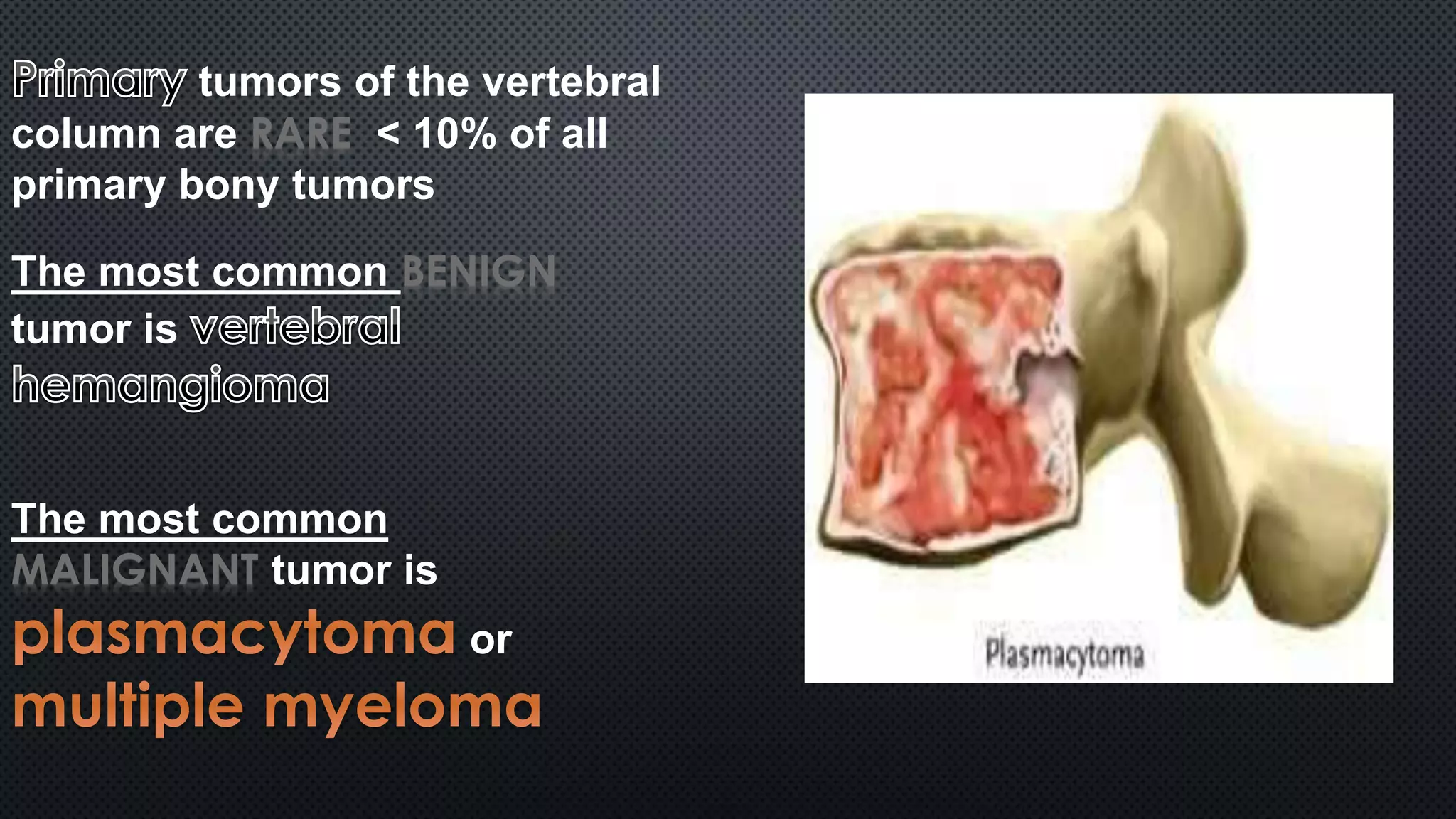
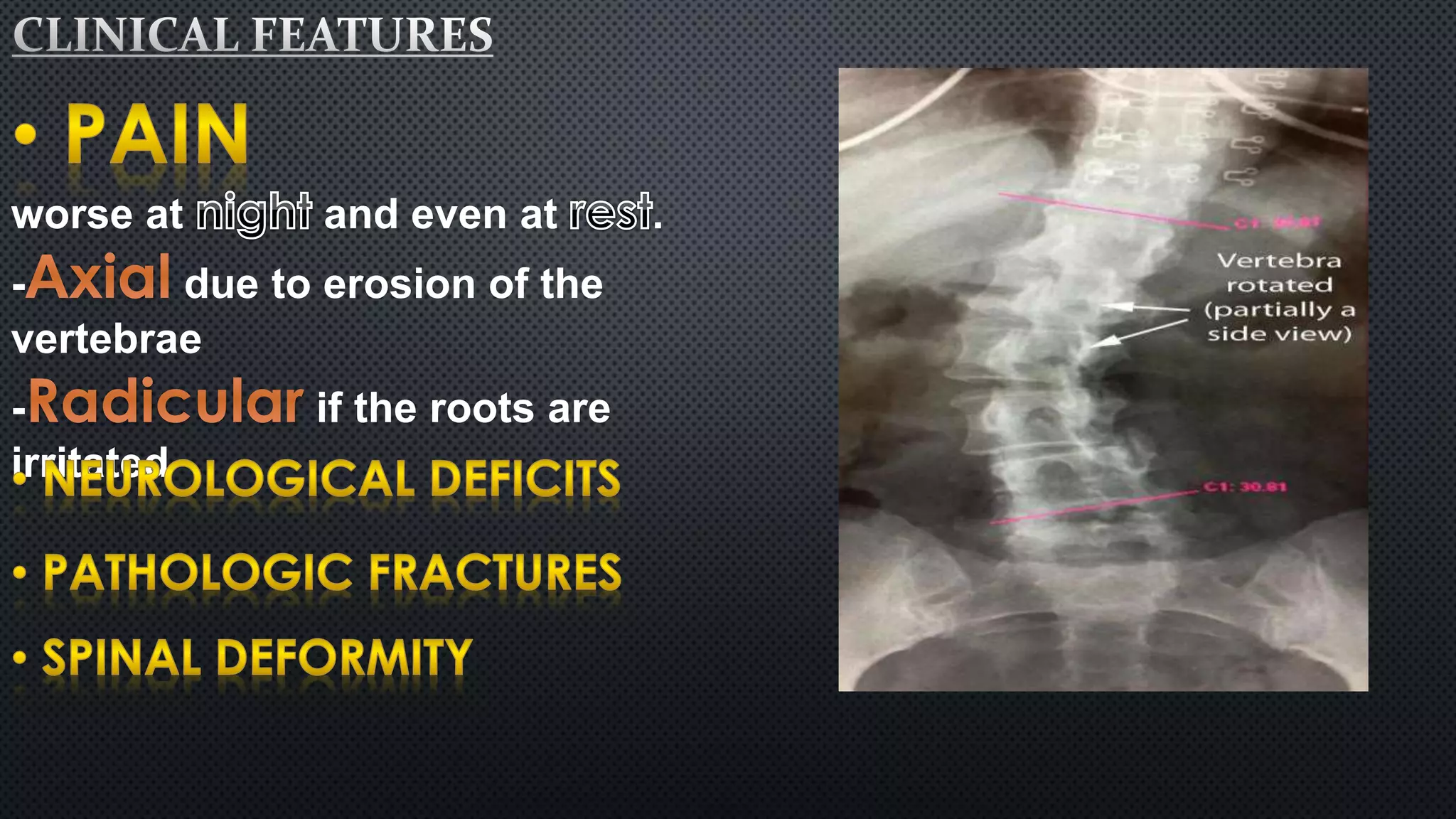
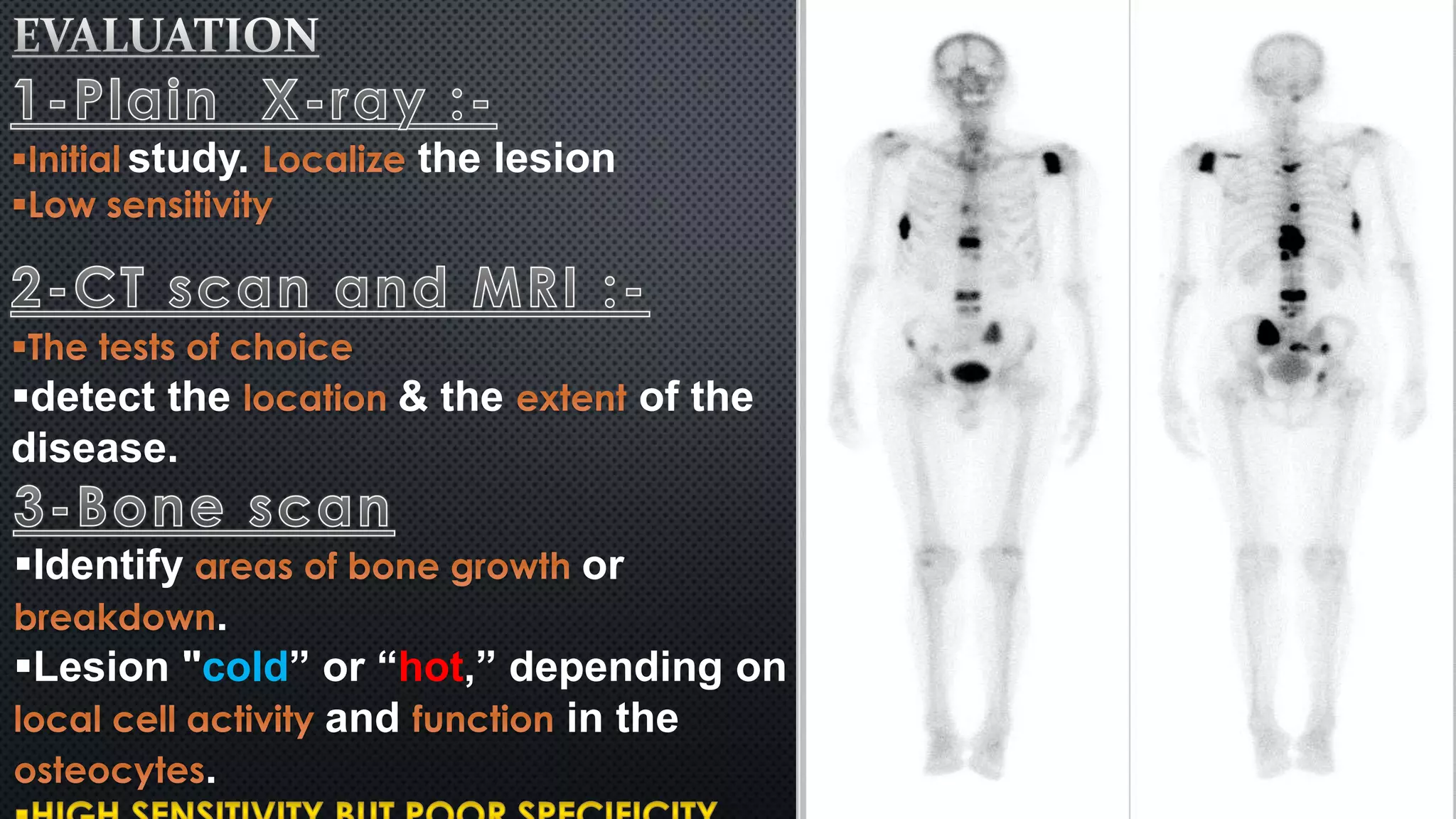
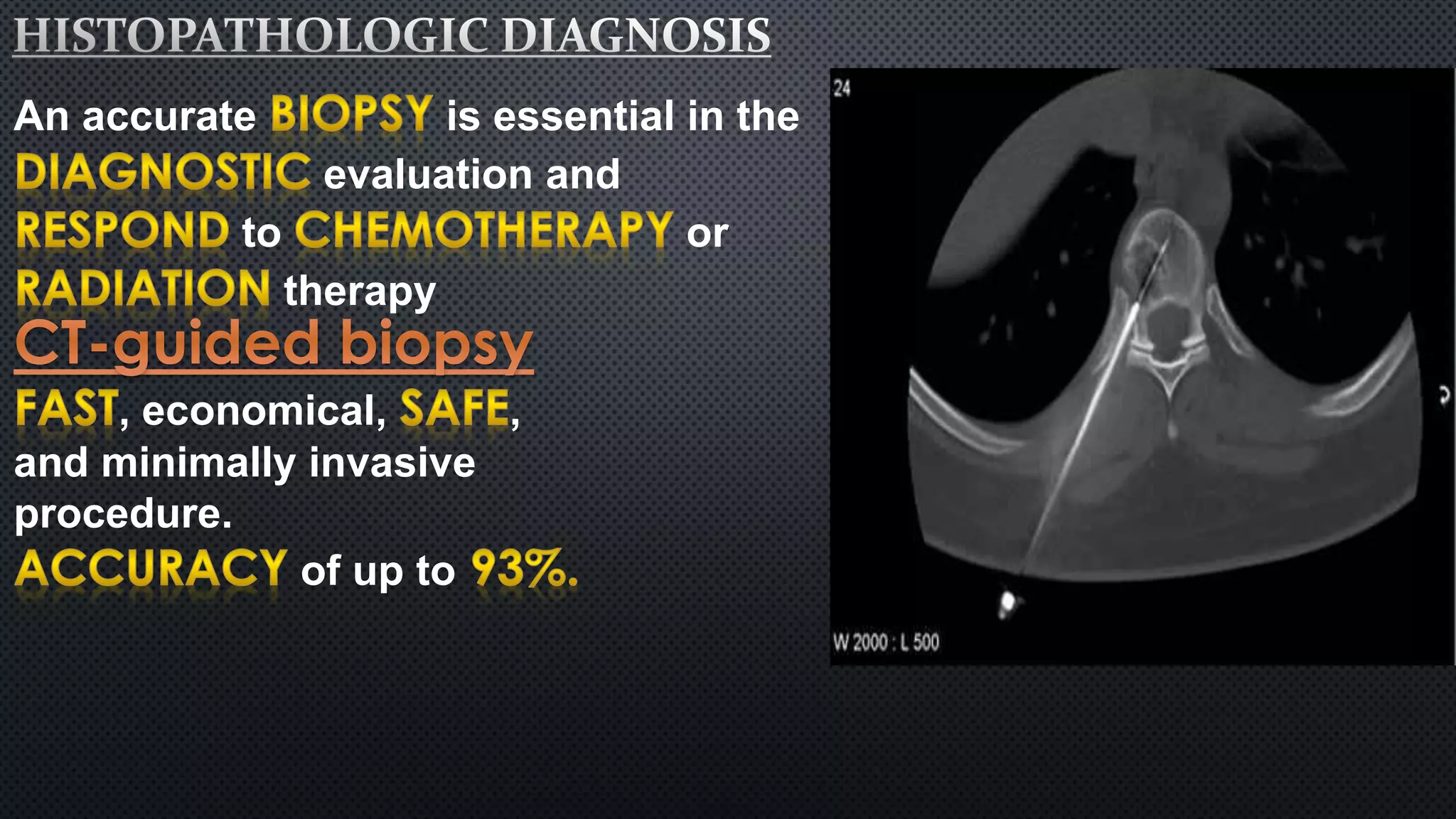
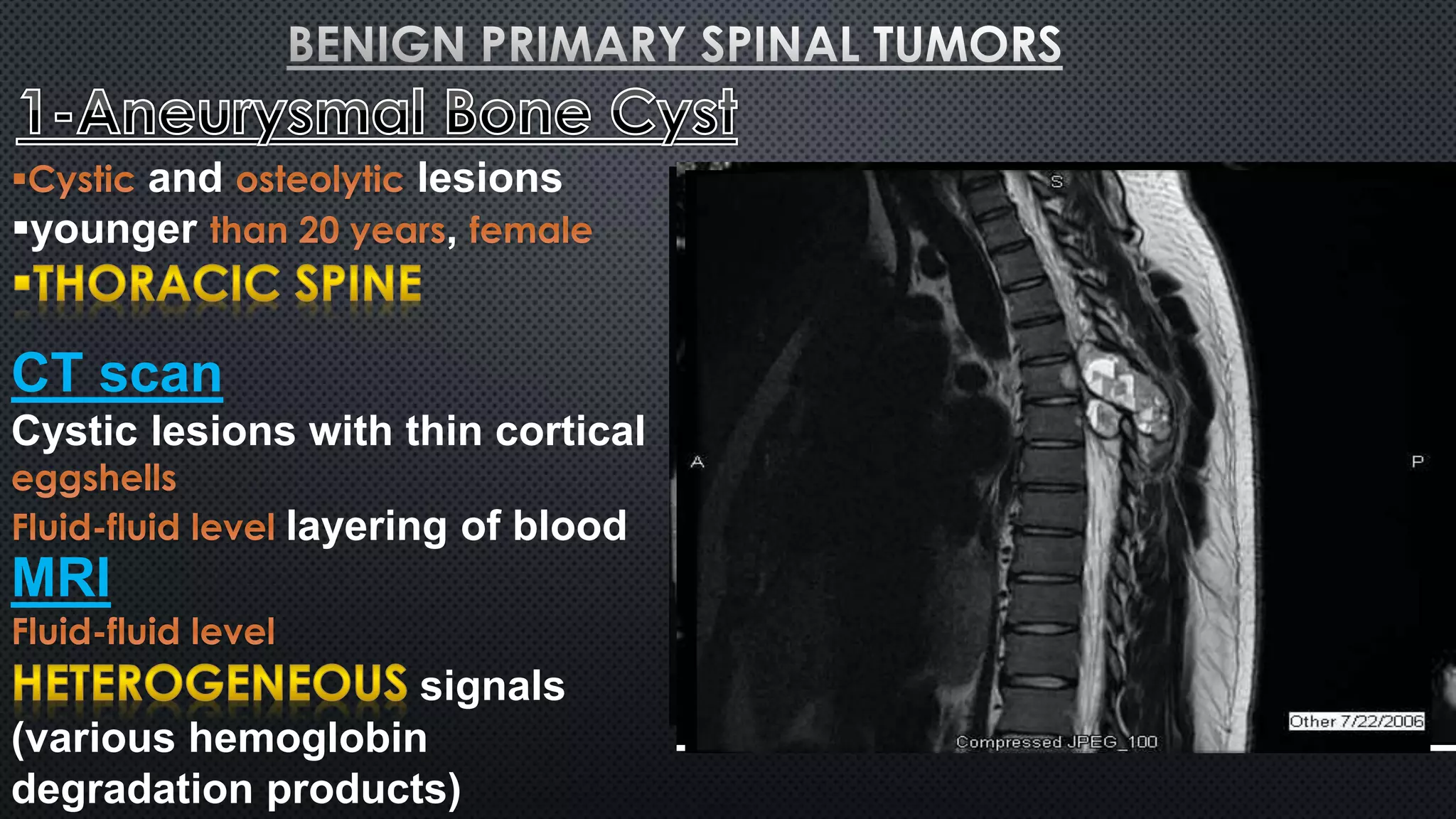
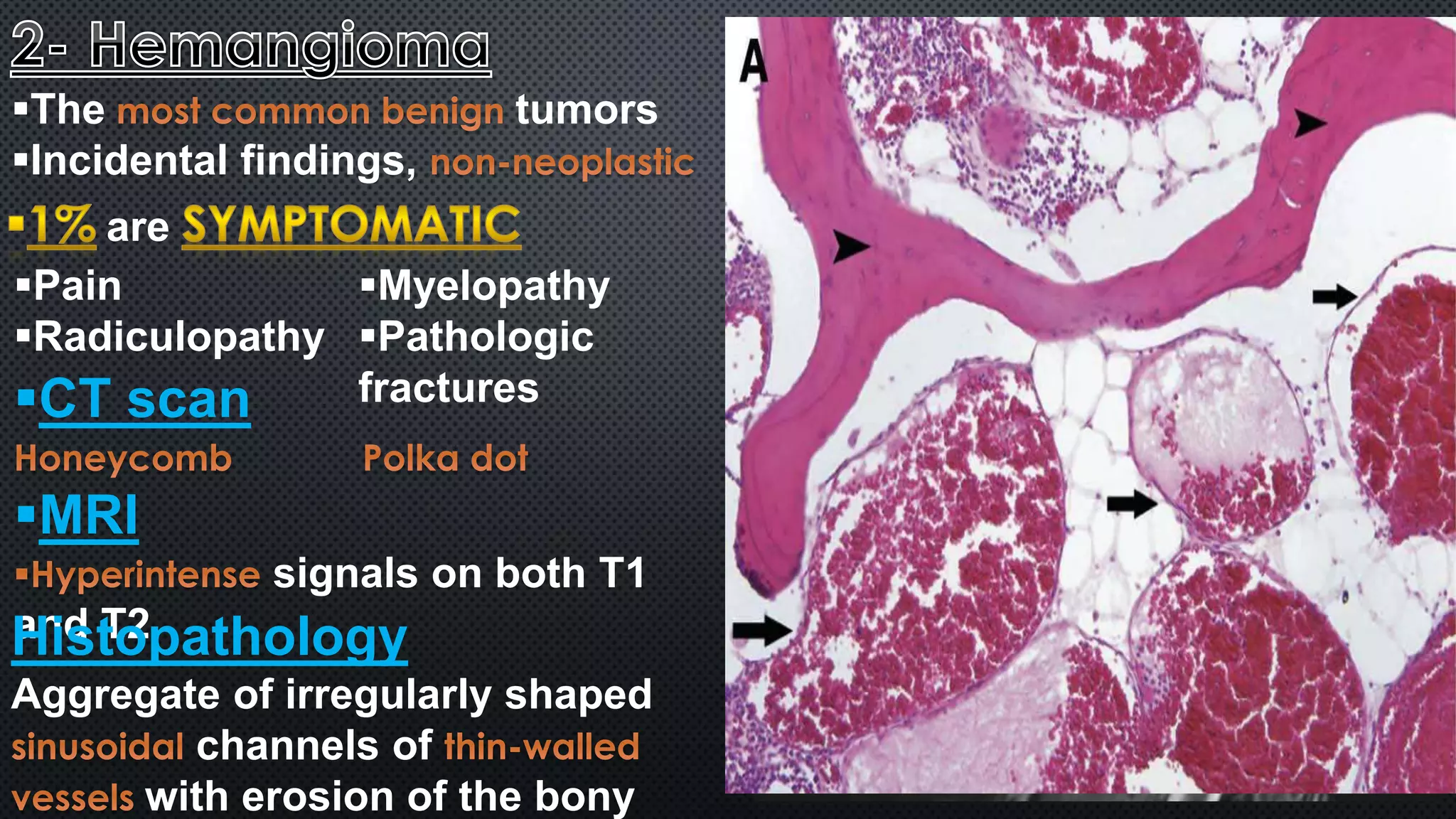
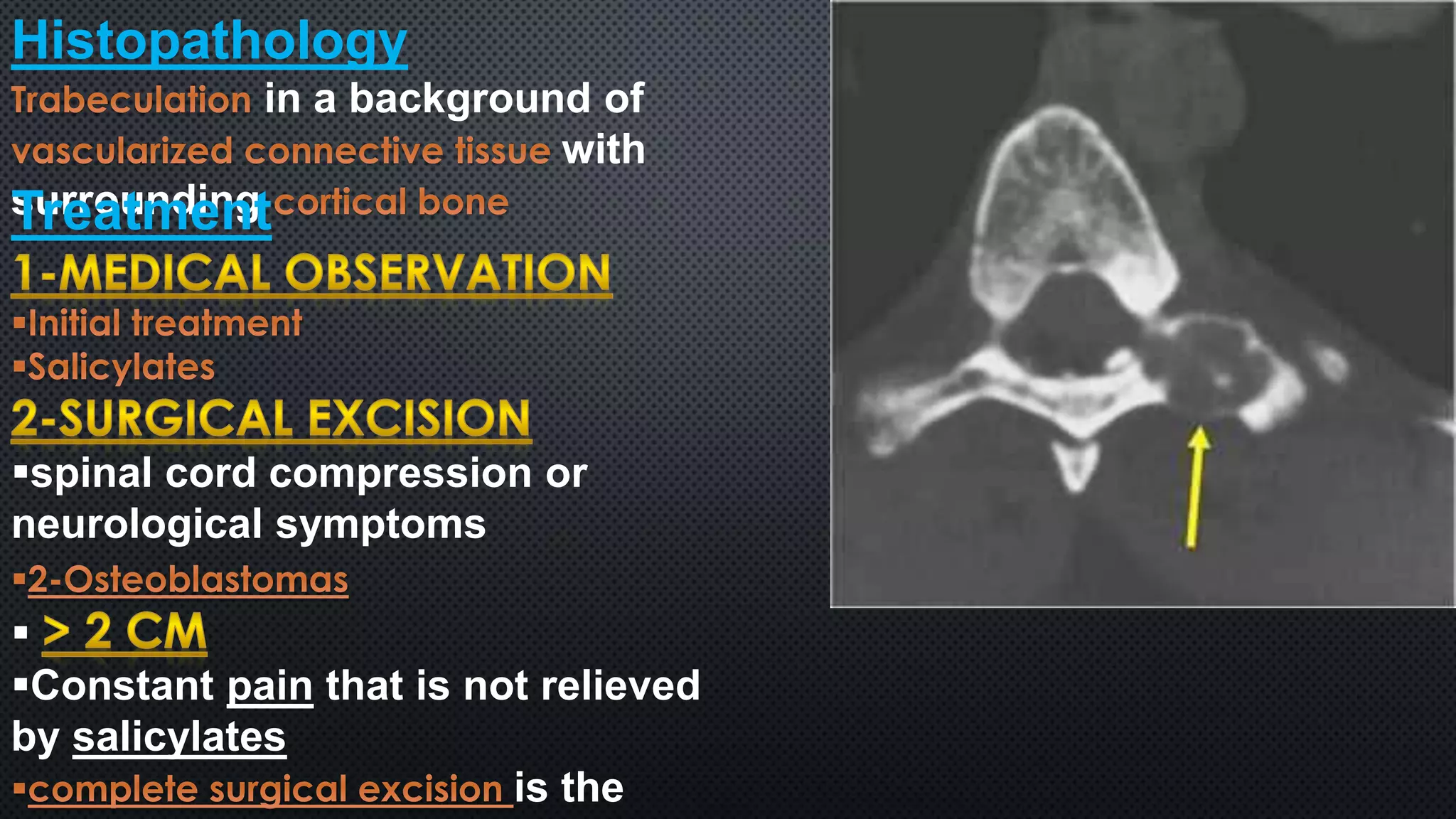
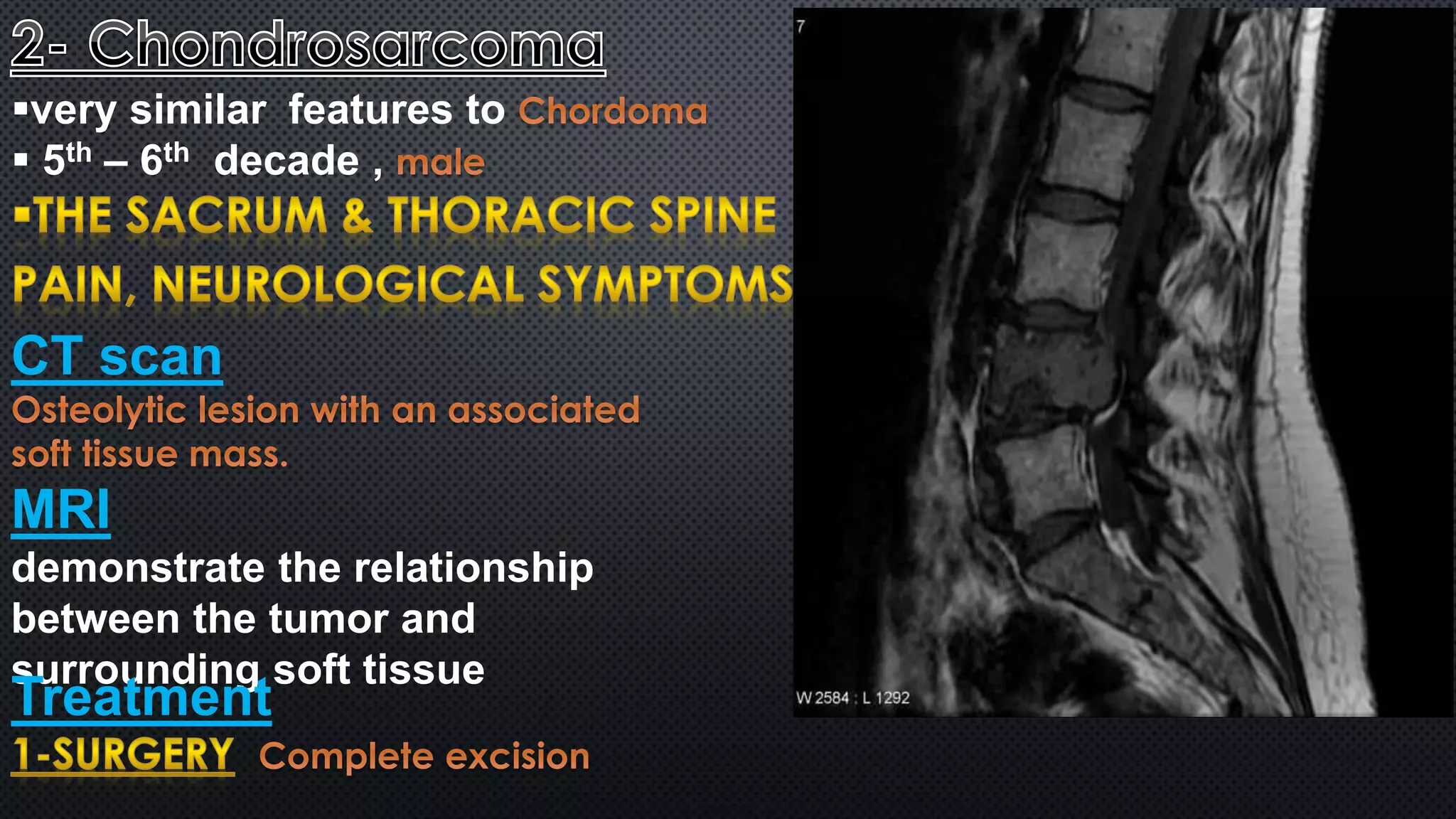
Tumors of the vertebral column are rare, comprising less than 10% of all primary bony tumors. The most common benign tumor is osteoid osteoma, while multiple myeloma is the most common malignant tumor. Imaging modalities such as CT and MRI scans are used to evaluate the lesions and determine the extent of involvement. An accurate diagnosis is essential to determine the appropriate treatment, which may include surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.