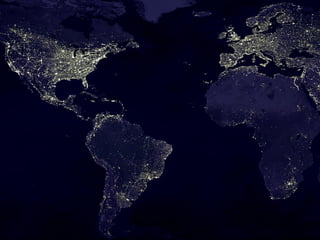
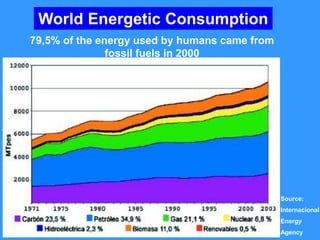
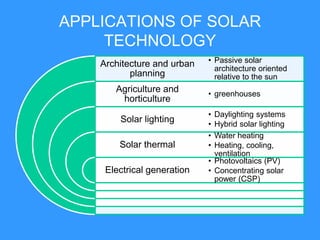
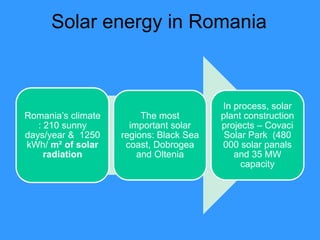
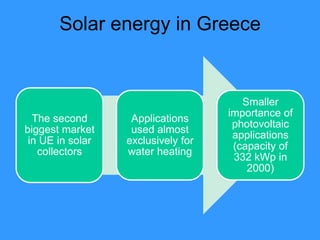
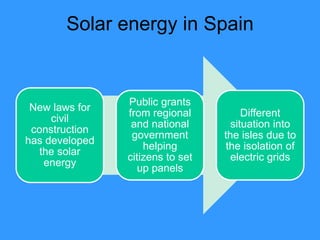
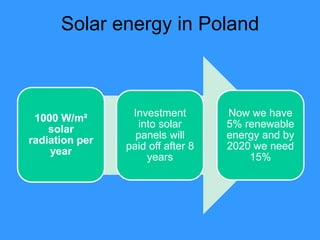
This document discusses solar energy in Europe. It provides information on different types of solar panels and technologies, both active and passive. Applications of solar technology include architecture, agriculture, lighting, thermal uses, and electrical generation. While solar energy has significant potential, challenges remain in developing large solar plants and retrofitting existing buildings. The document then discusses solar energy specifically in countries like Portugal, Romania, Greece, Poland, and Spain, noting the levels of solar radiation, key solar regions, and existing and planned solar energy projects in each country.