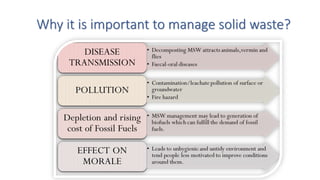
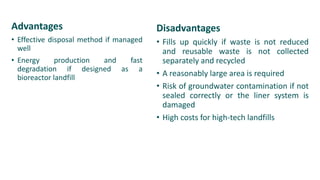
This document discusses different methods of solid waste management. It describes the types and sources of solid waste and provides details on various disposal and processing methods like open dumping, sanitary landfilling, composting, incineration, and pyrolysis. Landfilling is explained as the most common disposal method, where waste is buried in engineered pits with liners, leachate collection systems, and gas extraction. Composting converts organic waste into fertilizer via aerobic or anaerobic biological processes. Vermicomposting specifically uses earthworms. Site selection criteria for landfills and requirements for optimal composting are also outlined.