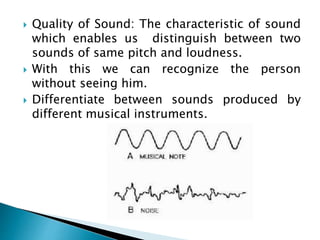
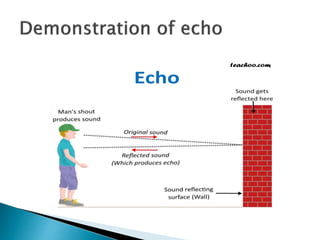
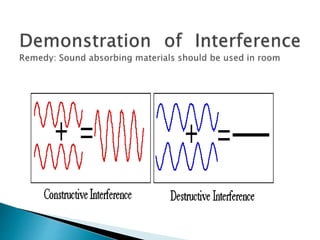
This document discusses acoustics and the reflection of sound waves. It covers topics like reflection of sound waves from rigid and curved surfaces, reflection between different media, intensity of sound waves, reverberation time, echoes, and reducing noise in buildings. The key points are:
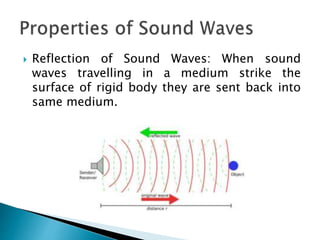
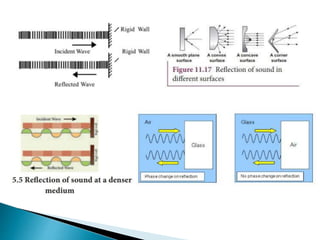
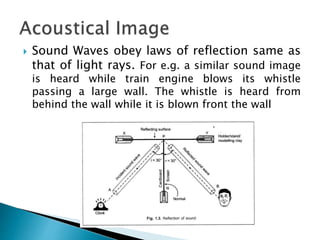
- Sound waves reflect in a similar manner as light waves, changing direction when reflecting off surfaces.
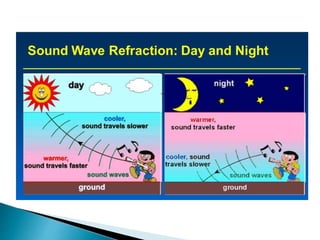
- Reflection depends on the properties of the reflecting surface and the media on either side.
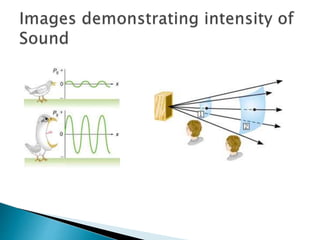
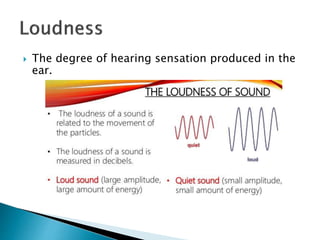
- Intensity of sound depends on factors like amplitude, frequency, area of sound source, and distance from the source.
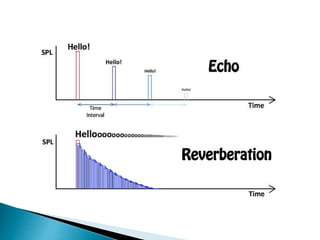
- Reverberation time is the time it takes for sound intensity to decrease by a million times after the source