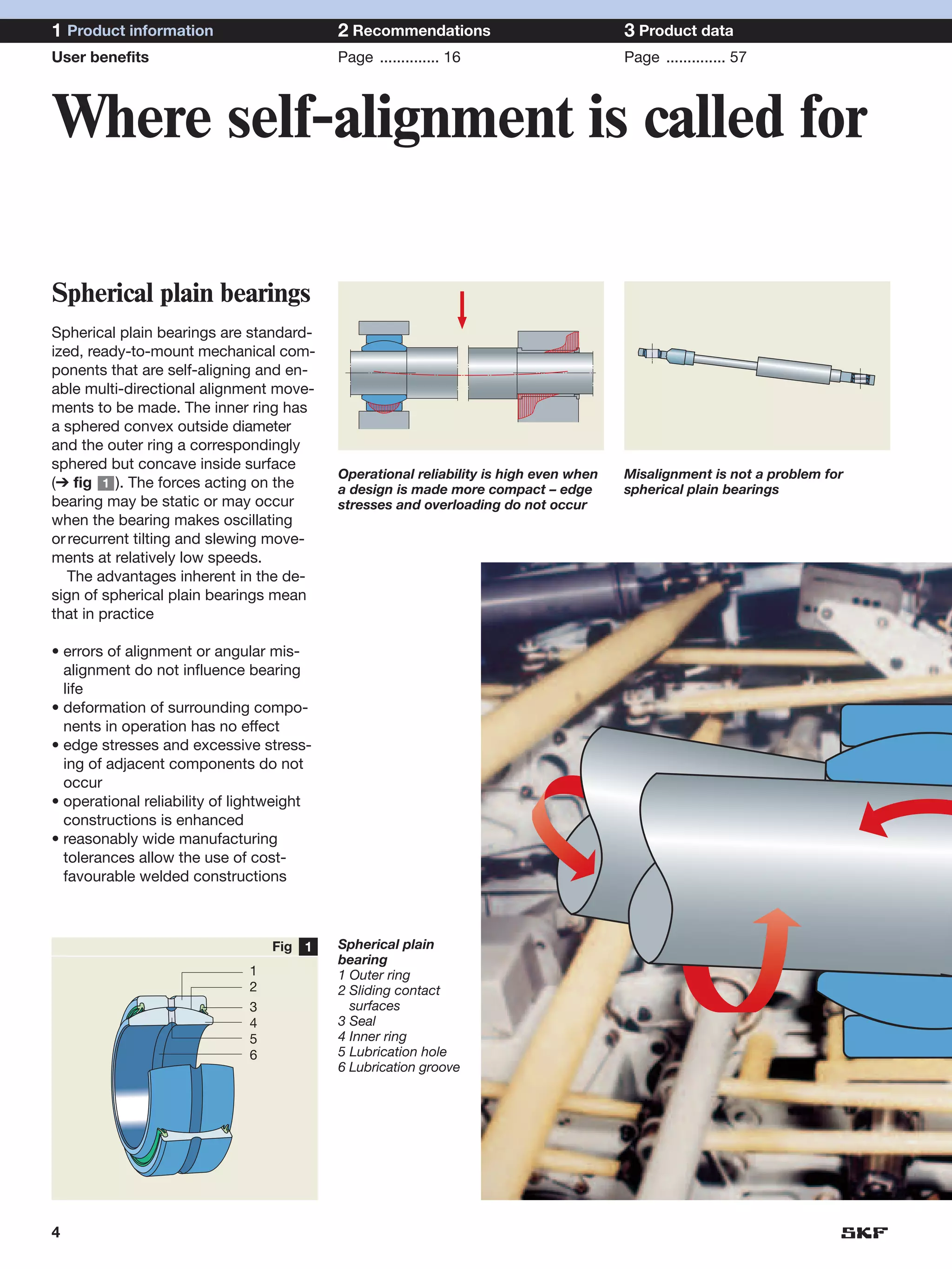
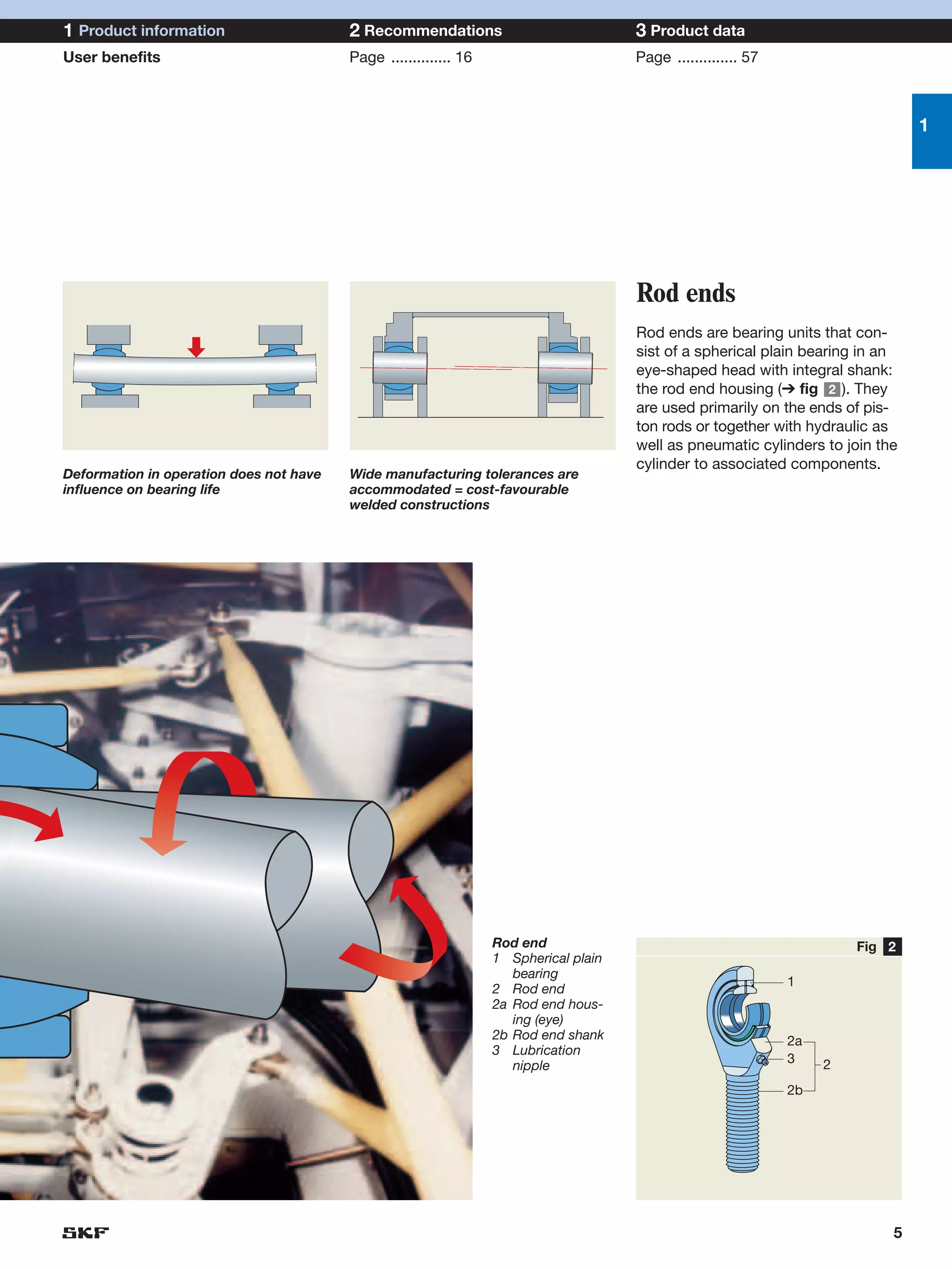
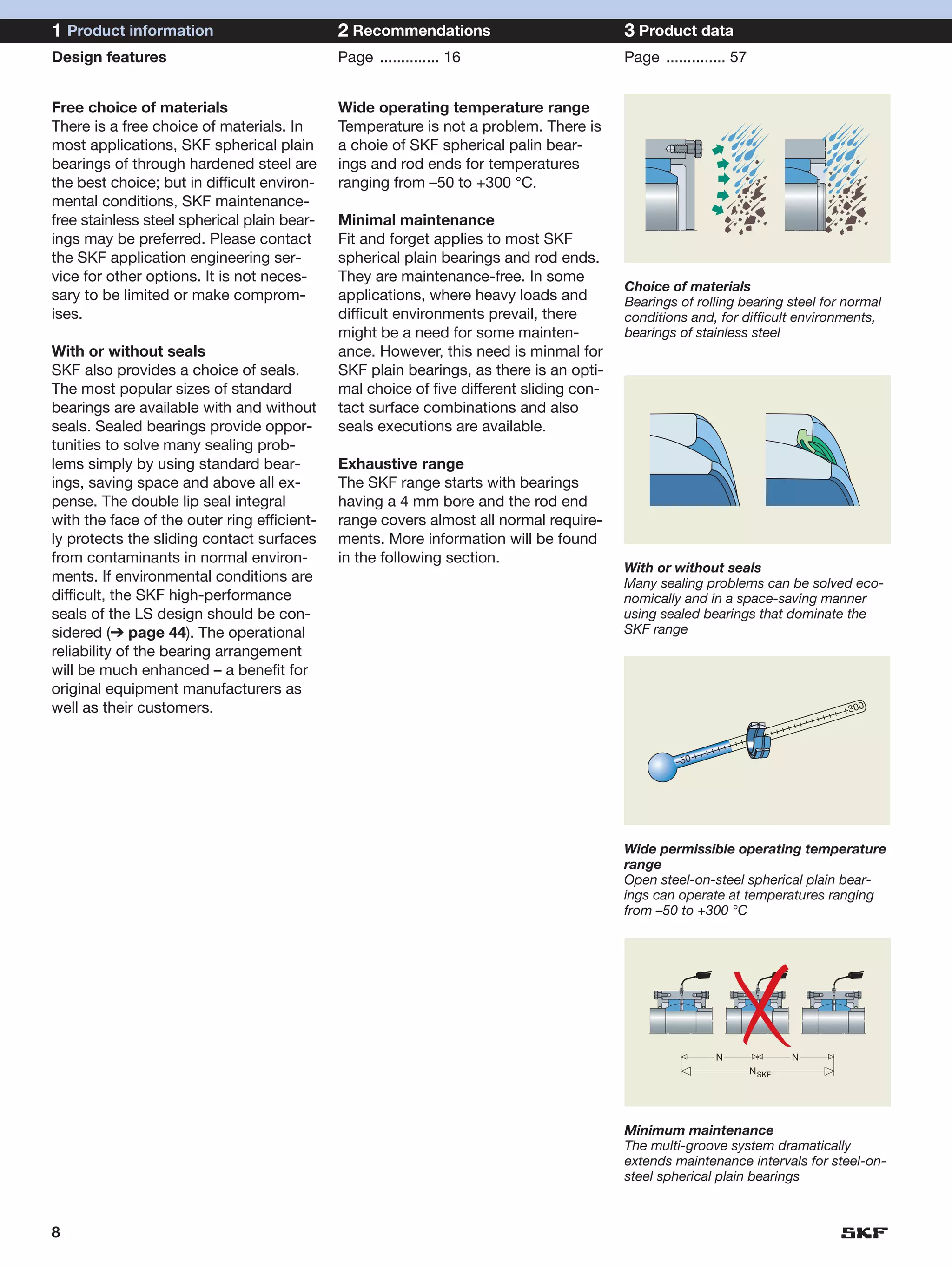
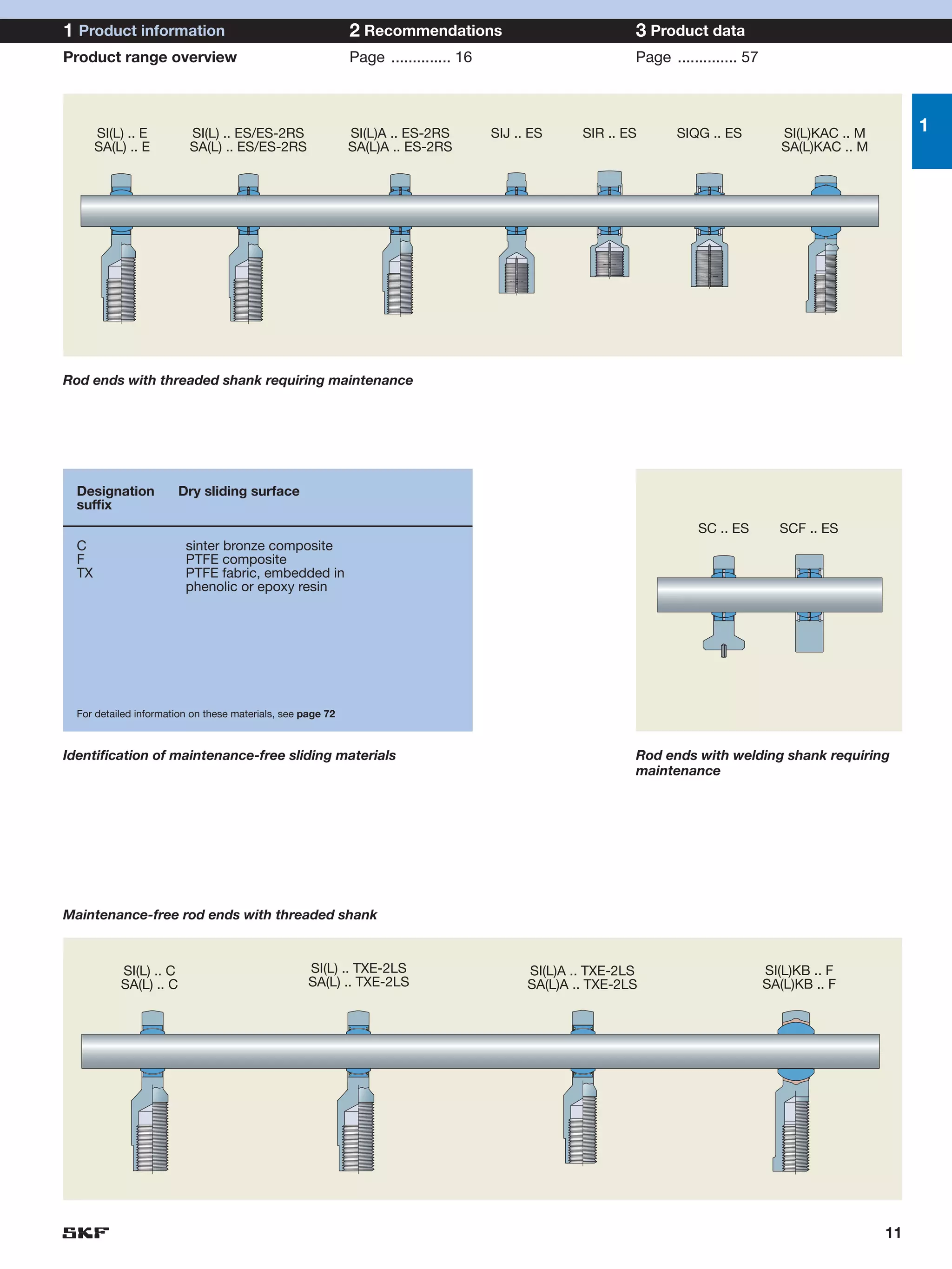
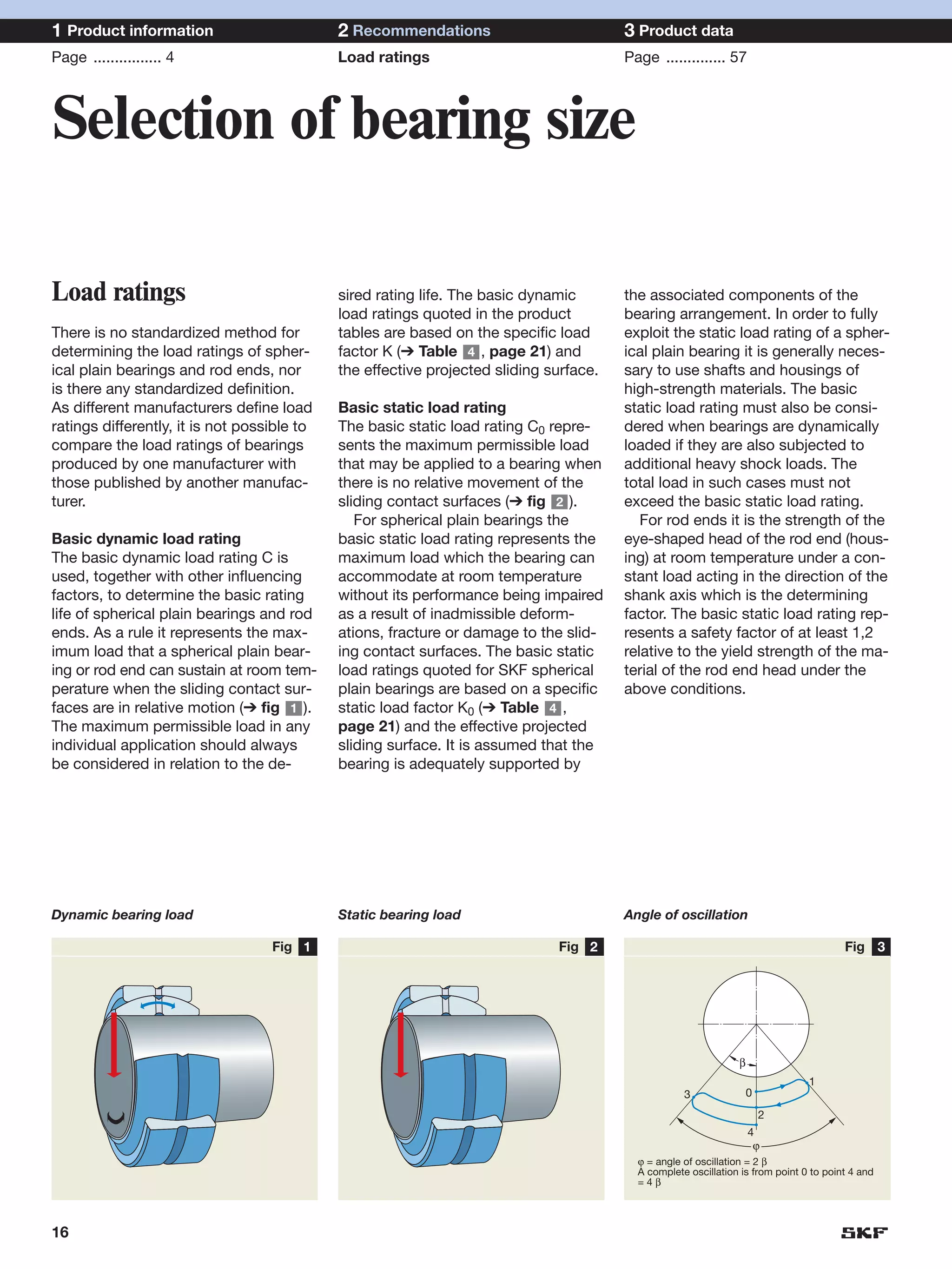
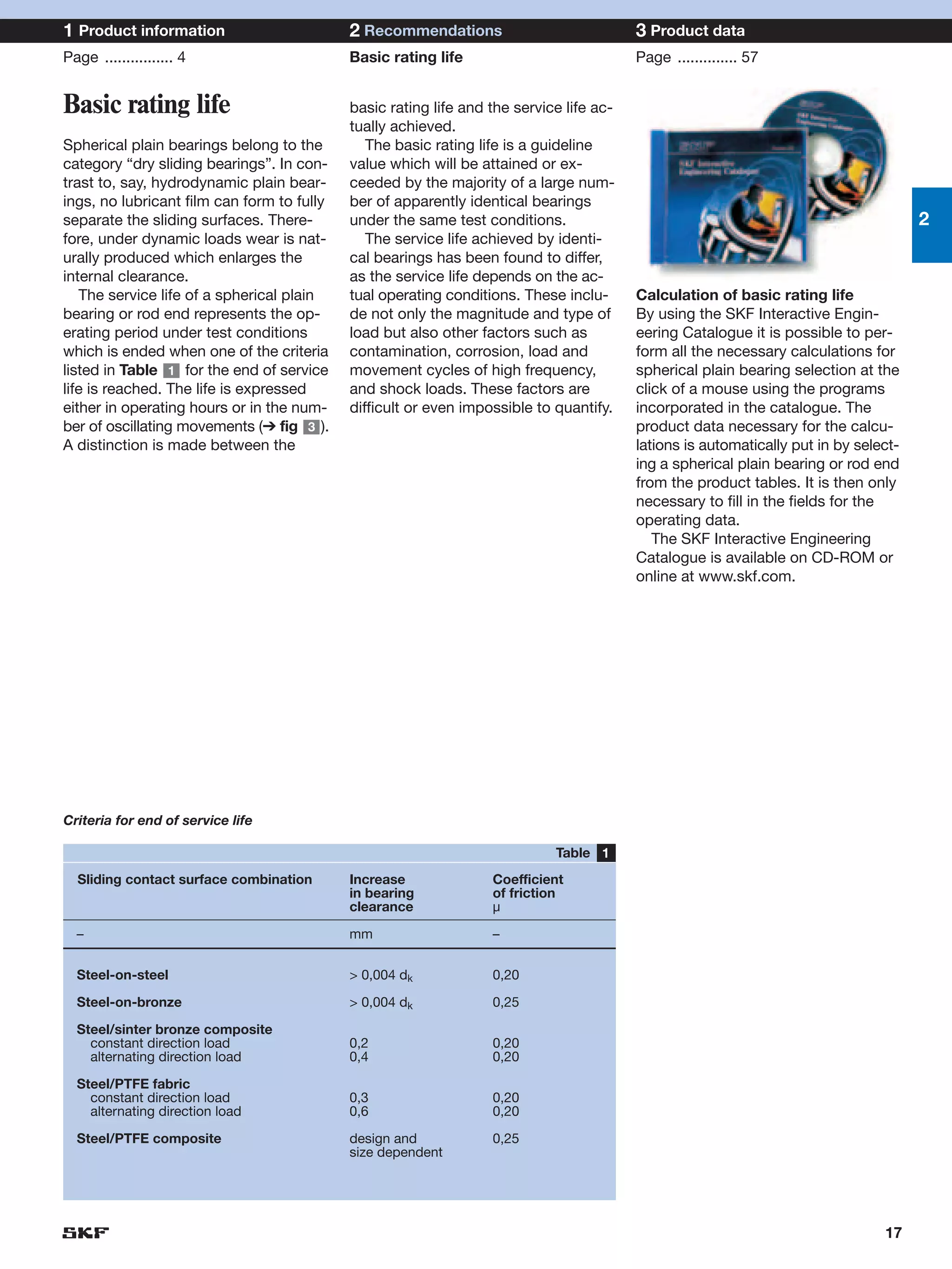
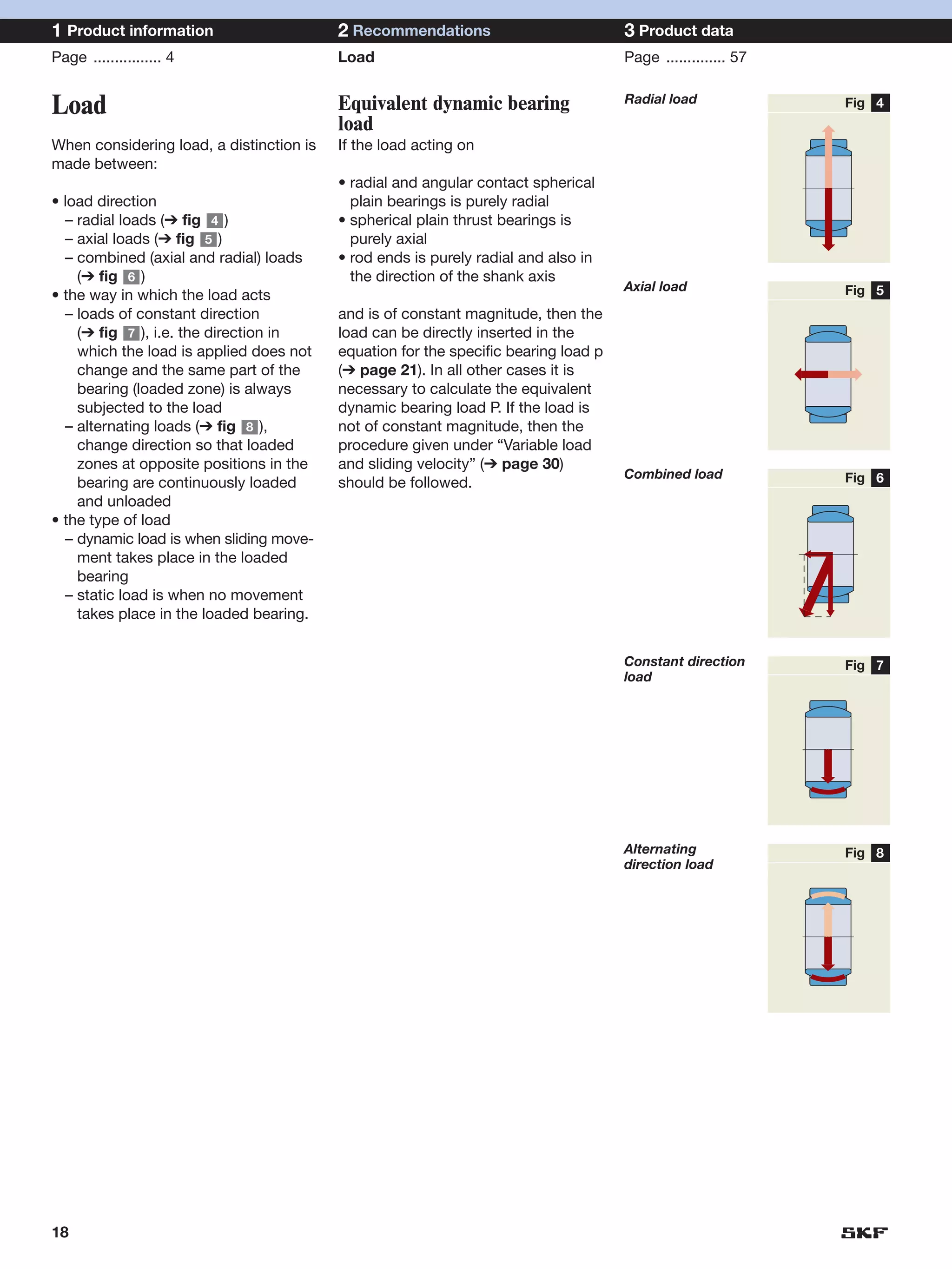
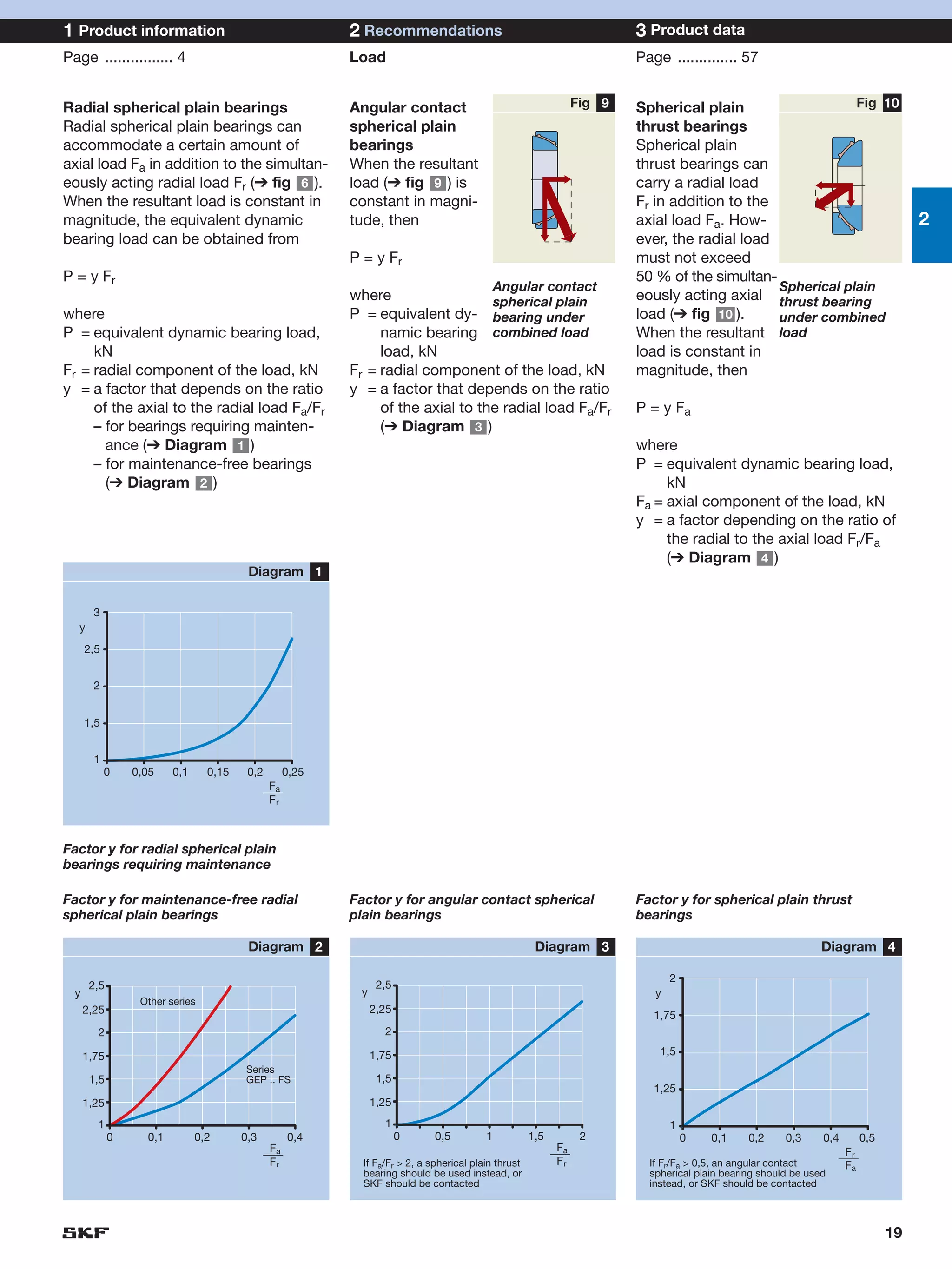
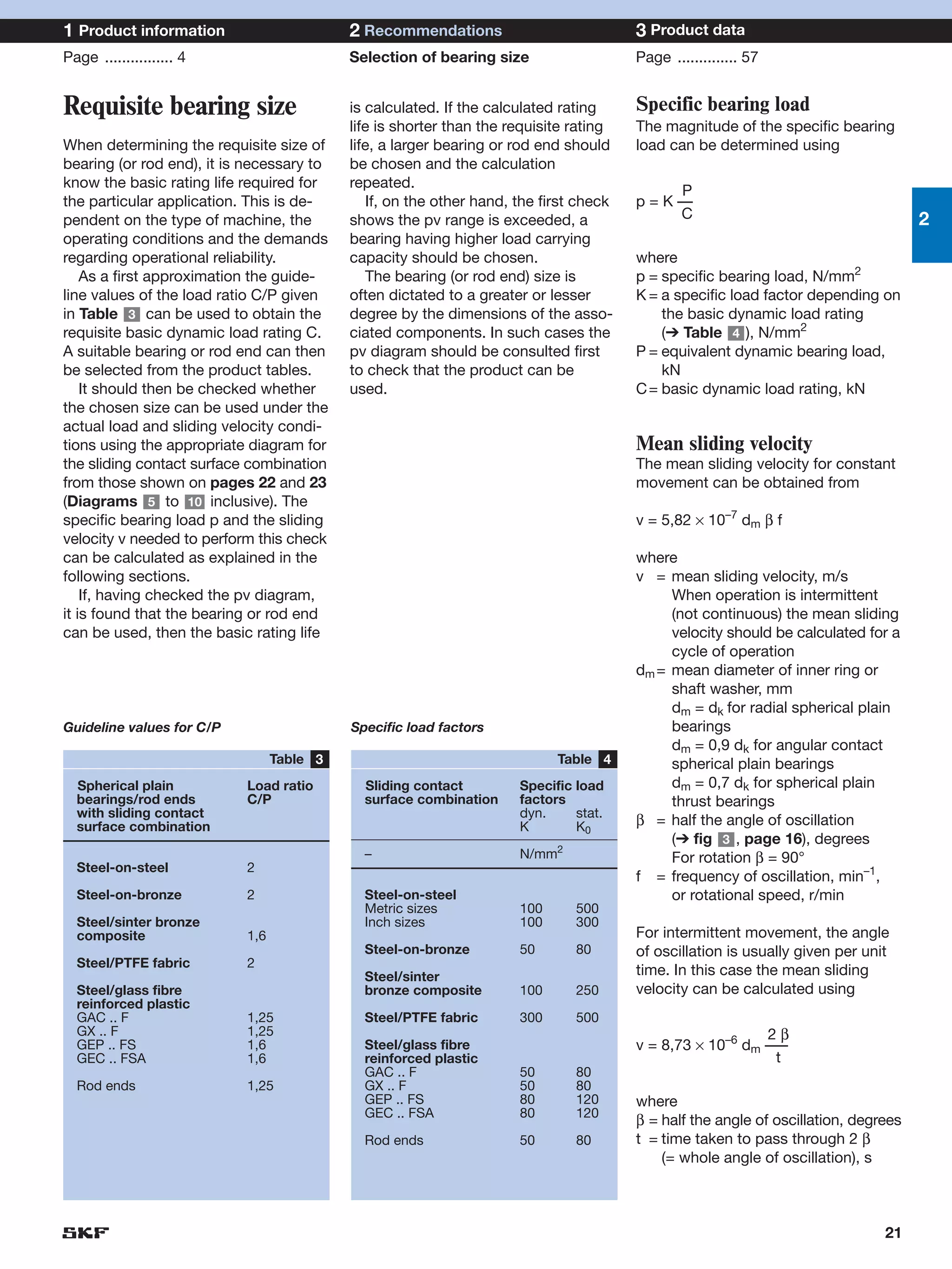
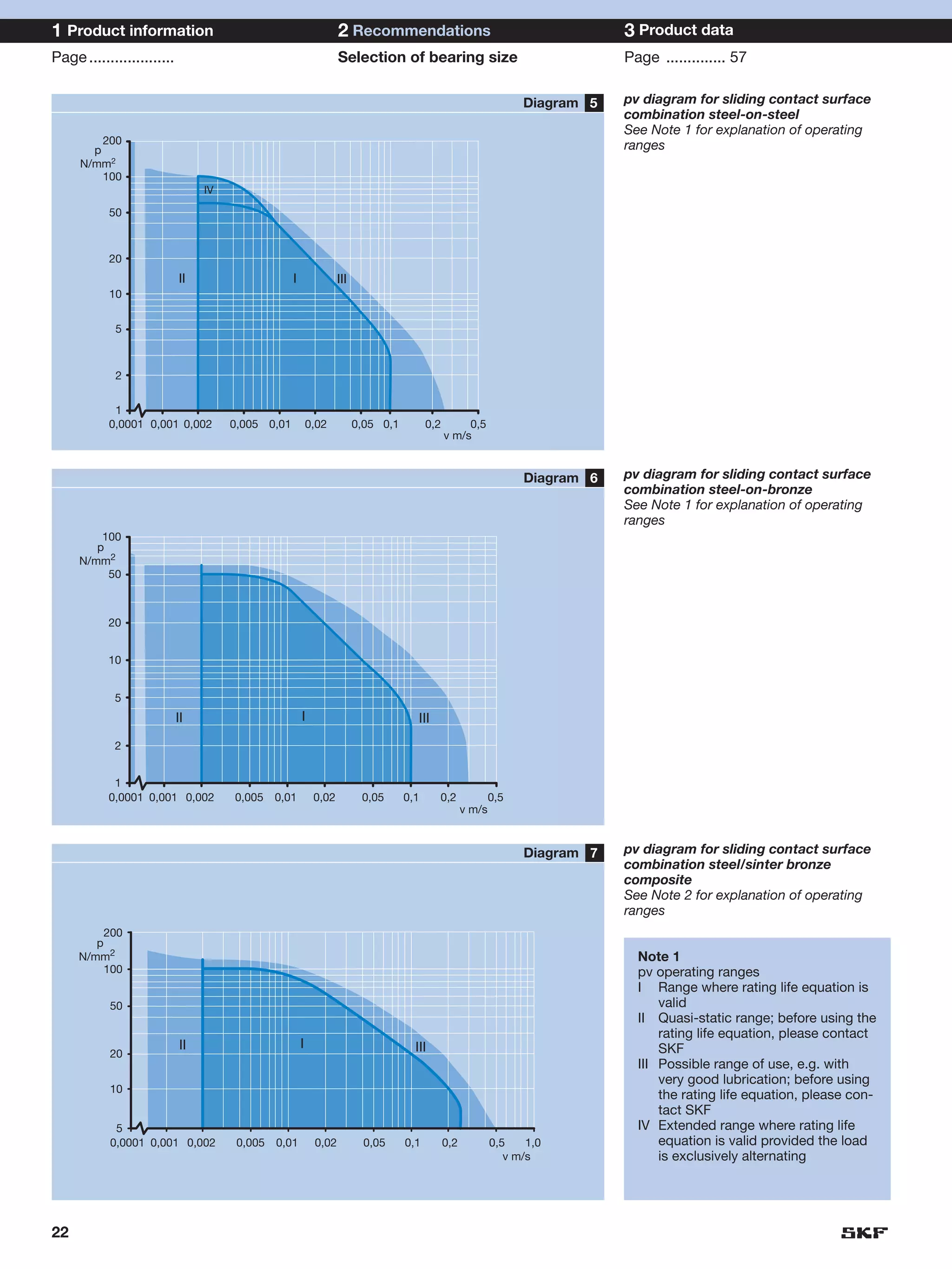
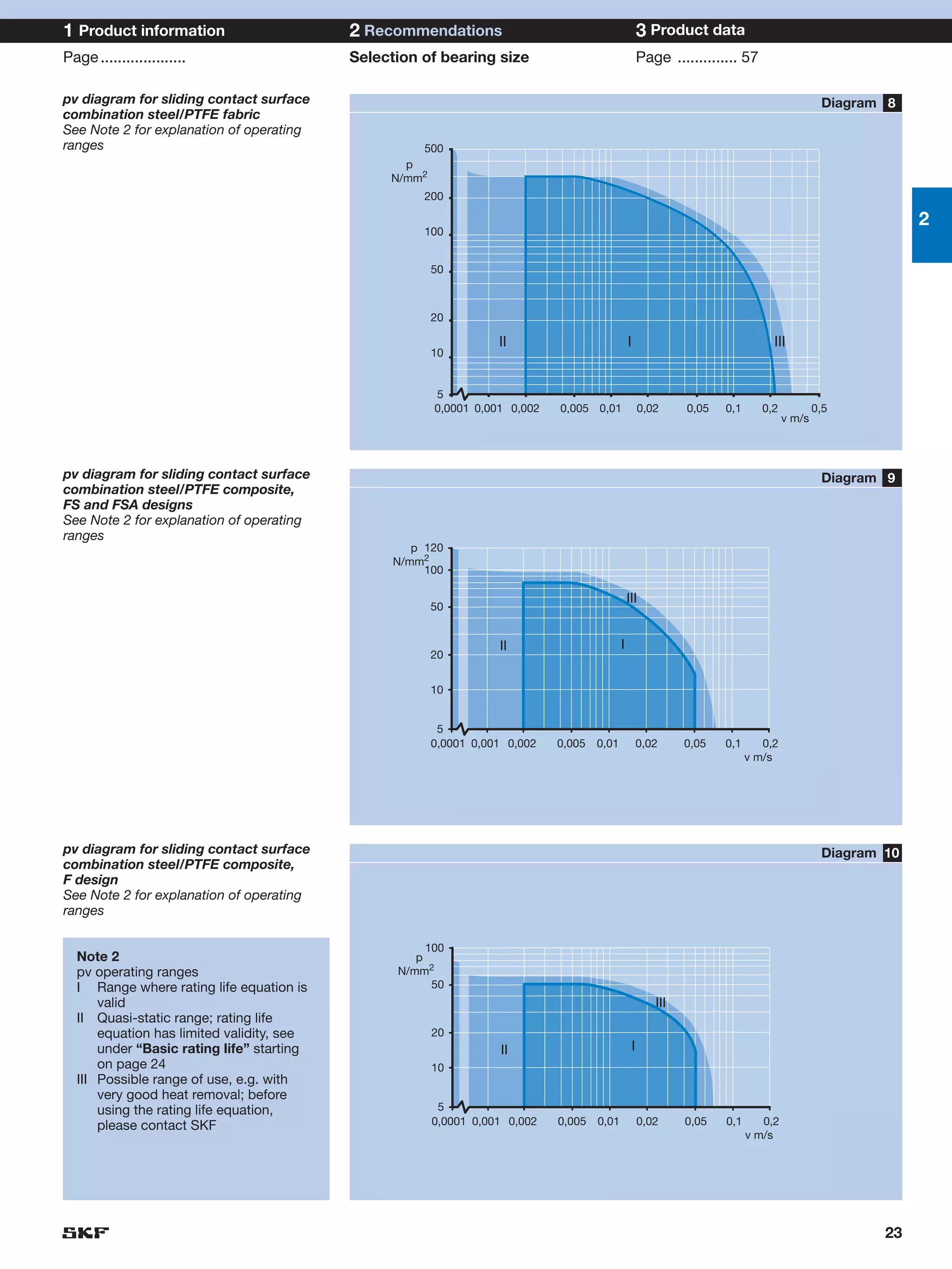
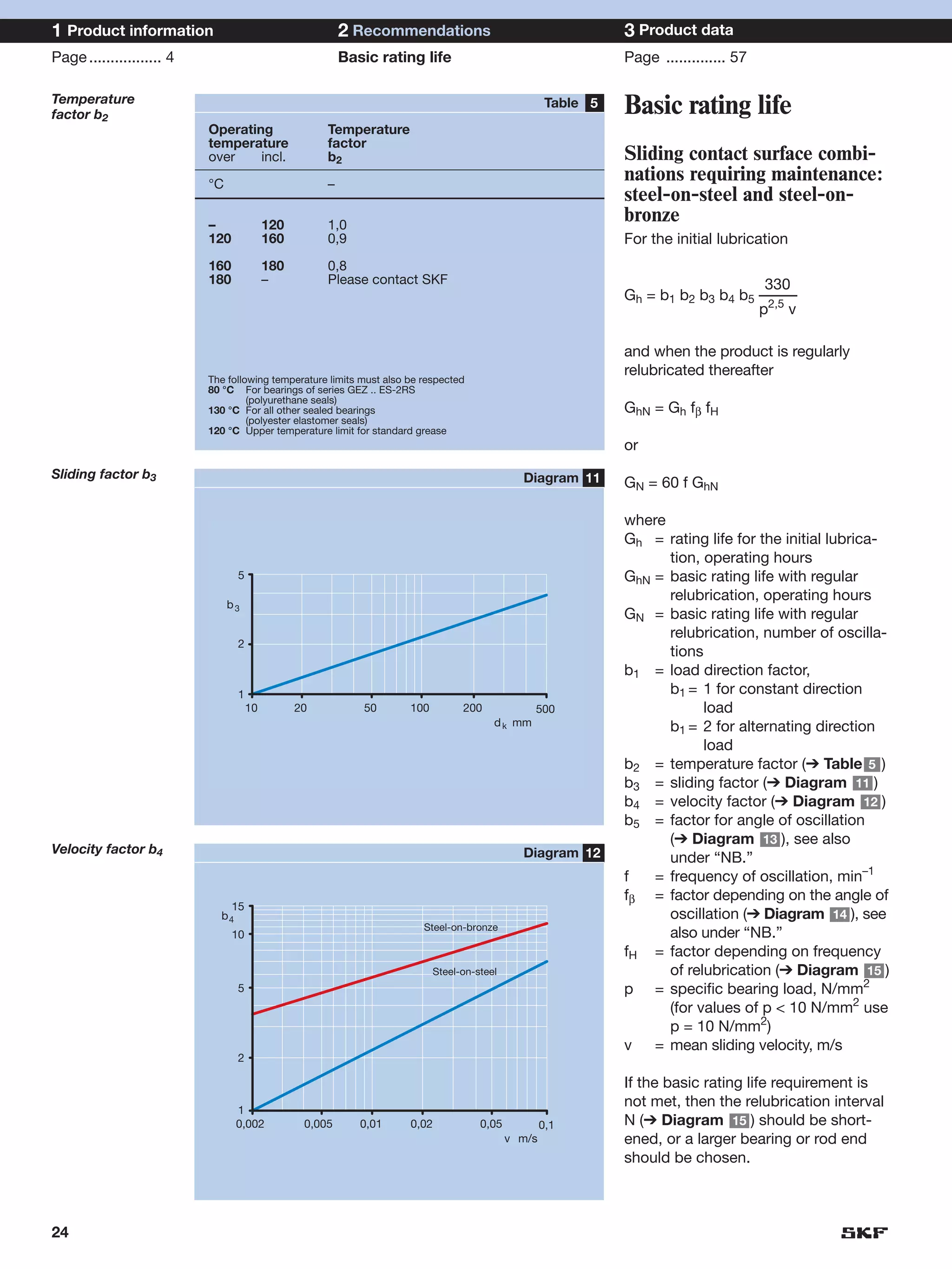
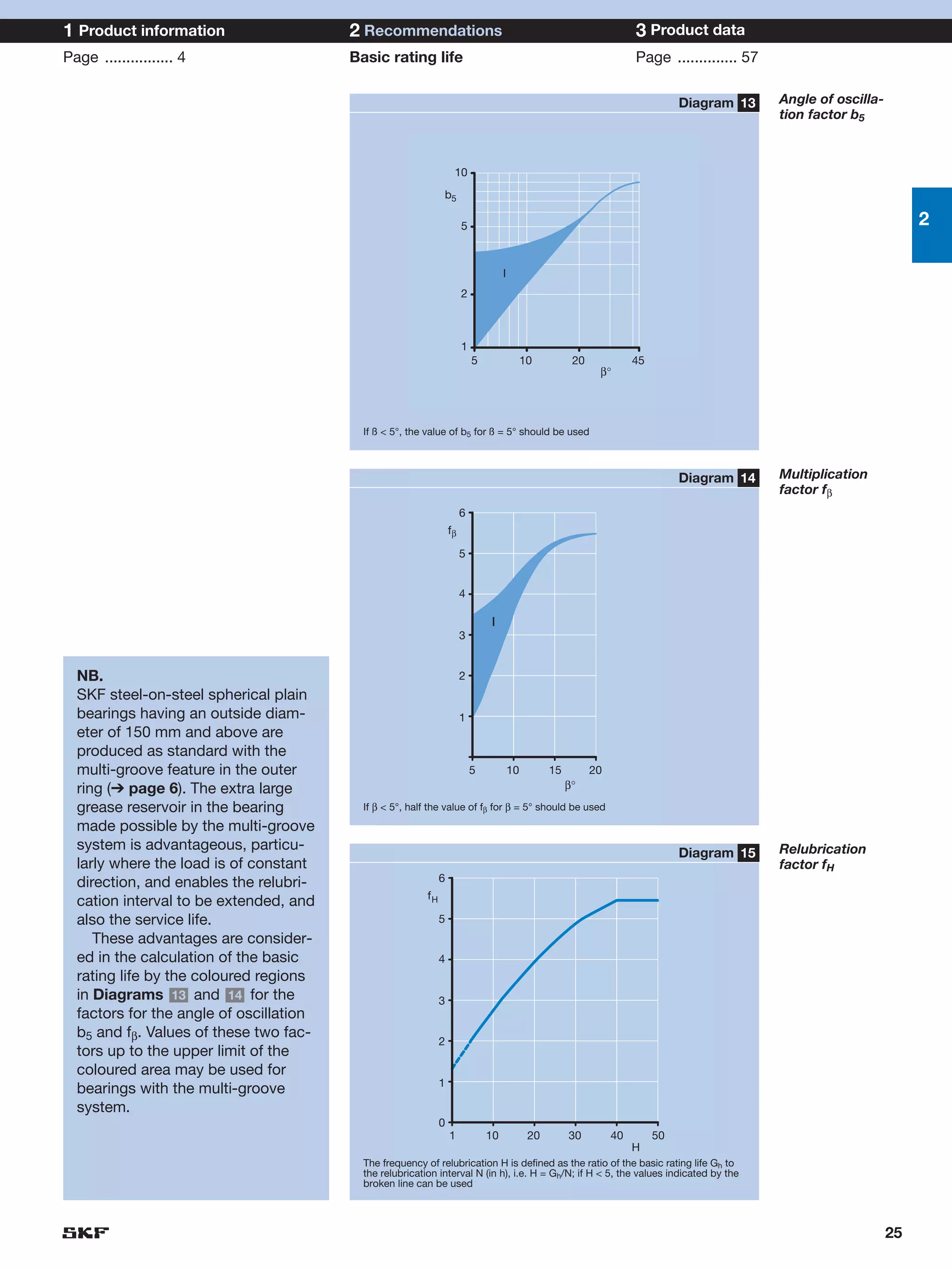
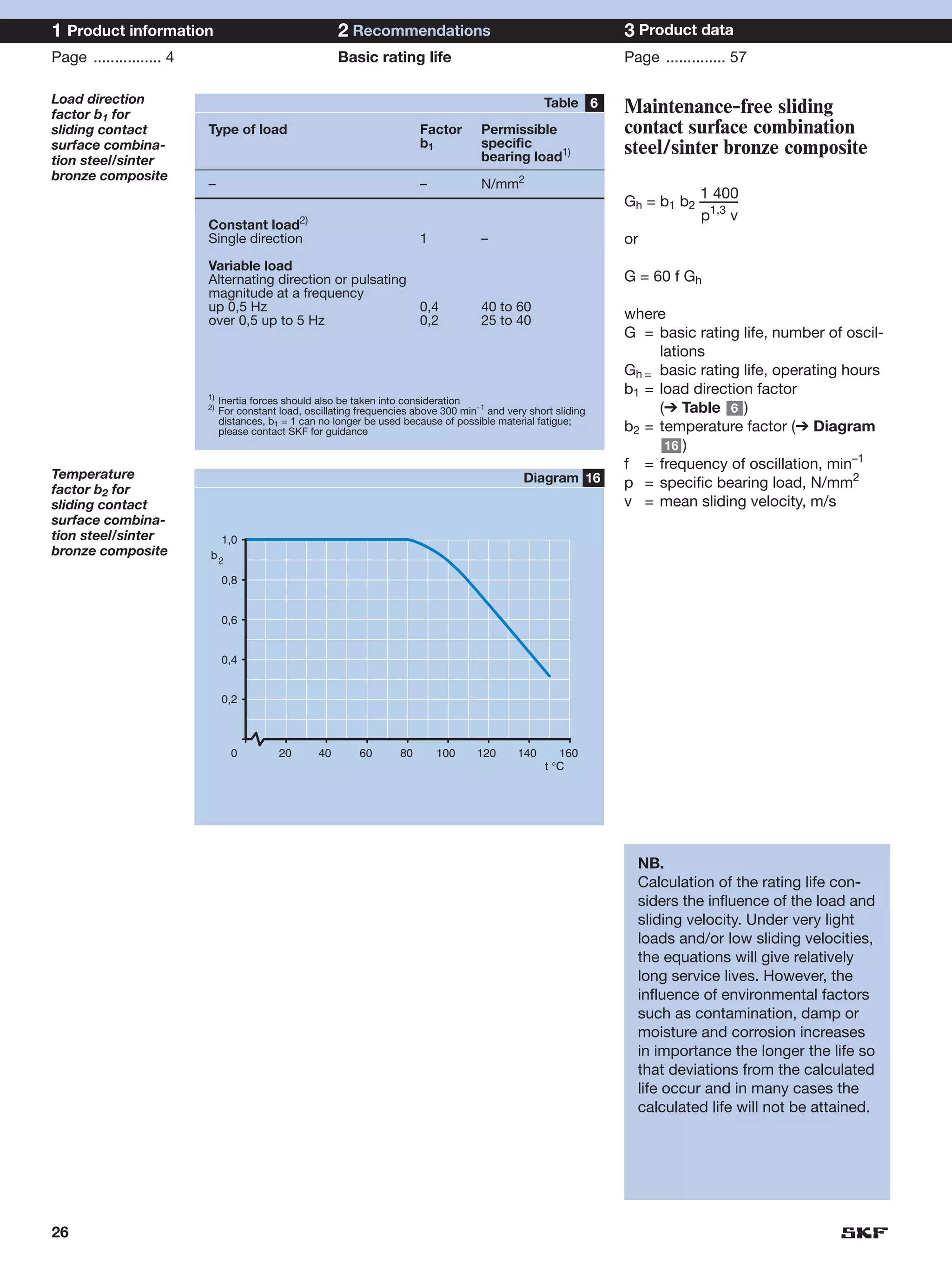
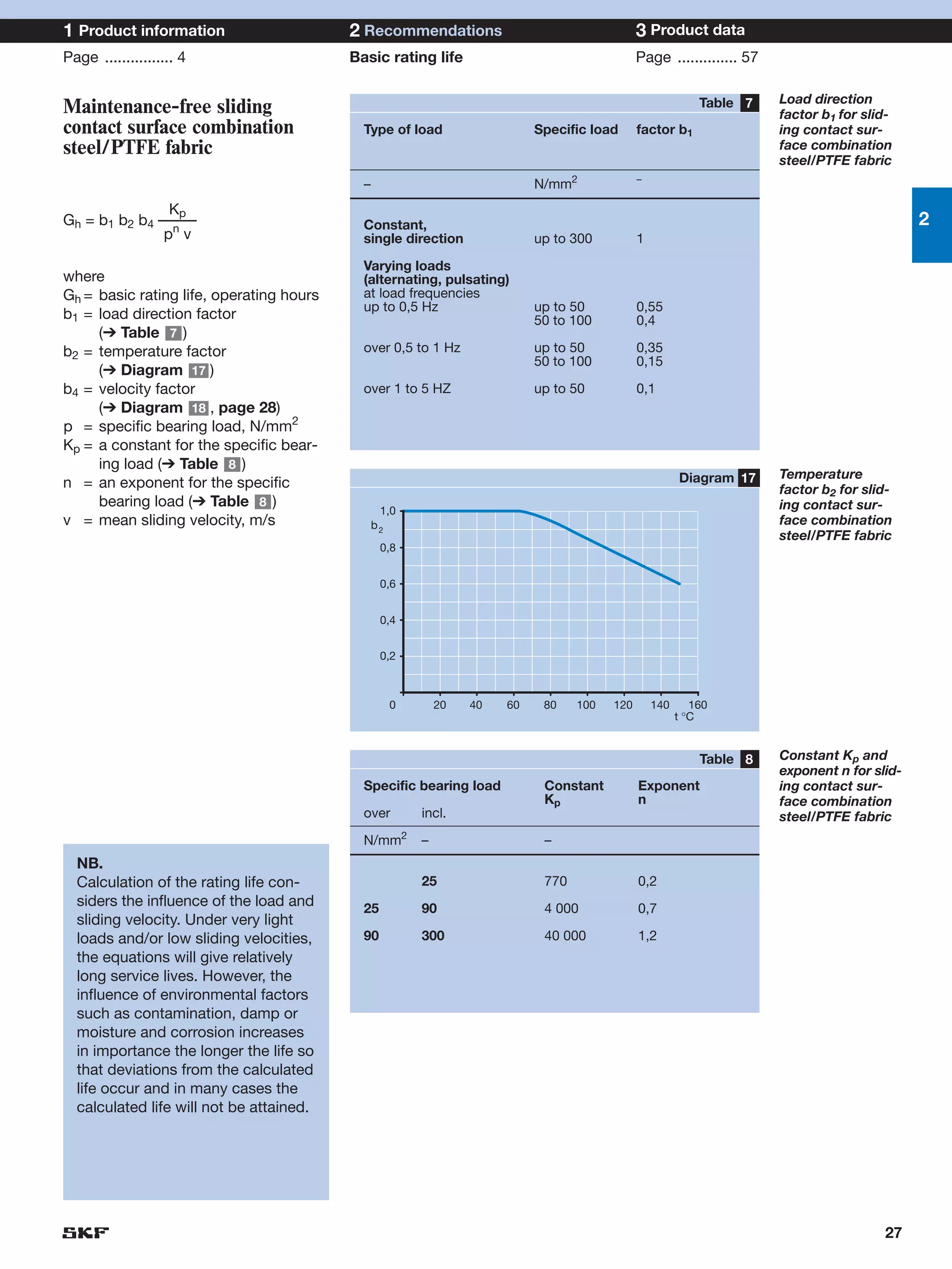
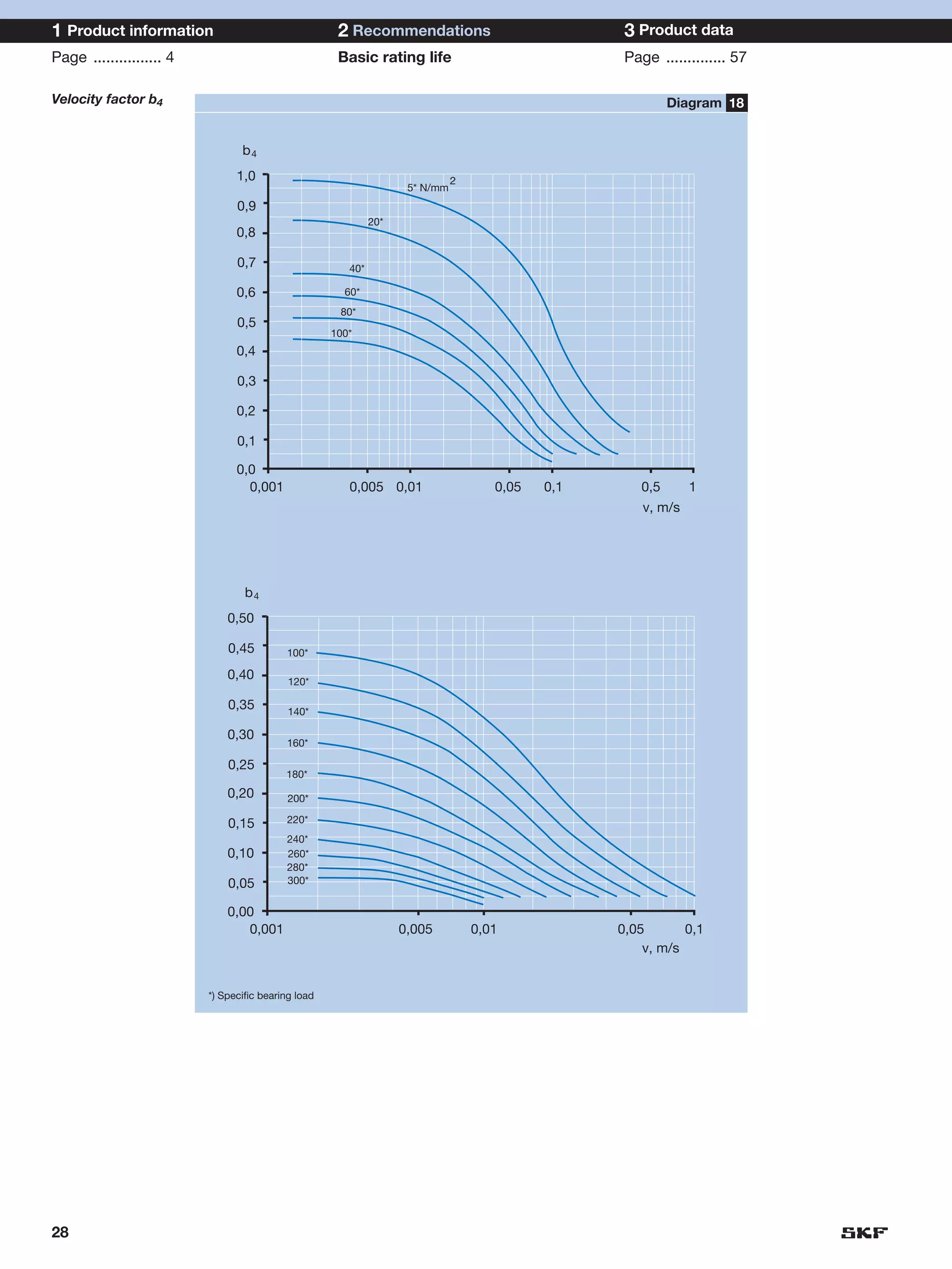
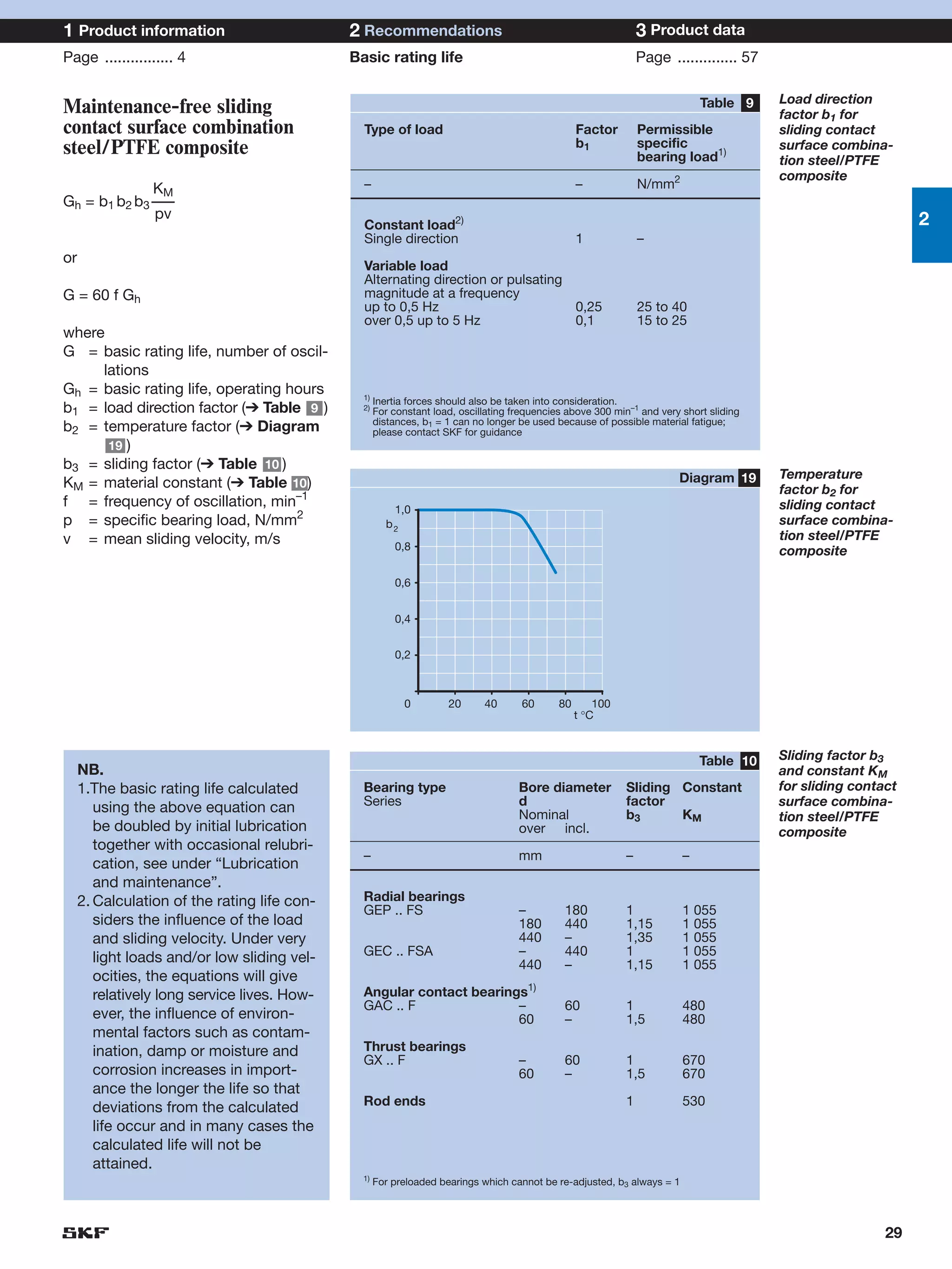
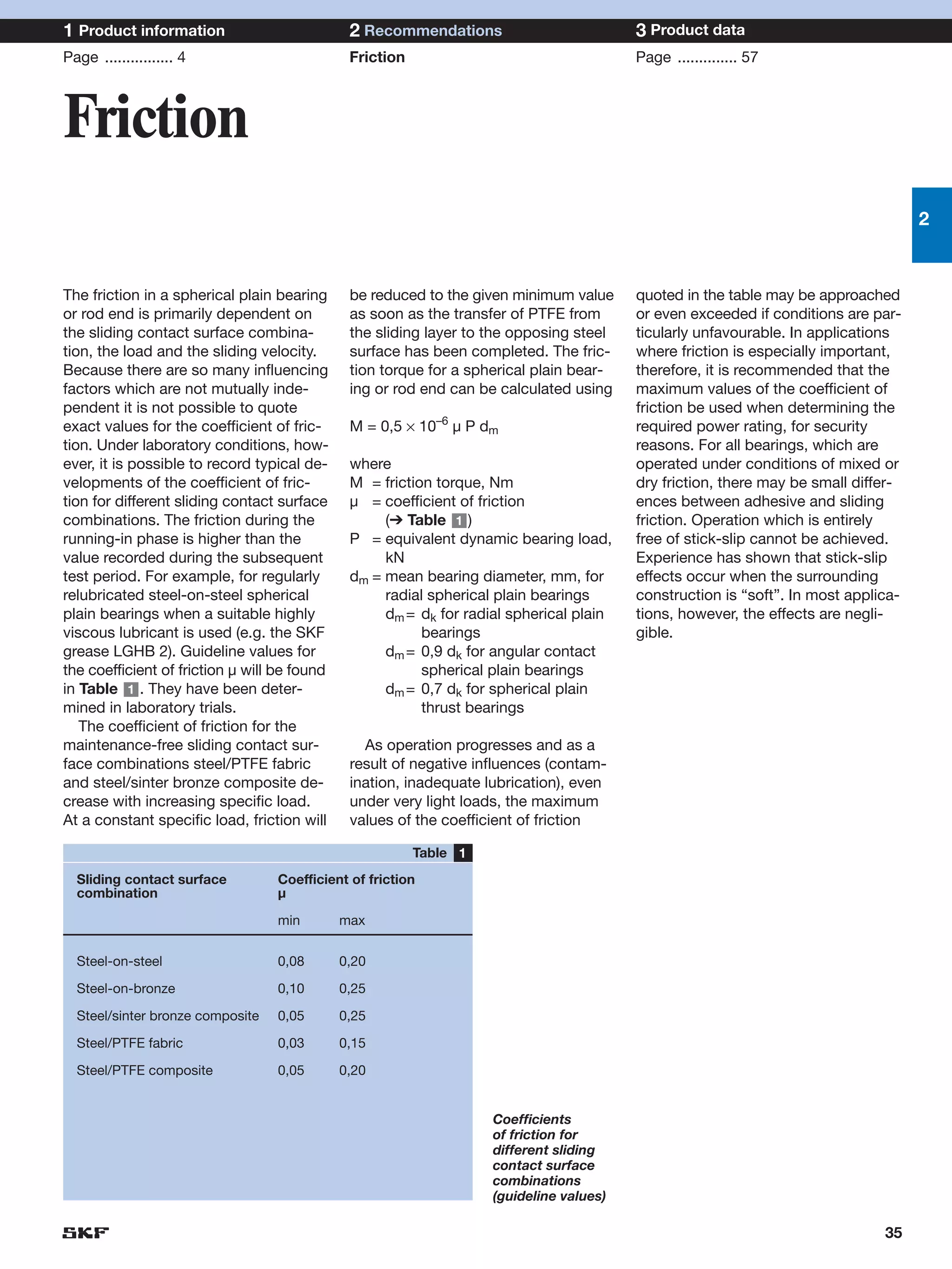
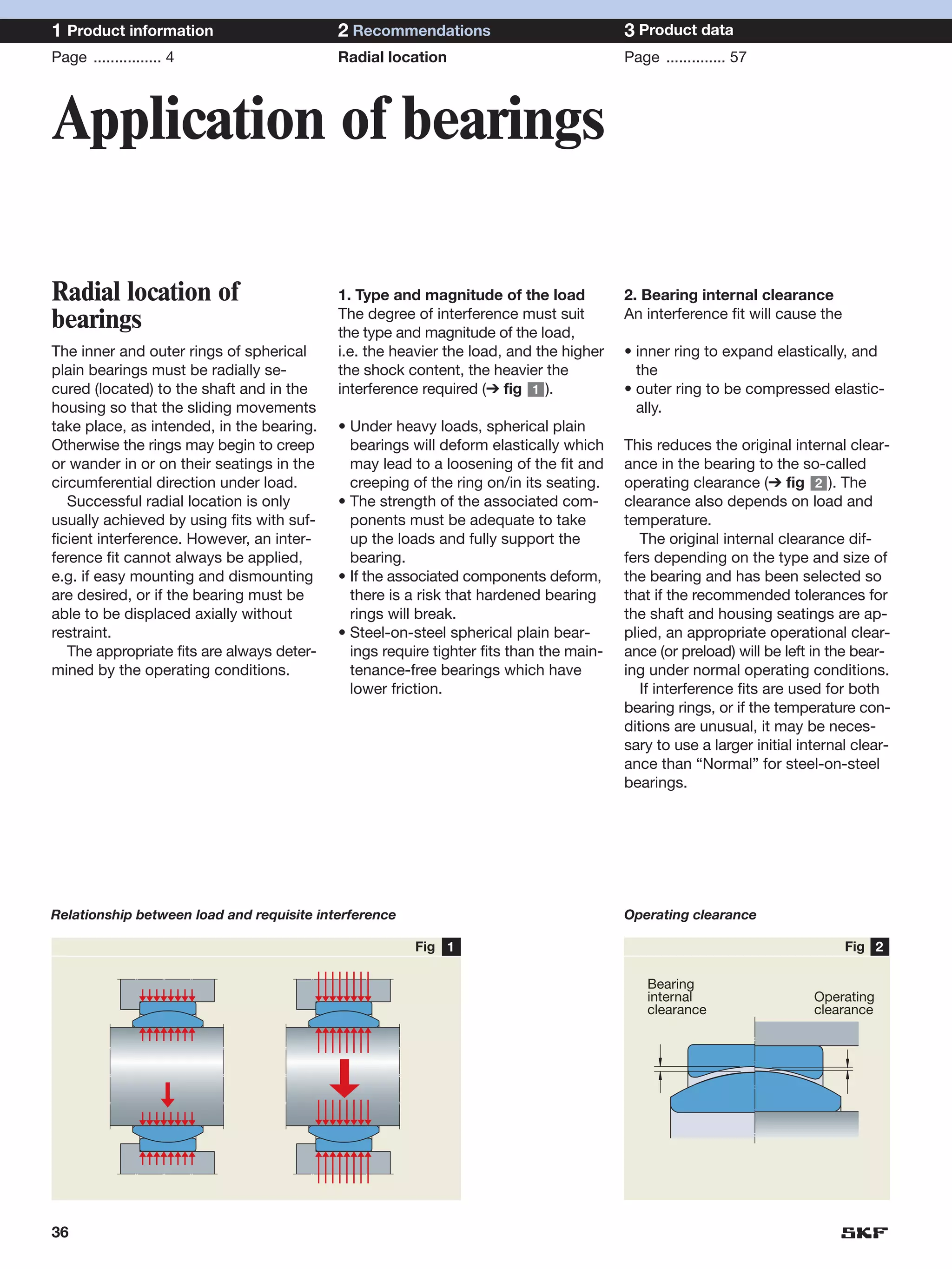
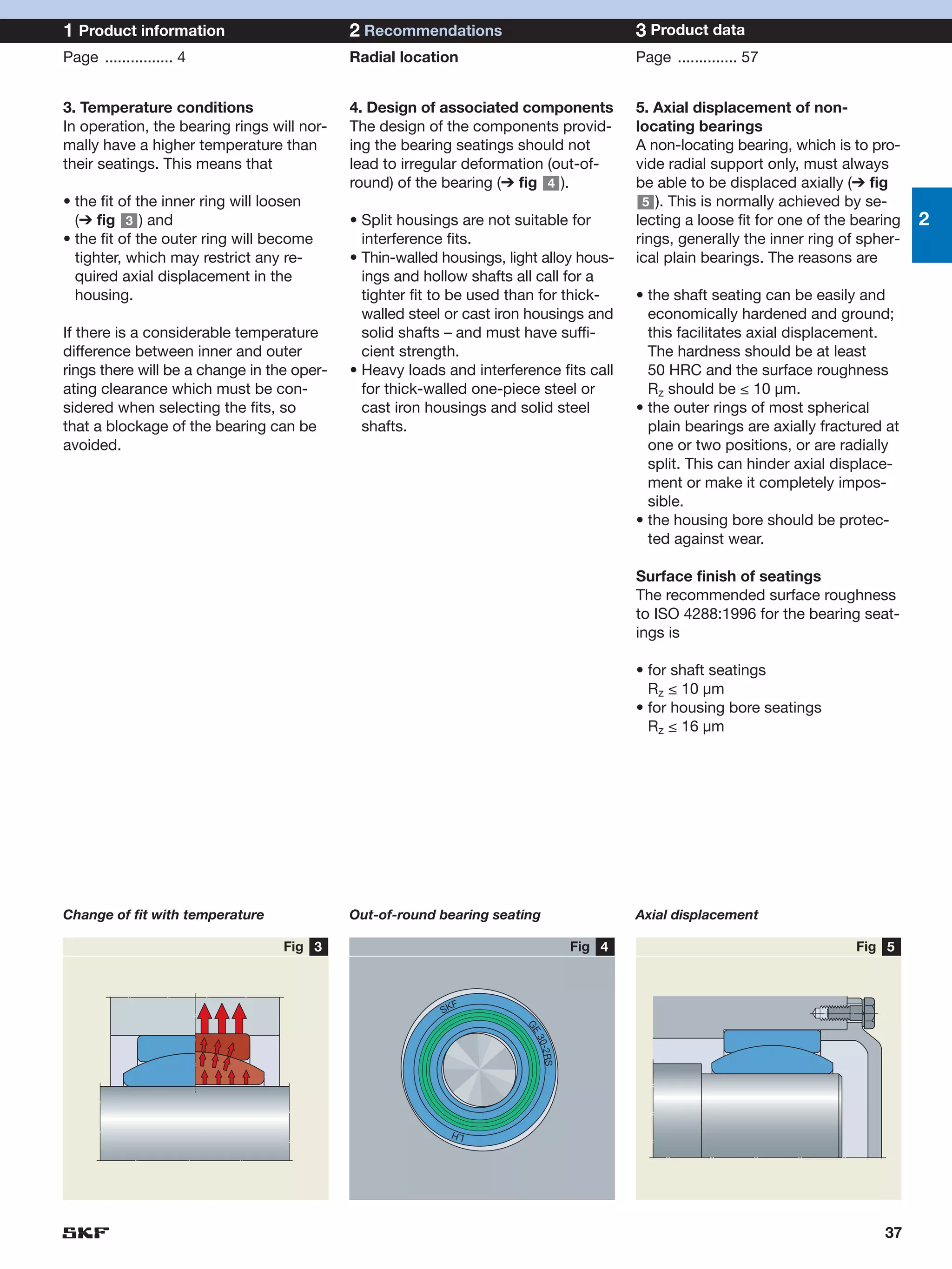
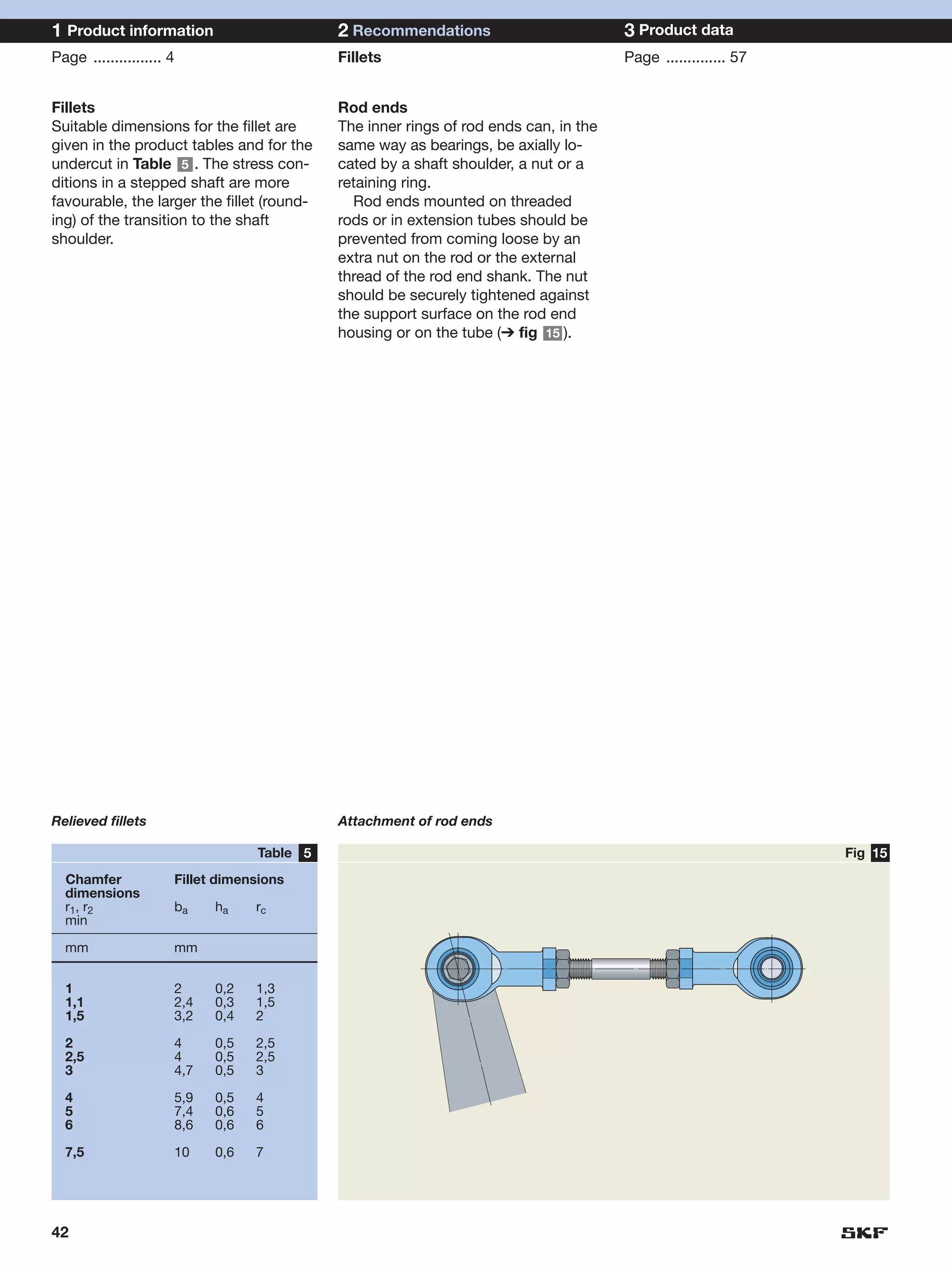
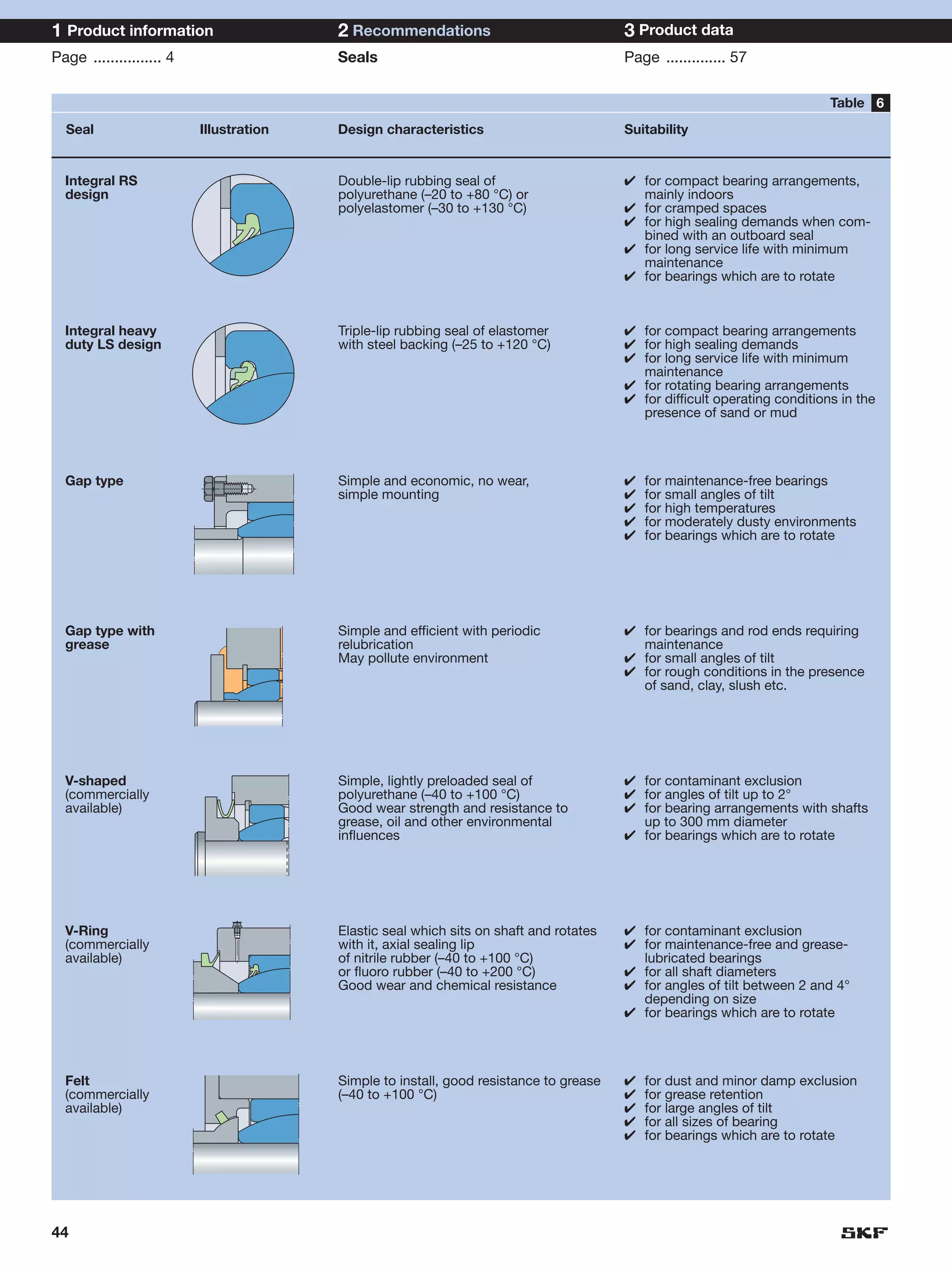
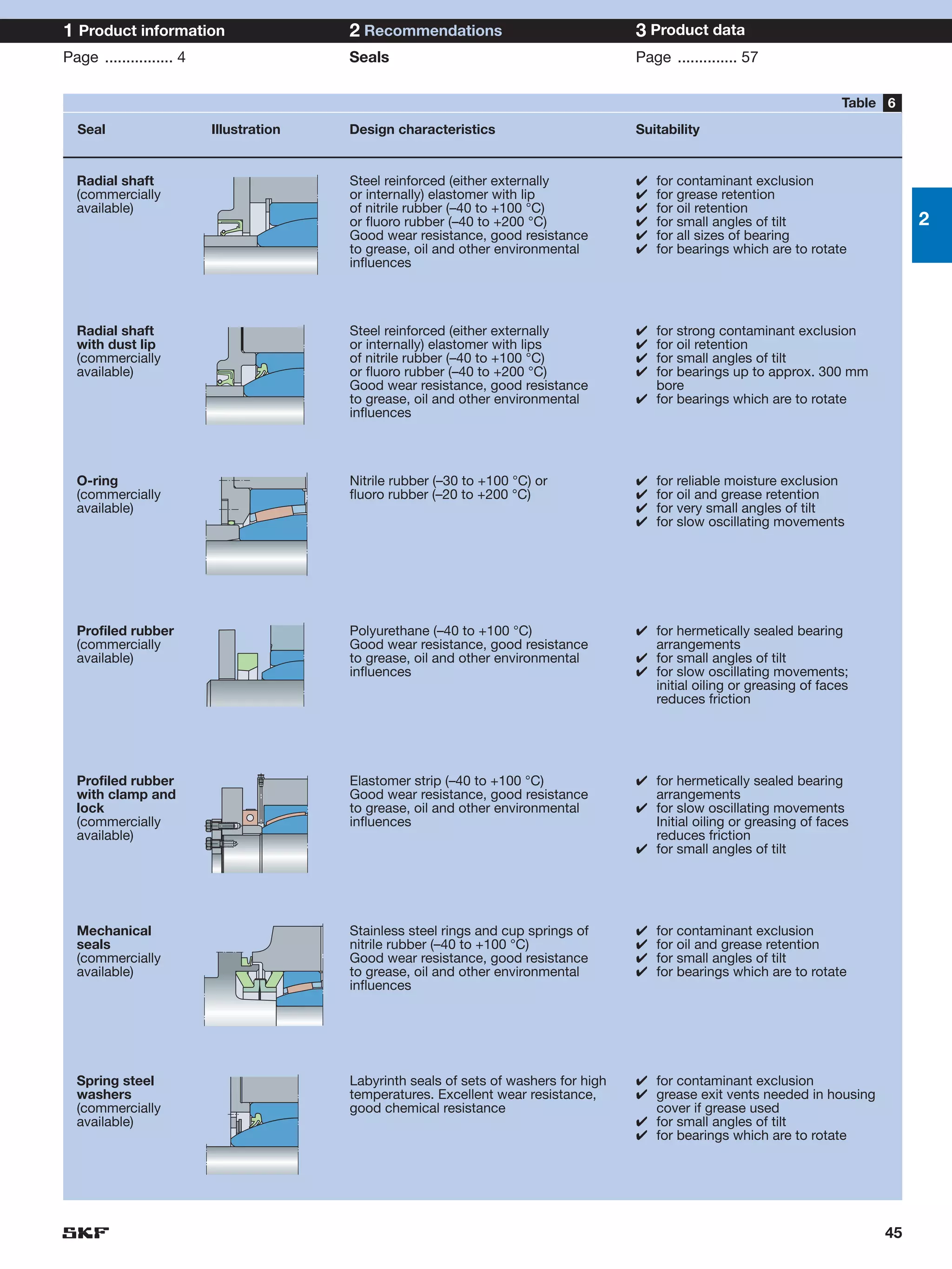
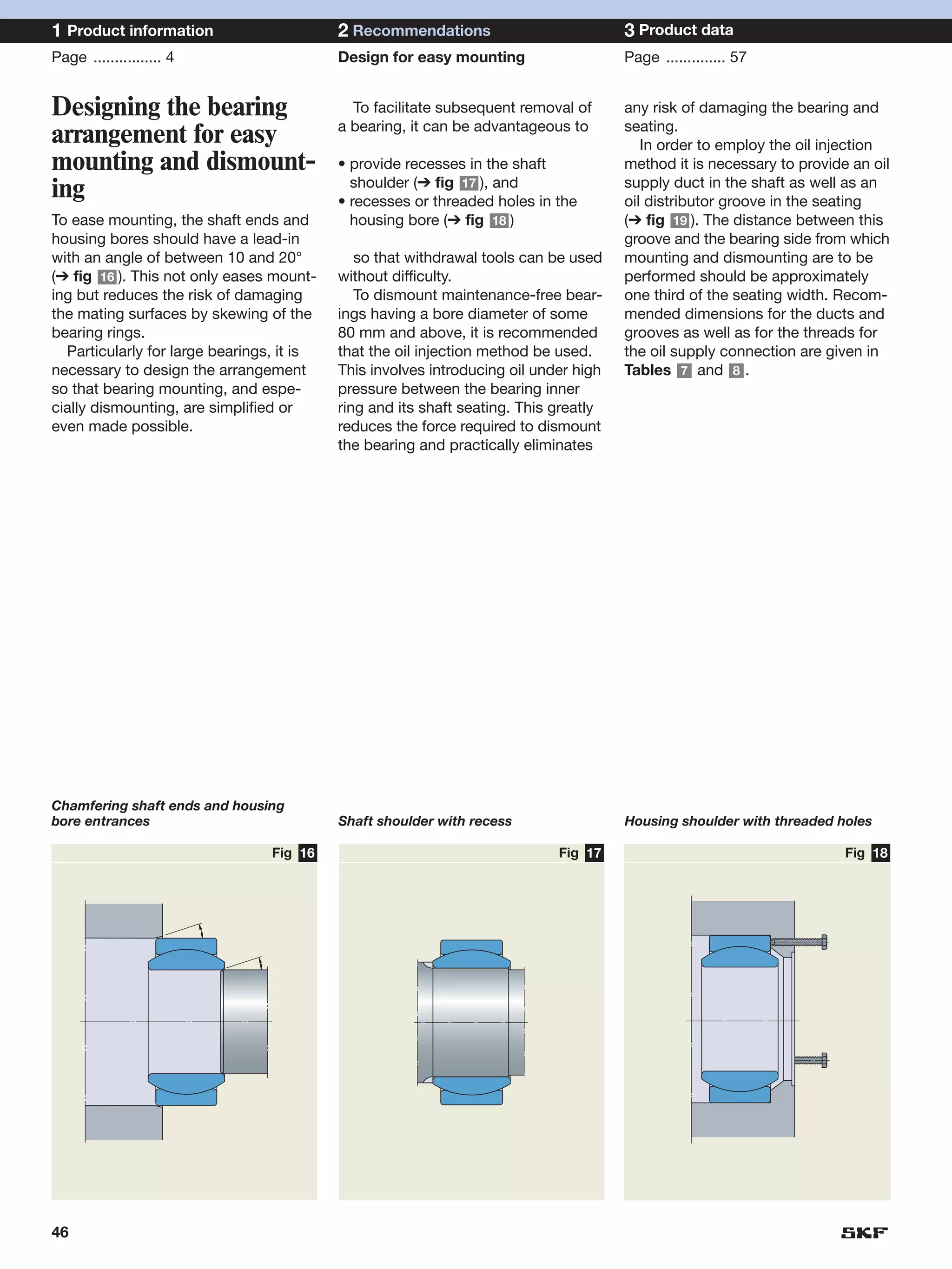
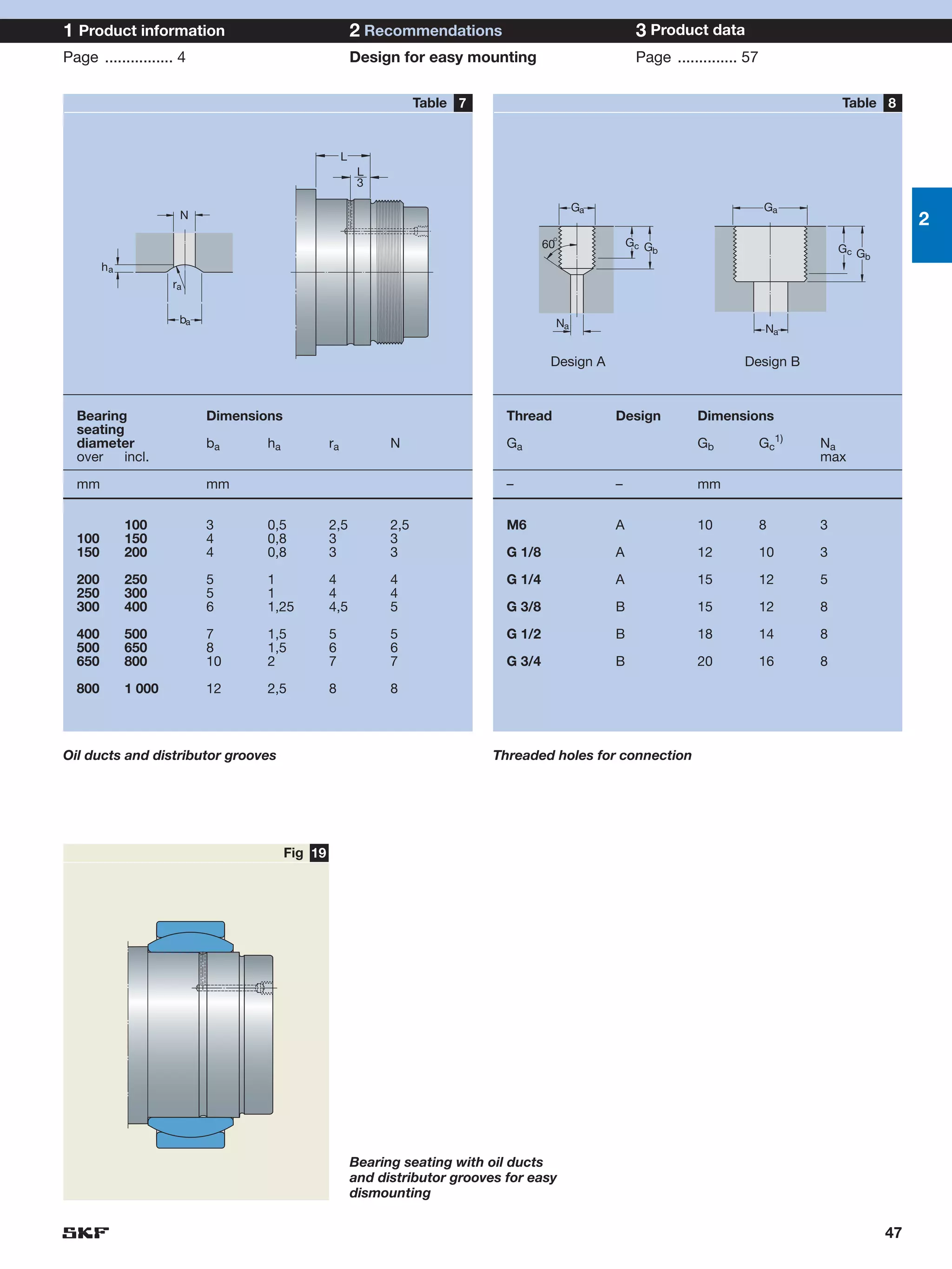
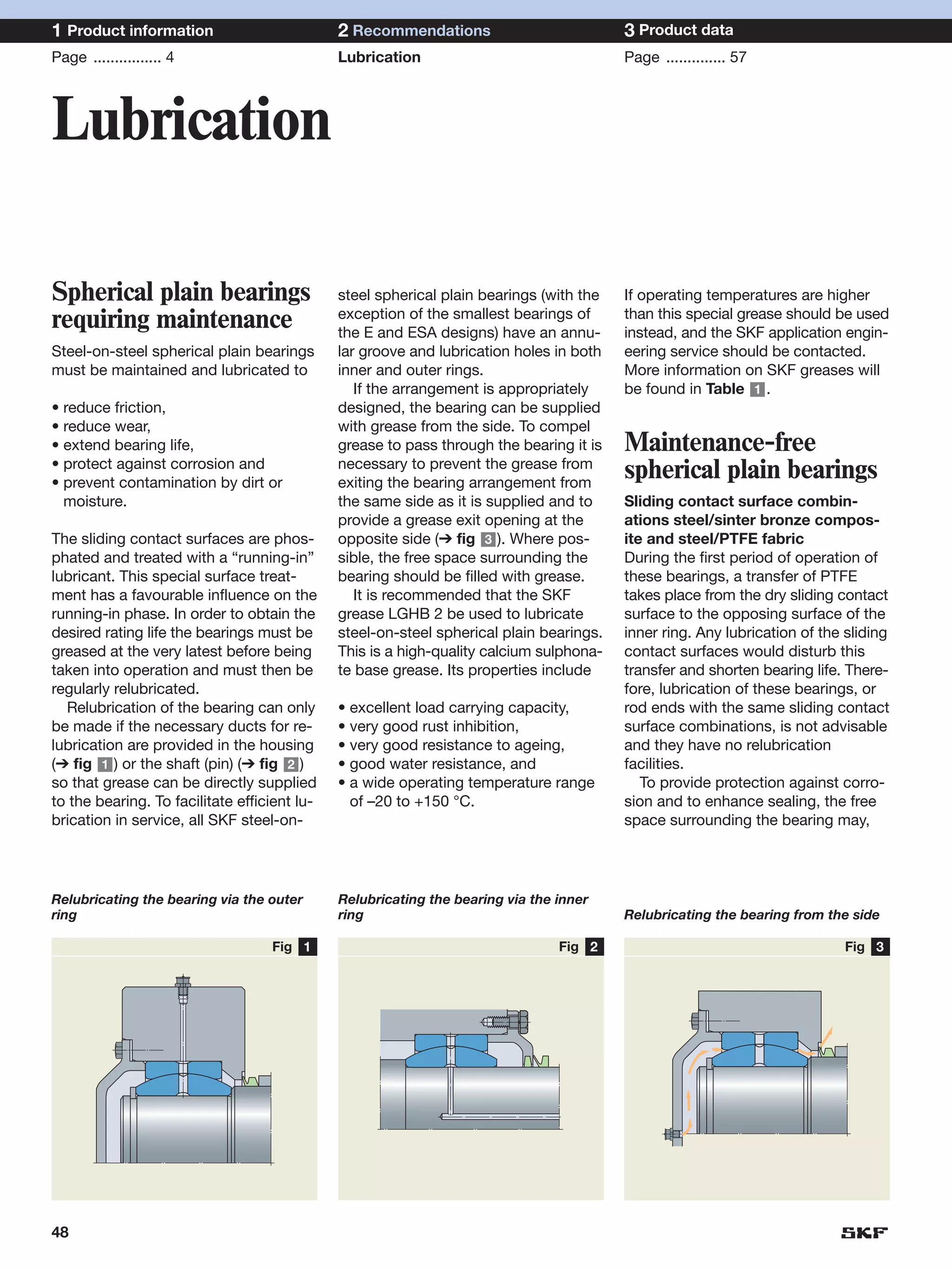
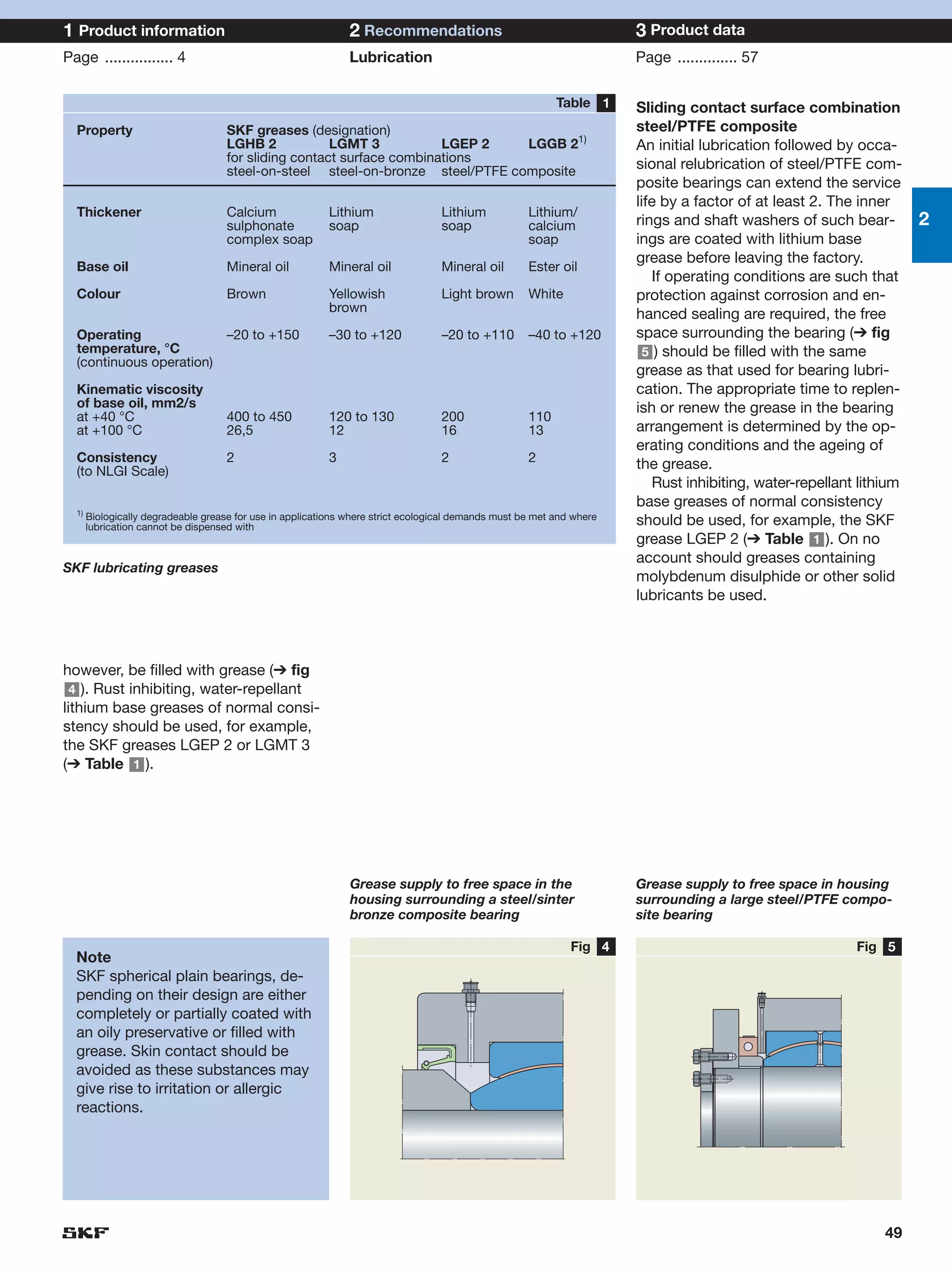
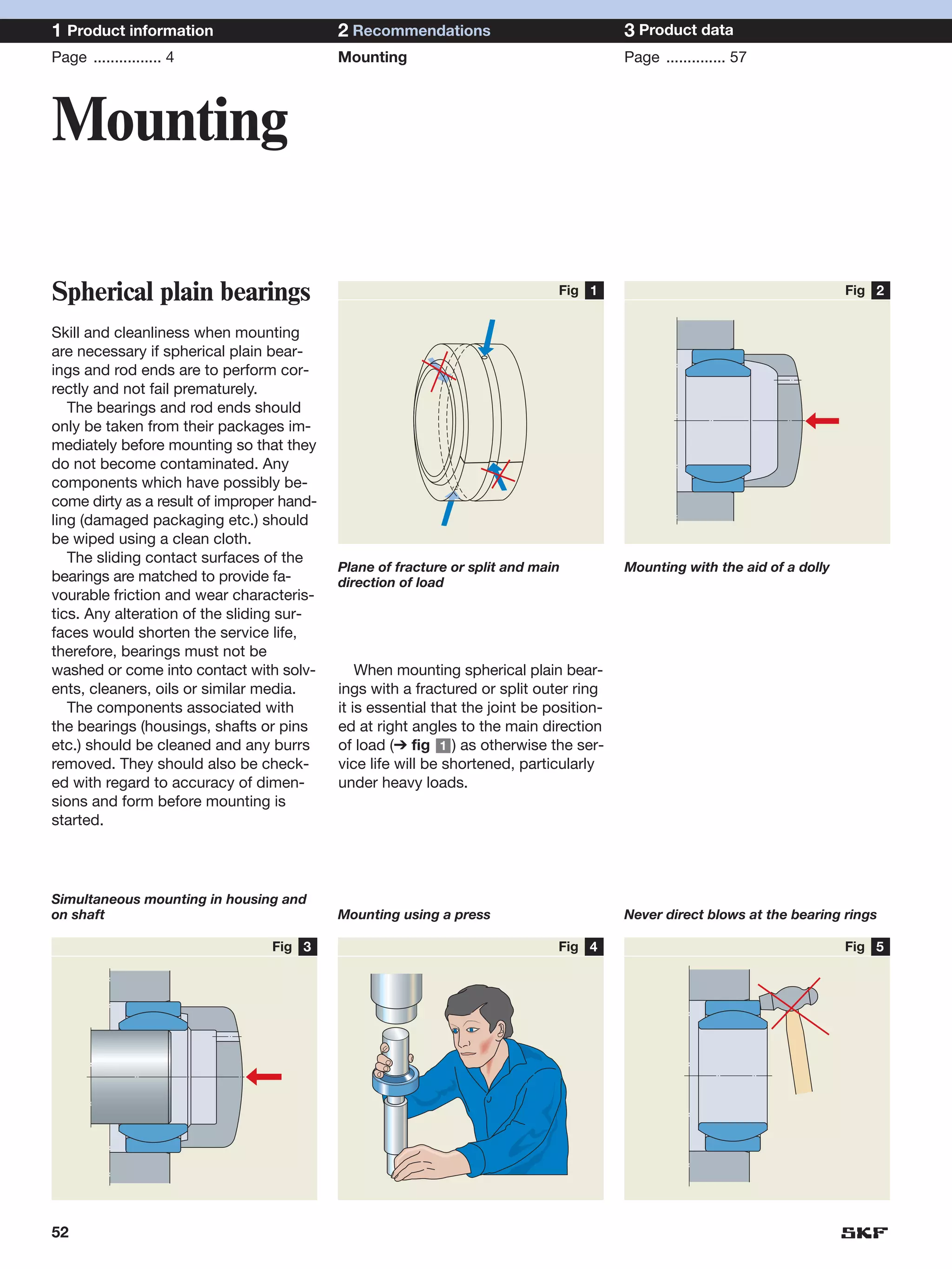
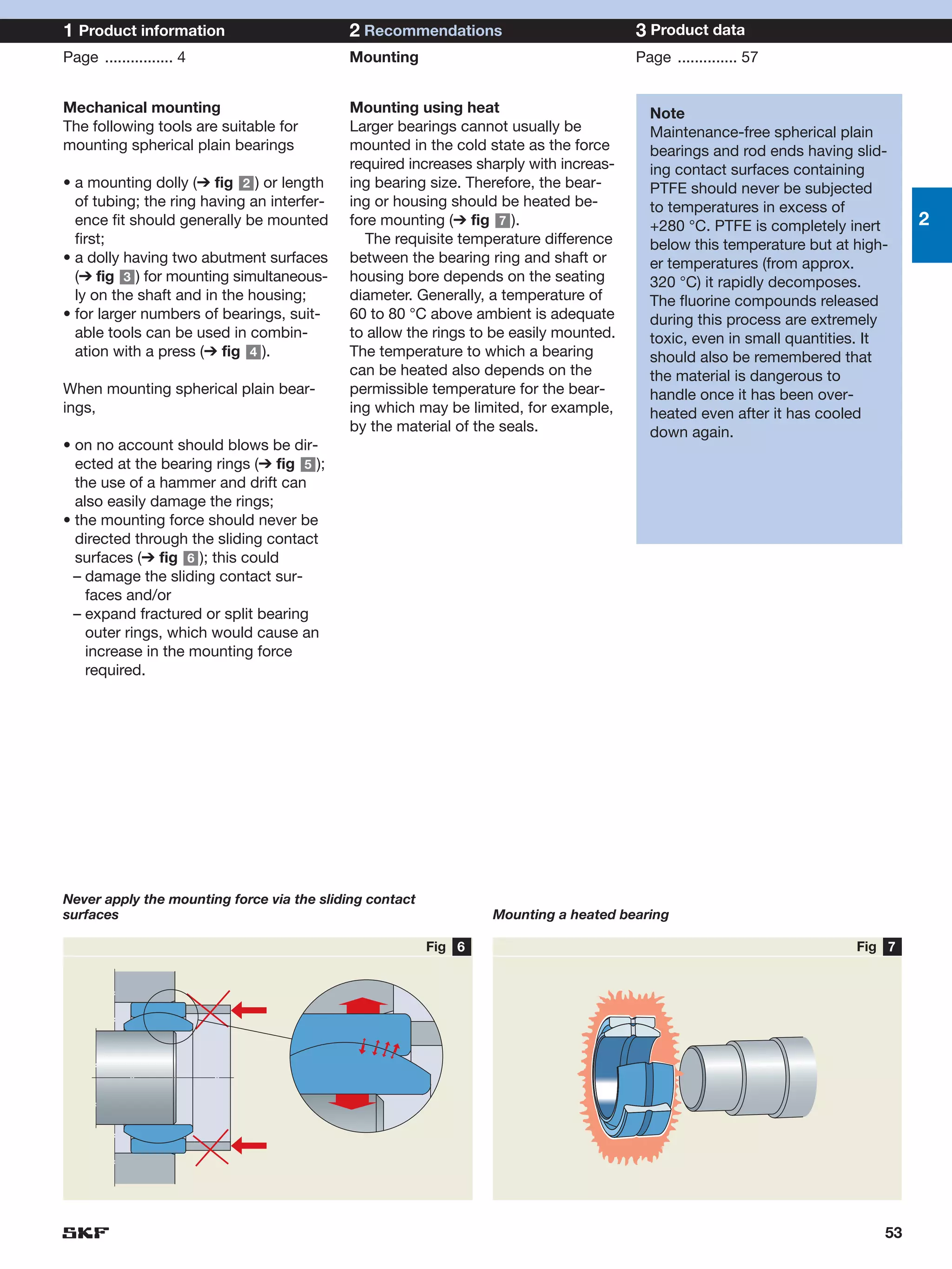
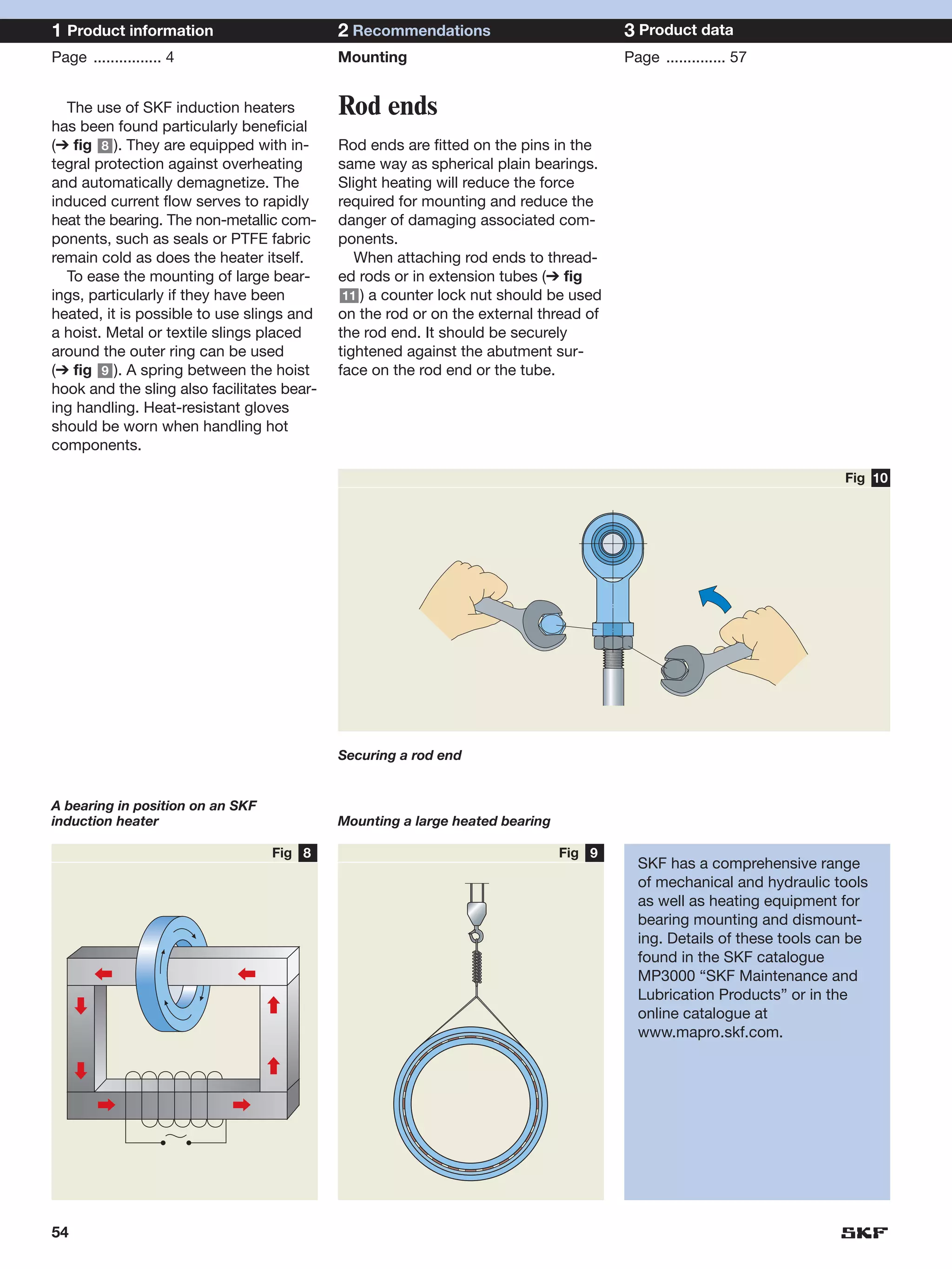
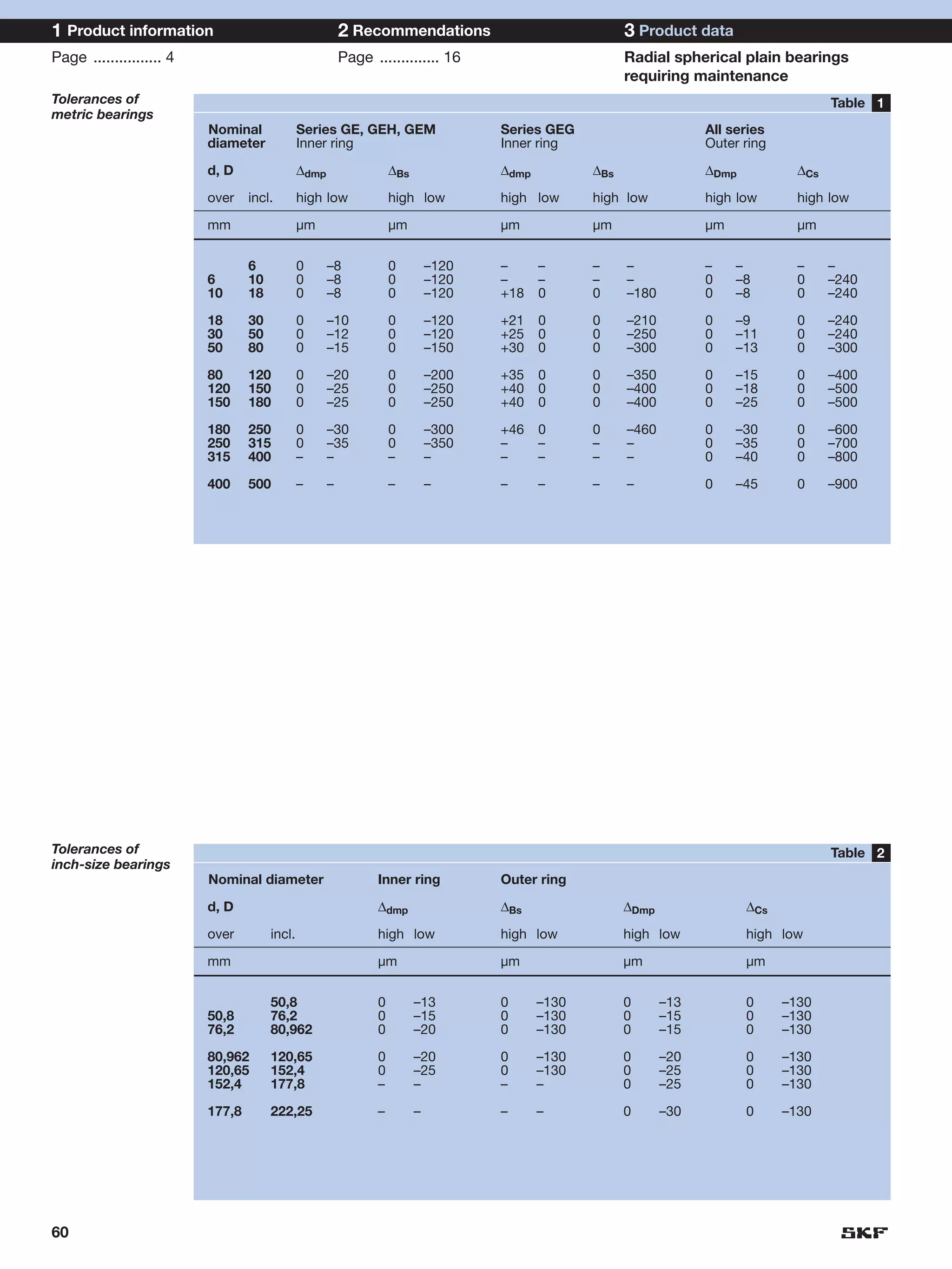
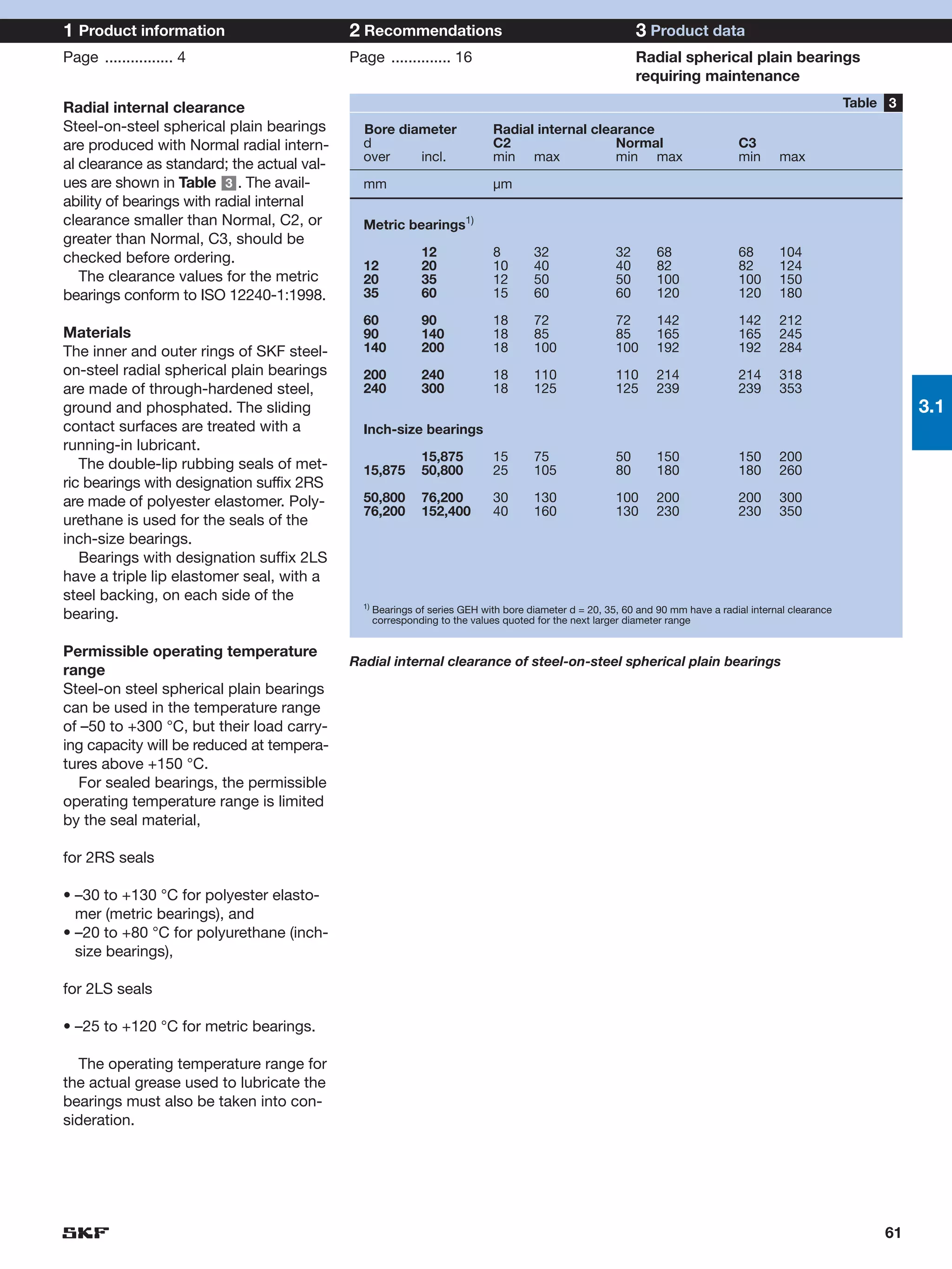
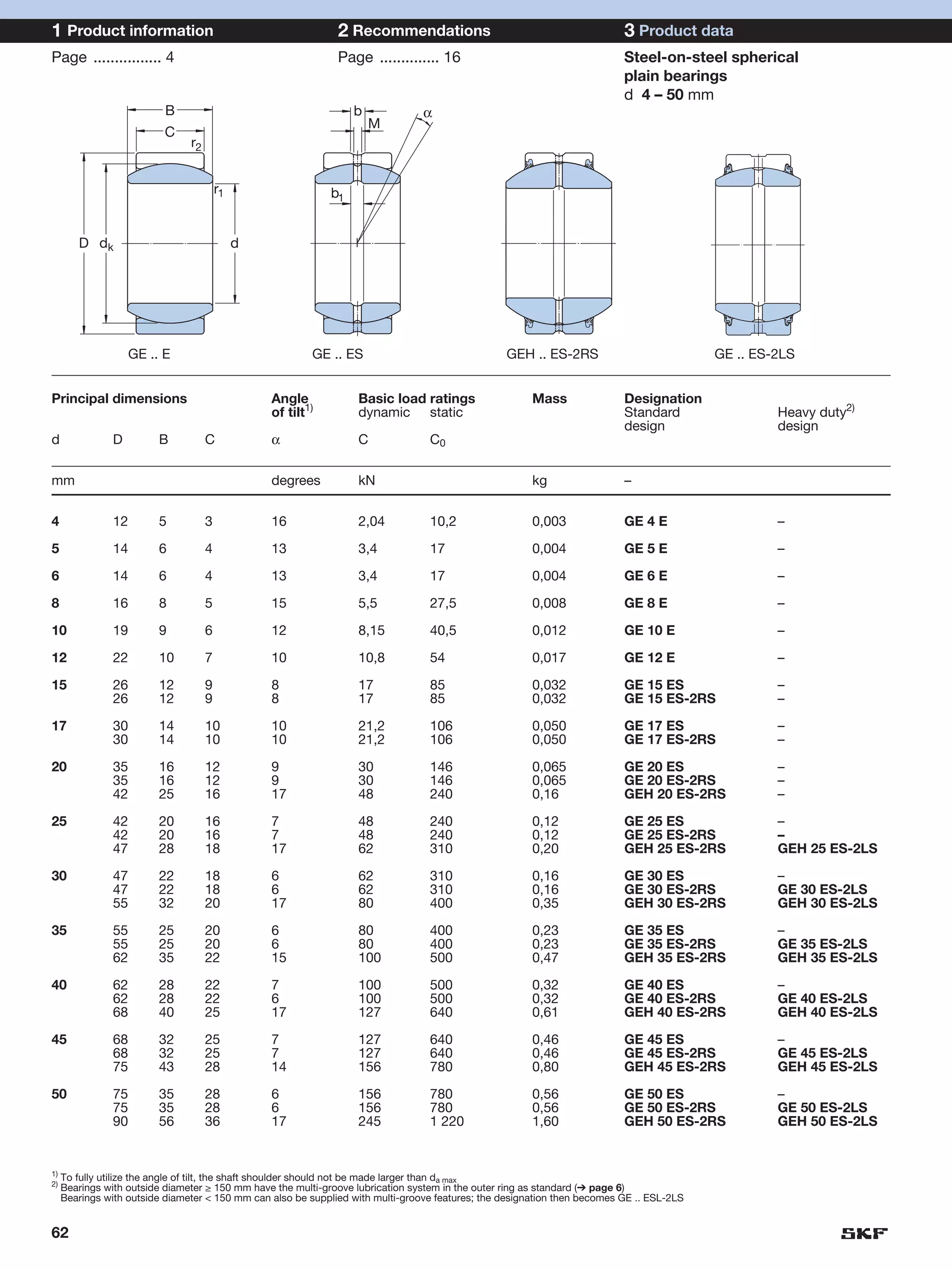
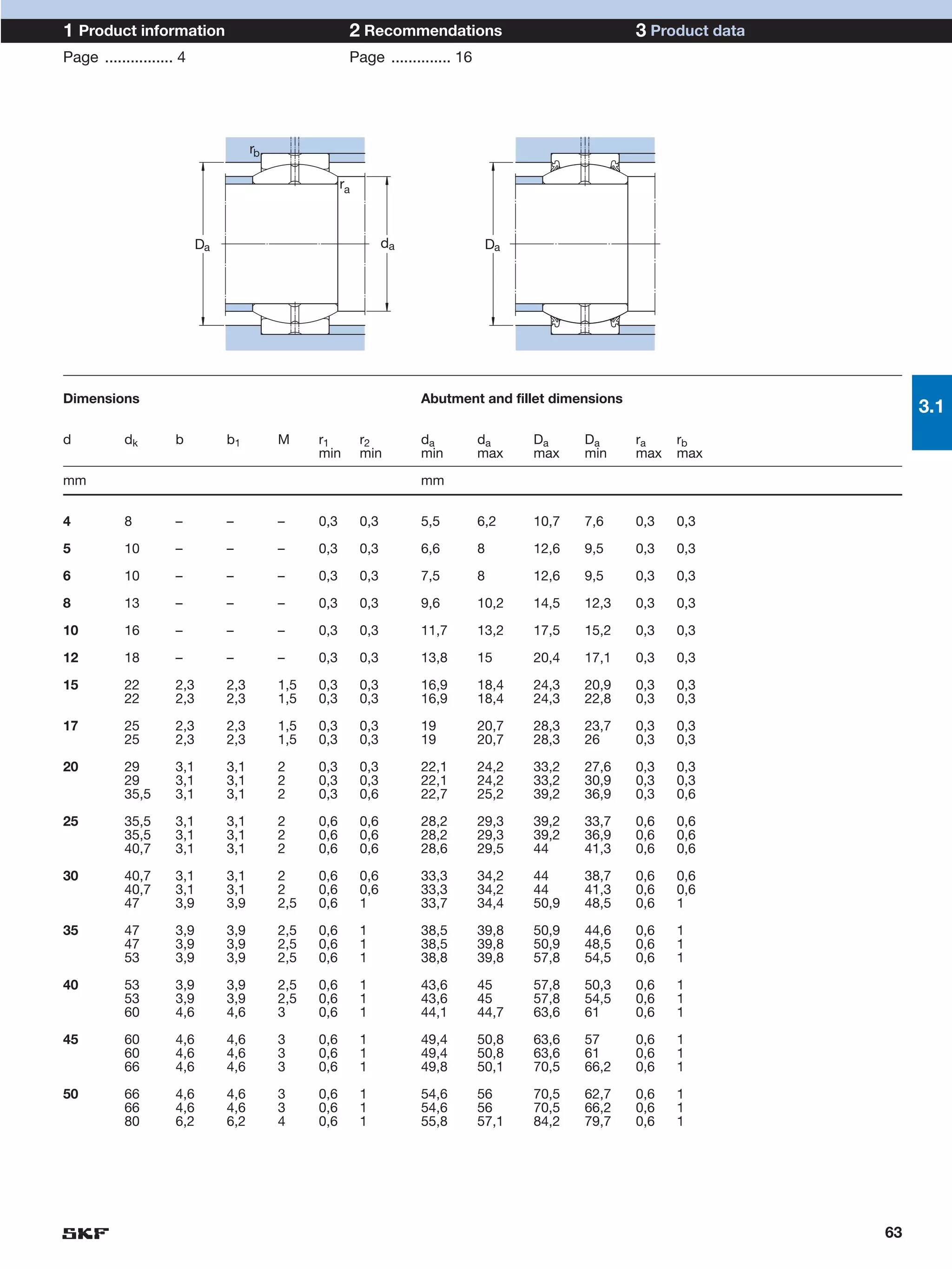
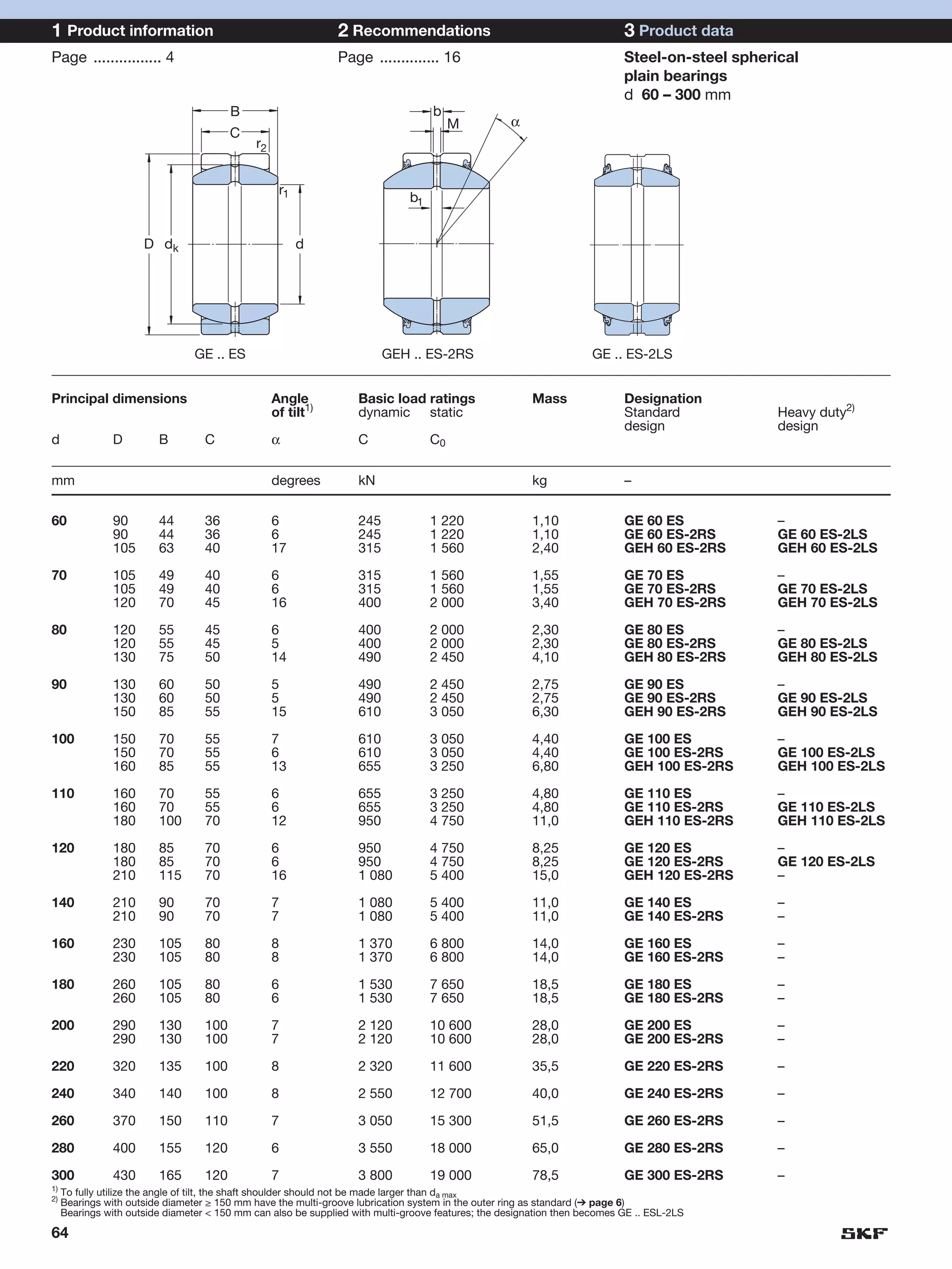
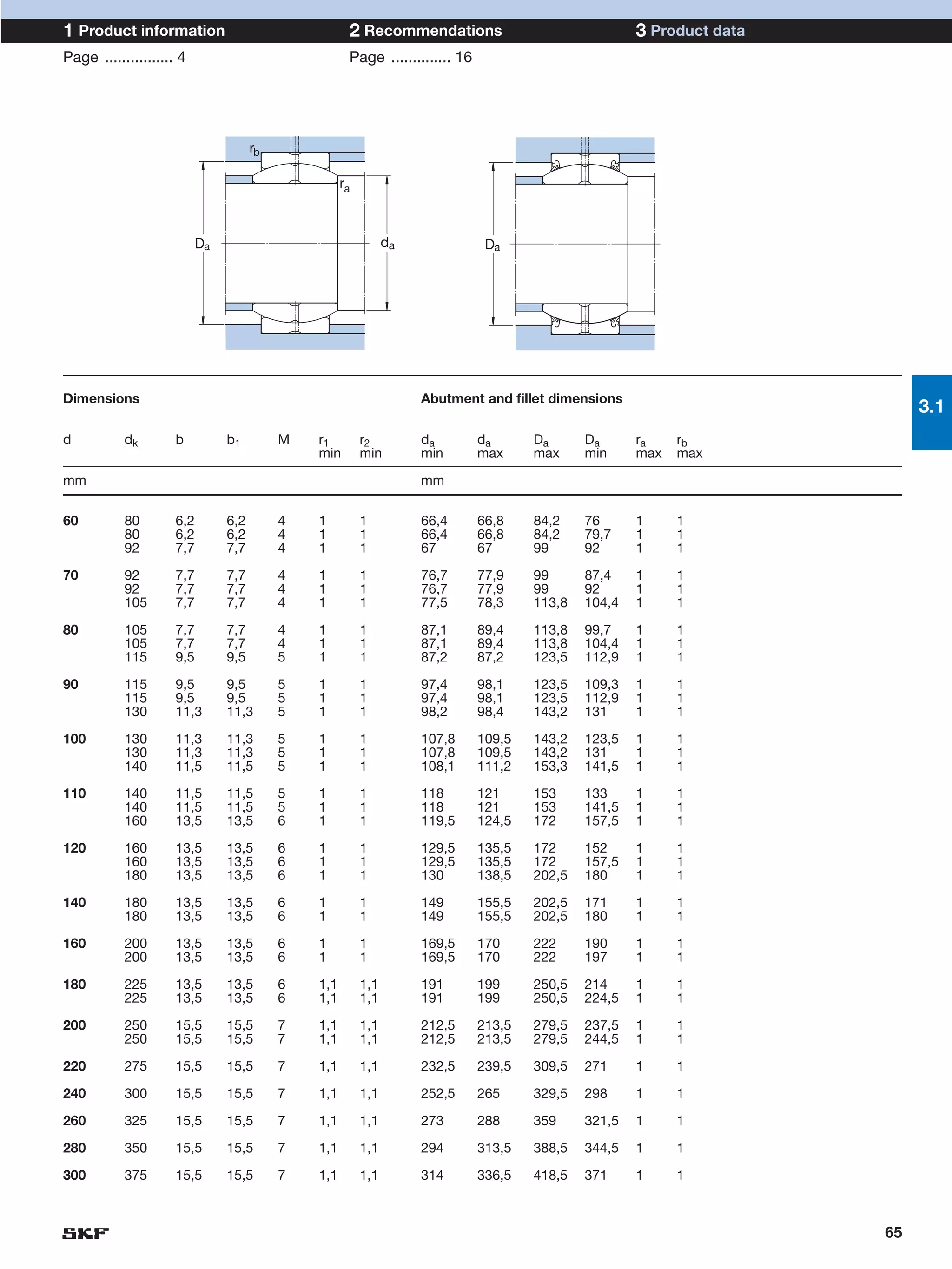
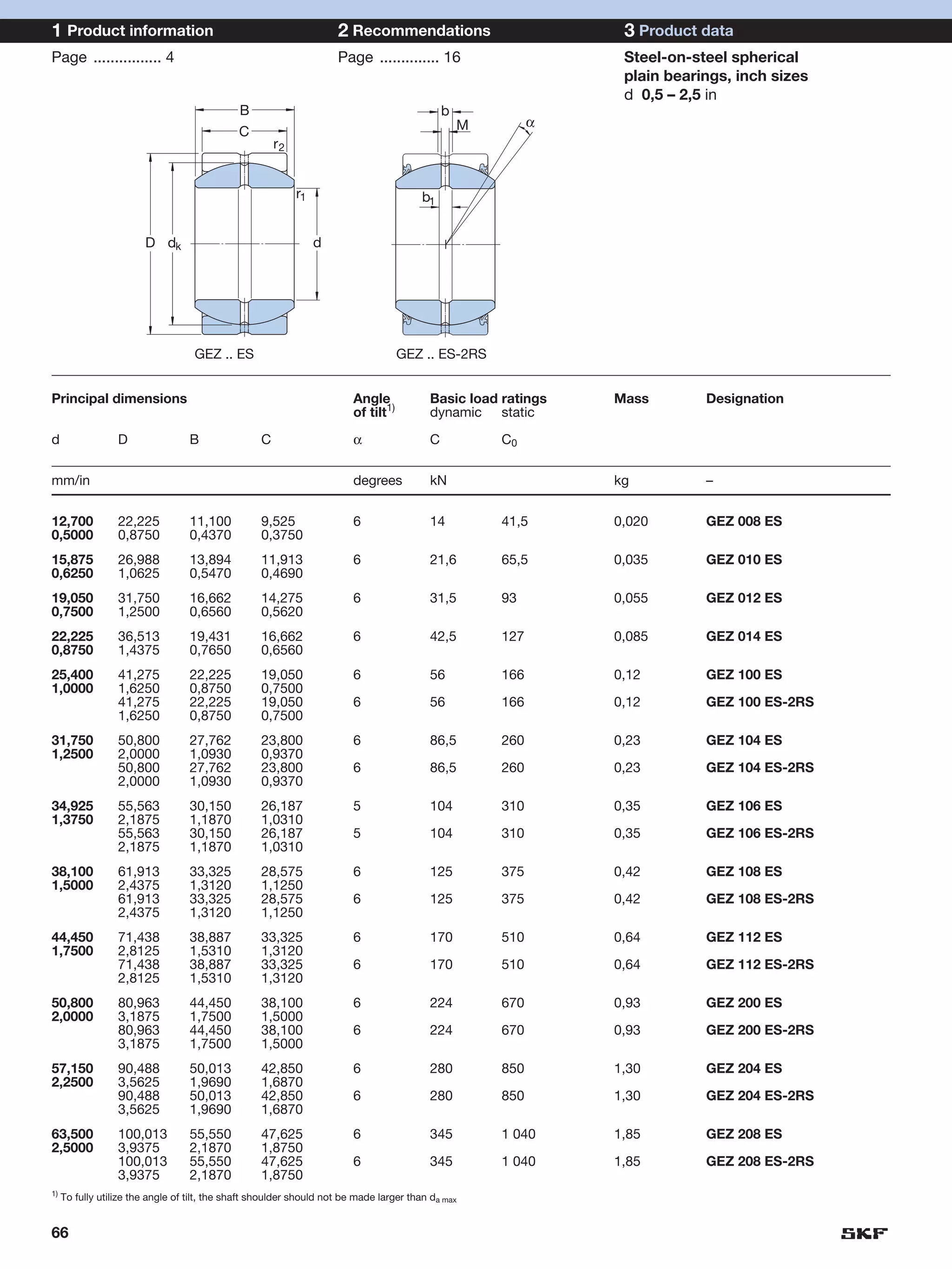
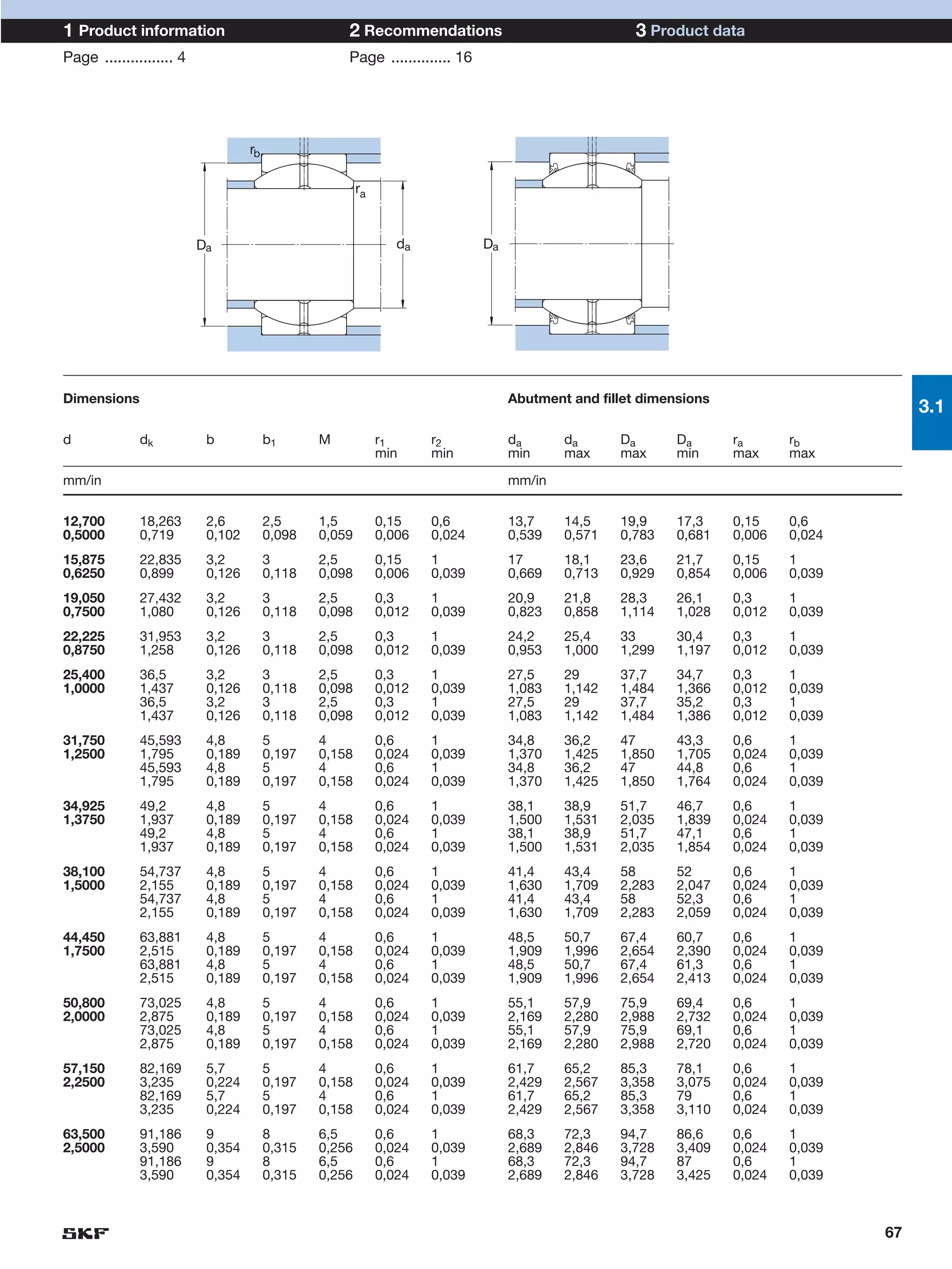
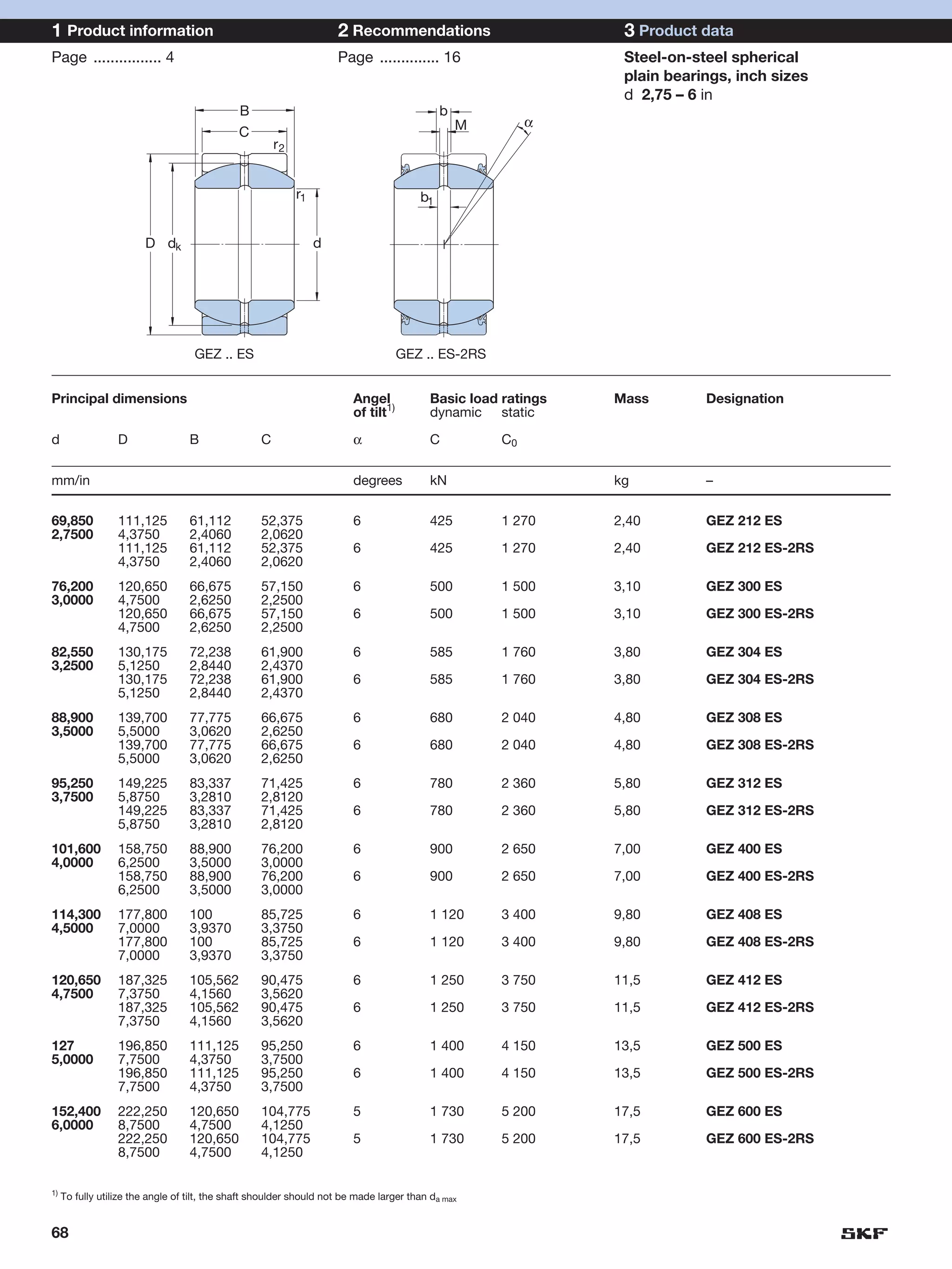
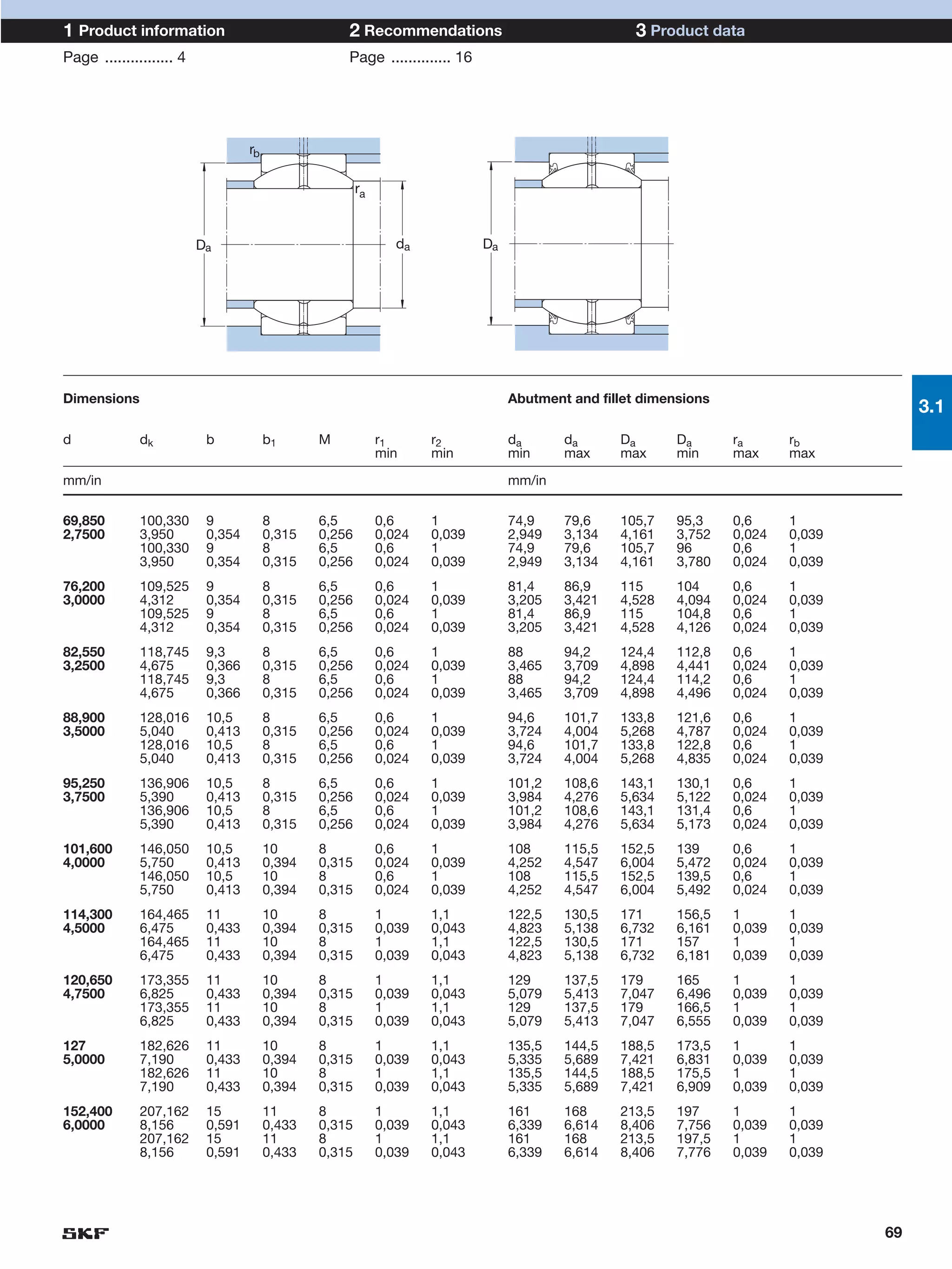
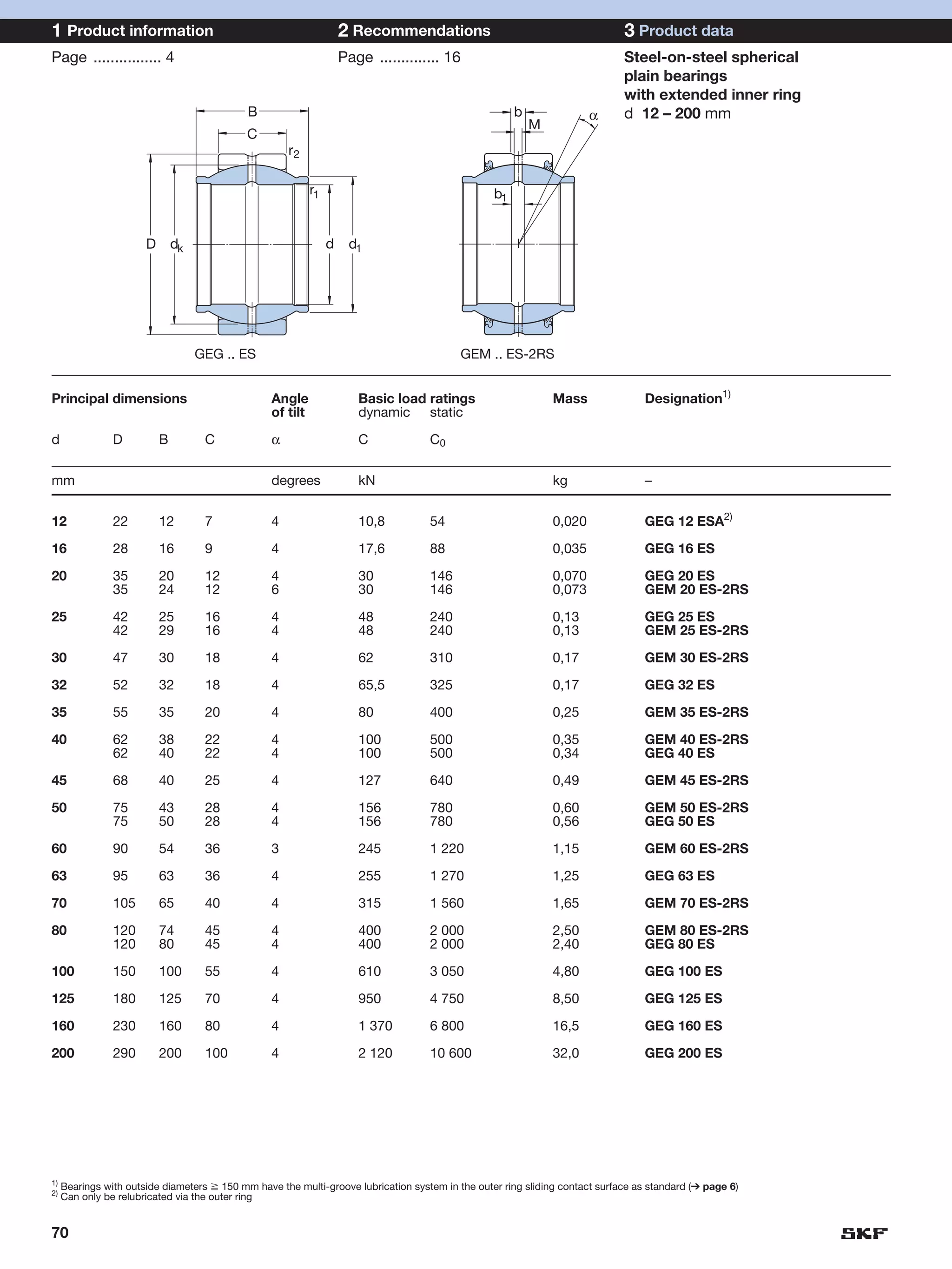
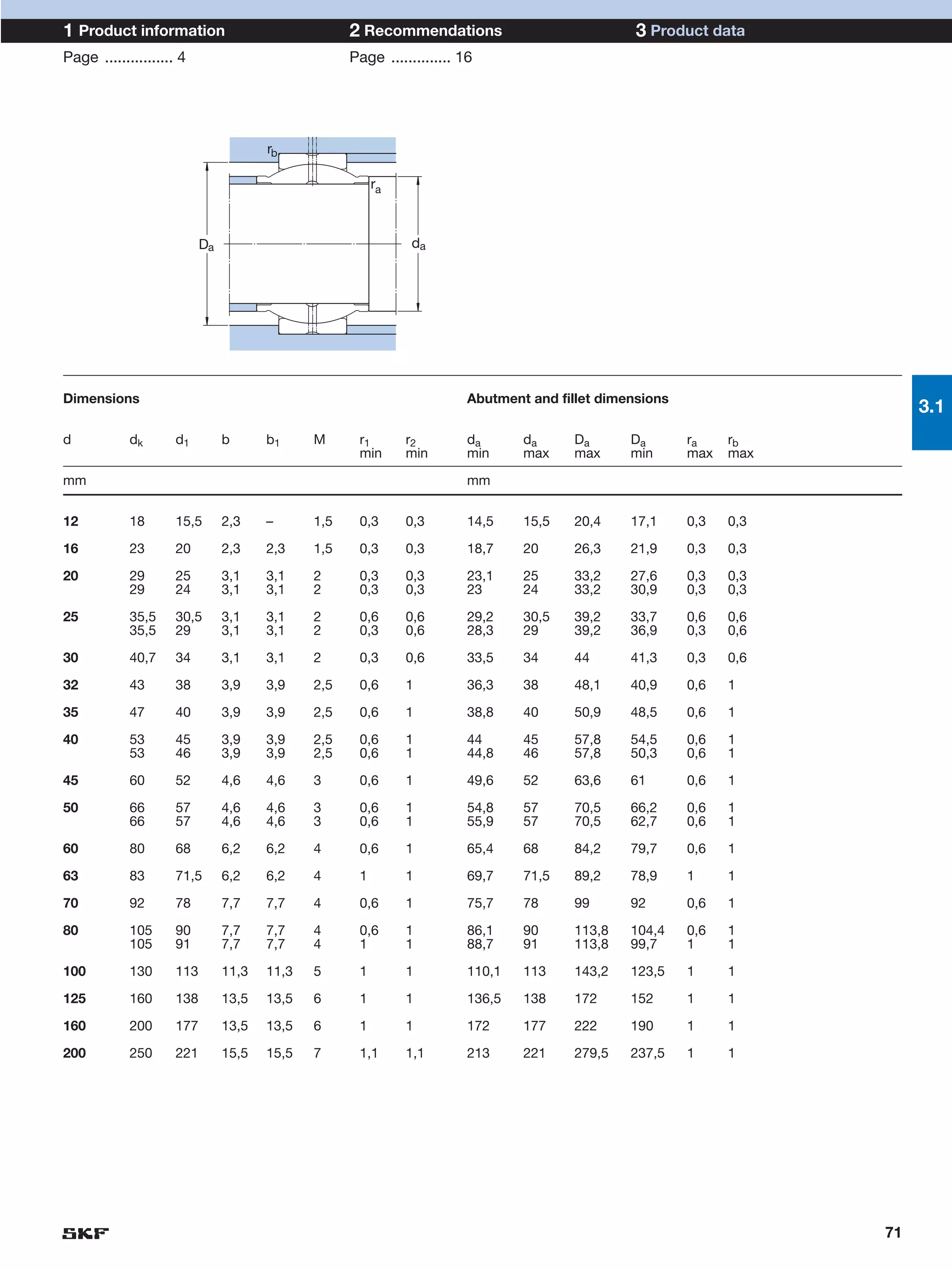
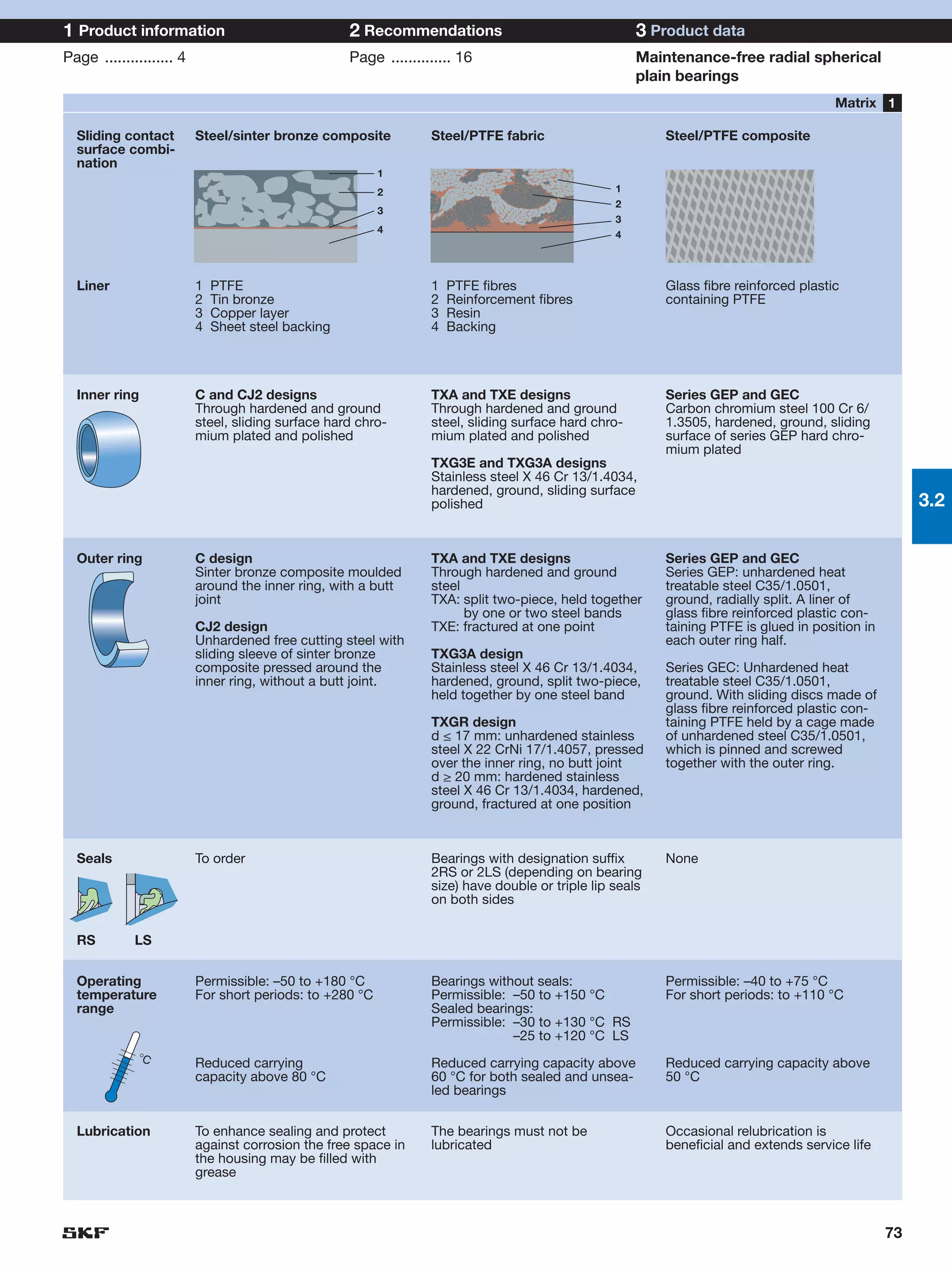
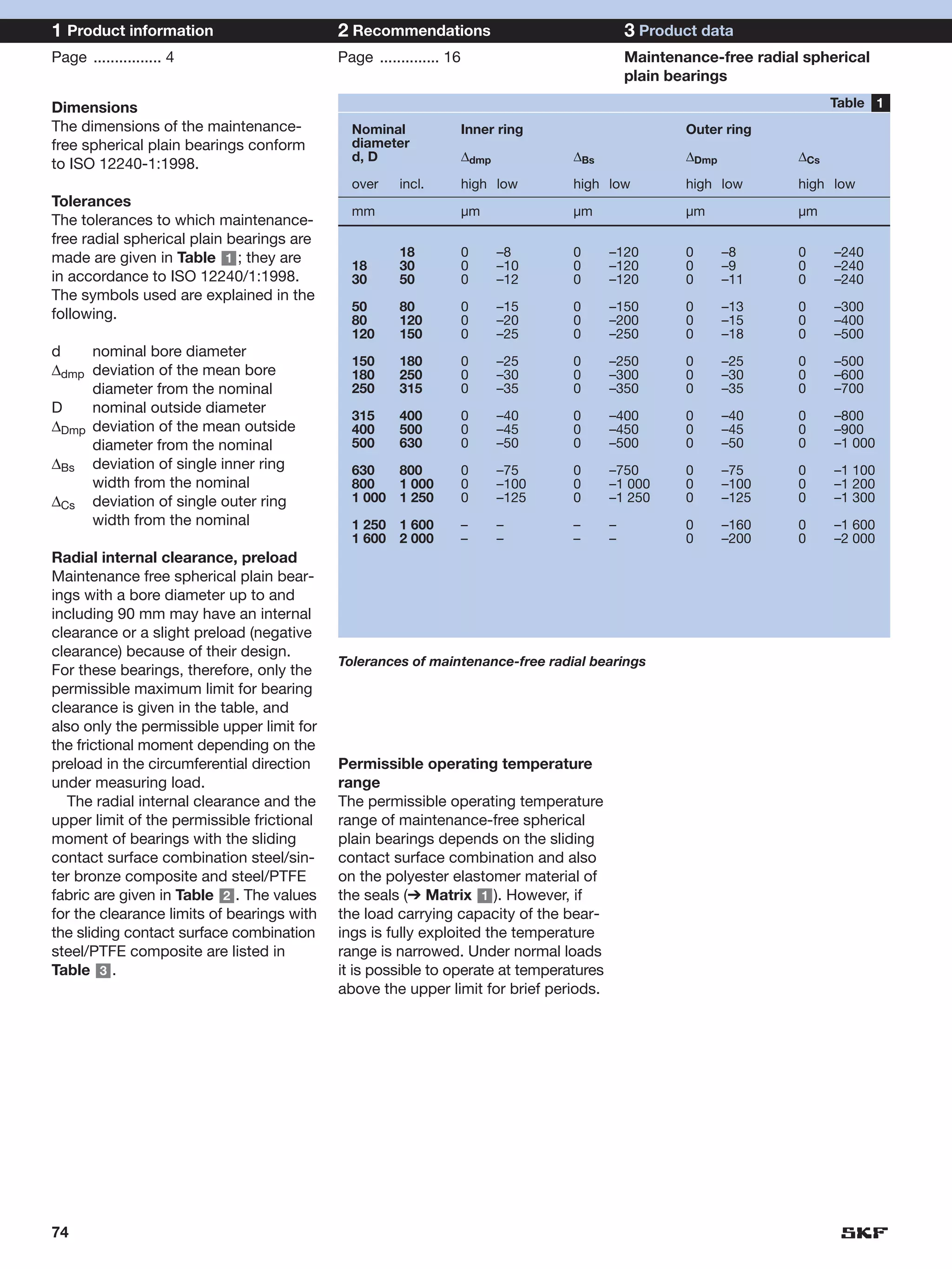
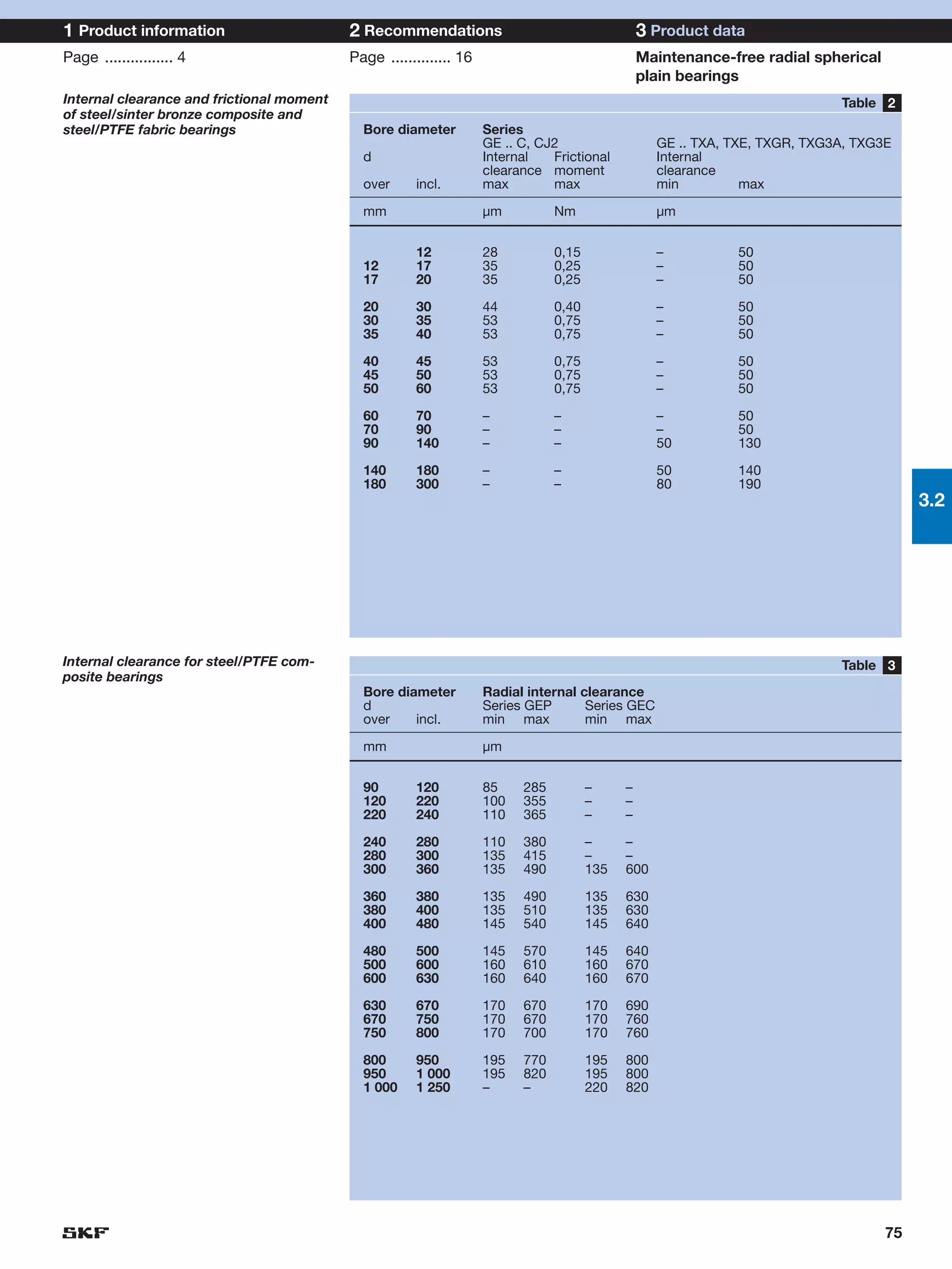
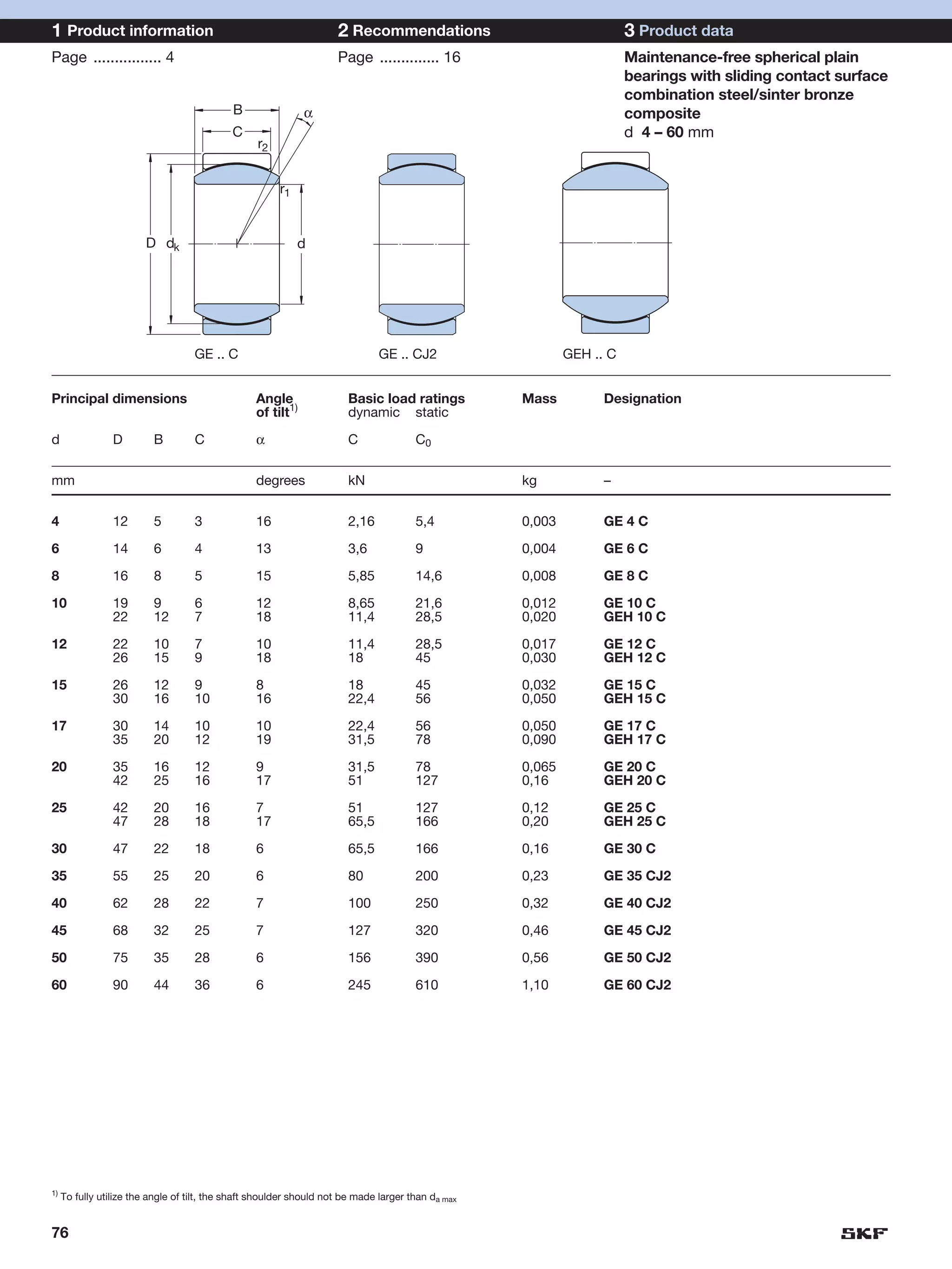
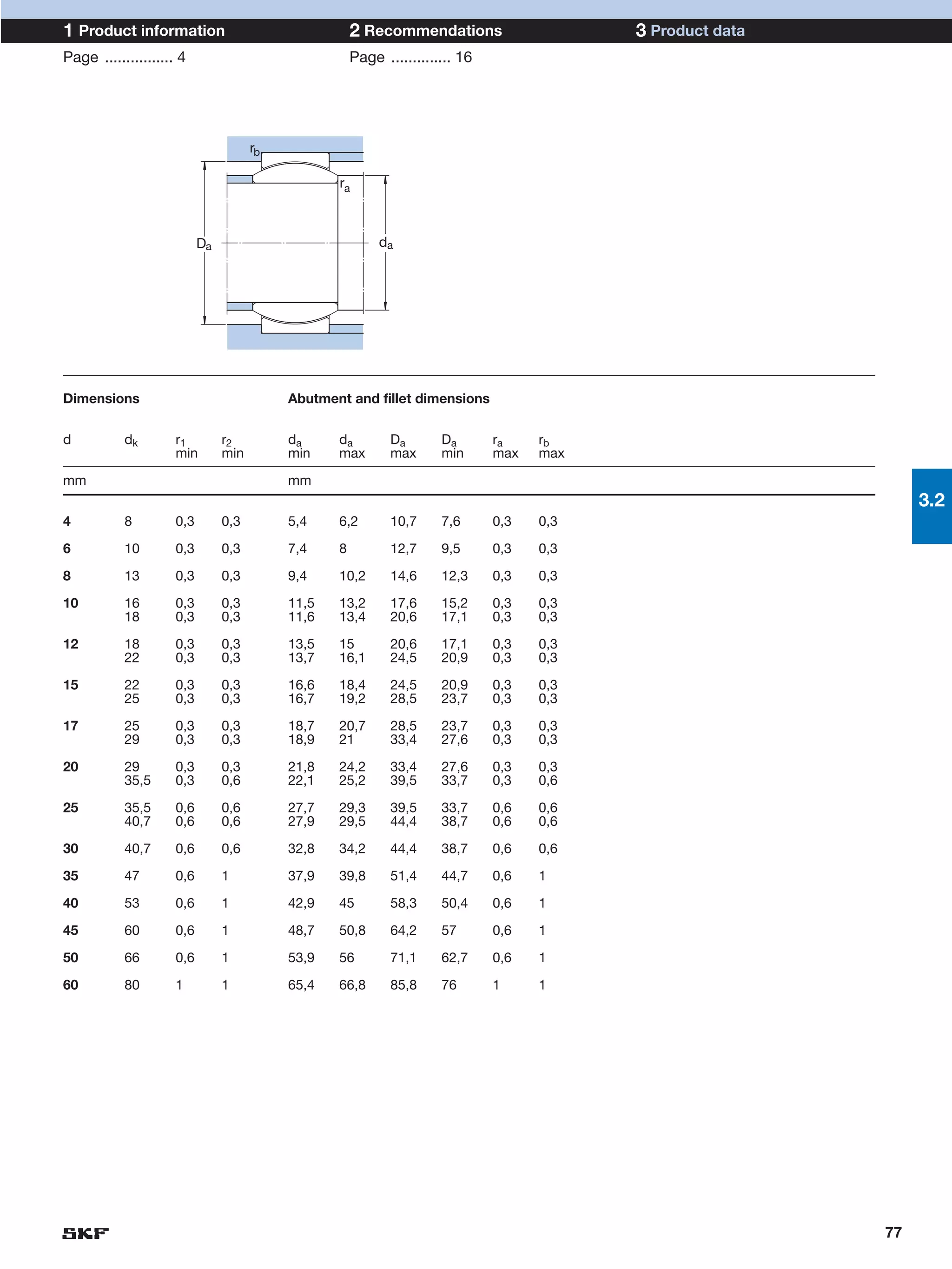
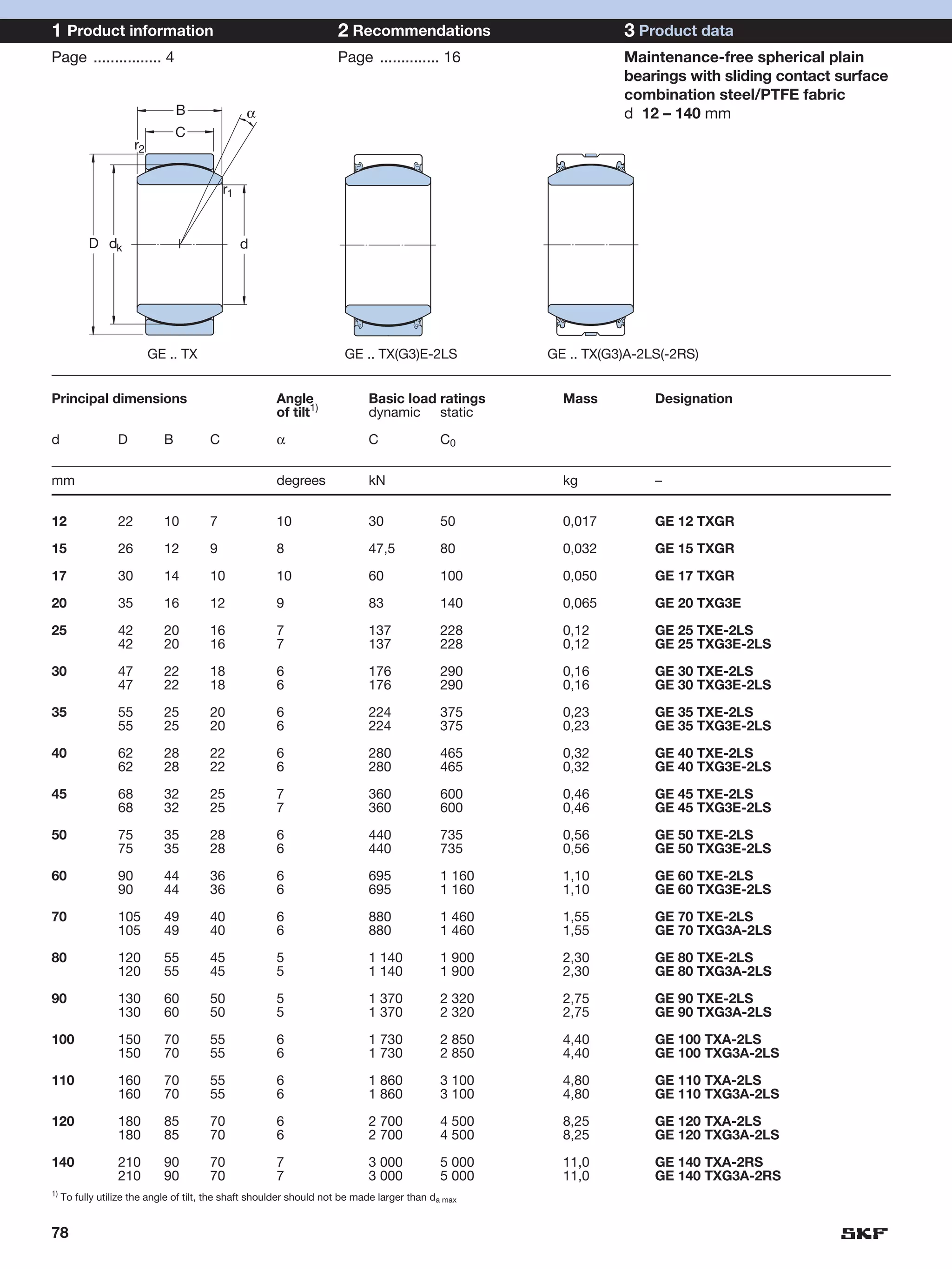
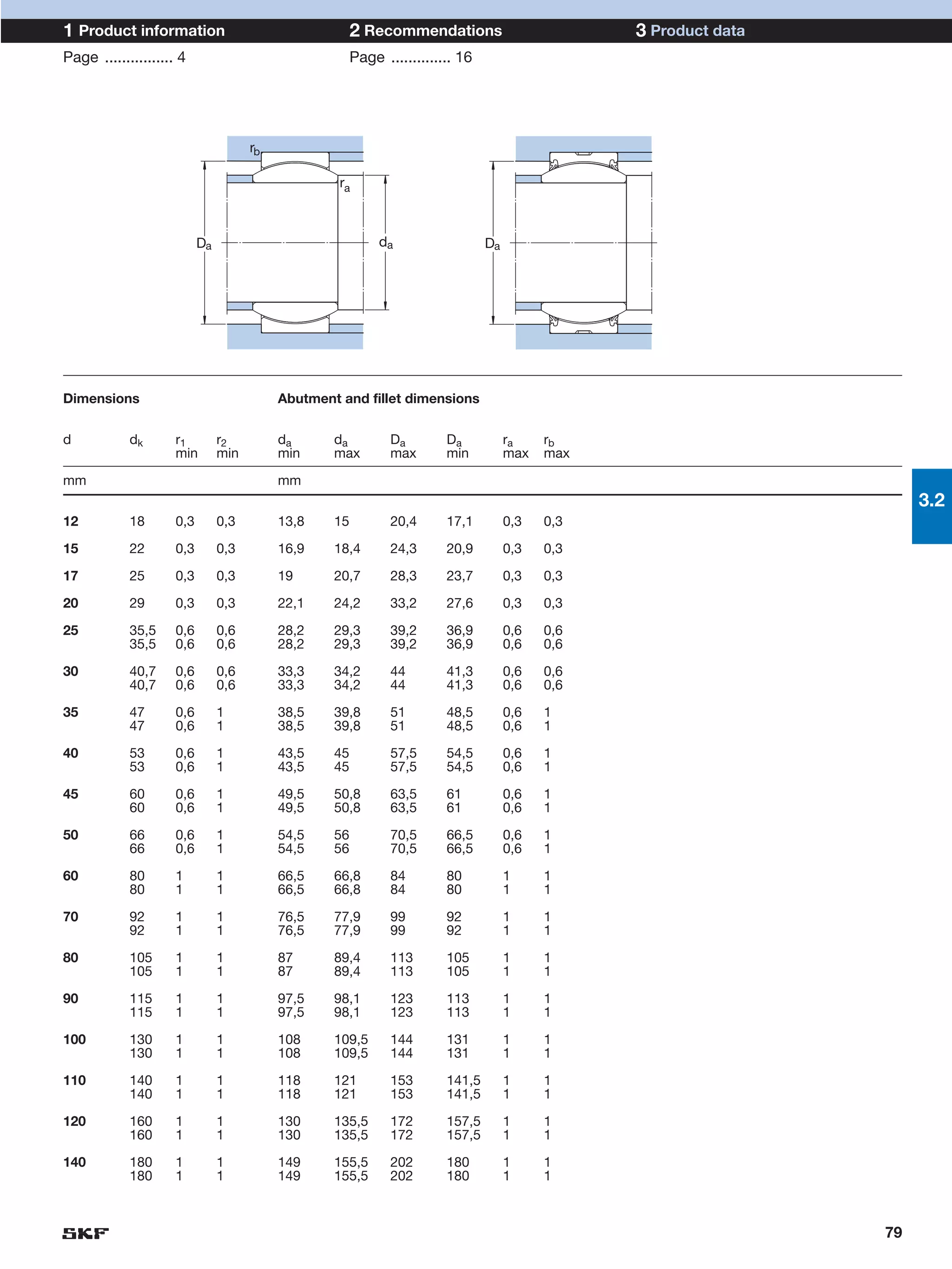
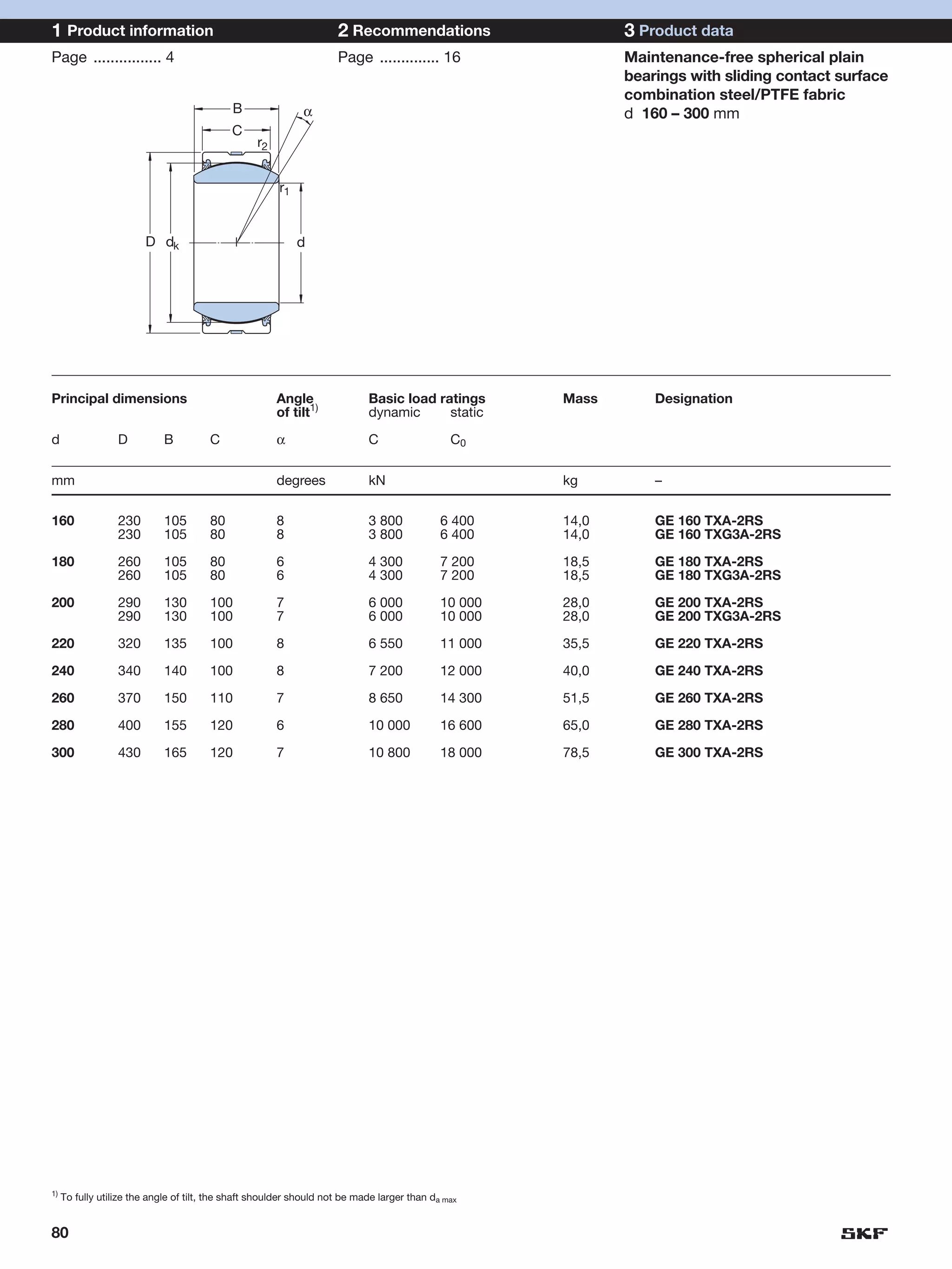
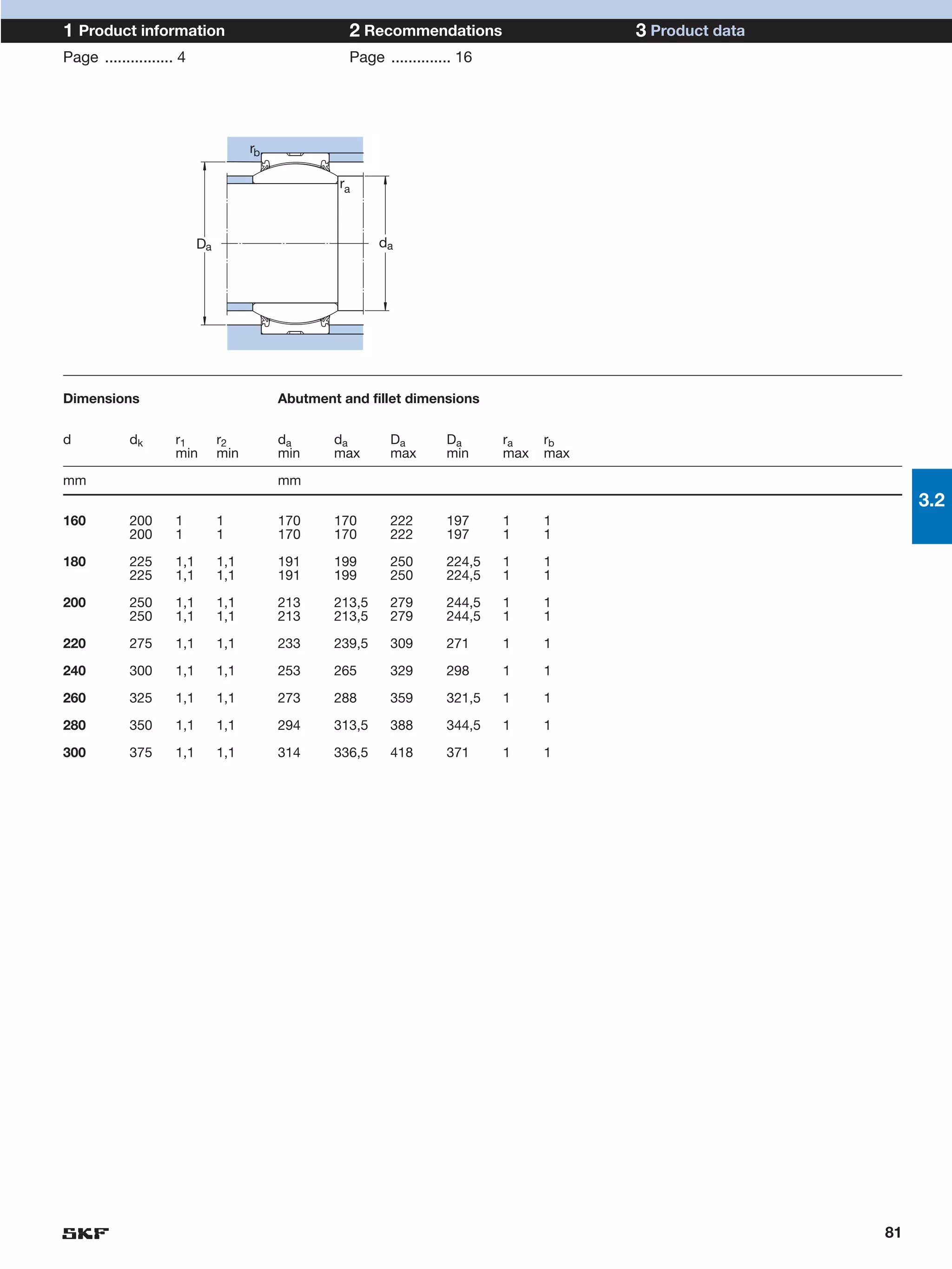
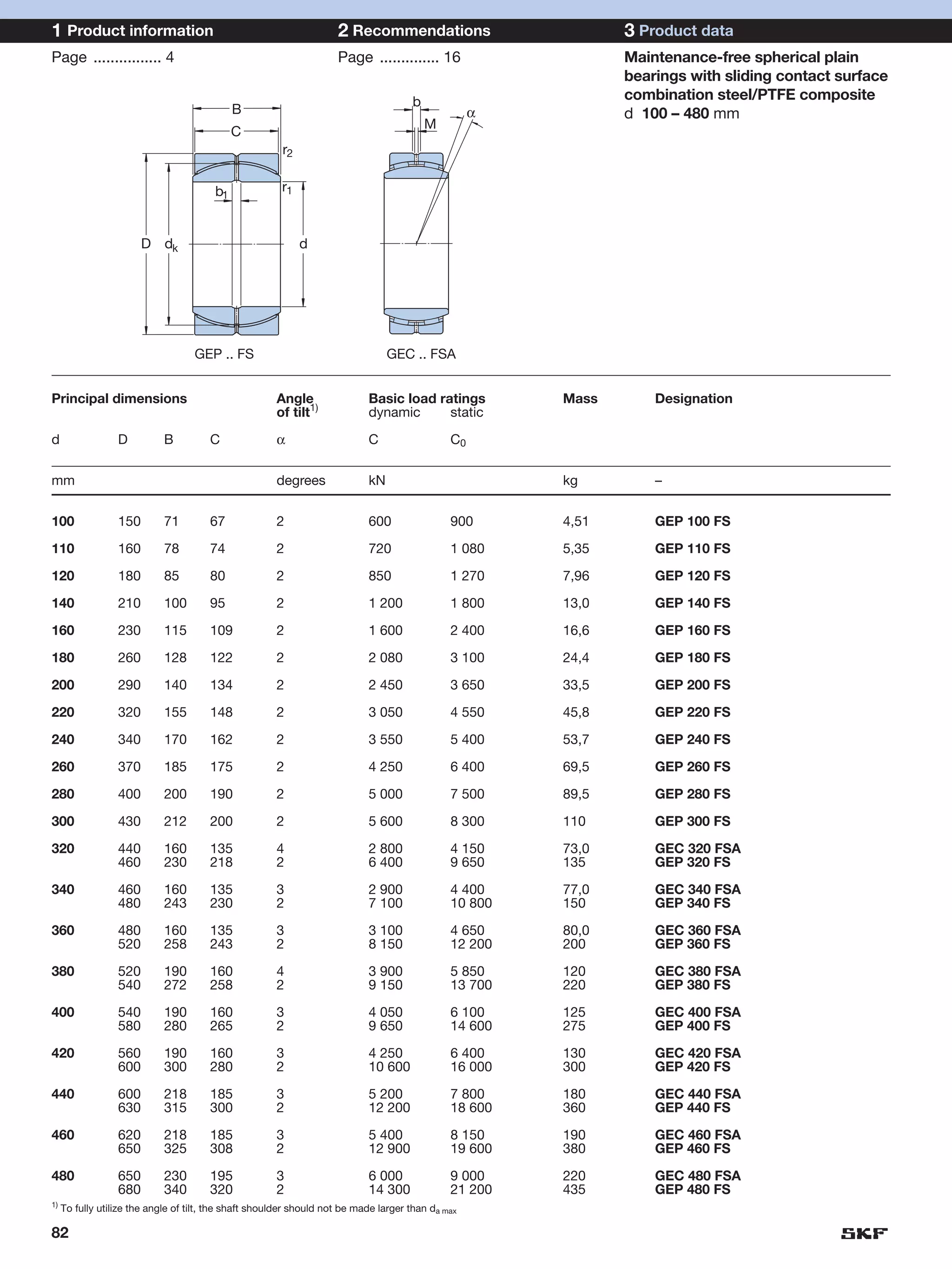
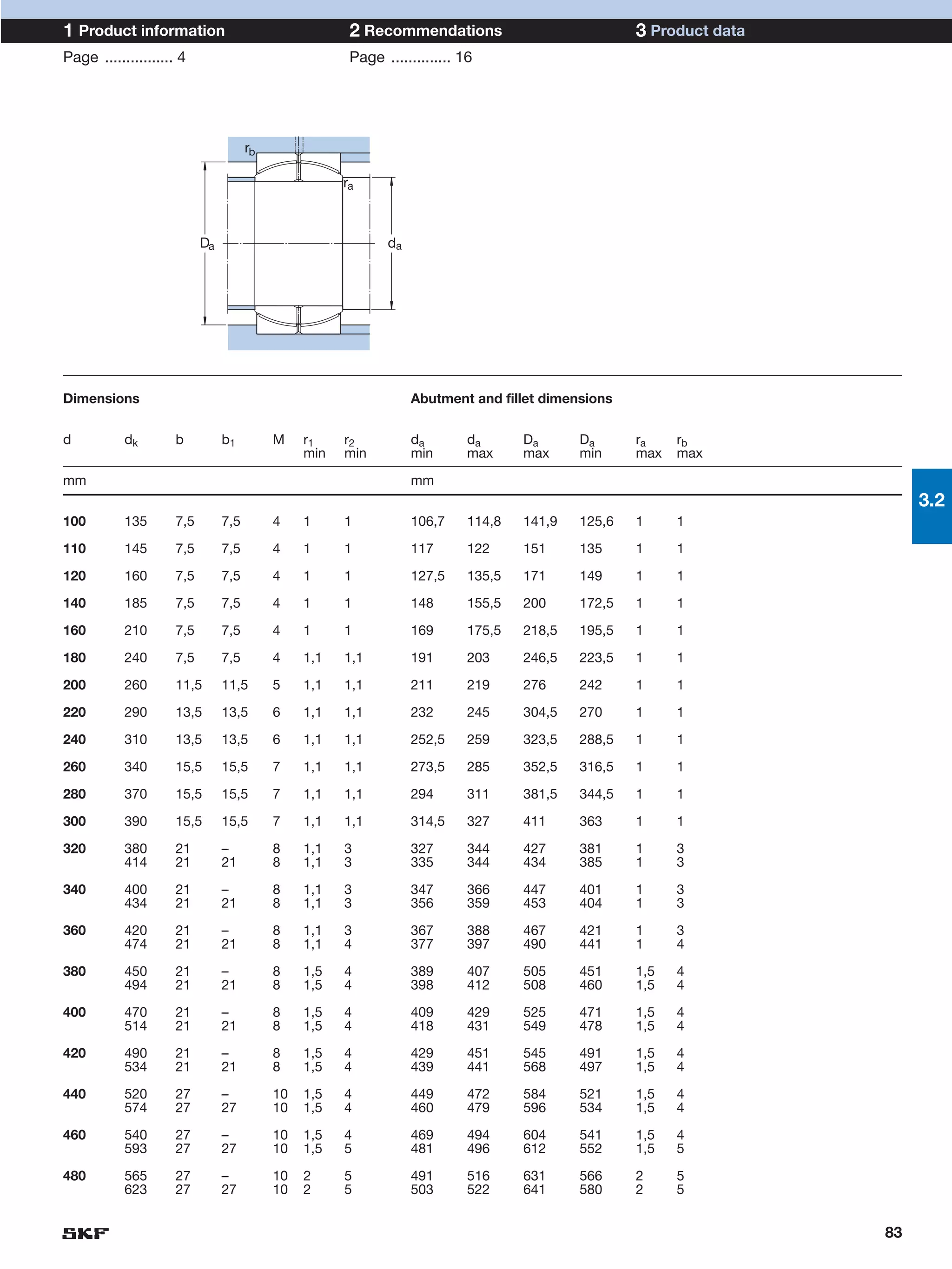
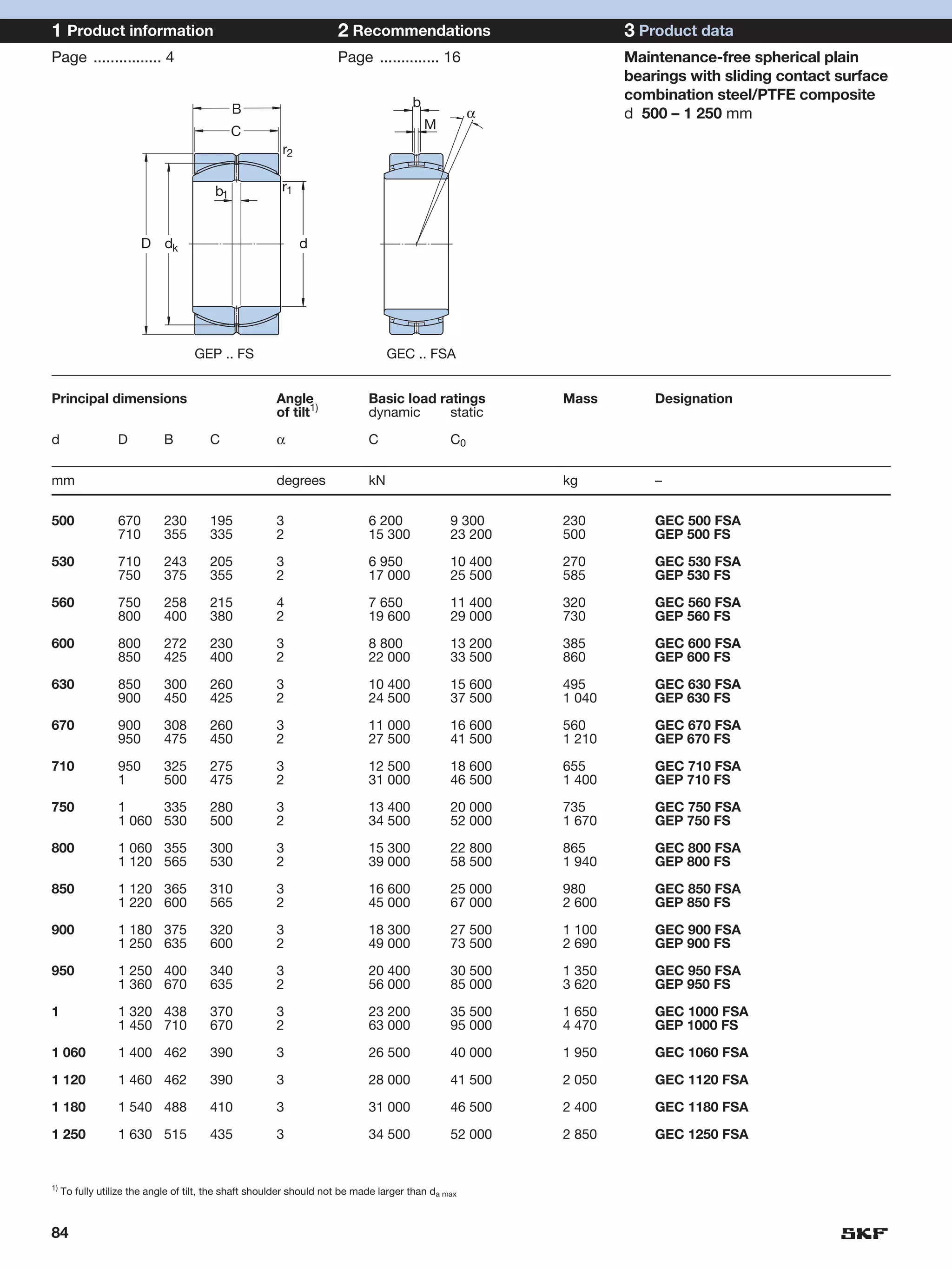
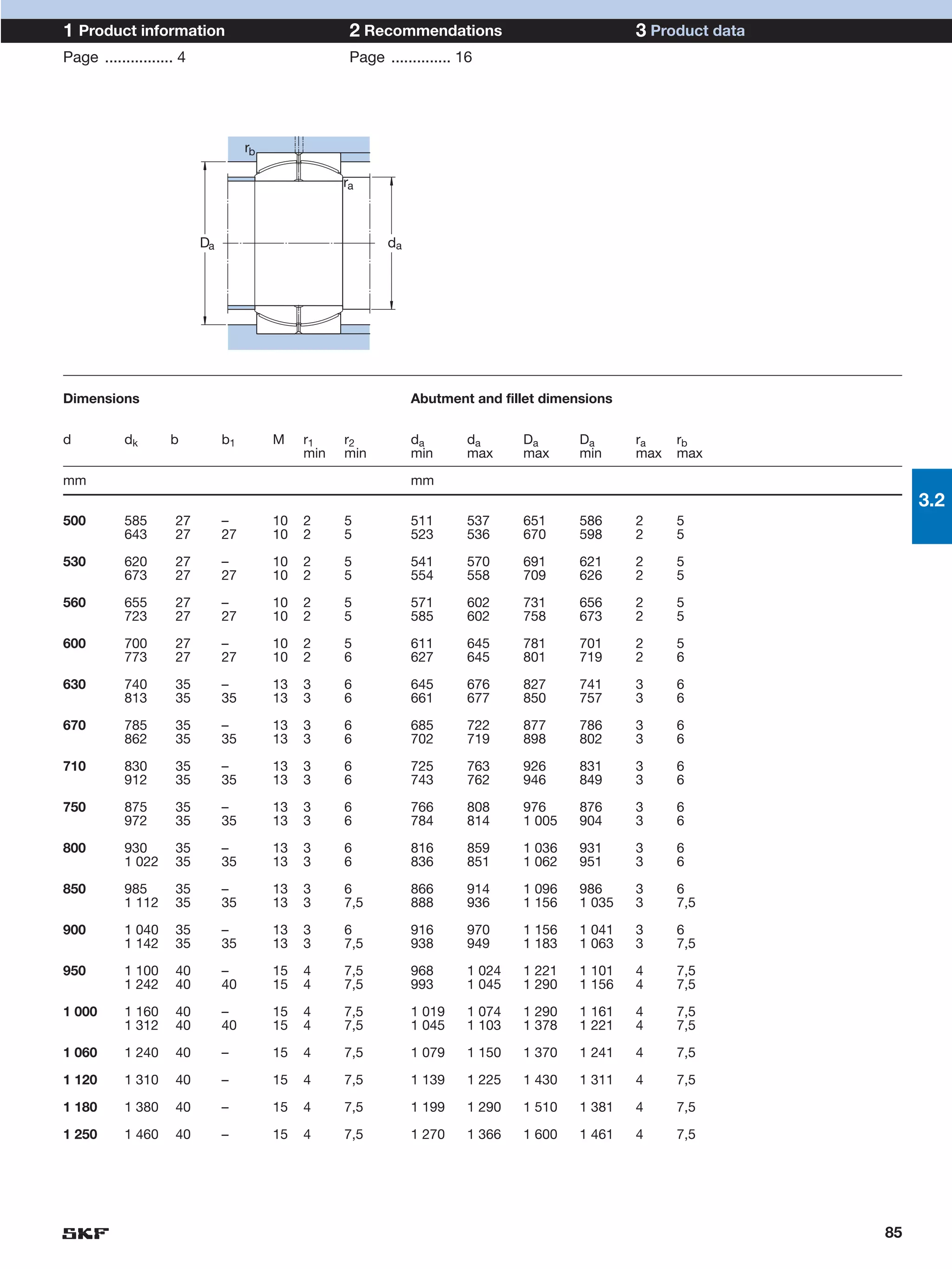
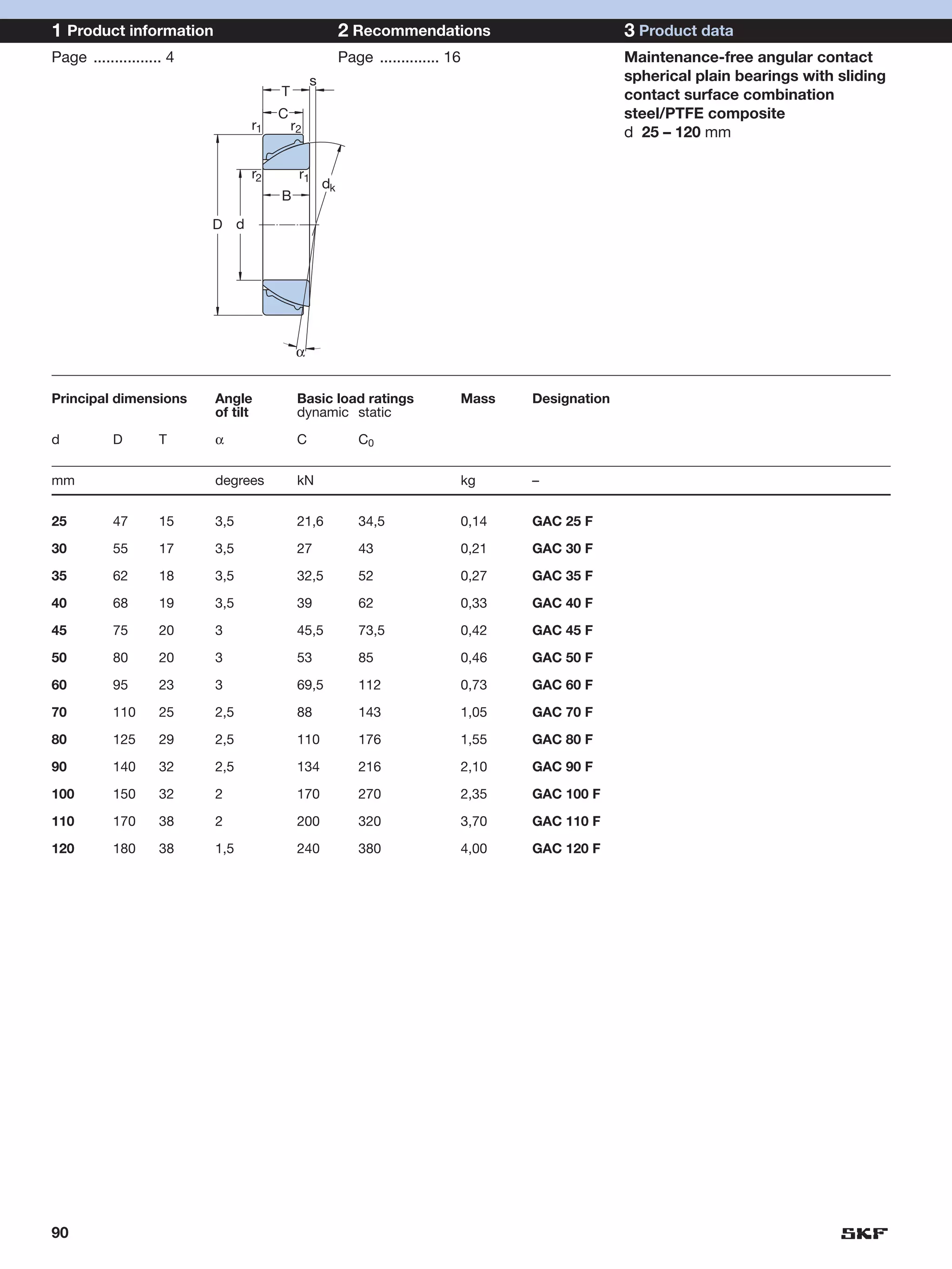
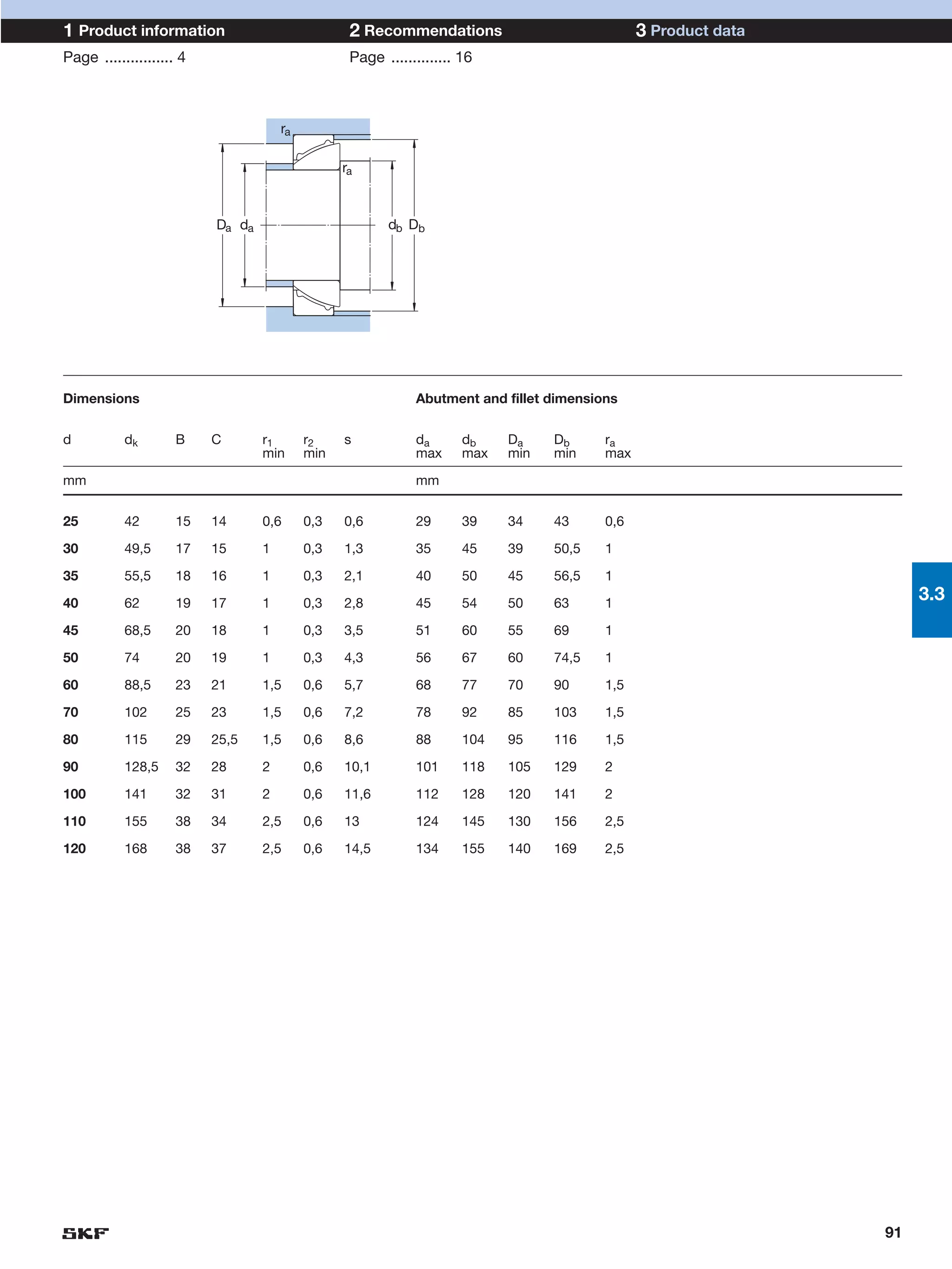
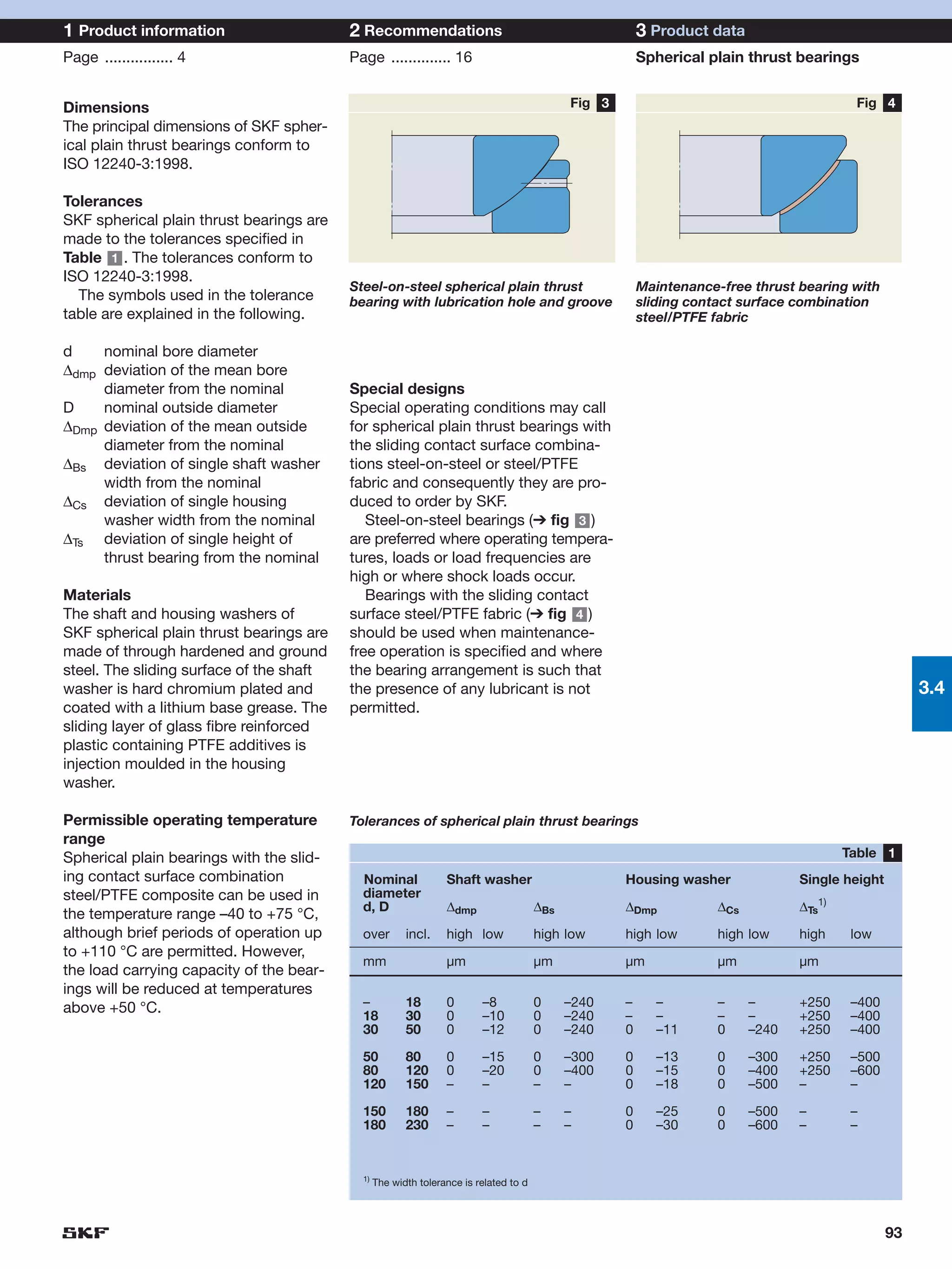
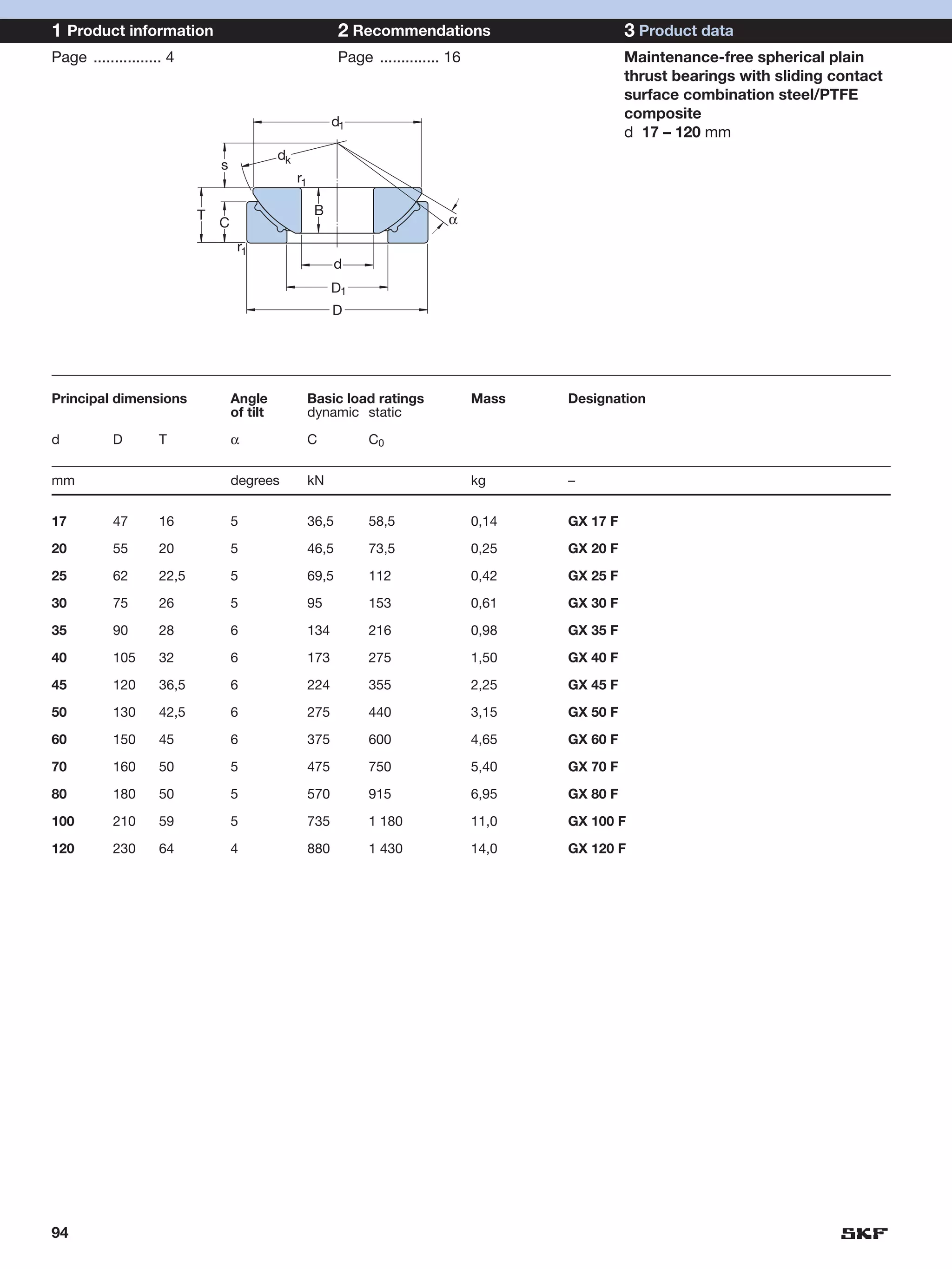
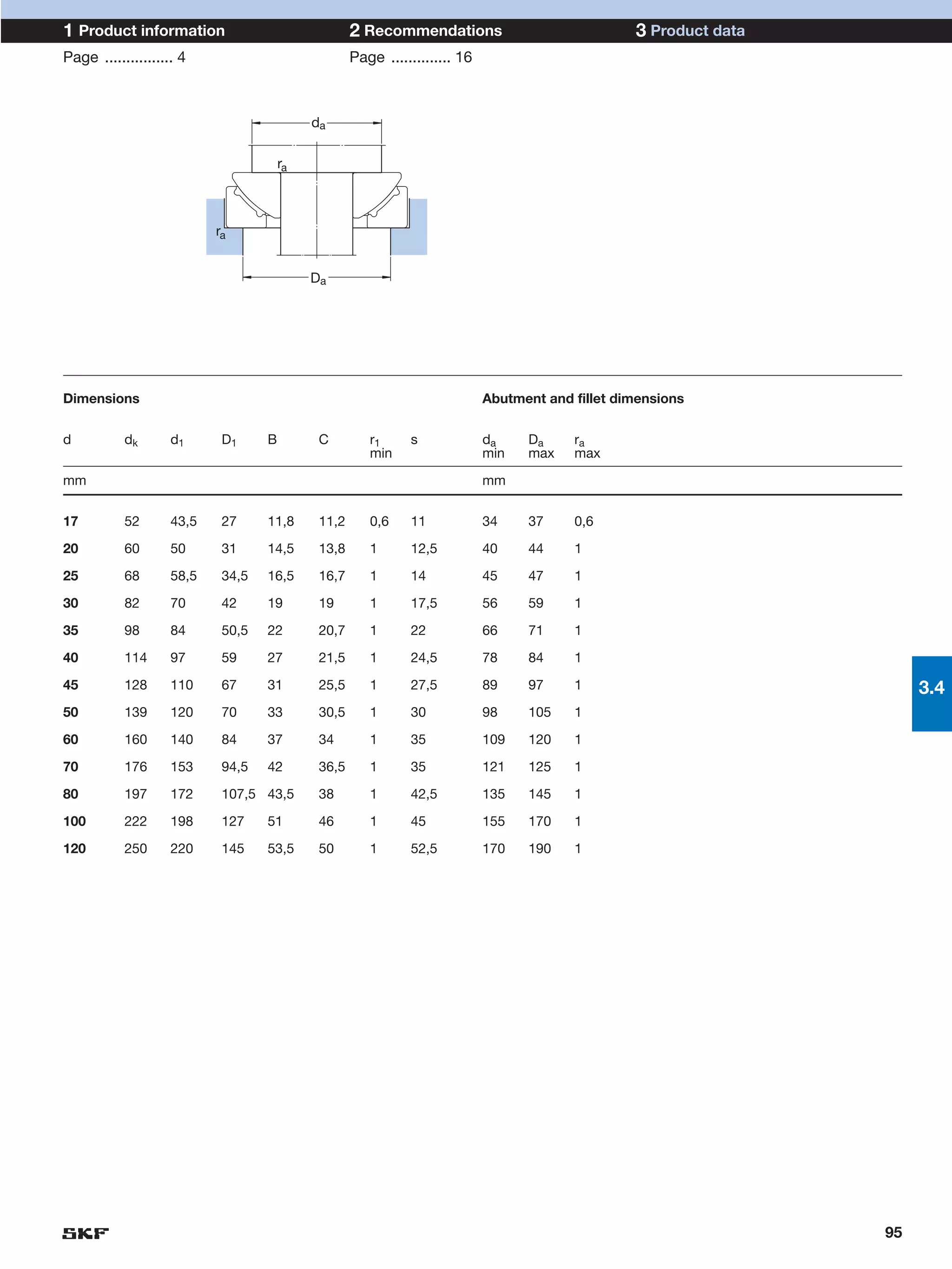
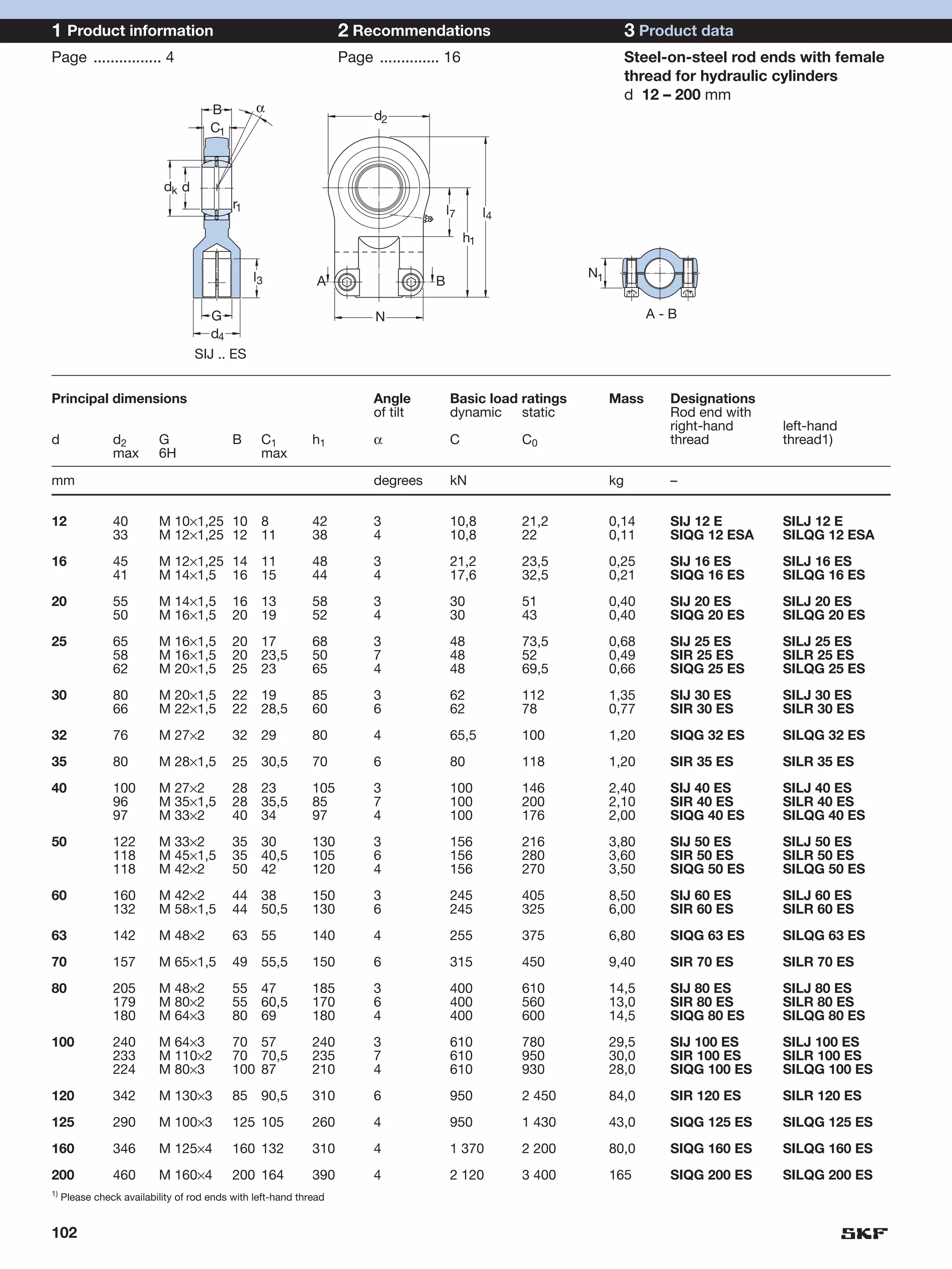
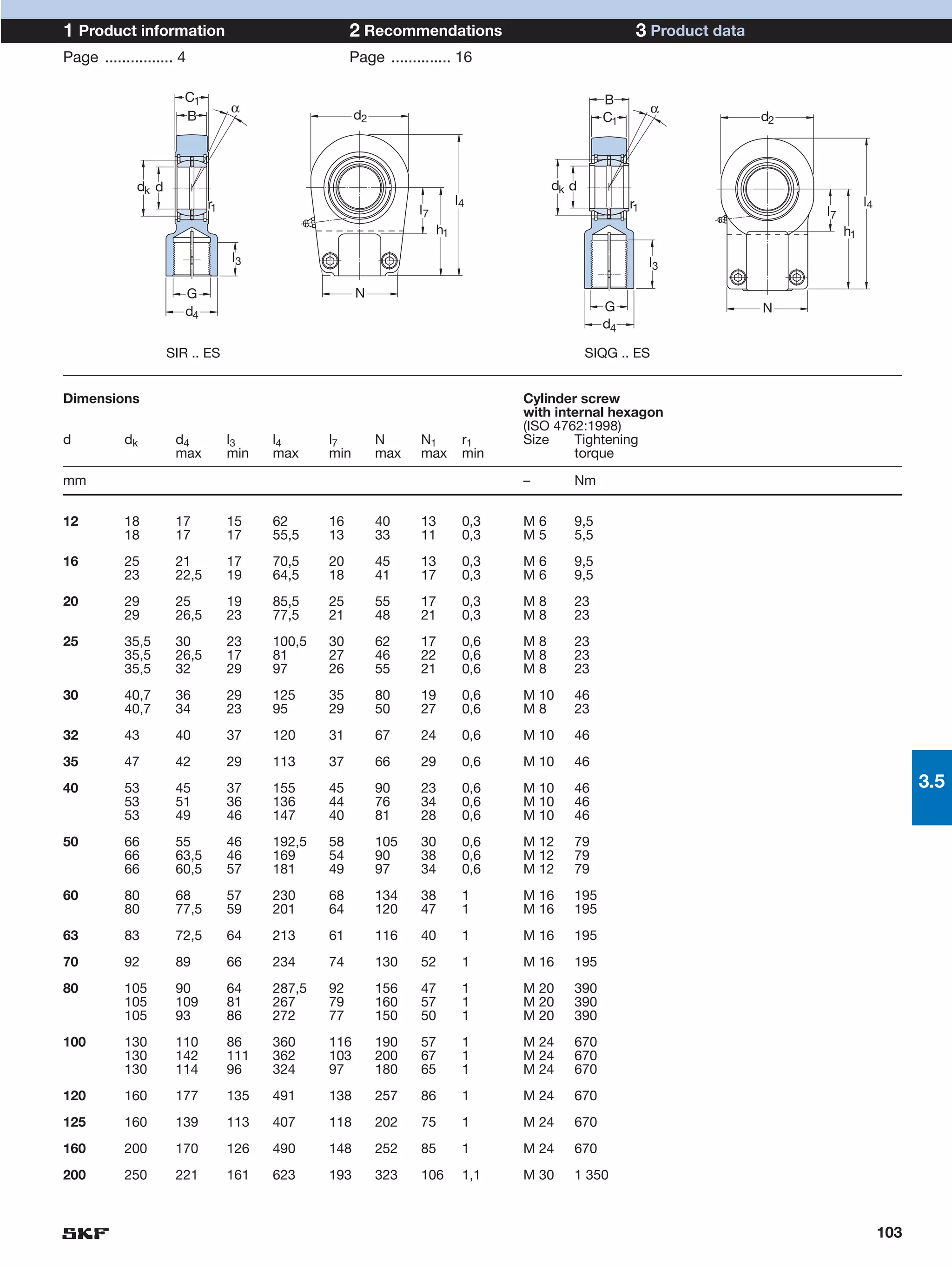
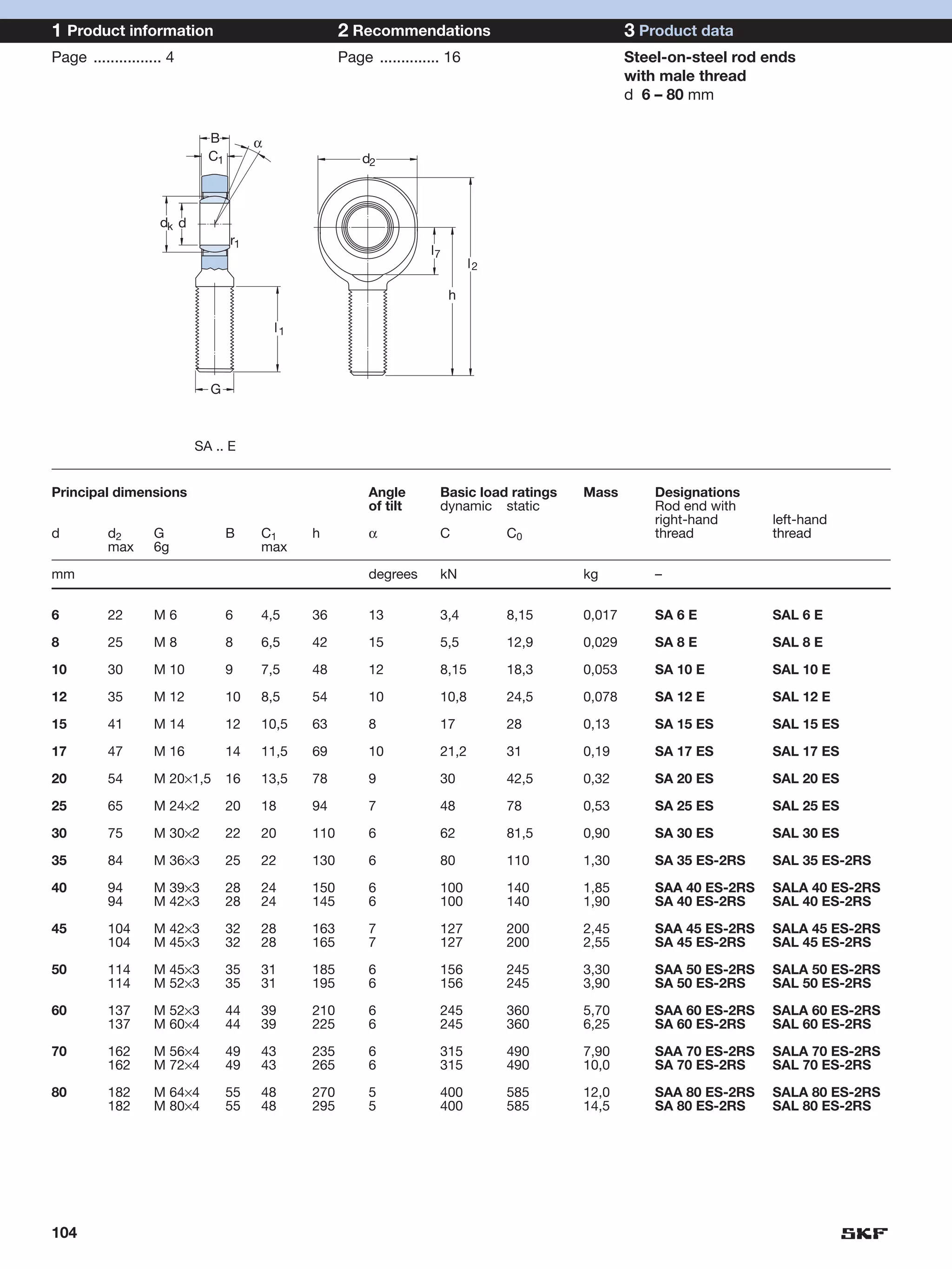
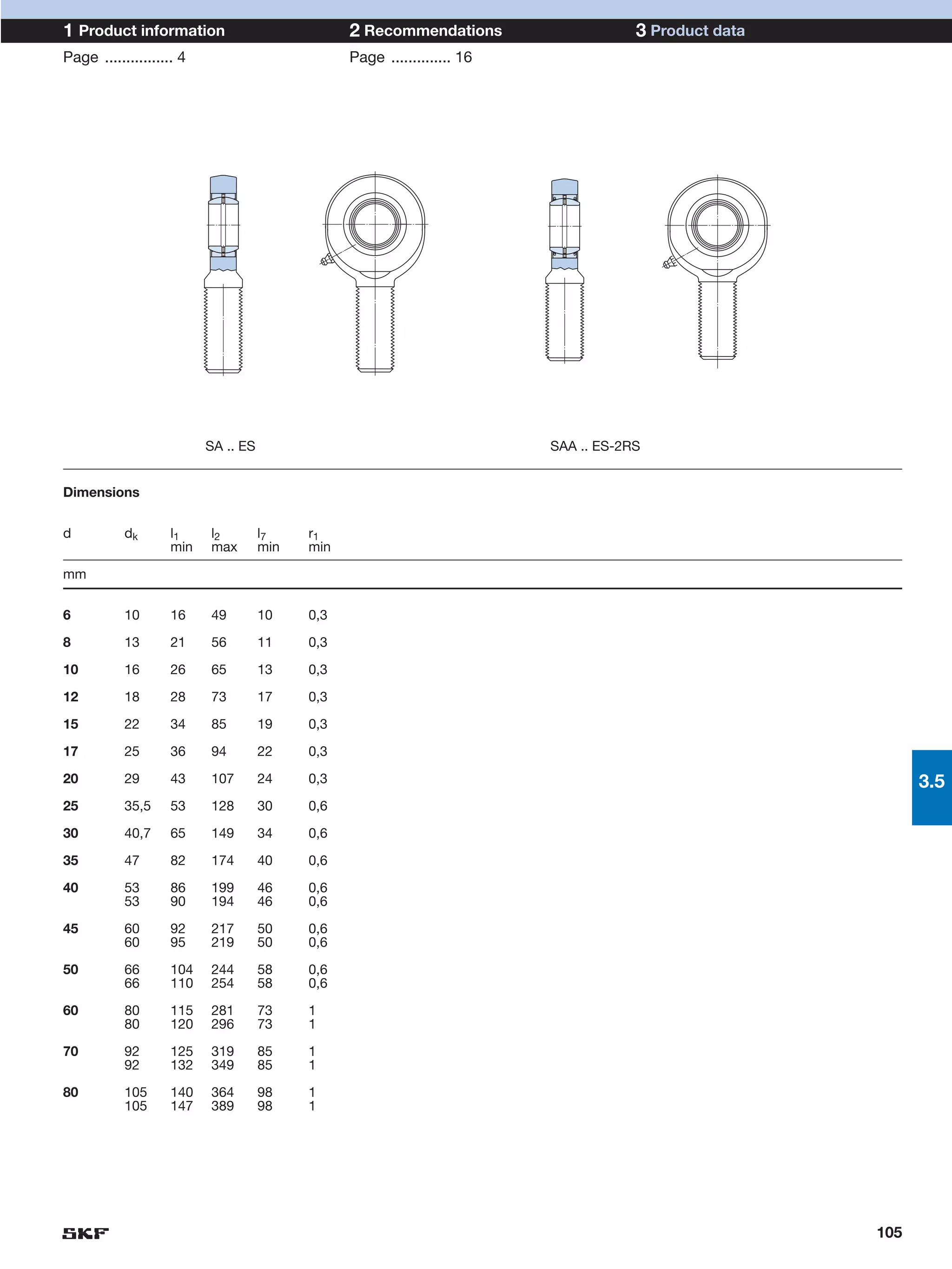
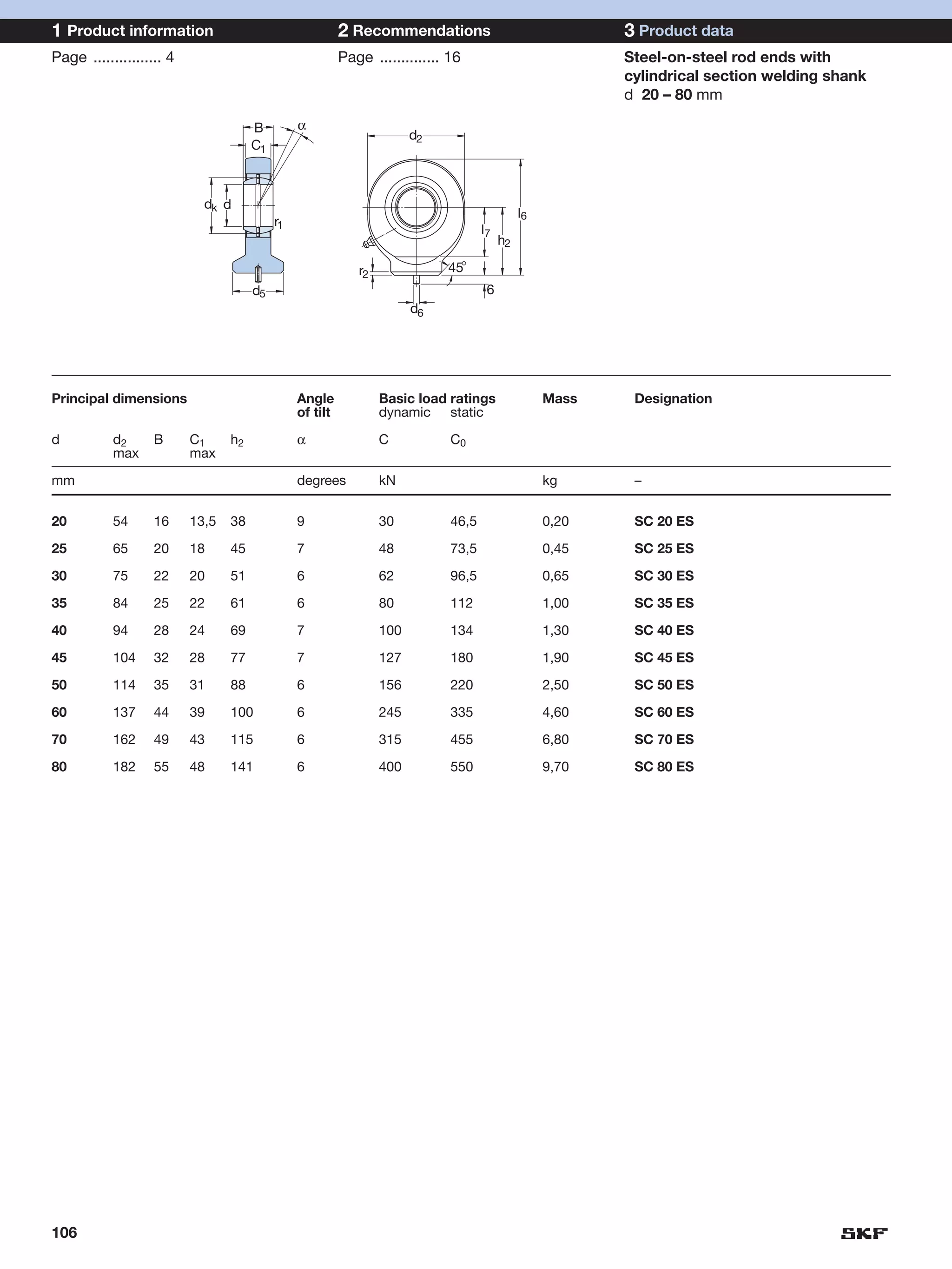
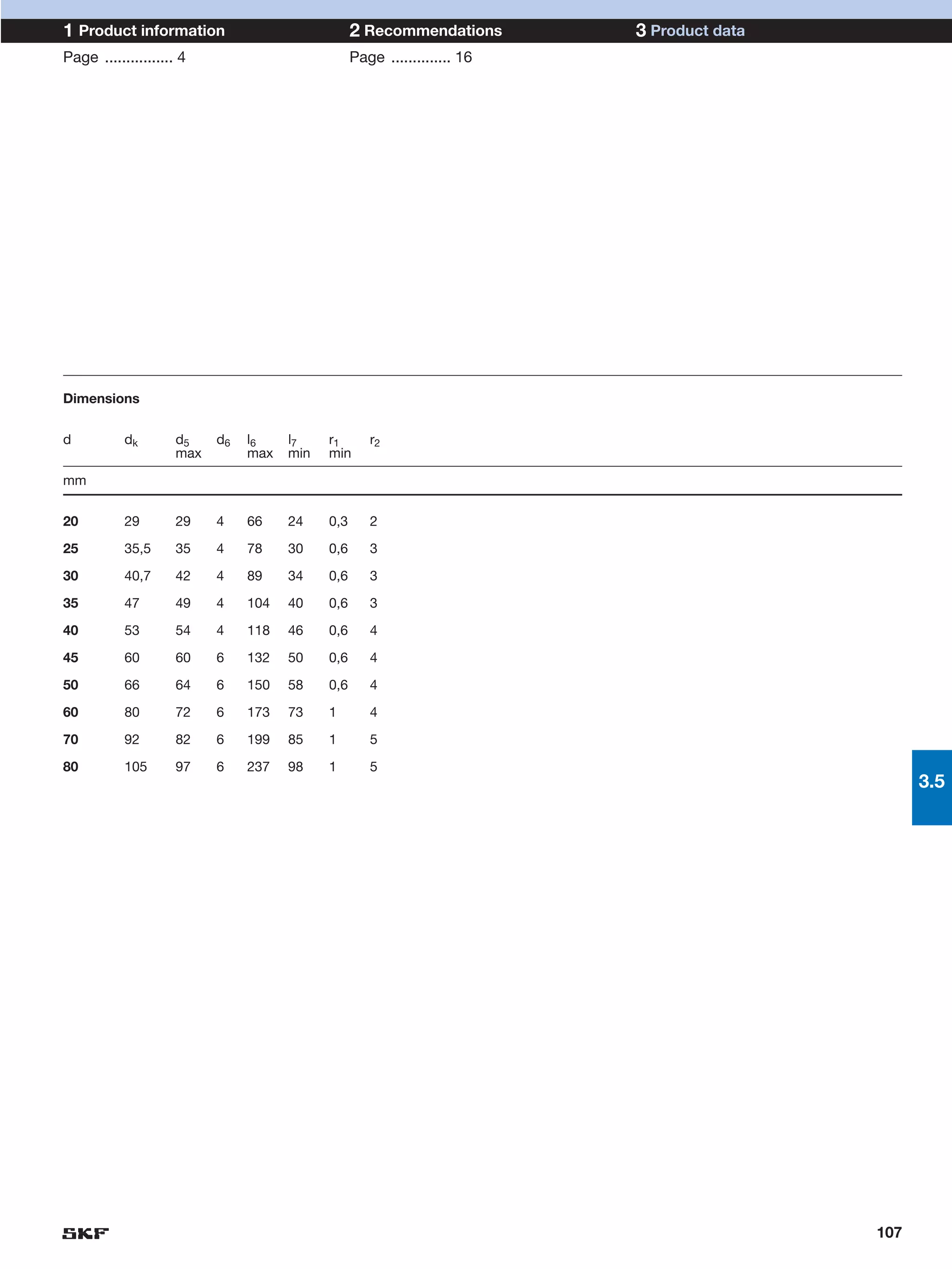
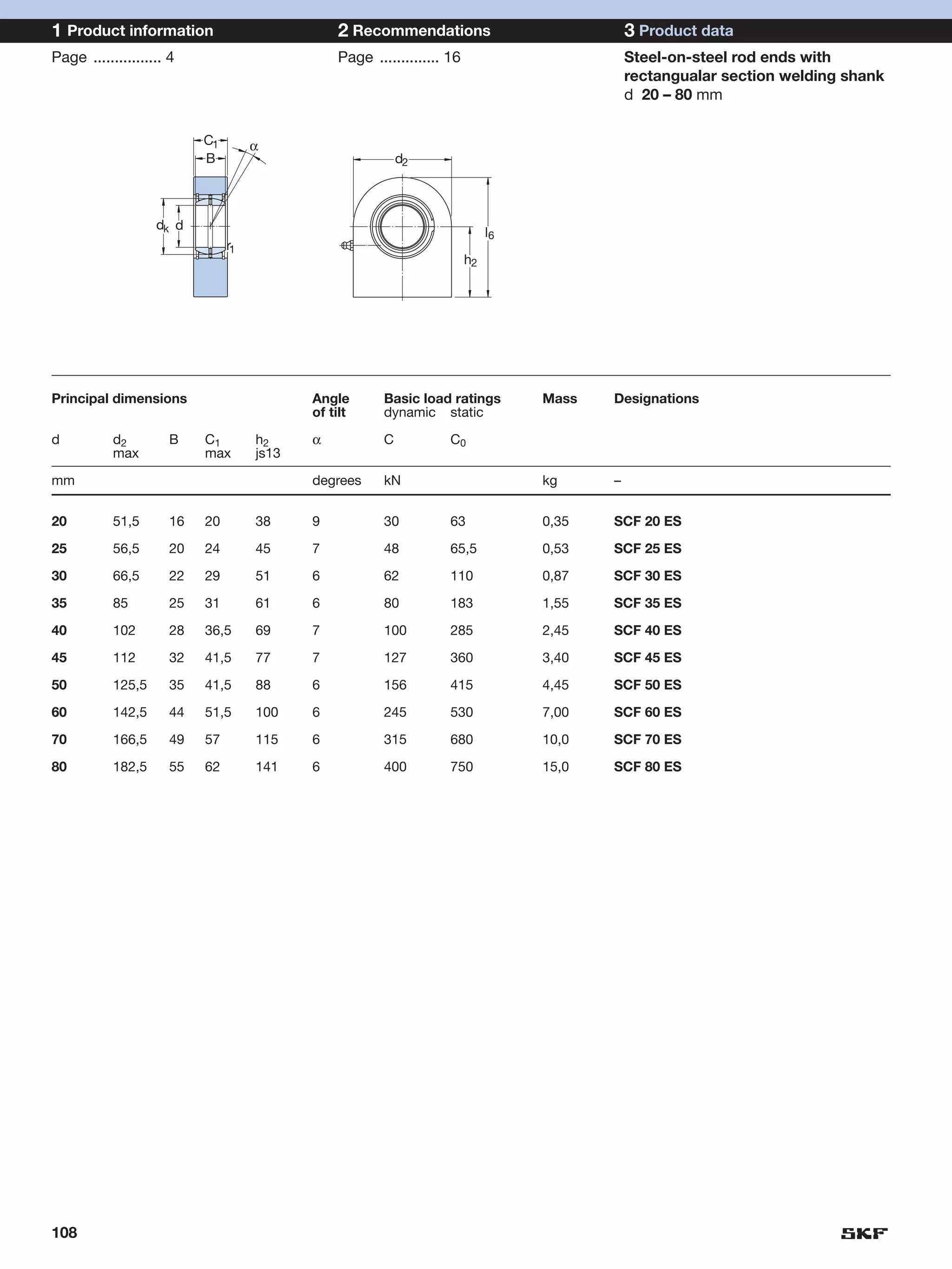
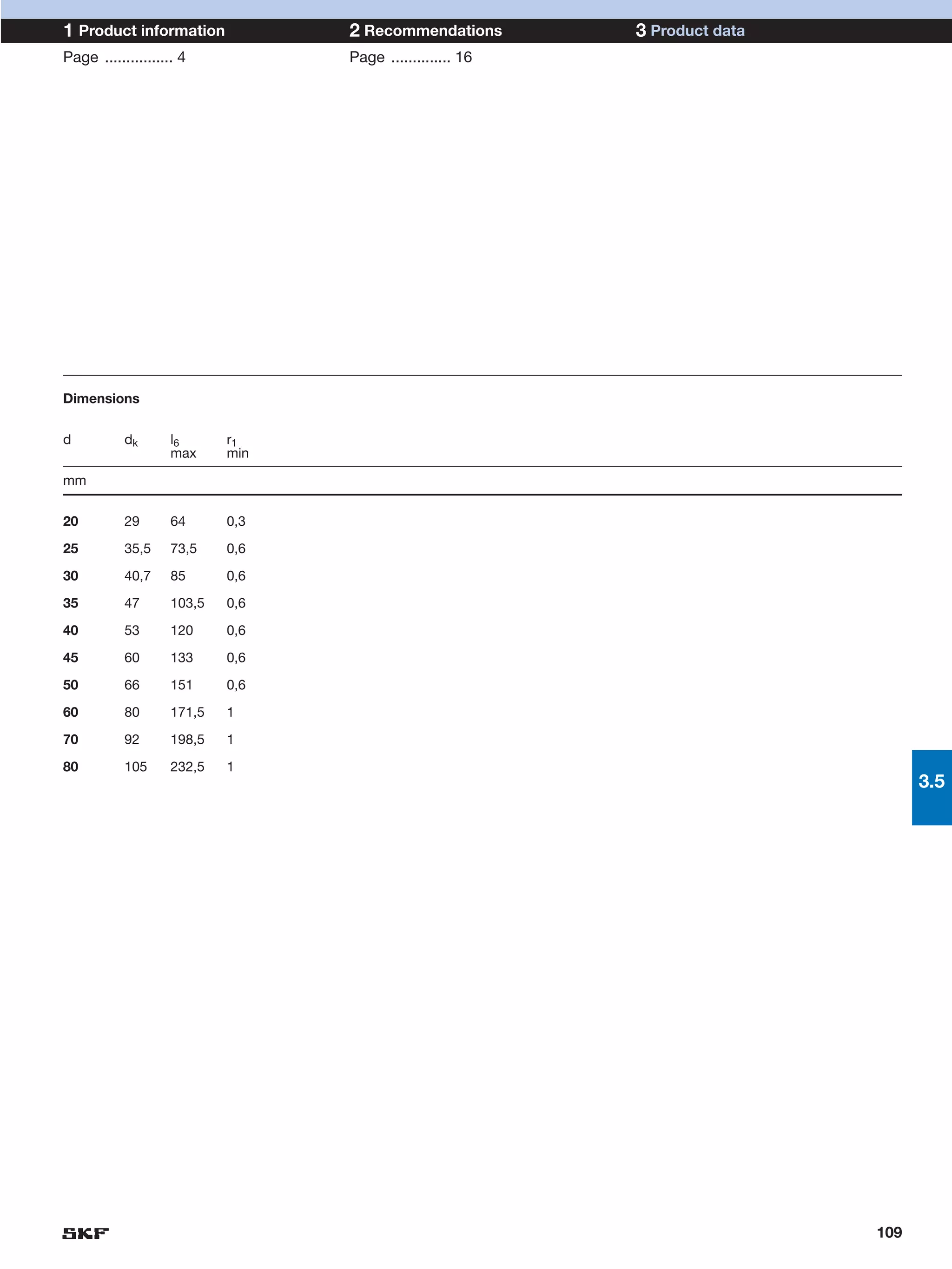
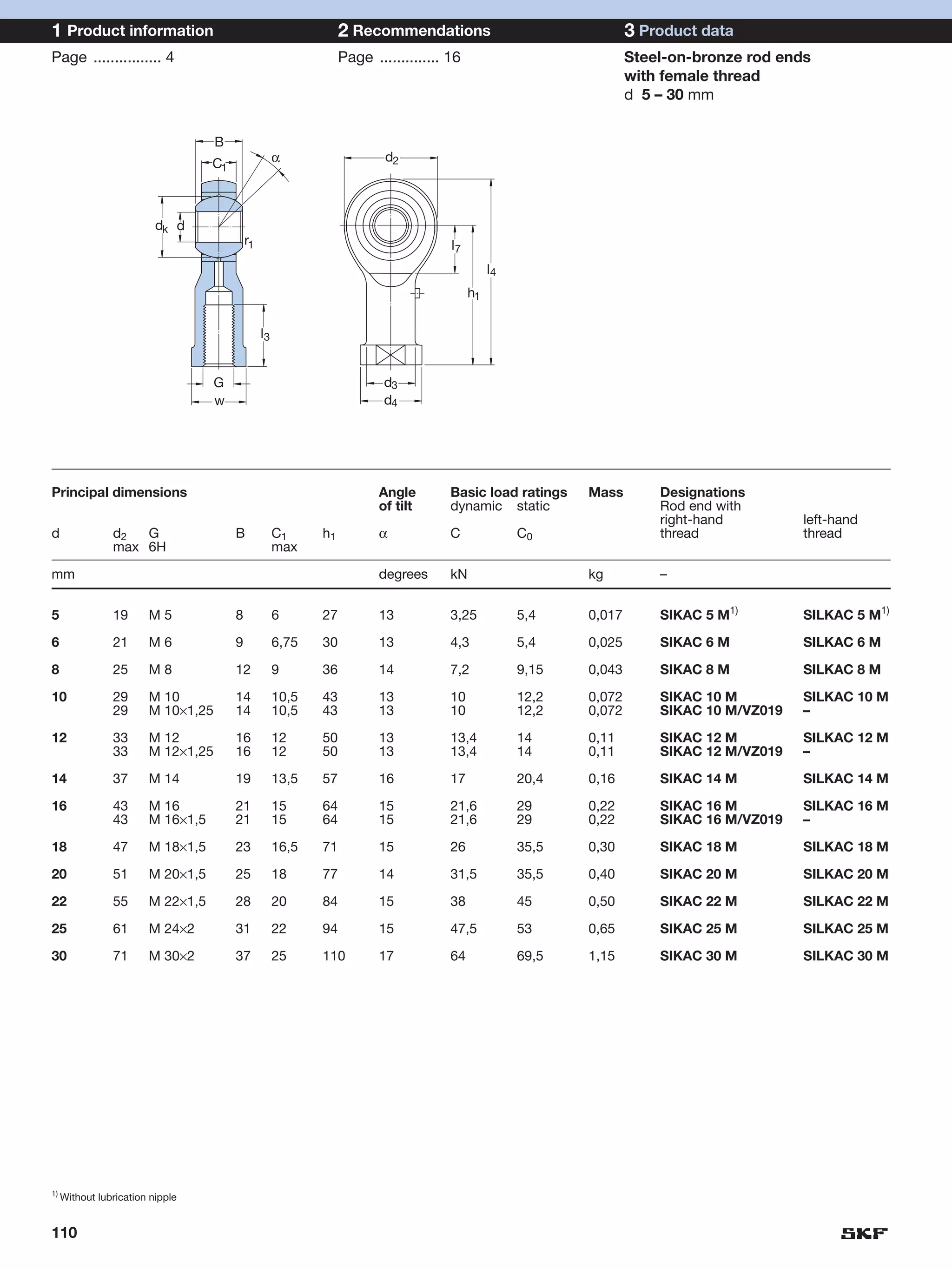
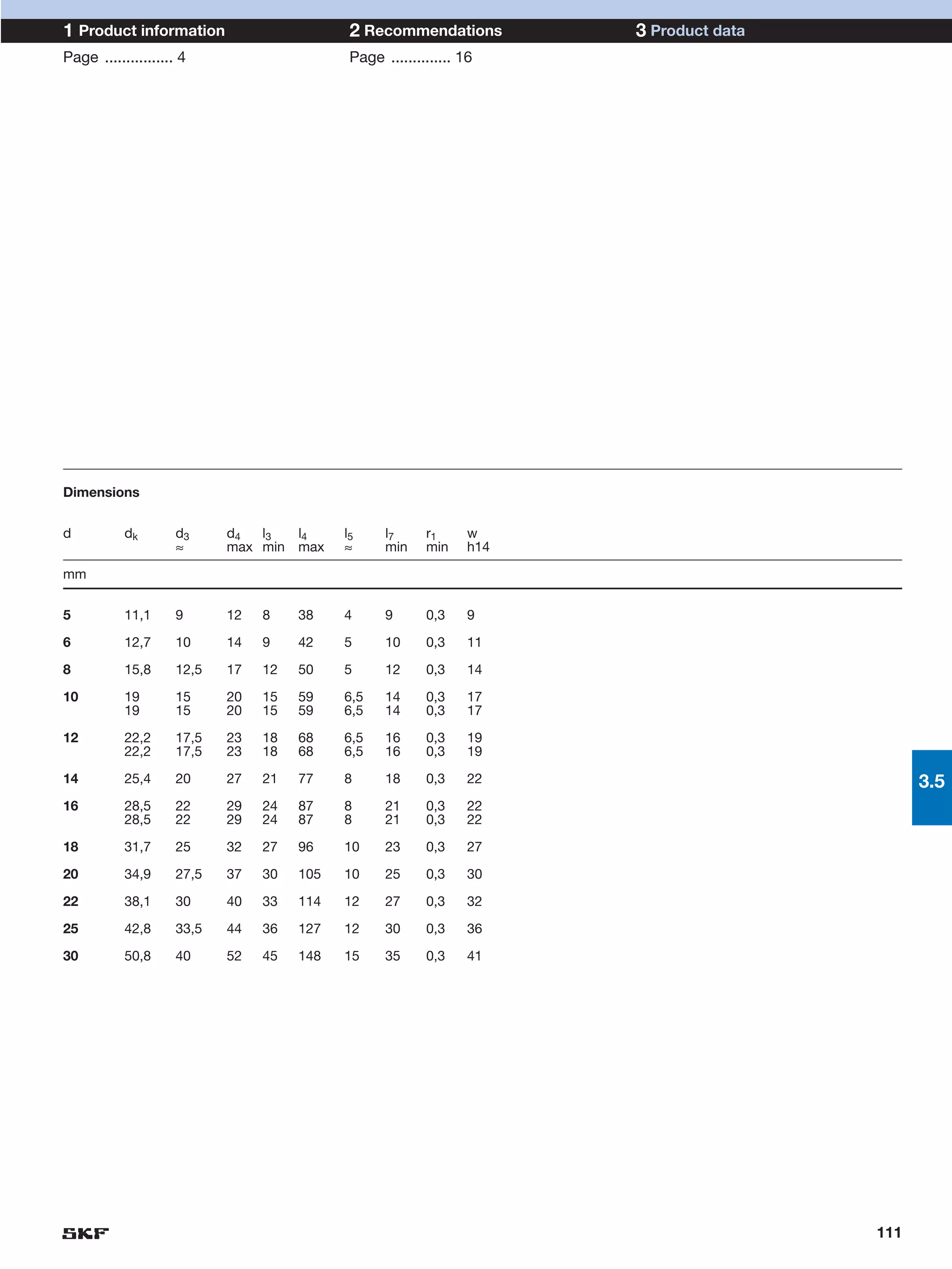
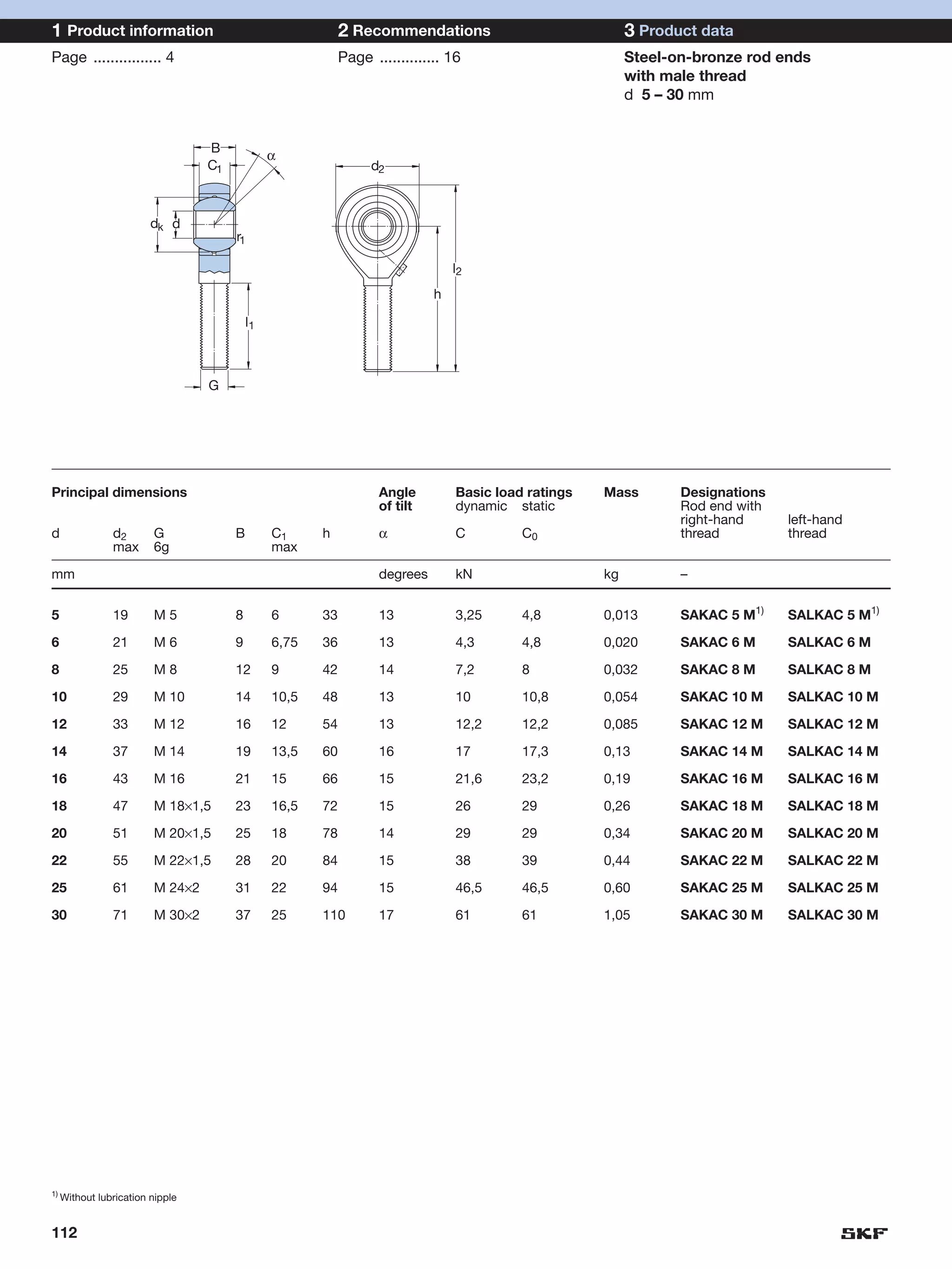
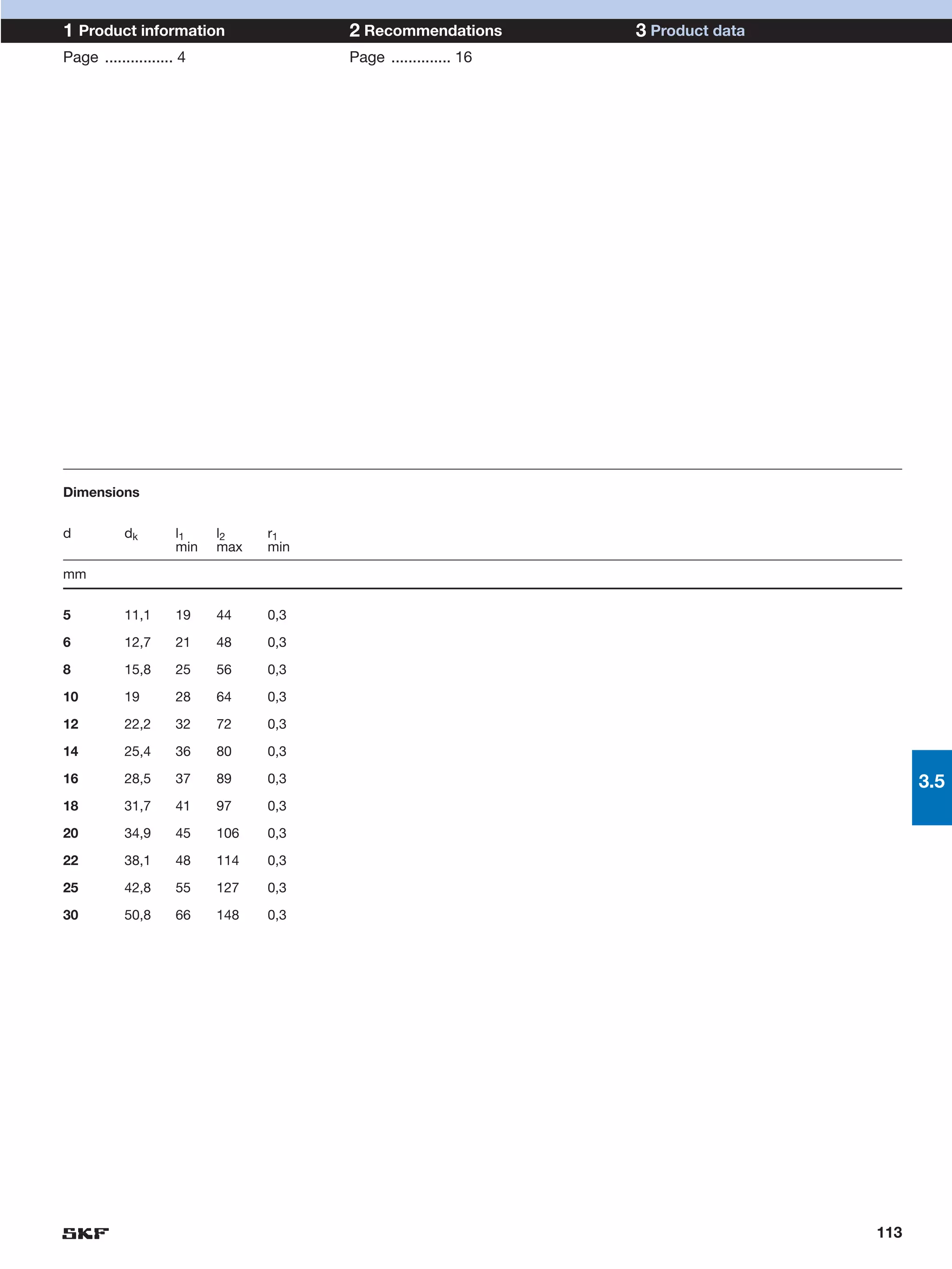
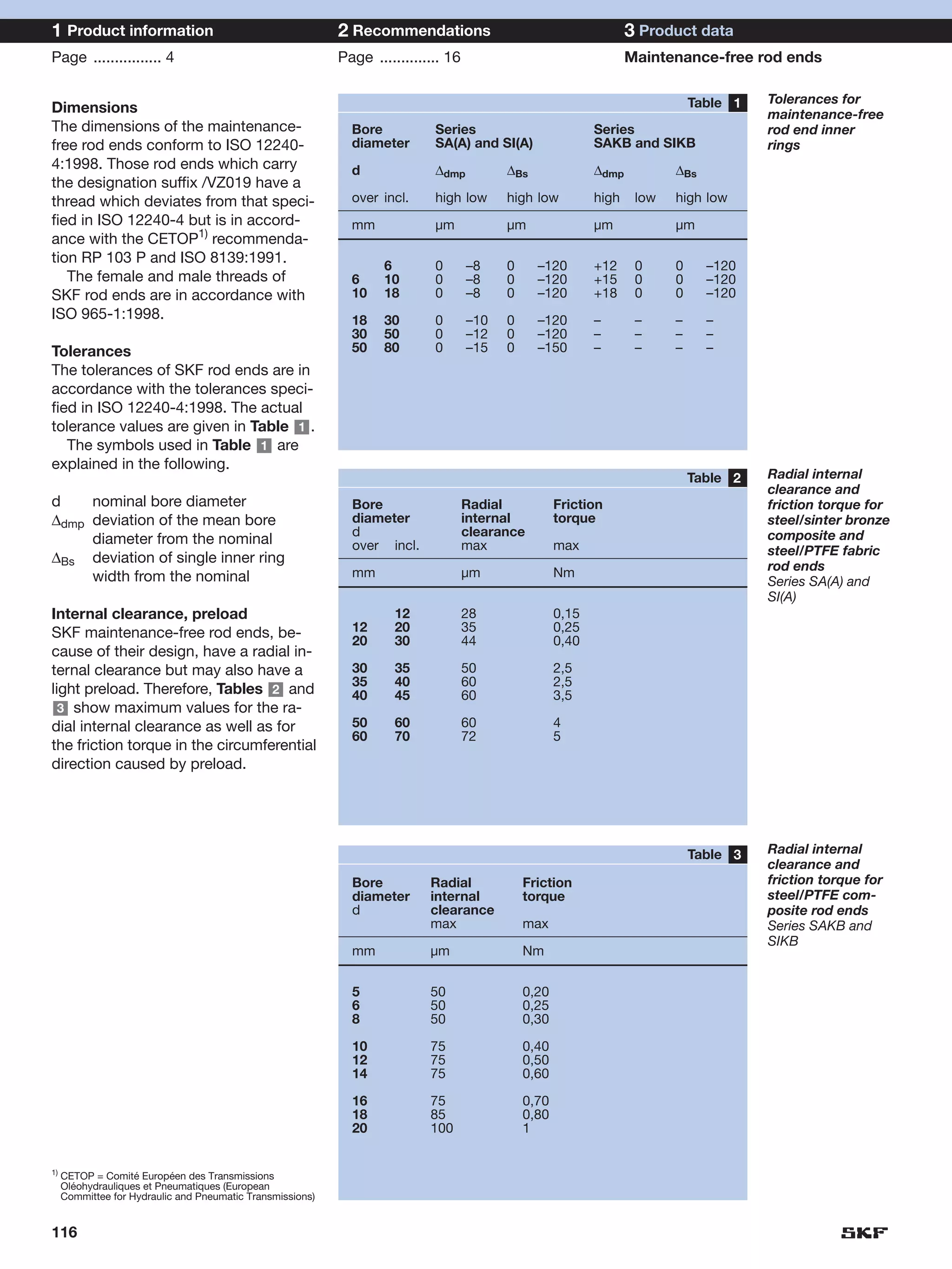
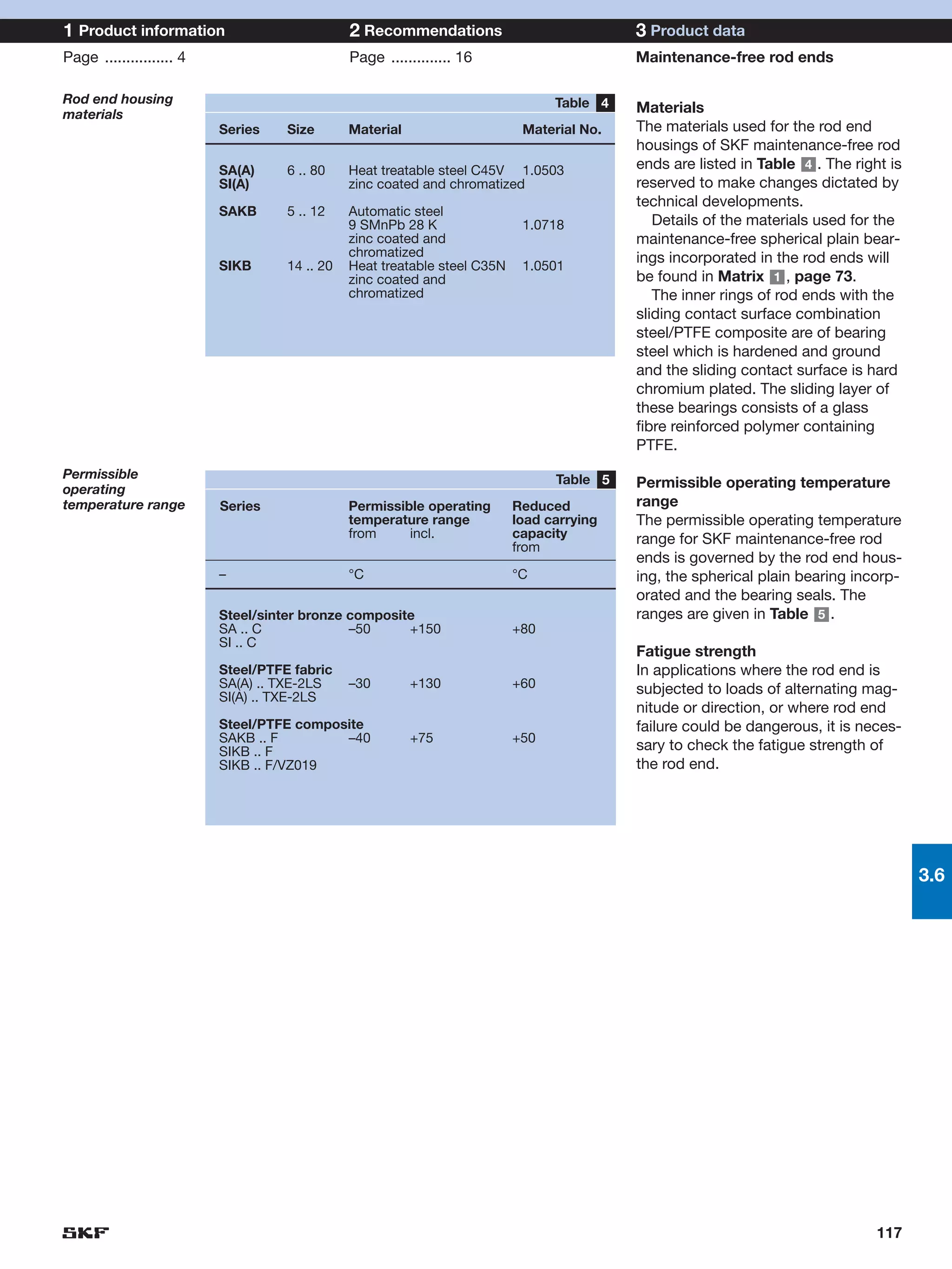
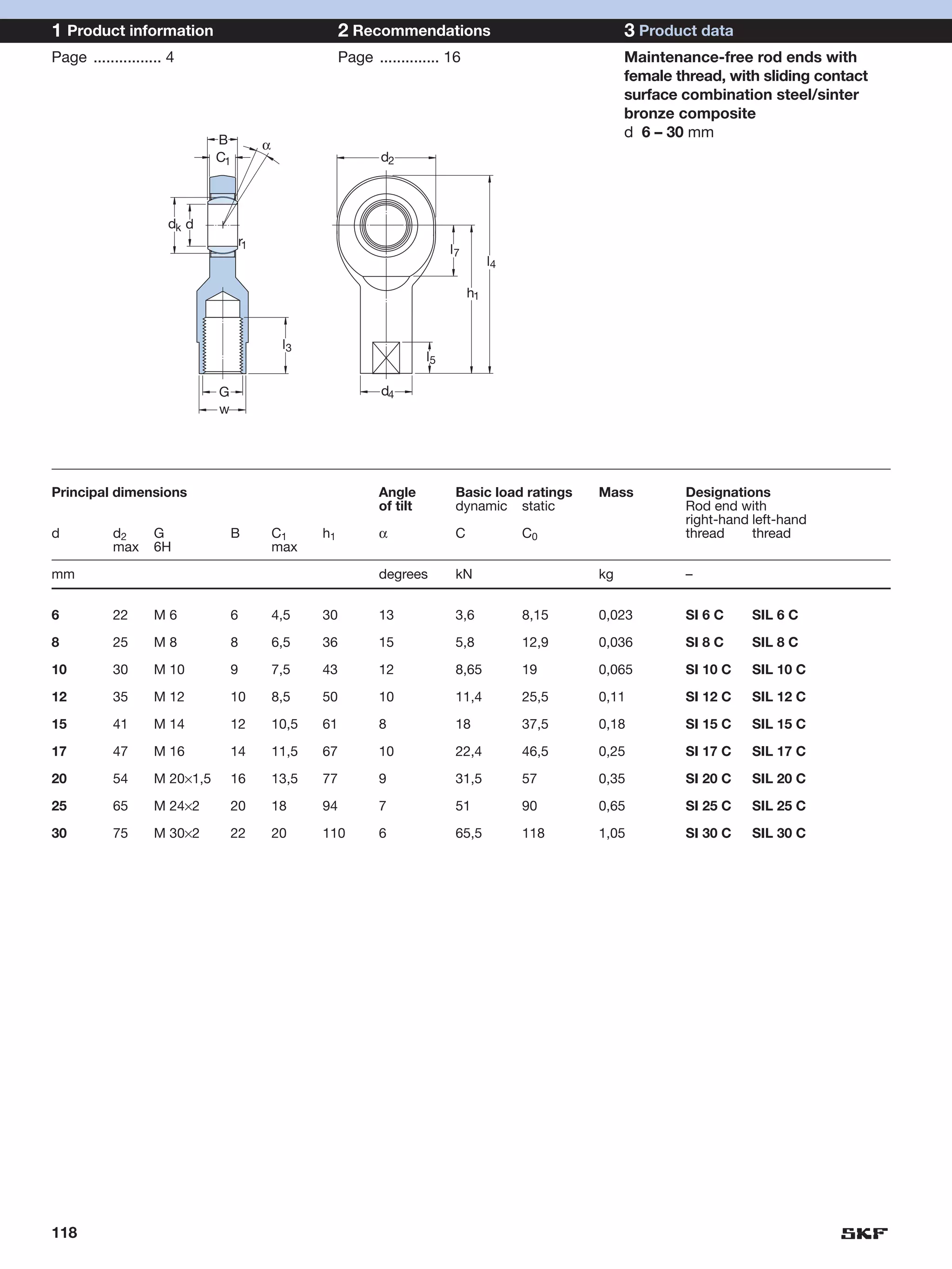
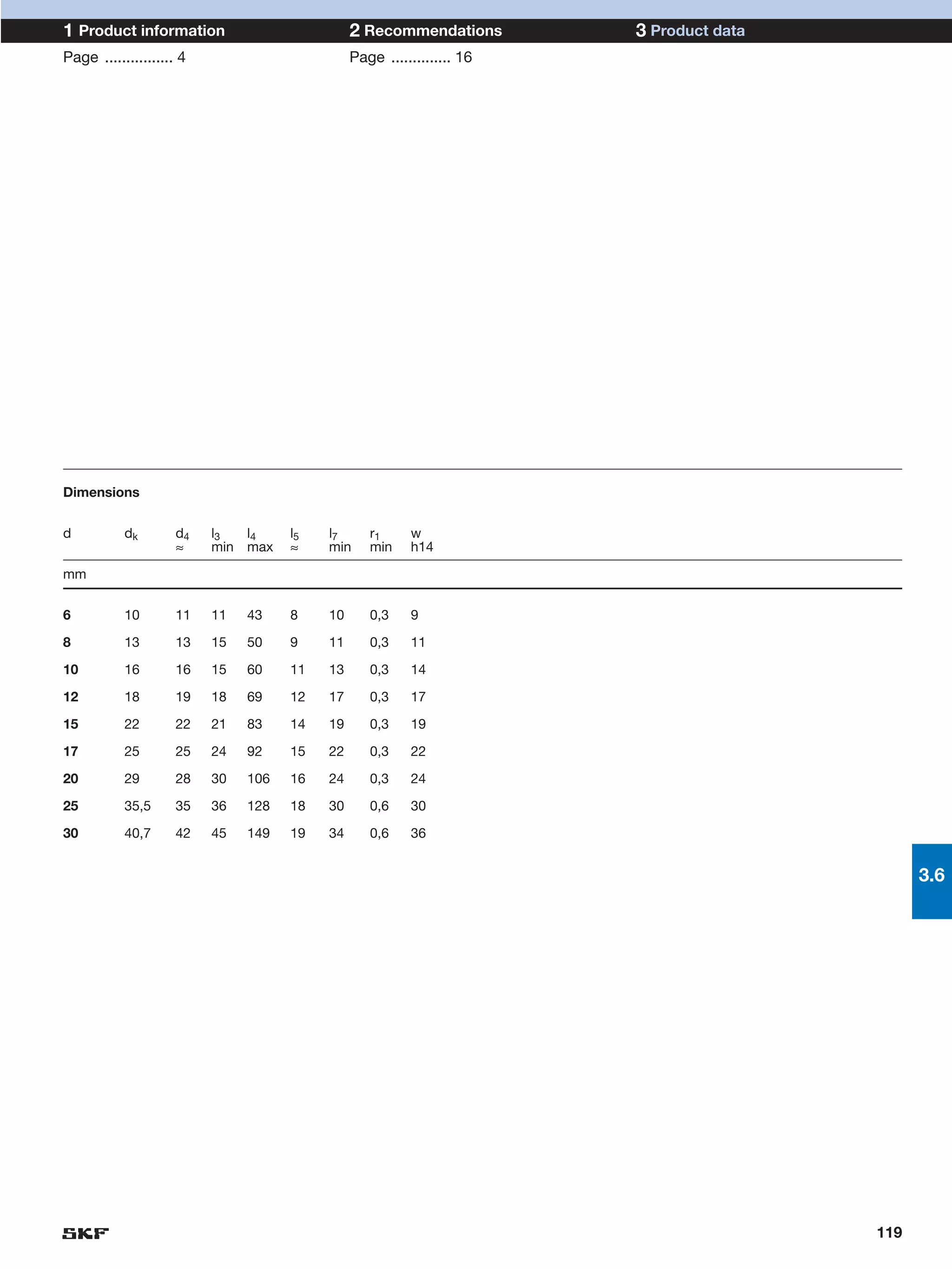
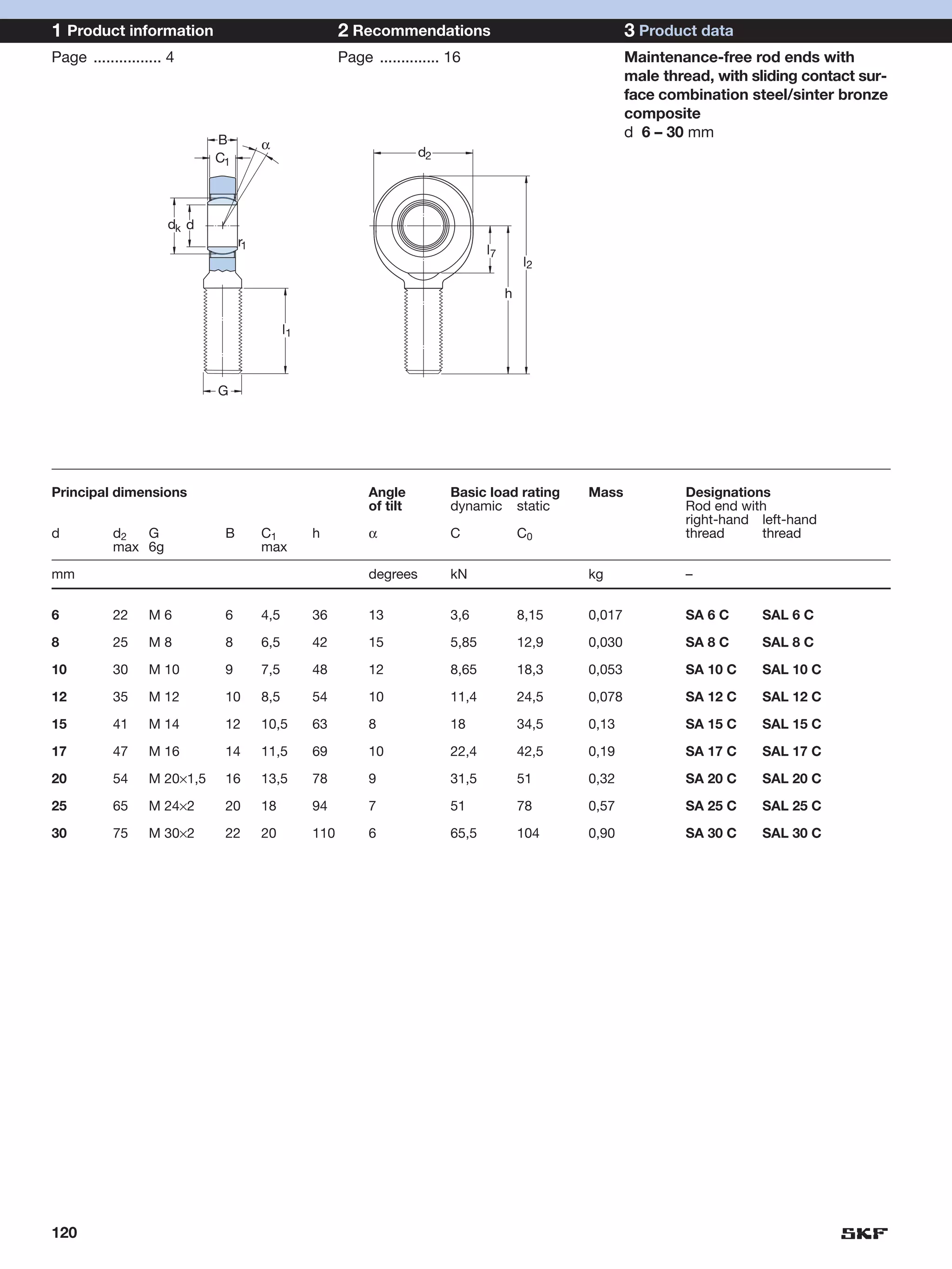
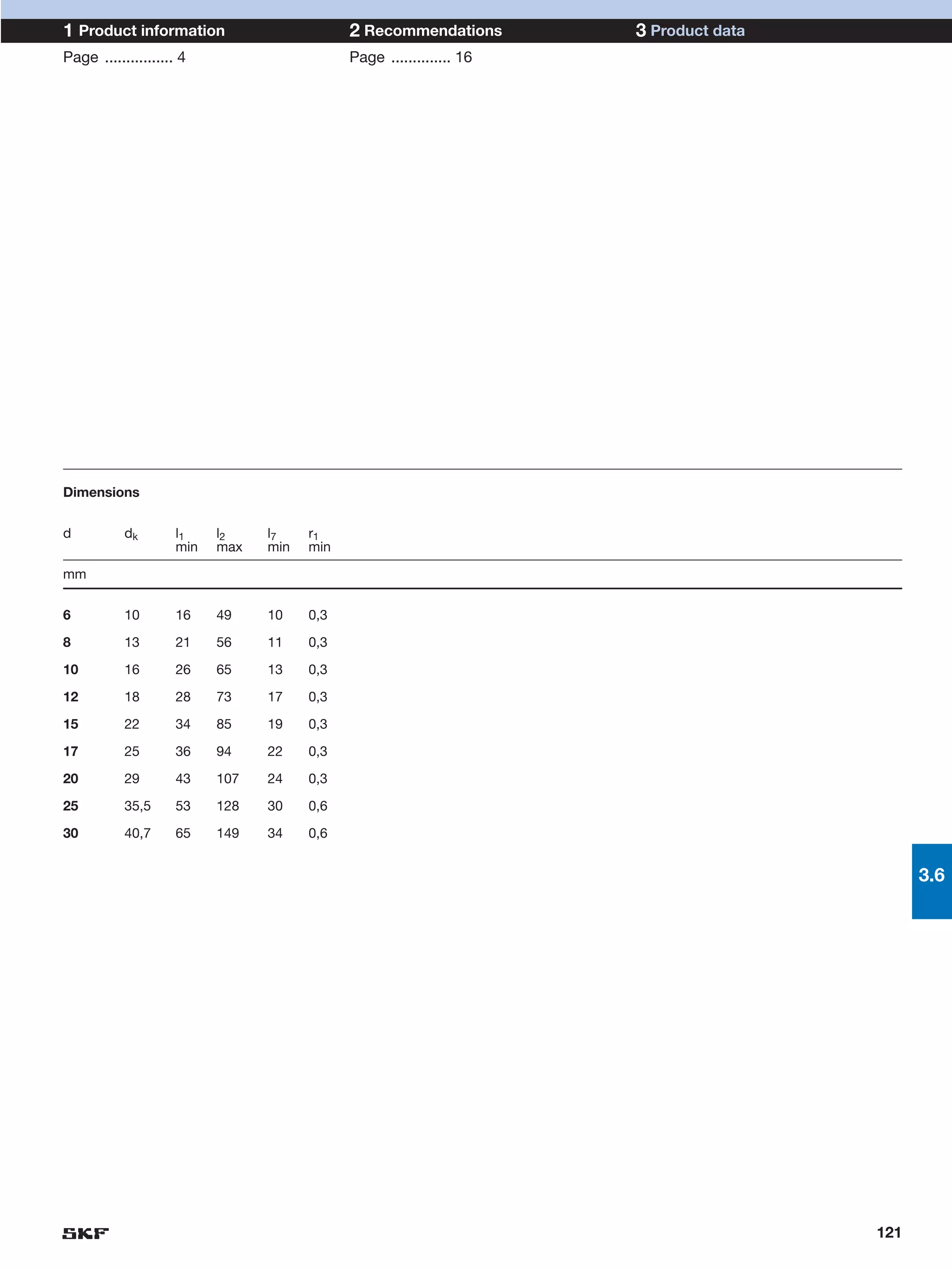
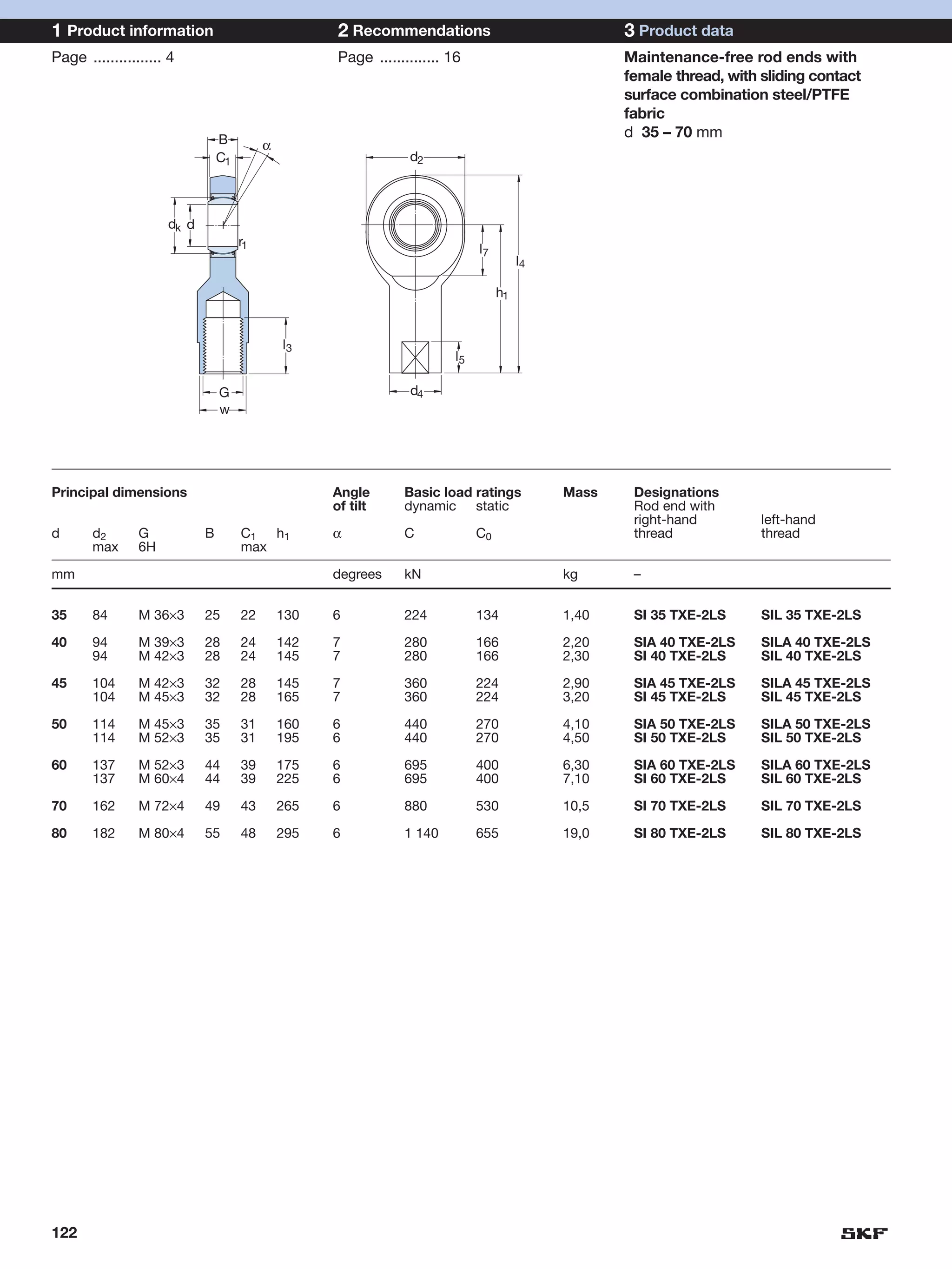
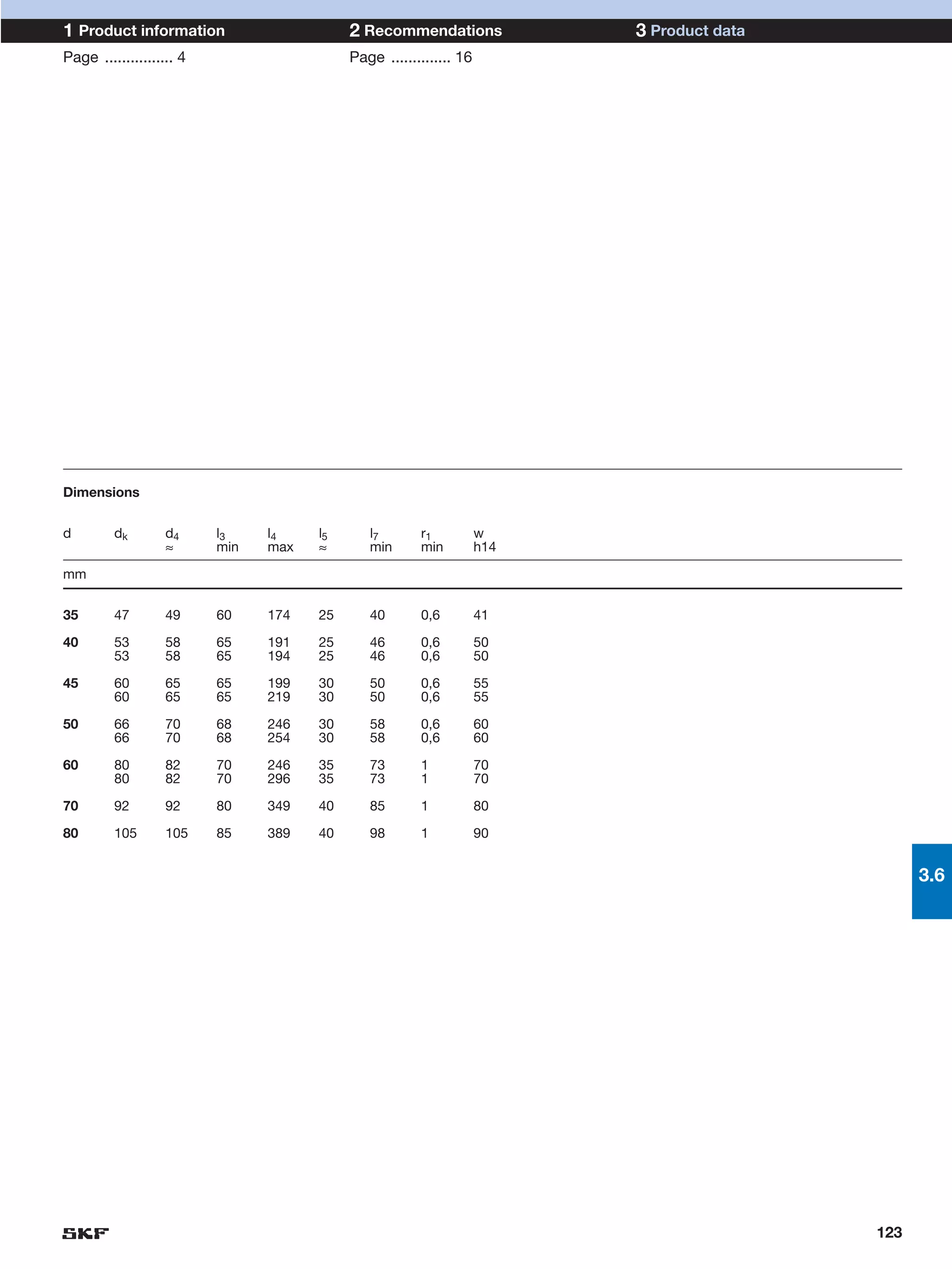
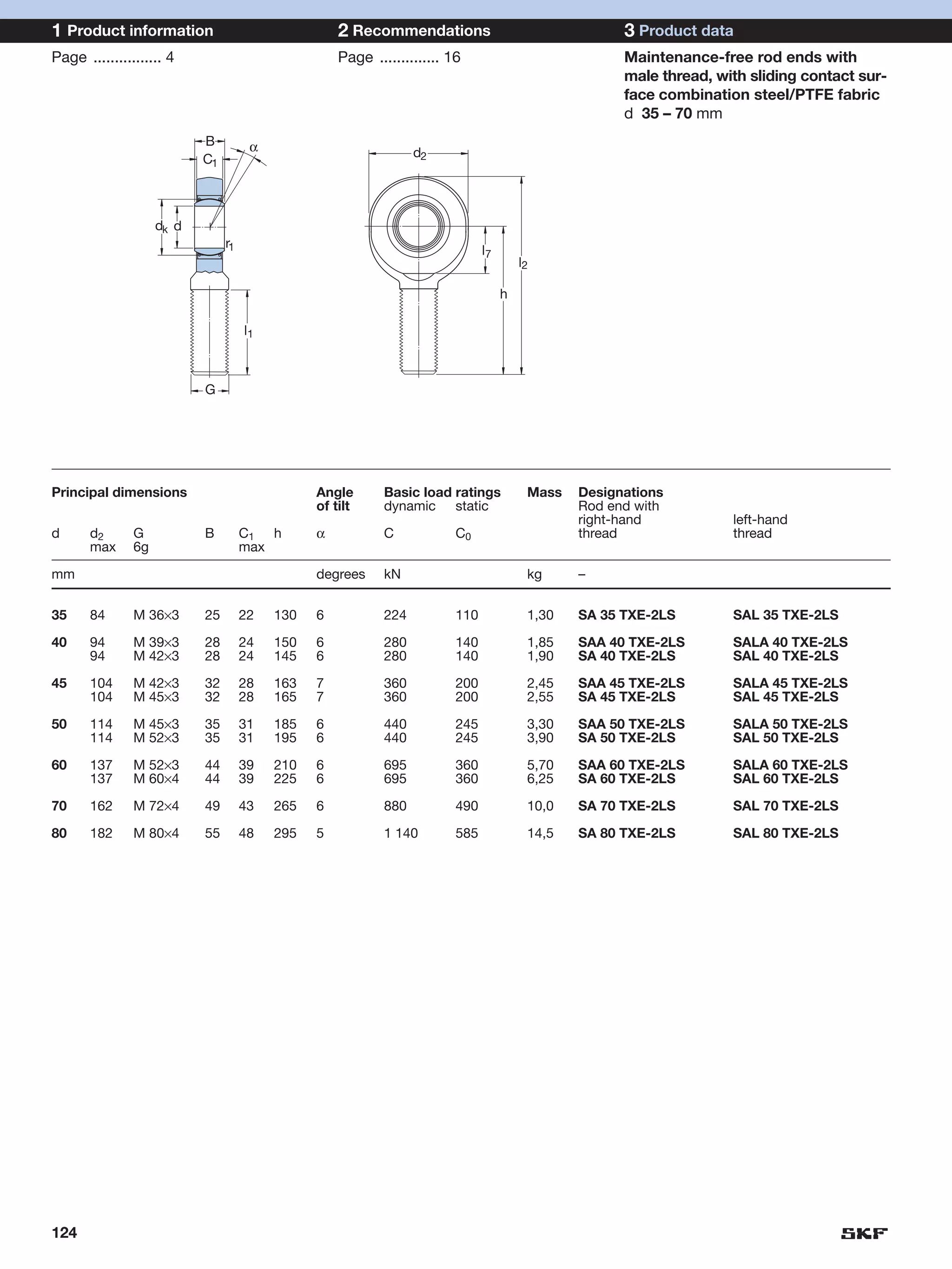
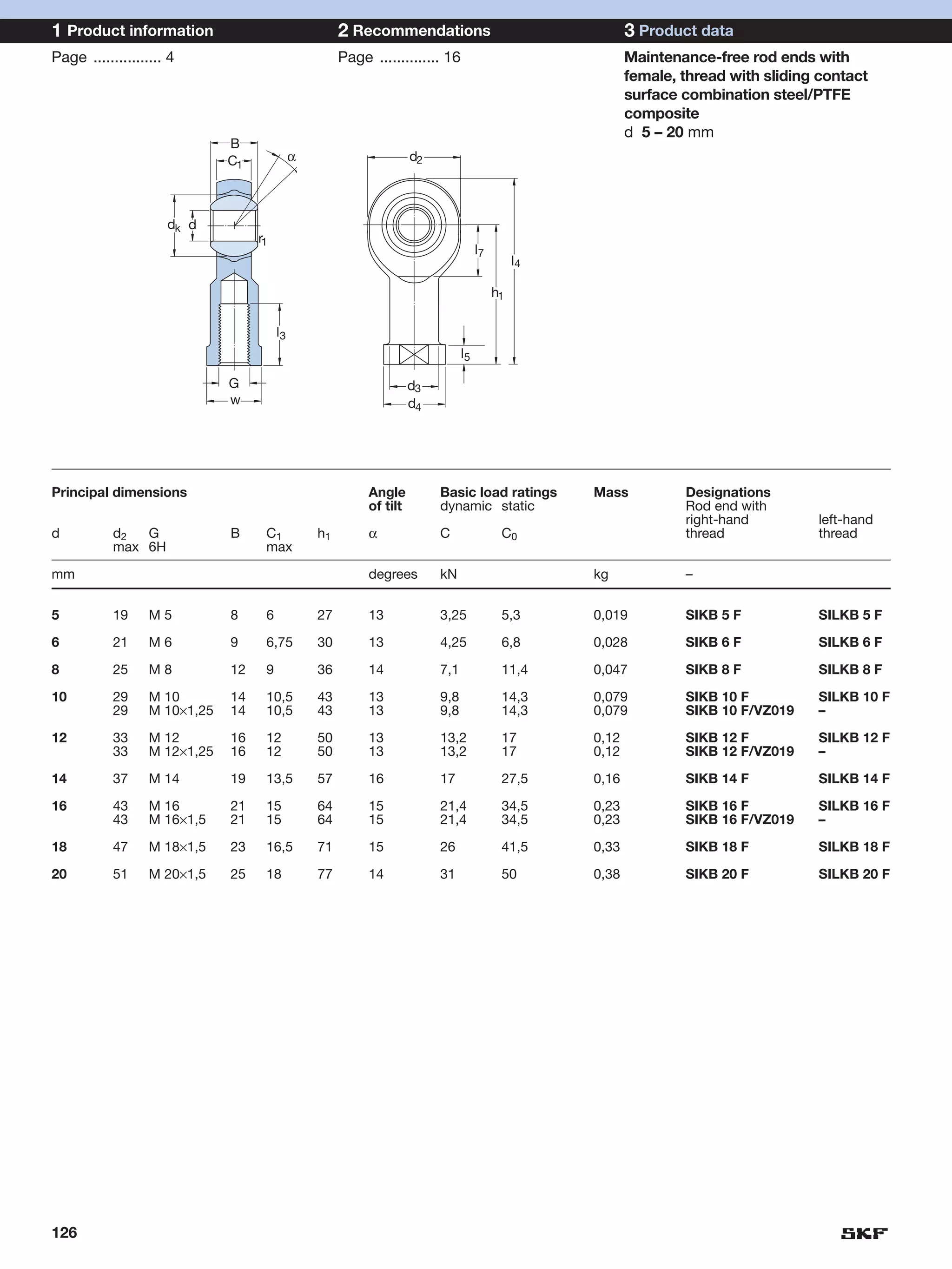
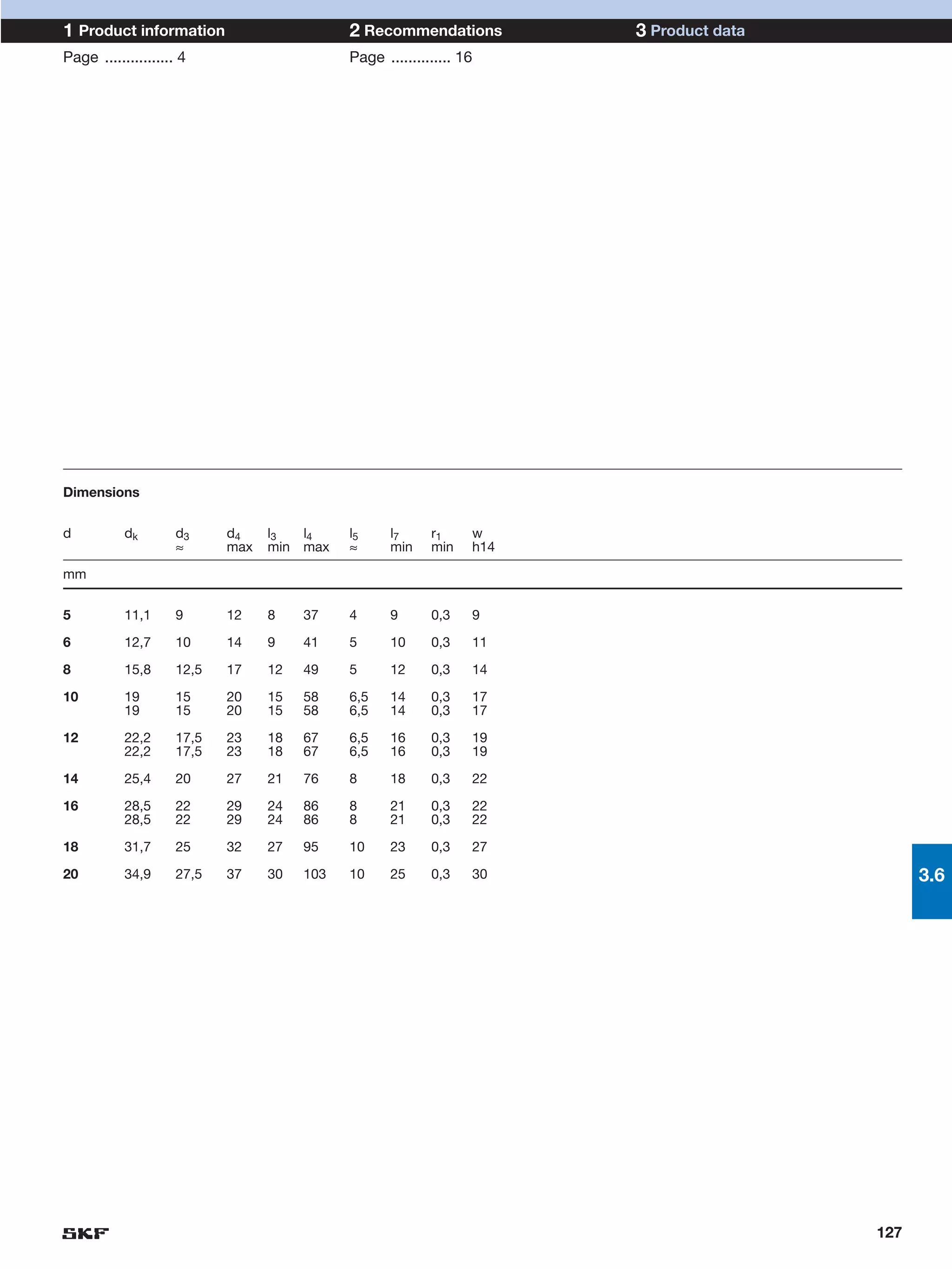
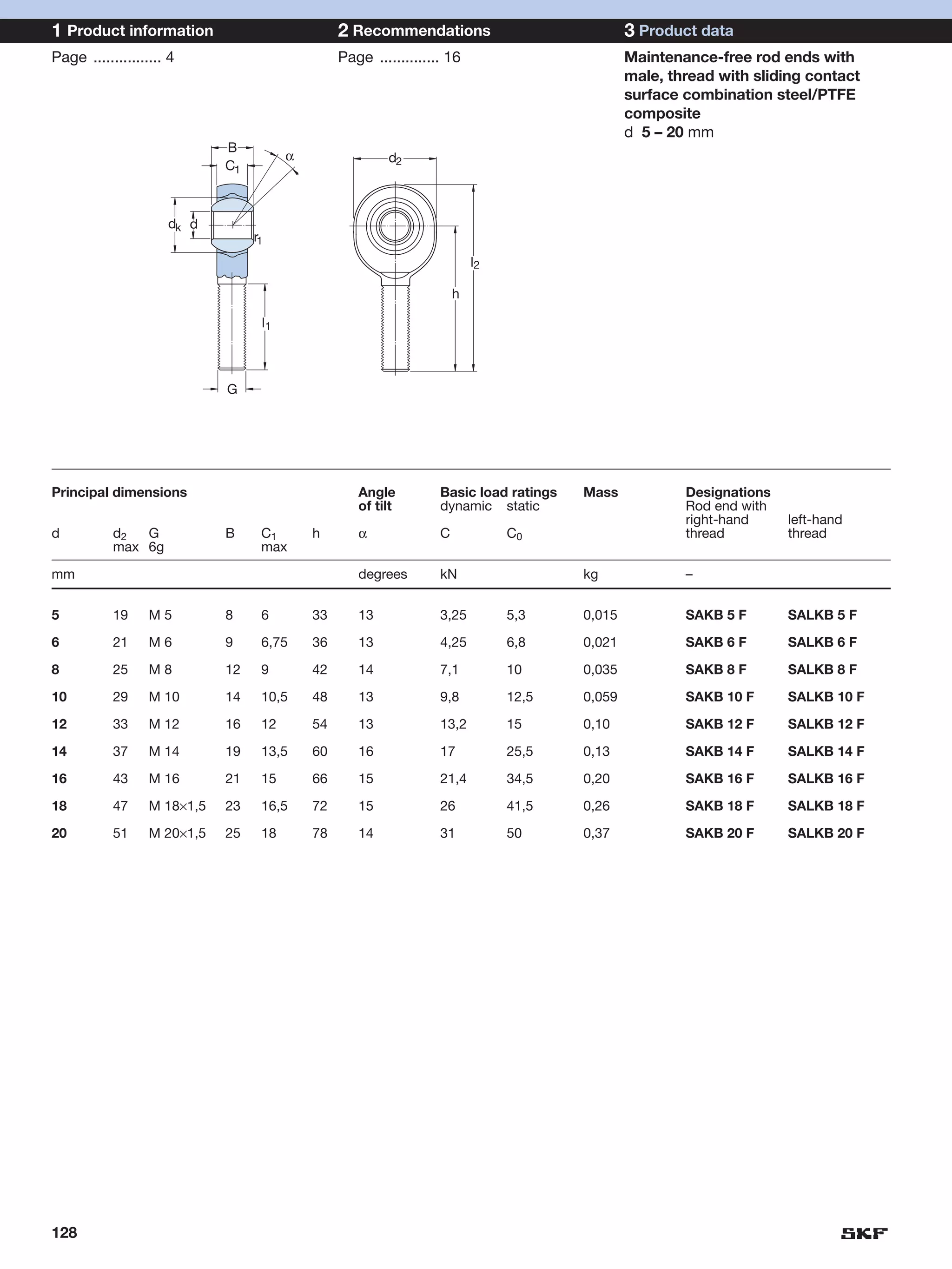
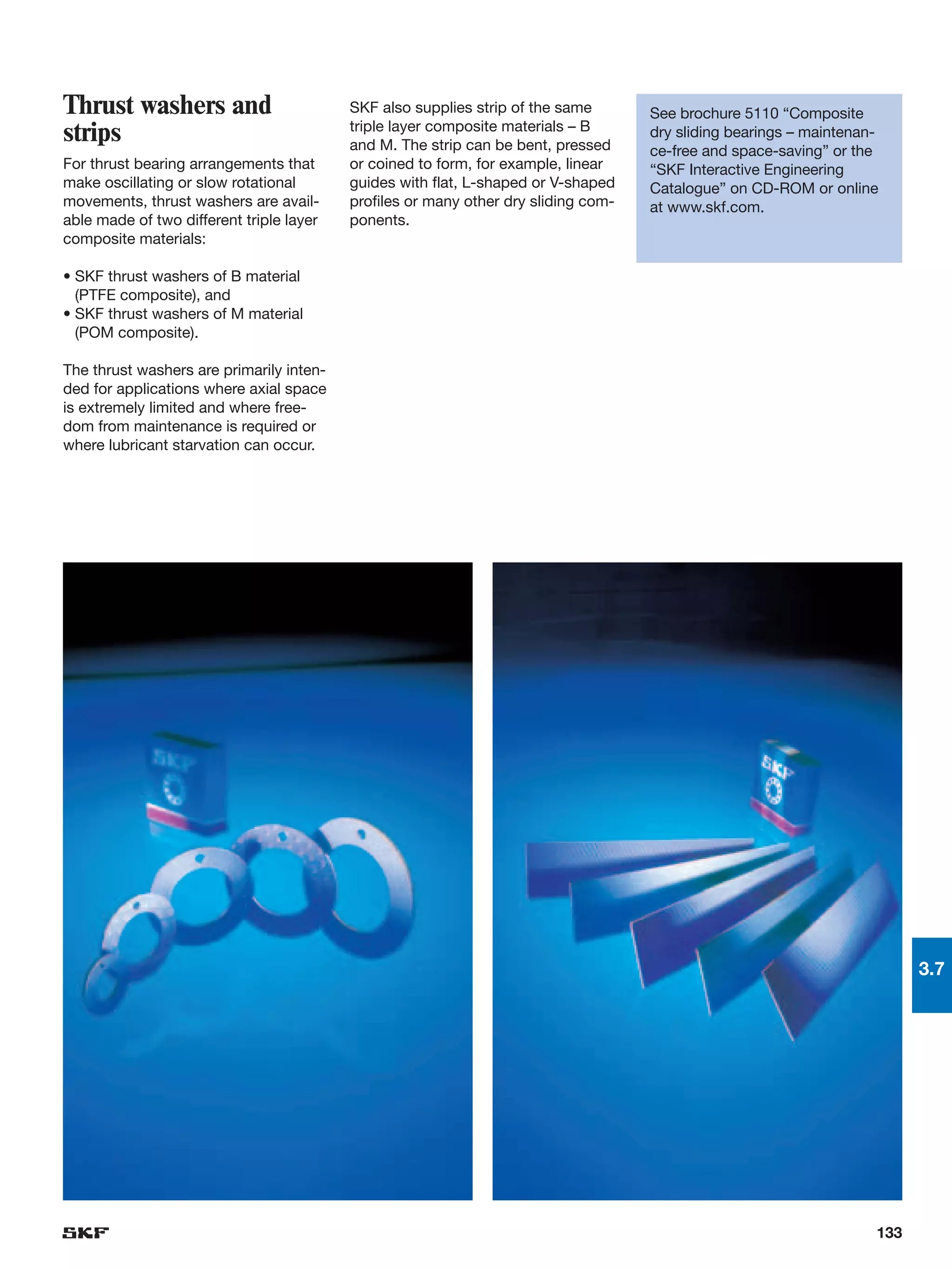
SKF provides a wide range of spherical plain bearings and rod ends for various applications. Their product range includes radial, angular contact, and thrust spherical plain bearings, as well as rod ends with different thread and shank configurations. These products offer benefits such as self-alignment, long service life, simple maintenance, high reliability, and compatibility with a variety of operating conditions and environments. SKF aims to provide customers with solutions rather than limit them through compromises.