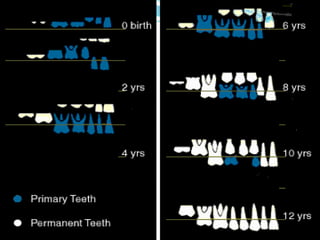
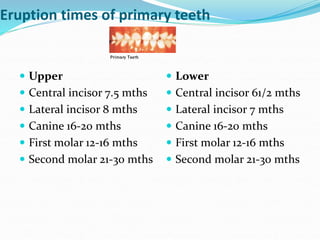
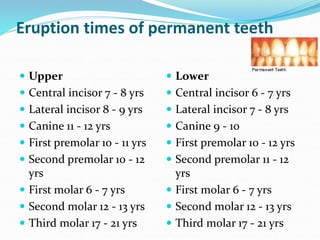
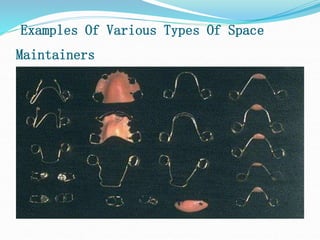
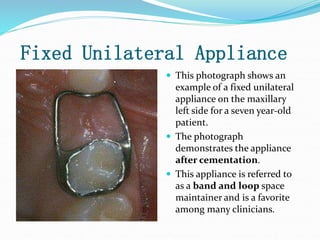
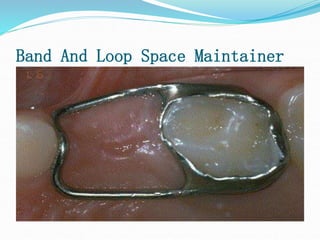
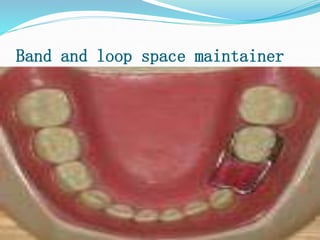
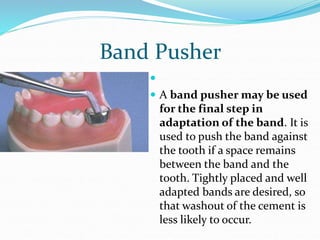
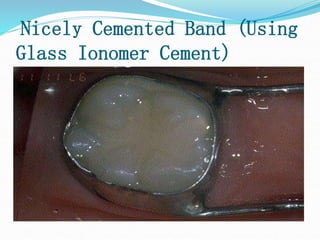
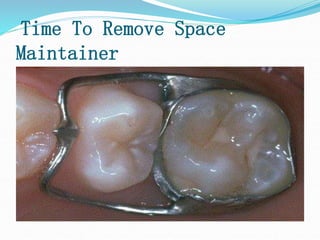
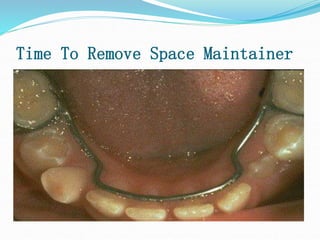
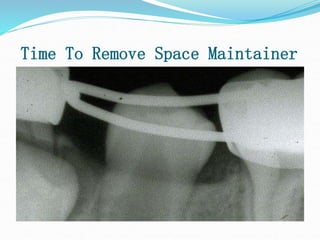
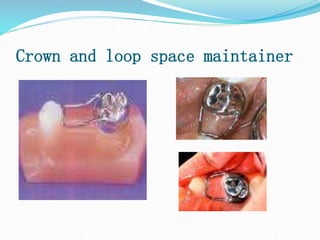
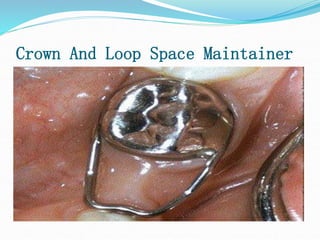
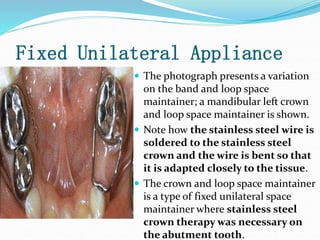
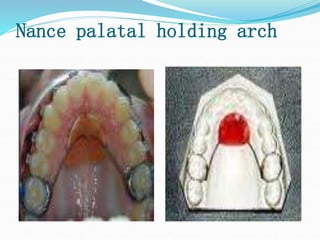
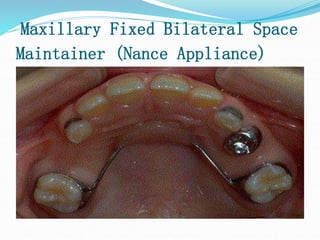
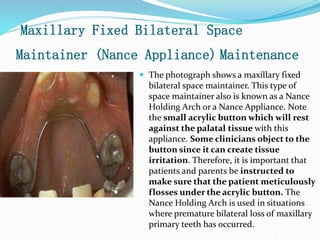
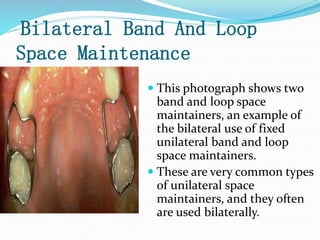
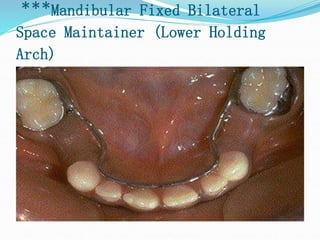
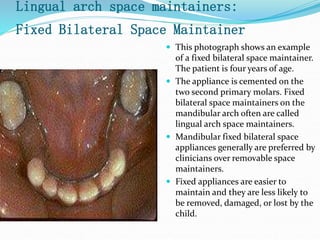
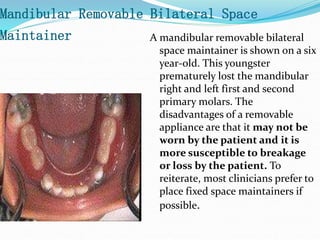
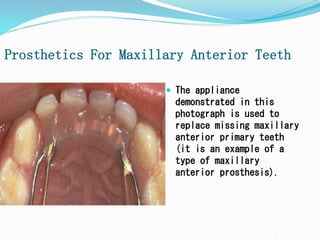
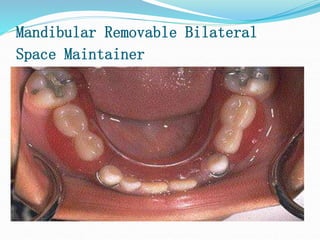
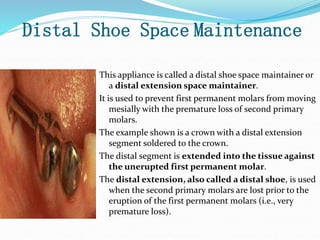
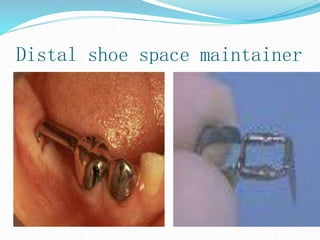
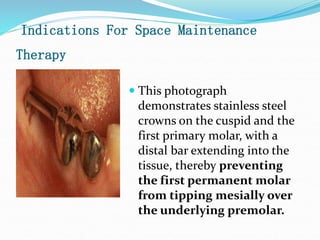
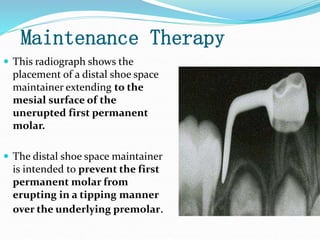
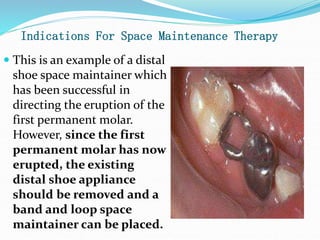
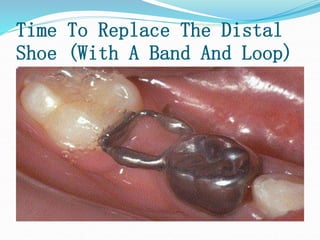
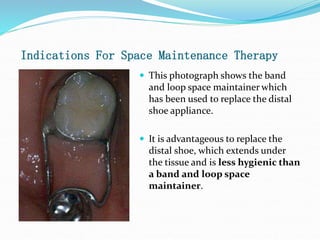
This document discusses various types of space maintainers used to prevent premature loss of space after primary teeth are lost. It describes fixed unilateral appliances like band and loop and crown and loop space maintainers. Bilateral fixed appliances discussed include Nance palatal holding arch and lower lingual arch. Removable appliances like Hawley retainers are also mentioned. Indications, advantages, and disadvantages of different space maintainers are provided. The steps of construction including fitting bands and fabricating the appliance are outlined.