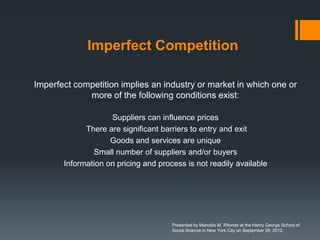
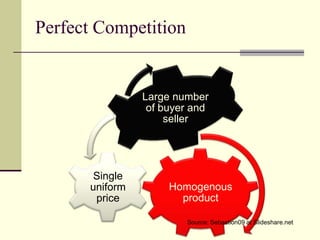
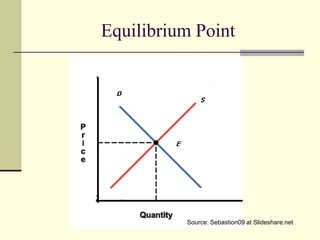
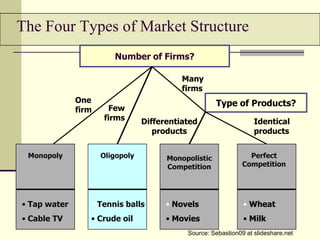
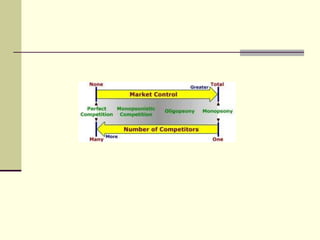
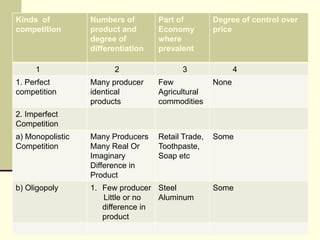
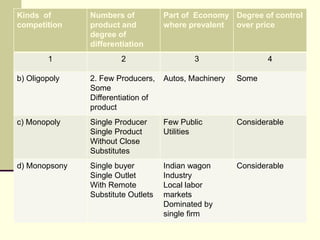
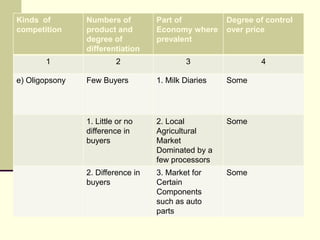
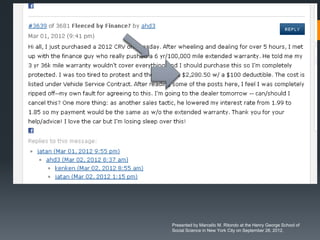
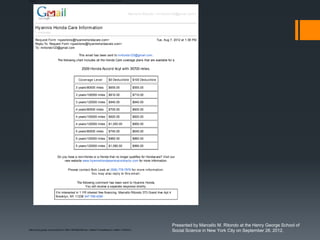
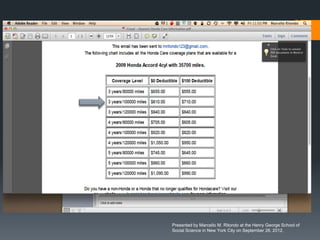
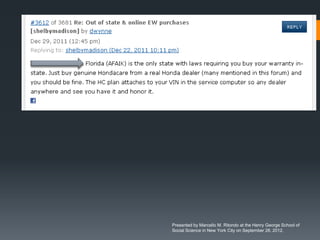
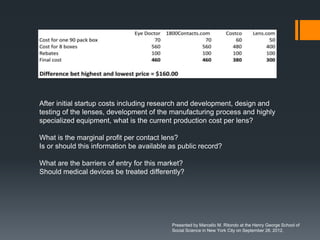
The seminar by Marcello M. Ritondo at the Henry George School discusses the factors influencing retail pricing beyond production costs, including various market structures such as perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly. Key topics include pricing fluctuations, price gauging, competition mechanics, and how different market conditions affect consumer prices. The presentation emphasizes the importance of awareness, competitive advantage, and technology in maintaining competitiveness in the marketplace.