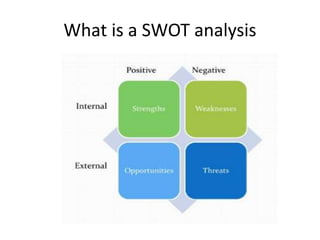
This document provides an overview of a SWOT analysis. It explains that a SWOT analysis links internal advantages/disadvantages with external environmental factors to understand a business's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Strengths and weaknesses are internal, like market share or product quality. Opportunities and threats are external, such as new markets or competition. The analysis identifies a firm's resources and capabilities as strengths or lack thereof as weaknesses. It also examines potential opportunities in the environment or threats from factors such as new technologies. The SWOT framework provides information to match a business's strategy to its competitive situation.