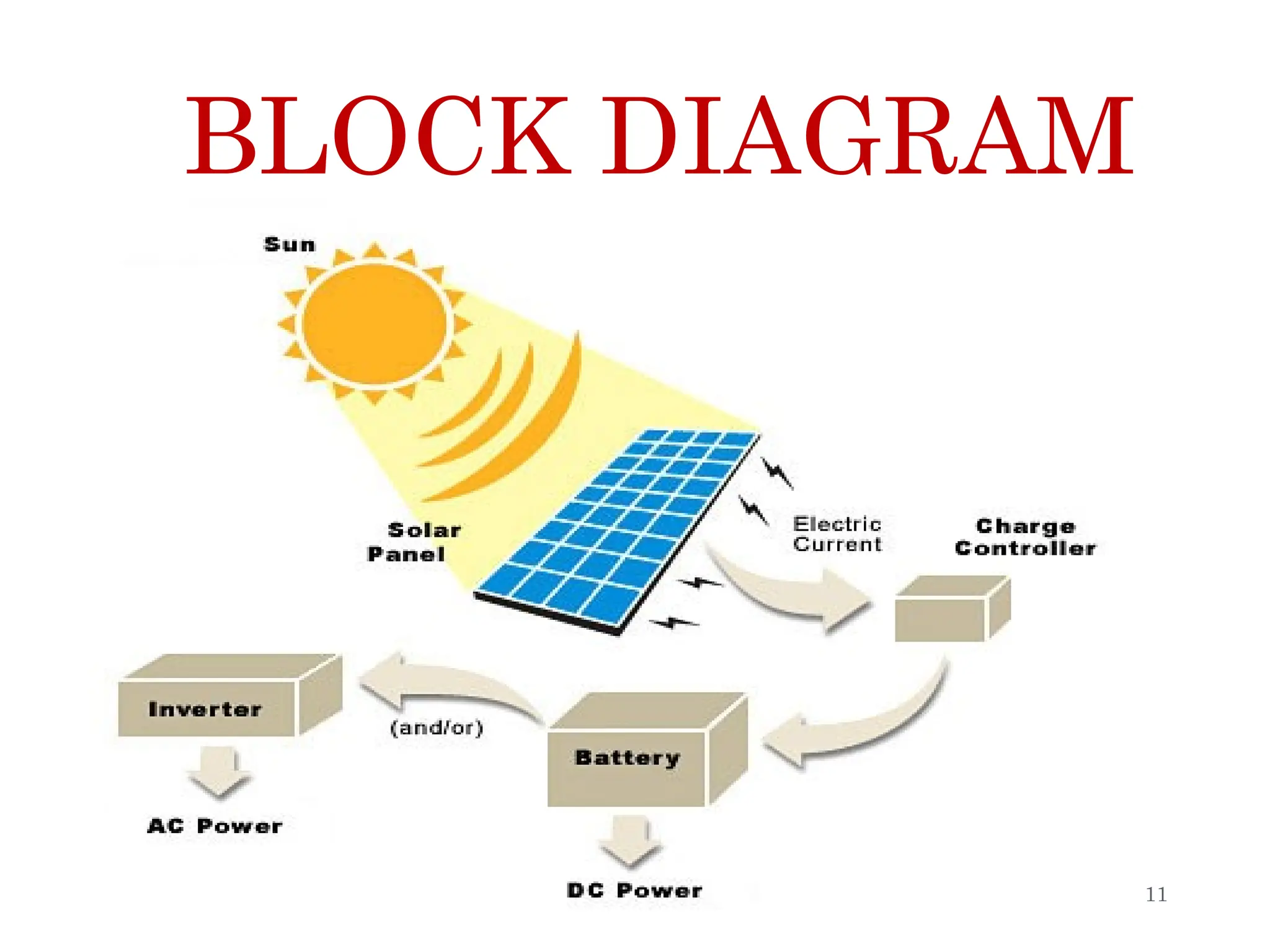
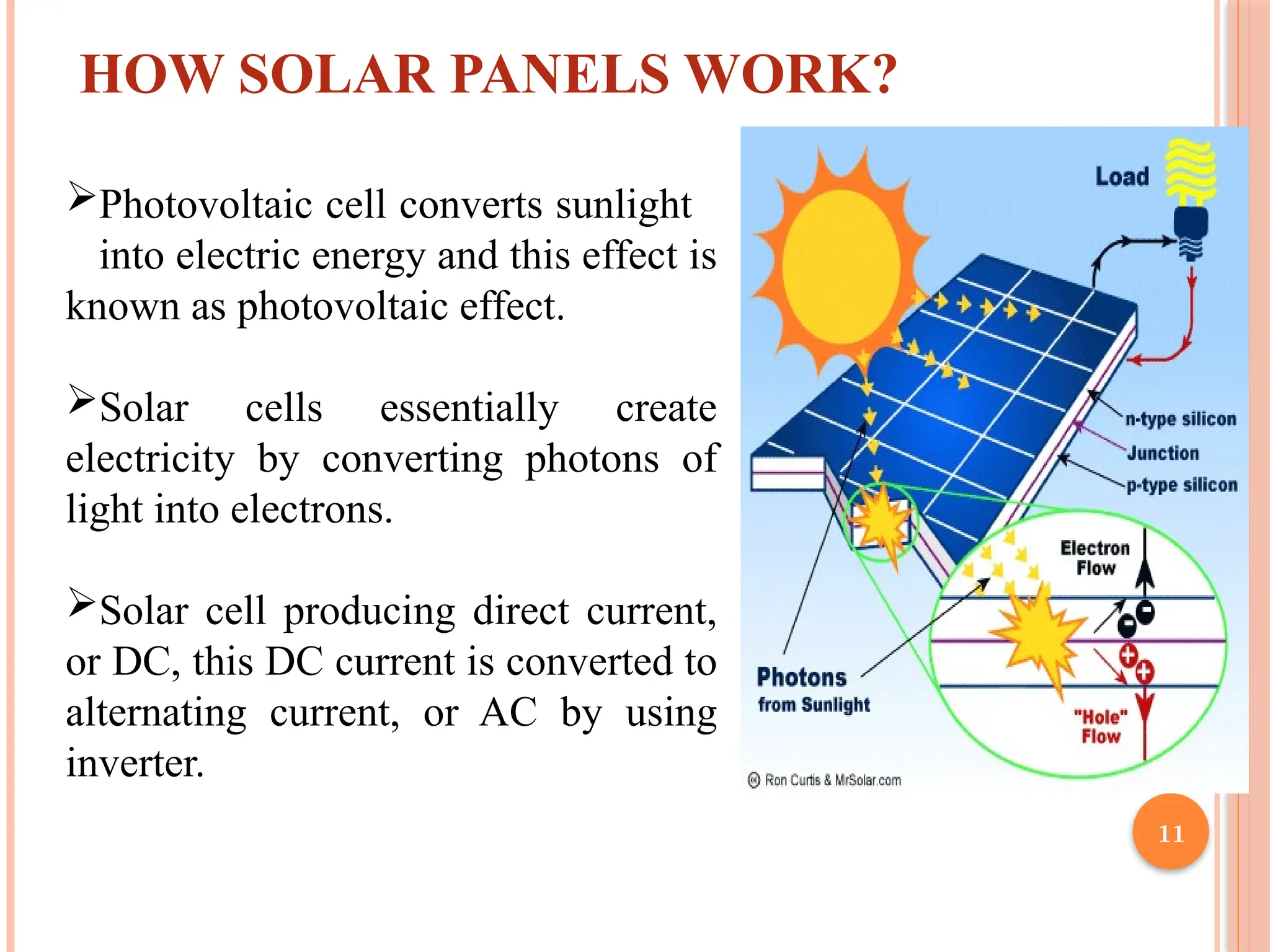
The document discusses the concept of solar trees, innovative structures utilizing photovoltaic cells arranged like a tree to generate renewable energy while minimizing land use. Key aspects include their components, advantages over traditional solar systems, applications in India, and future prospects for energy generation. Despite some disadvantages, solar trees present a viable solution for addressing energy demands in densely populated areas.