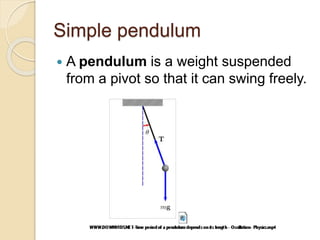
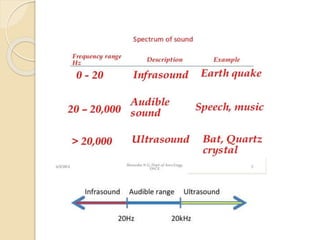
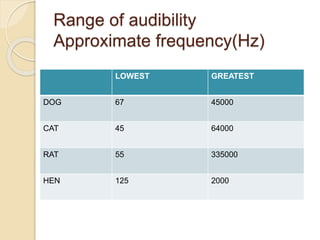
Sound is a form of energy that allows us to hear and is caused by vibrations traveling through a medium. It can be produced from both natural and man-made sources at different frequencies and pitches. The human range of hearing is typically reported as between 20-20,000 Hz, though it varies between individuals and decreases with age. Noise pollution occurs when environmental sounds are loud enough to damage hearing, disrupt normal activities, or diminish quality of life. It is a major problem caused by transportation, construction, and industrial sources that can be addressed through regulations, barriers, and protective equipment.