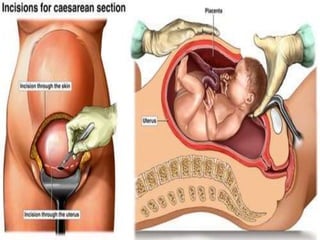
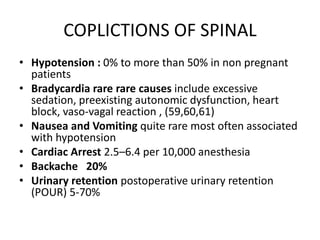
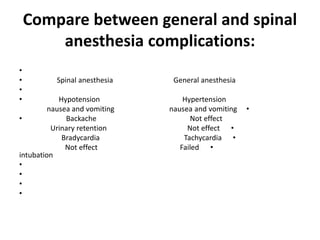
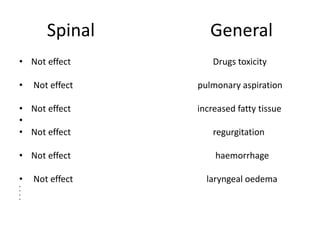
Spinal anesthesia is generally preferred over general anesthesia for cesarean sections. While general anesthesia is faster to induce and can be used in emergency situations, spinal anesthesia allows the mother to remain awake and avoids risks of maternal aspiration and neonatal depression. Complications of spinal anesthesia include hypotension, nausea, vomiting and backache, while general anesthesia risks include failed intubation, aspiration, hypertension and drugs toxicity. The conclusion is that spinal anesthesia is simpler, safer and preferred for cesarean sections due to reduced risks for both mother and fetus, though general anesthesia may be necessary in some urgent cases. Future research on modern spinal techniques with fewer complications is recommended.