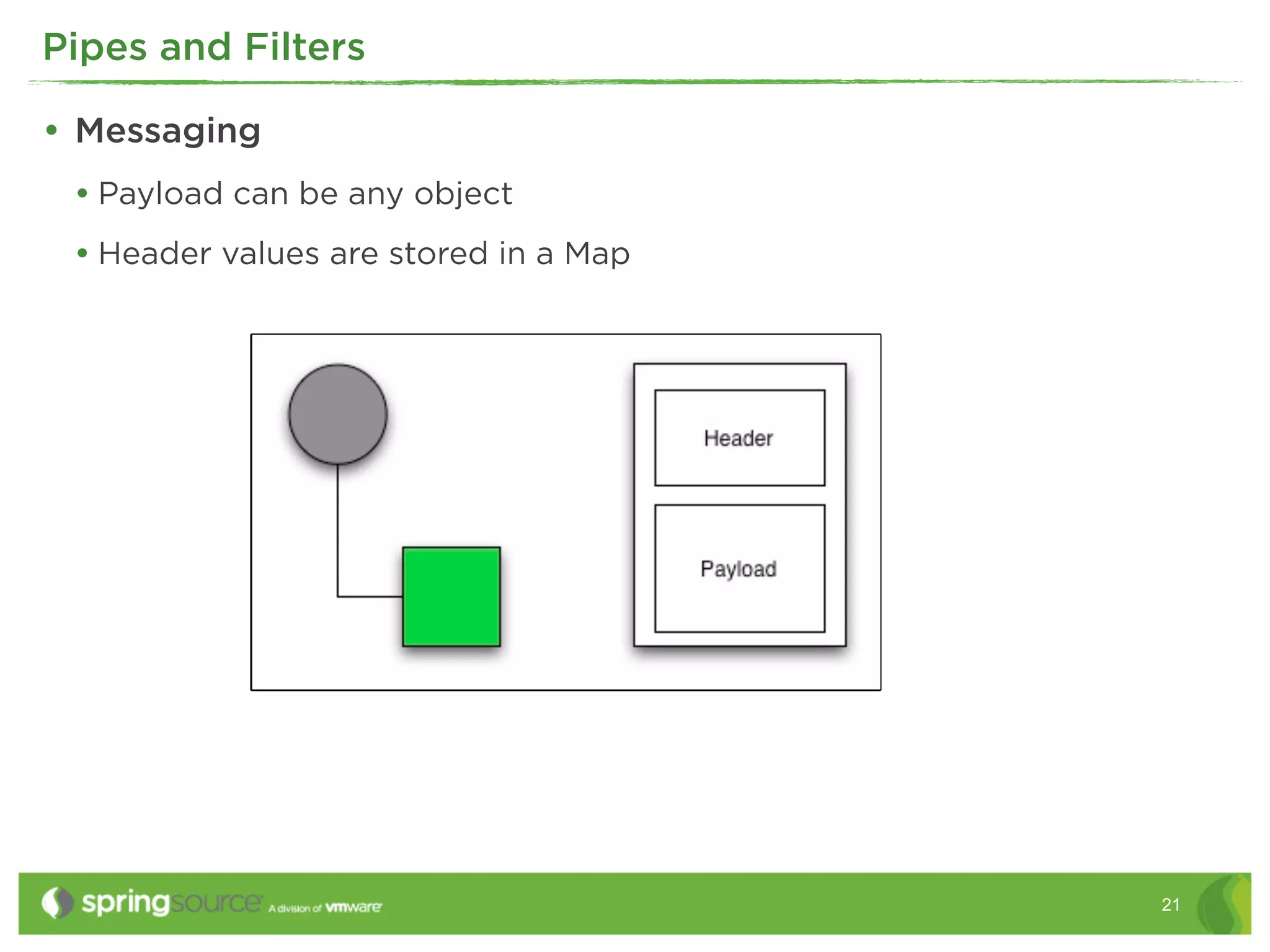
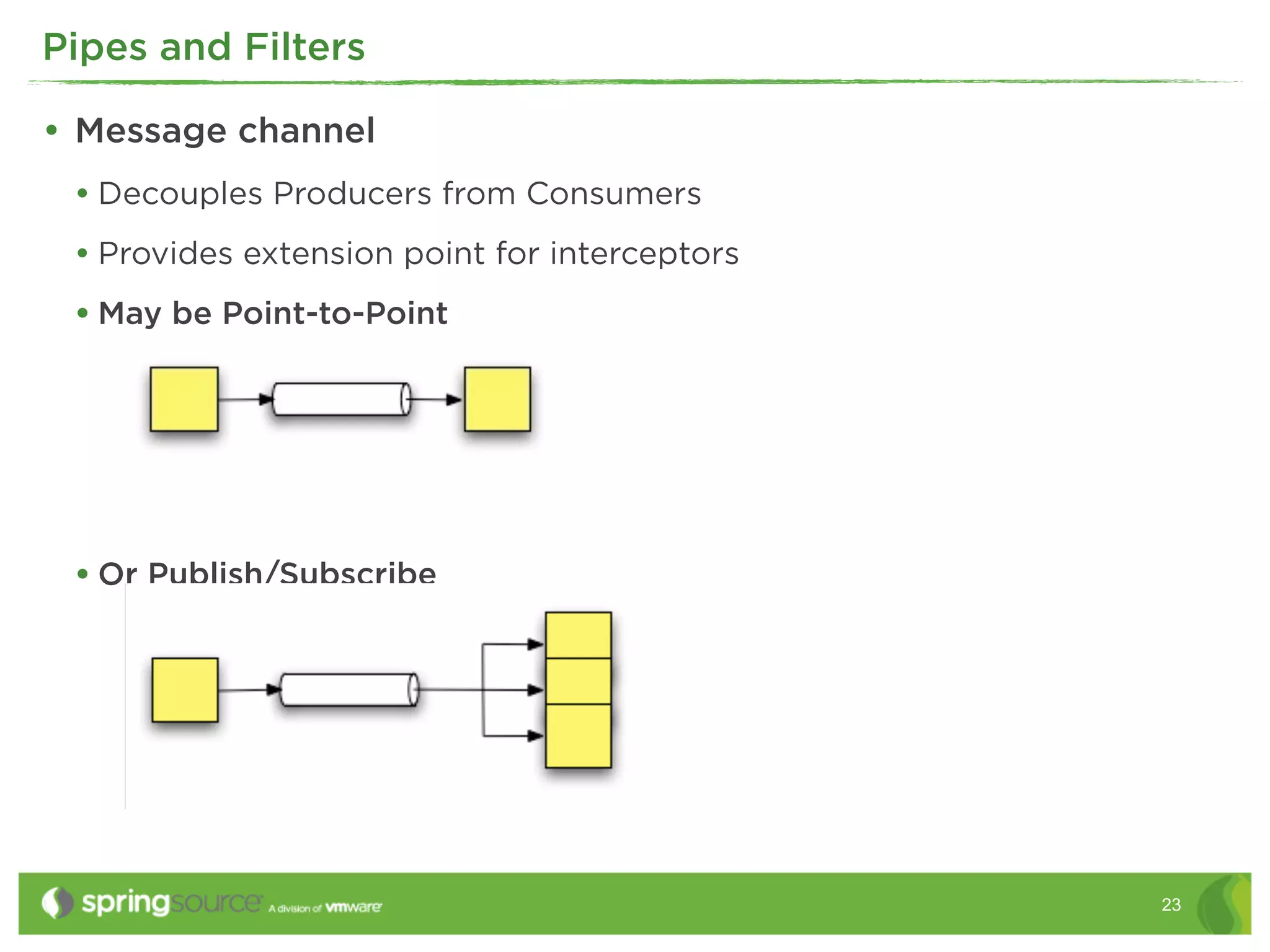
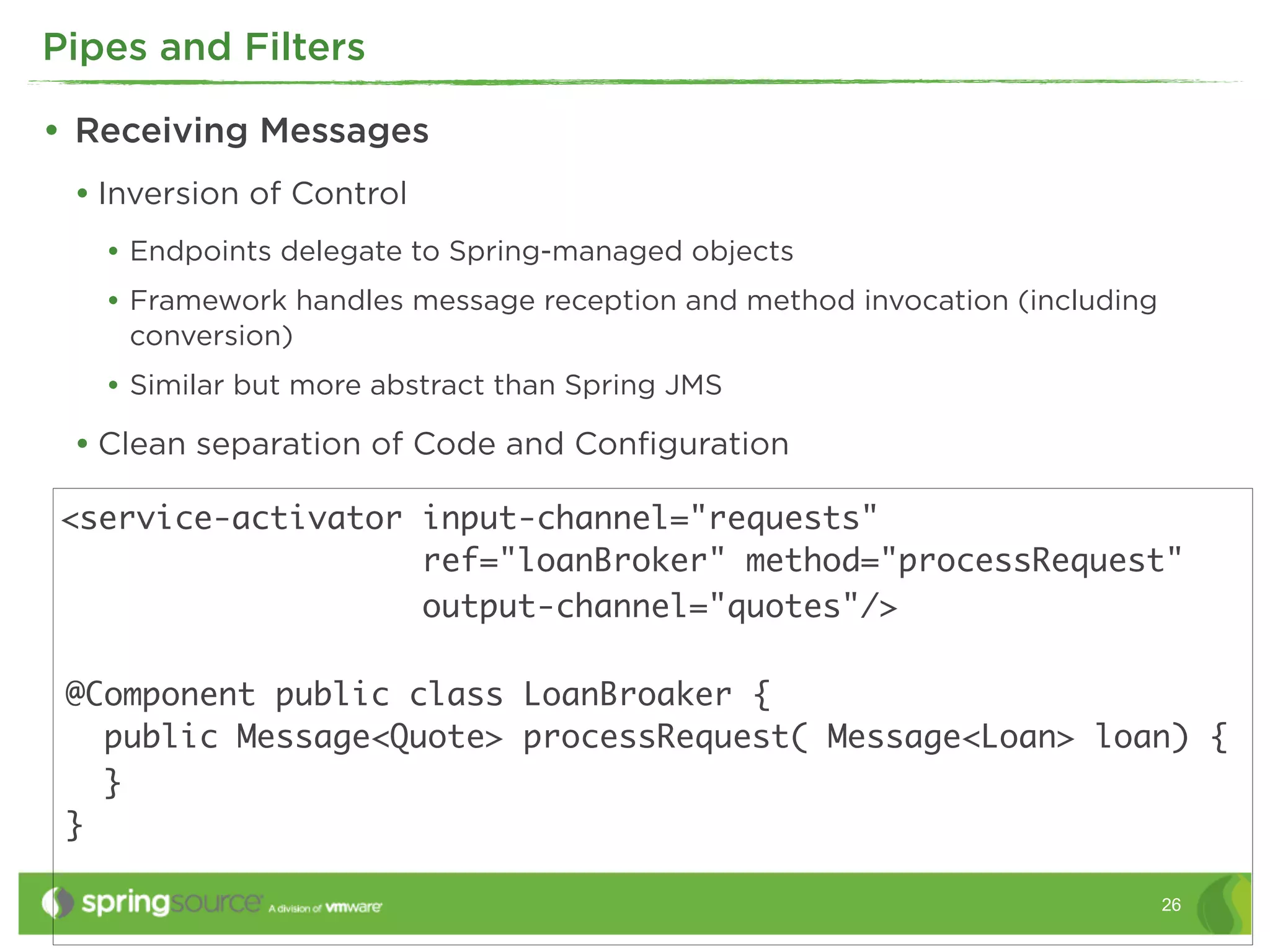
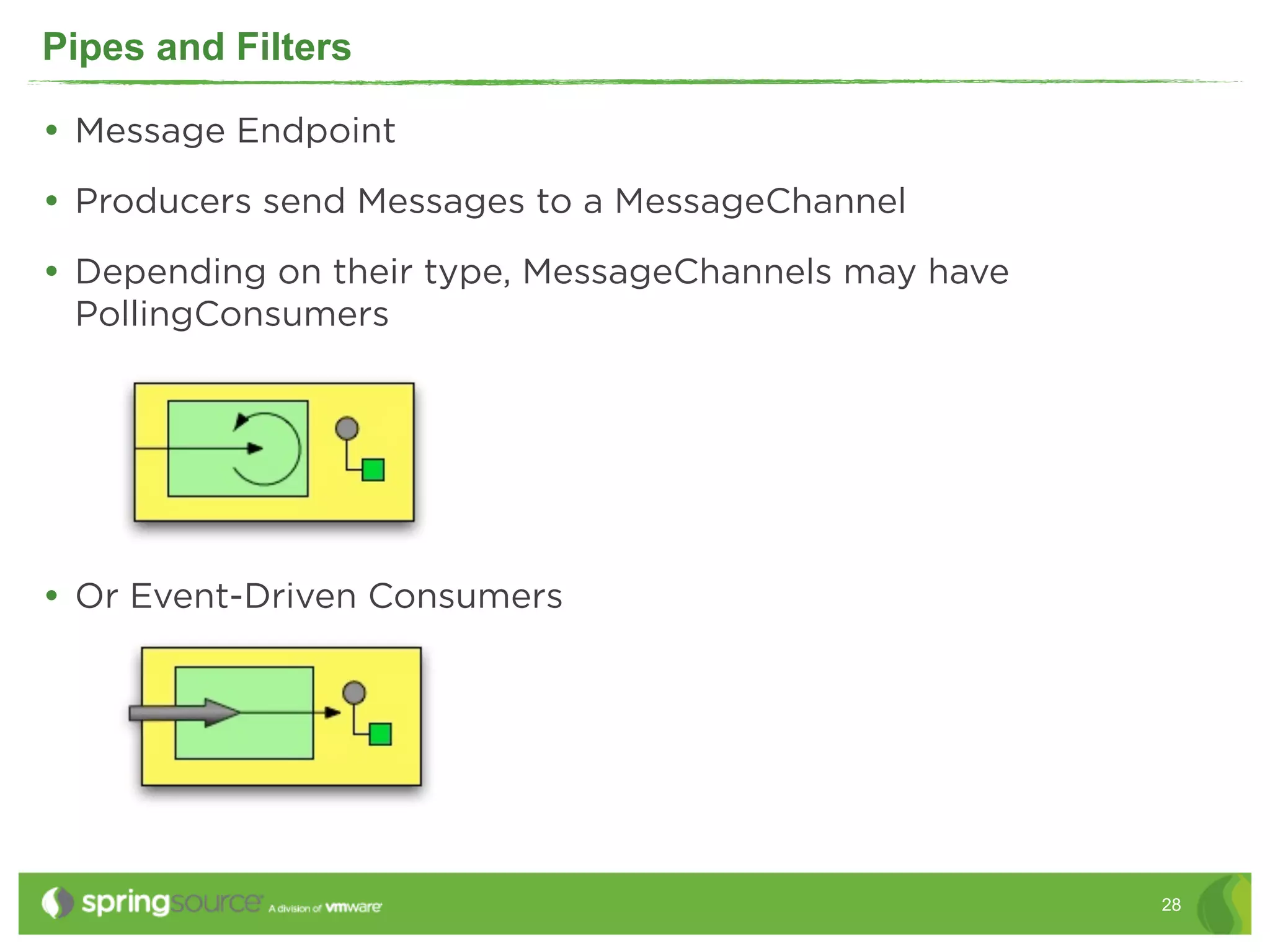
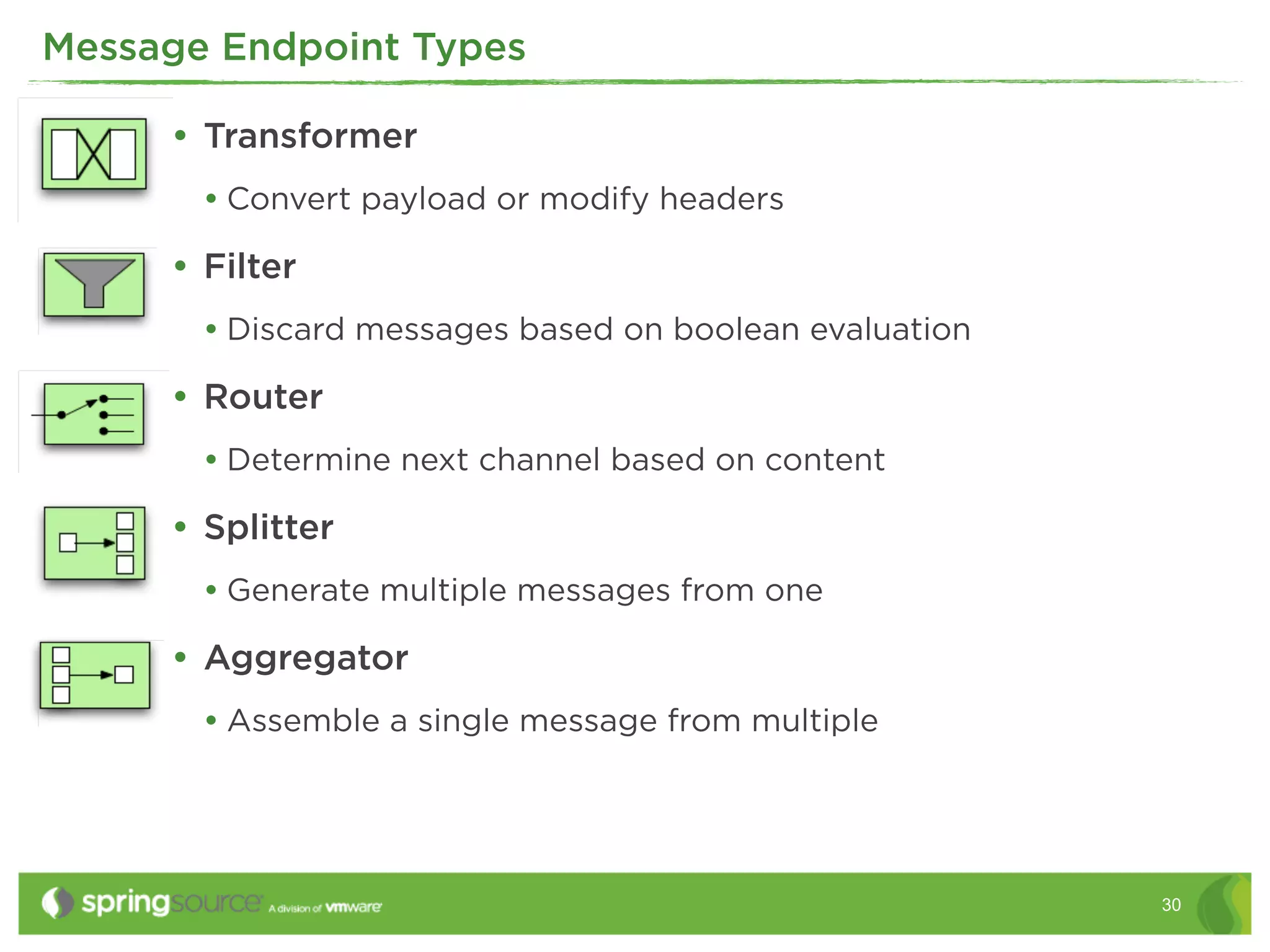
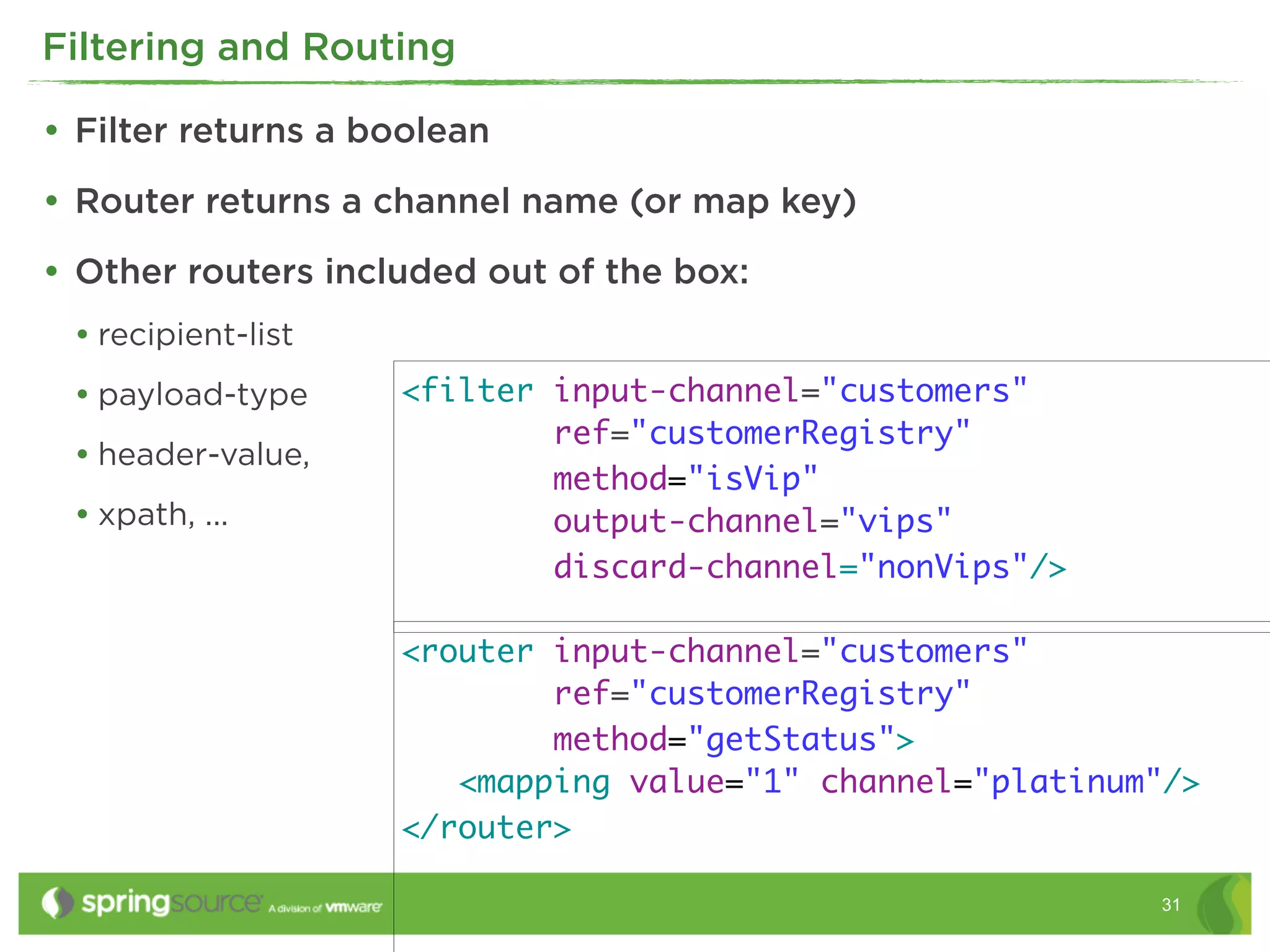
This document discusses EAI (Enterprise Application Integration) patterns using Spring Integration. It provides an overview of messaging, pipes and filters, and common EAI patterns. It then demonstrates how Spring Integration implements these patterns through its API, with an emphasis on messaging channels. Examples are given for sending and receiving JMS, AMQP, HTTP, and email messages. Common patterns like filtering, routing, splitting, and aggregating messages are also explained.


















![Channel Adapters (one-way)
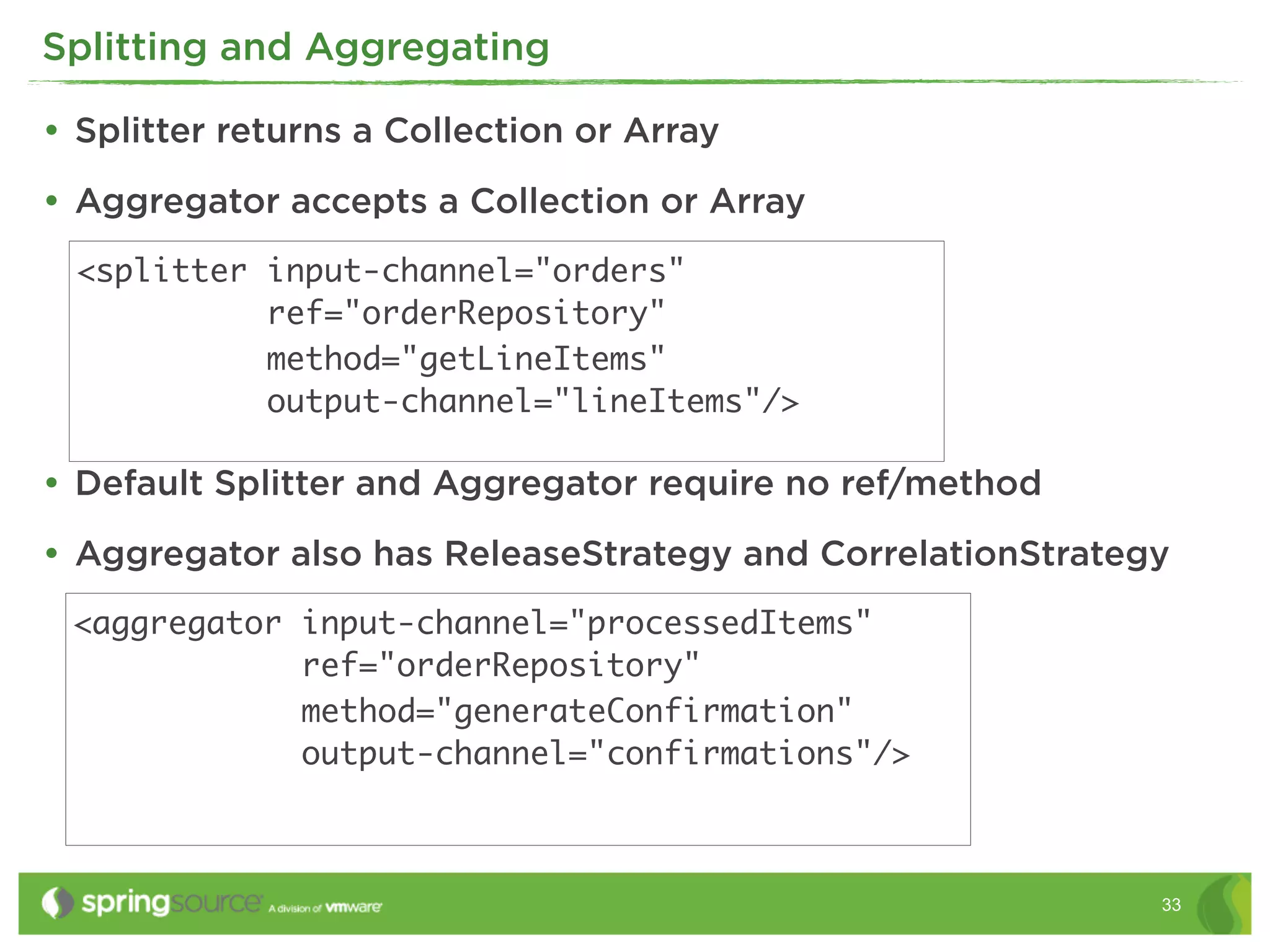
<file:inbound-channel-adapter
channel="fromFile"
directory="${java.io.tmpdir}/input"
filename-pattern="[a-z]+.txt">
<si:poller fixed-delay="5000" />
</file:inbound-channel-adapter>
<jms:outbound-channel-adapter channel="toJms"
destination="exampleQueue"/>
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springintegration-110822145507-phpapp02/75/Spring-integration-39-2048.jpg)


![Spring 3.0
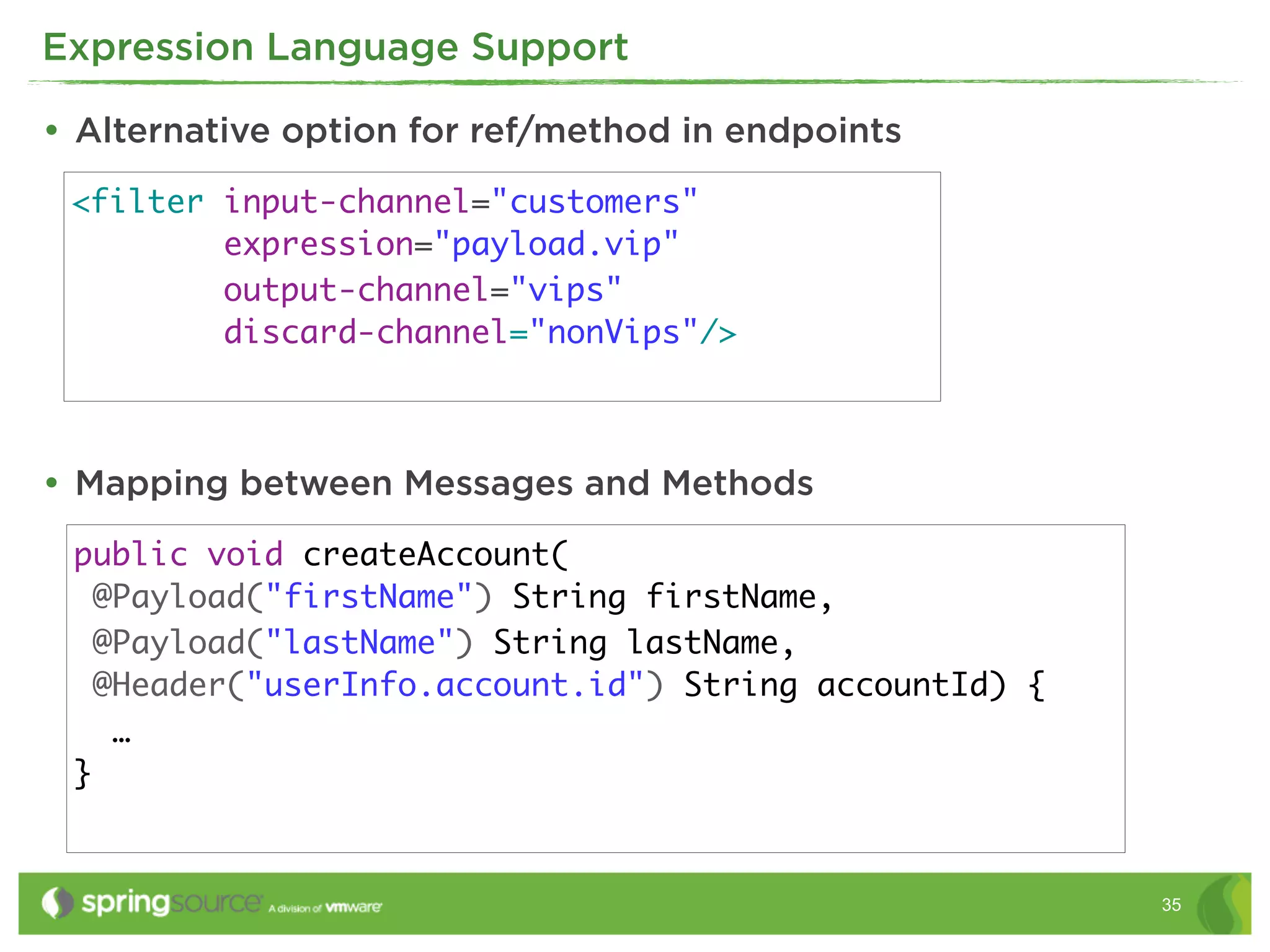
• Spring Expression Language
• through XML or Java
<int:transformer input-channel="inChannel"
output-channel="outChannel"
expression="payload.toUpperCase() + '- [' +
T(java.lang.System).currentTimeMillis() + ']'" />
<filter input-channel="input" expression="payload.matches(
#{filterPatterns.nonsensePattern}
)" />
45](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springintegration-110822145507-phpapp02/75/Spring-integration-45-2048.jpg)