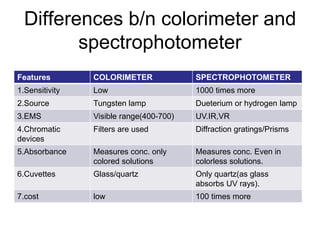
Colorimetry is a method used to estimate substances in biological materials by developing and comparing colors with known standards, while spectrophotometry extends this capability to measure light absorption beyond visible colors, making it suitable for colorless compounds. The key differences between colorimeters and spectrophotometers include sensitivity, light sources, measurement ranges, and types of cuvettes used. Spectrophotometers are more advanced, allowing for greater sensitivity and accuracy across UV, visible, and IR wavelengths.