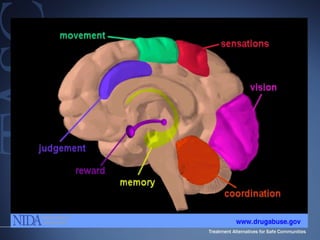
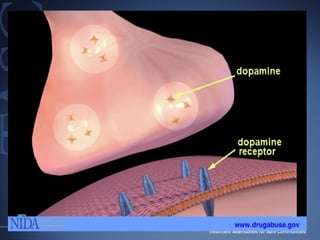
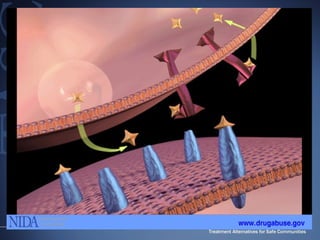
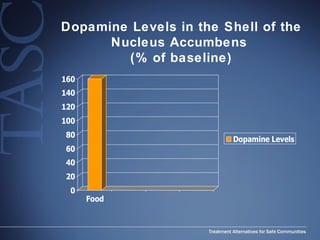
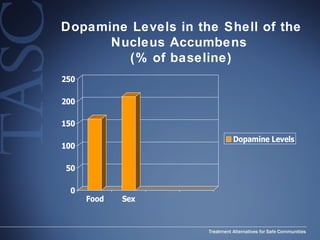
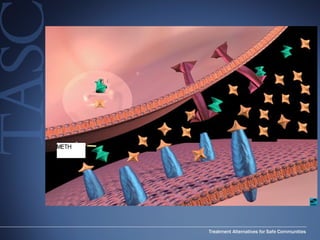
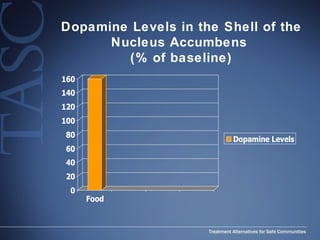
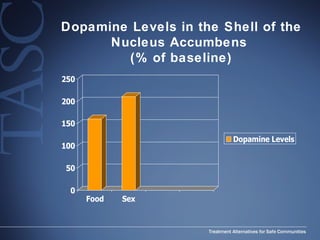
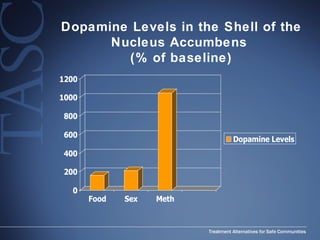
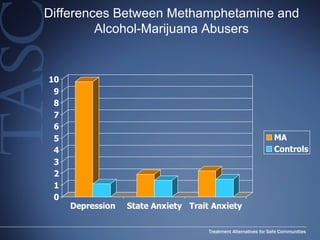
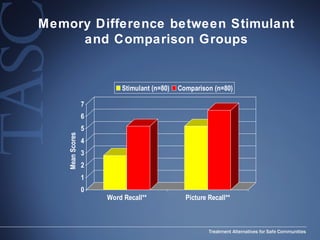
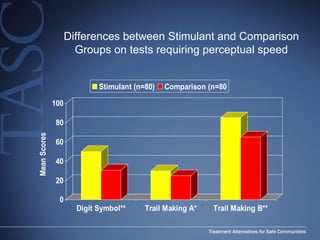
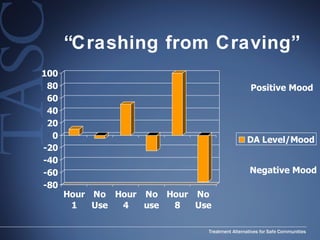
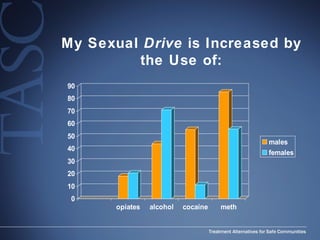
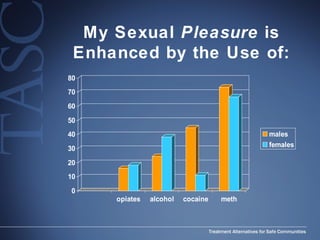
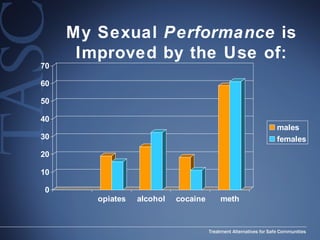
The document discusses the special needs of methamphetamine addicts, focusing on the effects of the drug on reward pathways and associated psychiatric risks such as acute and chronic depression, and various forms of psychosis. It highlights cognitive impairments, cravings, and the heightened risk of sexual behaviors among users. The information underscores the need for addressing cravings promptly to prevent adverse outcomes like 'crashing.'