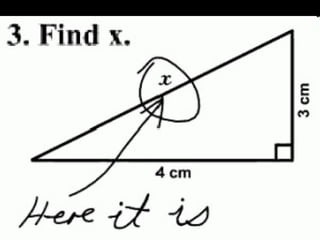
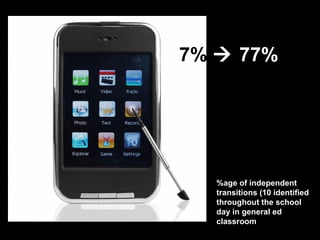
This document discusses assistive technology and high incidence disabilities. It notes that around 5-8% of students have math disabilities, and that the technology to support math learning is less developed than for reading and writing. Some common difficulties students face include problems with math calculations, identifying signs and meanings, fact recall, and word problems. Low-tech options to support math learning are discussed such as number lines, calculators, and graph paper. Various assistive technology tools are also presented including digitized textbooks, math casts, screencasts, and software like IntelliTools Classroom Suite 4. The importance of metacognition, executive function, strategies, memory, organization and notetaking are discussed. Overall the document provides an overview