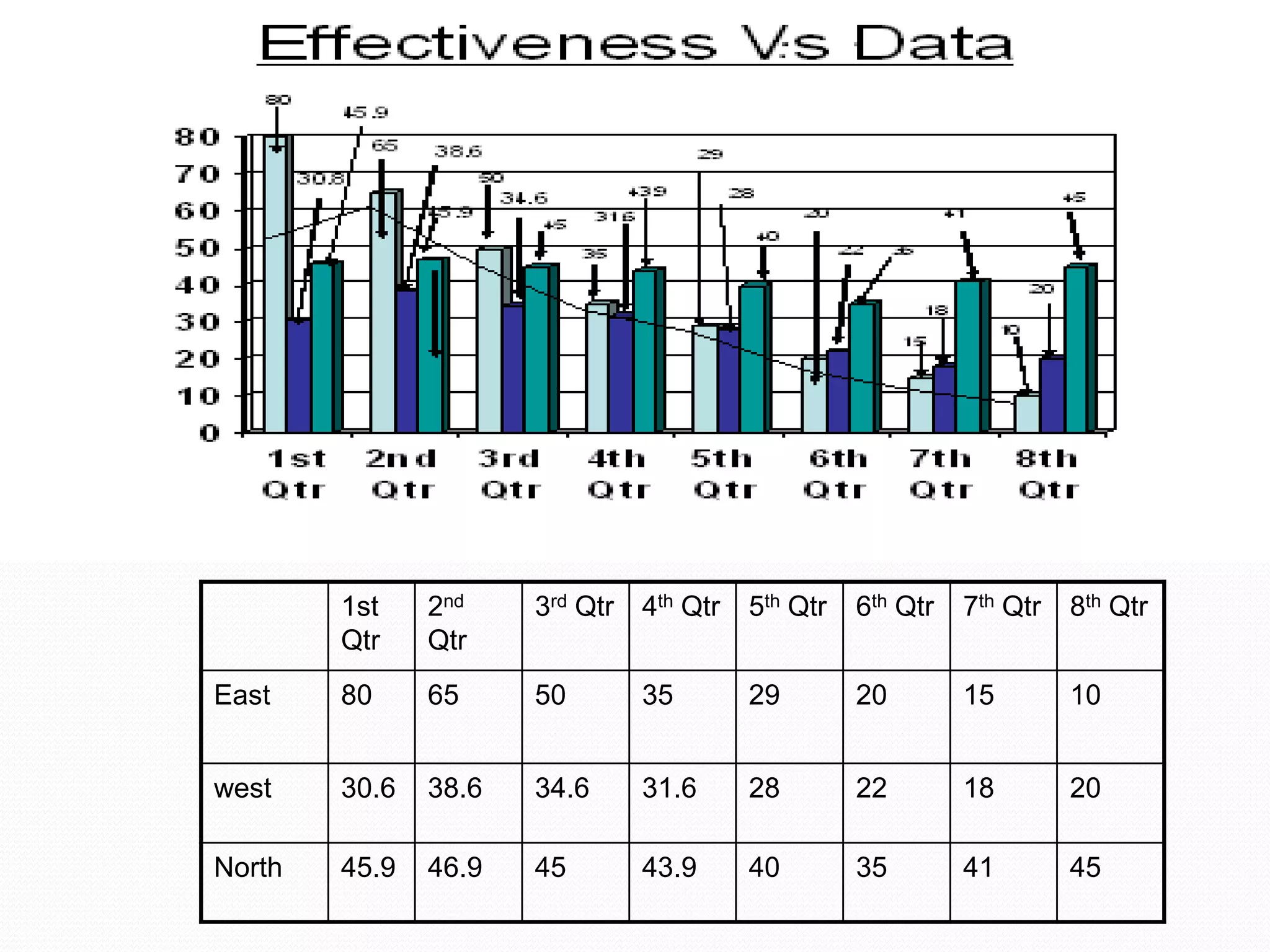
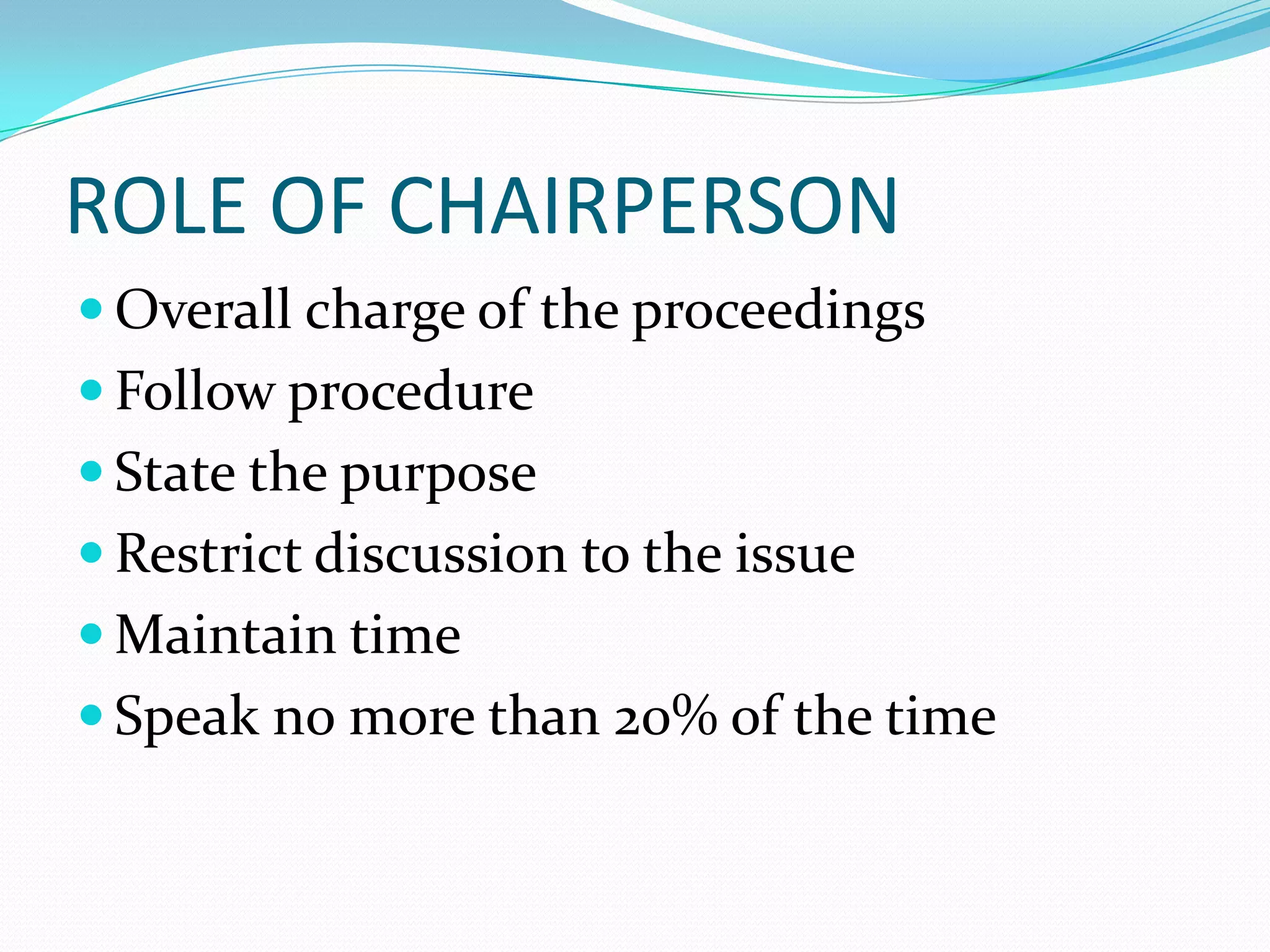
The document discusses various types of formal oral communication including public speeches, presentations, meetings, group discussions, and interviews. It provides tips for each type of communication as well as dos and don'ts. For public speeches, it suggests doing research, organizing ideas logically, and using techniques like eye contact. For meetings, it outlines the roles of chairperson, secretary, and participants. Group discussions allow people to share views and are beneficial for skills development. Proper preparation and positive qualities are keys for successful job interviews.