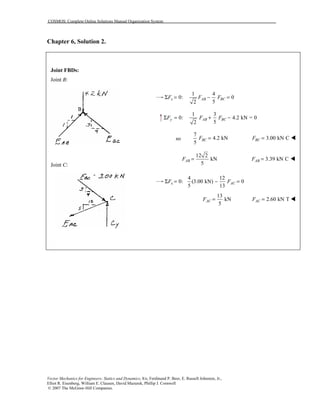
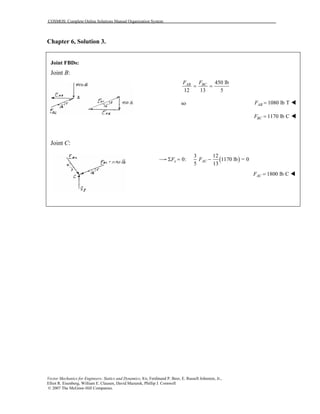
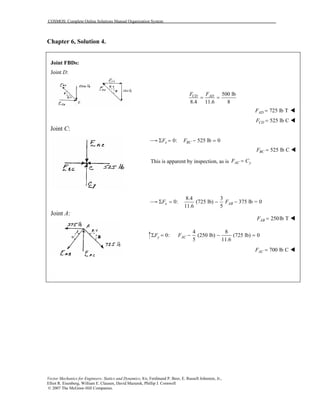
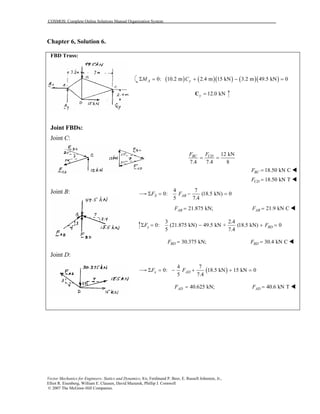
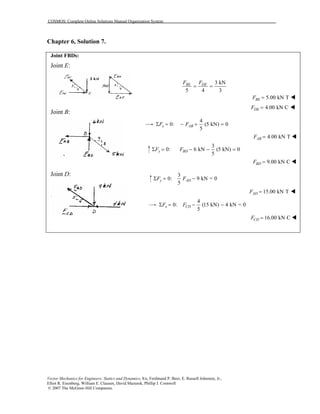
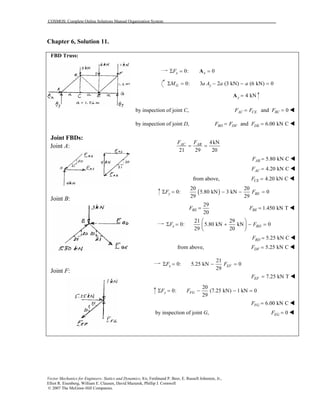
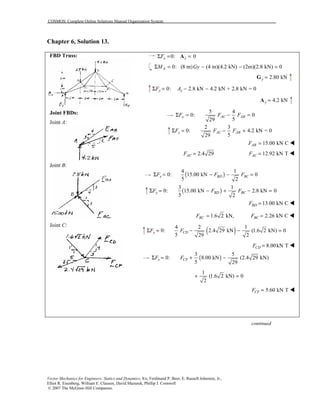
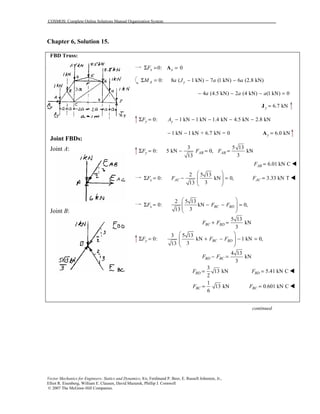
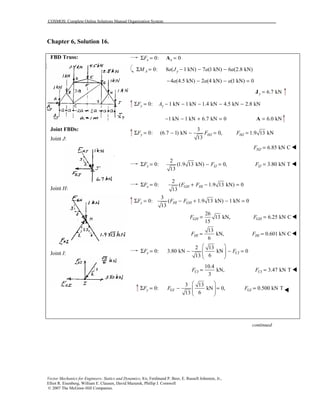
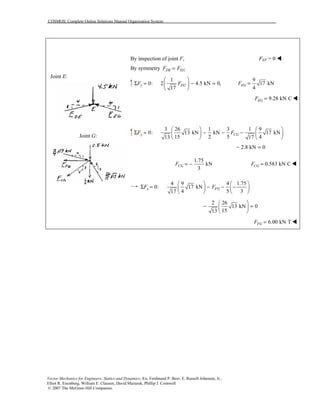
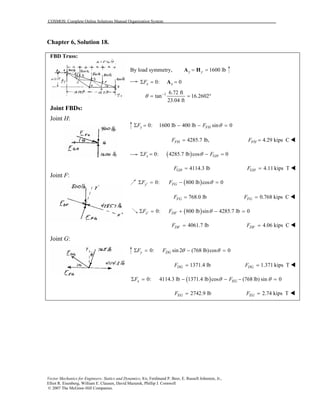
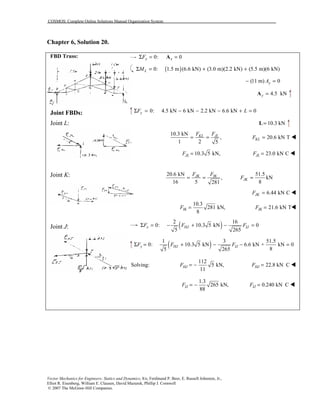
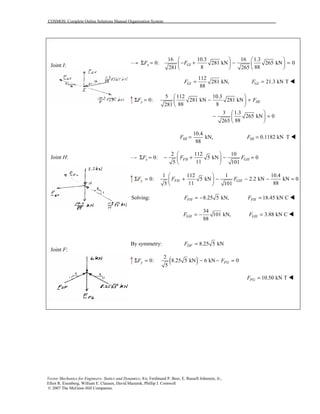
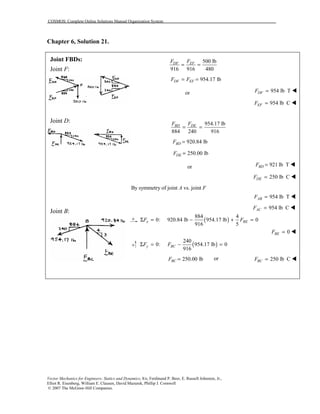
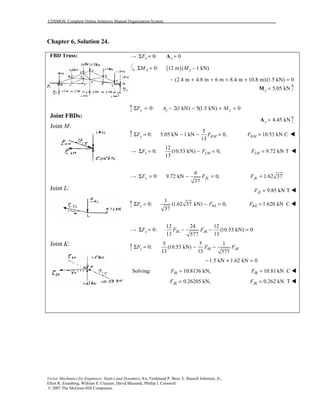
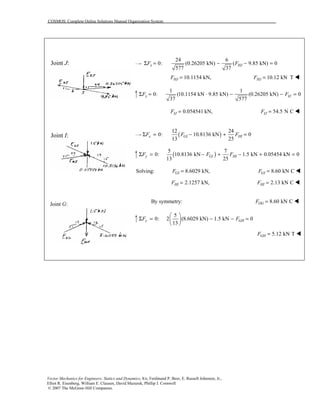
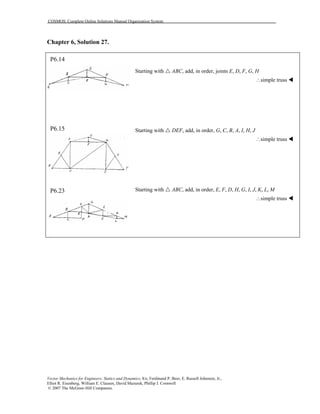
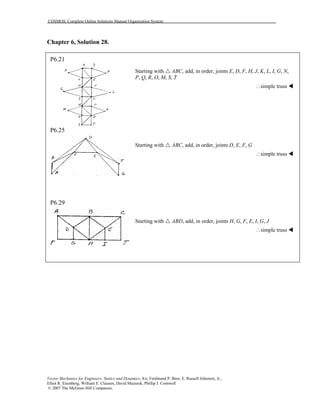
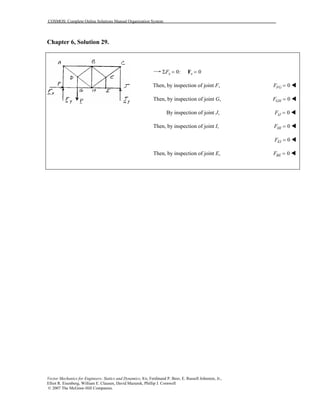
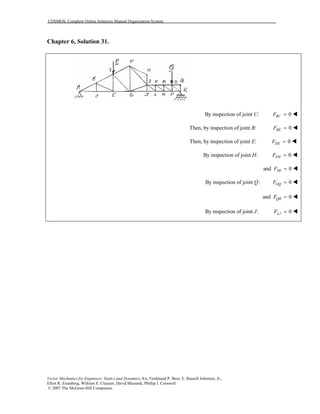
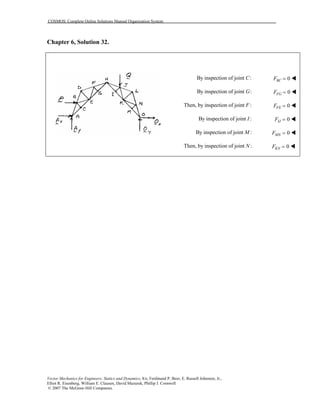
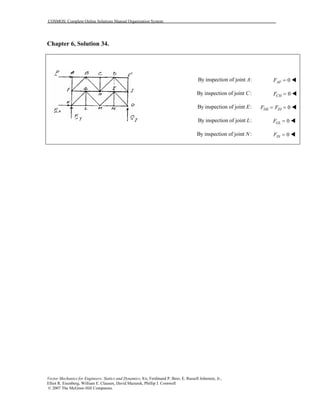
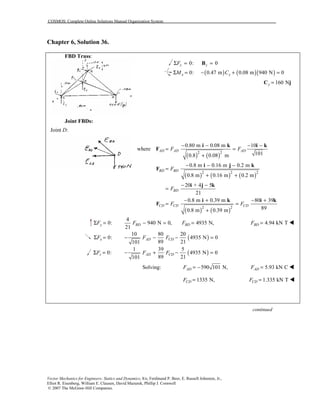
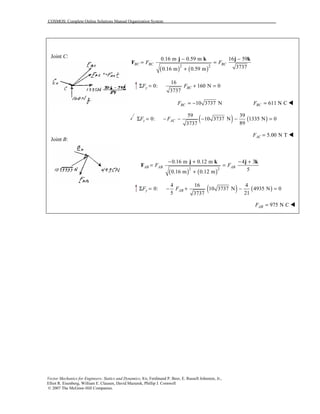
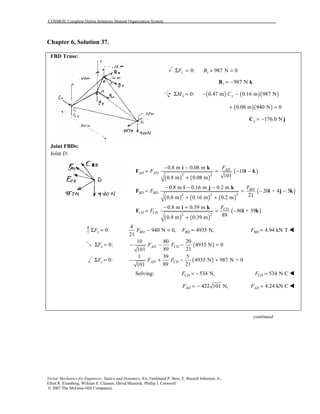
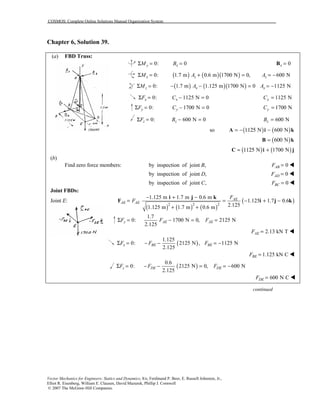
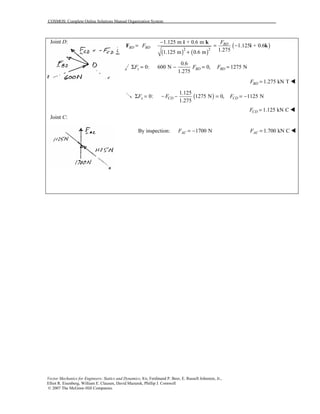
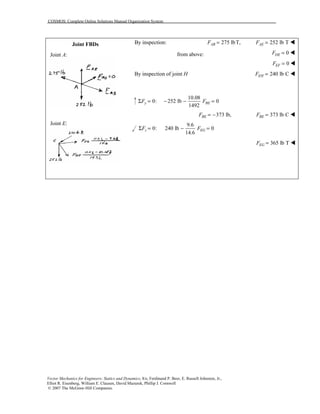
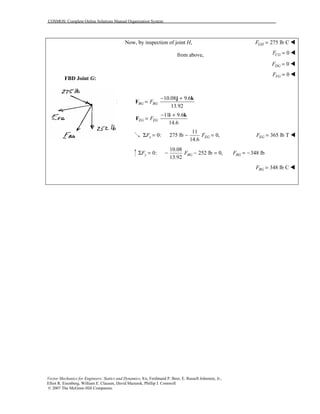
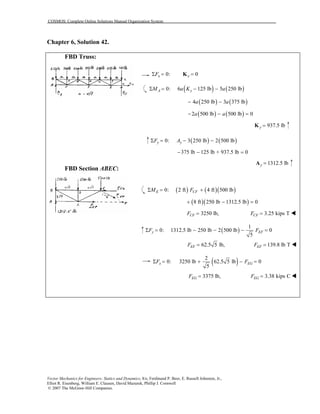
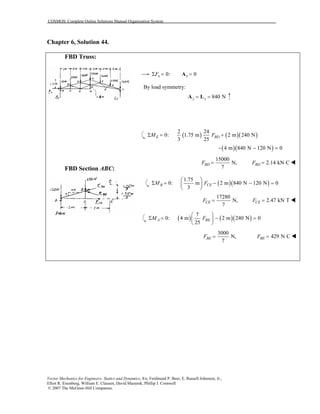
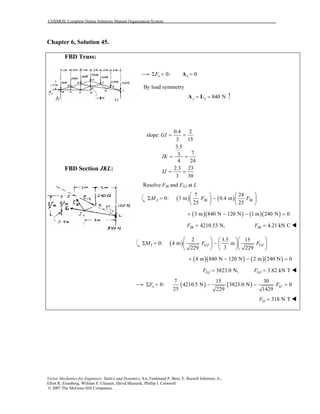
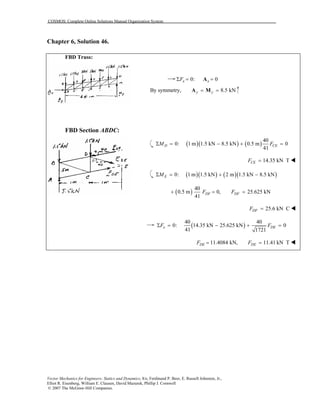
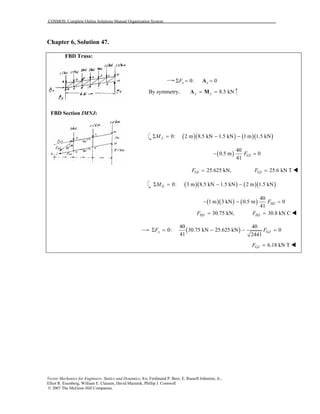
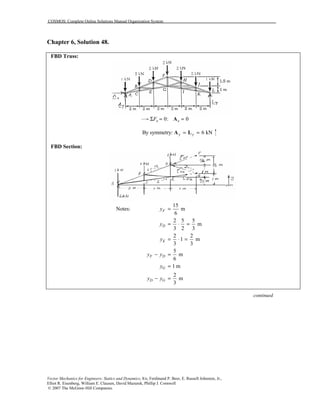
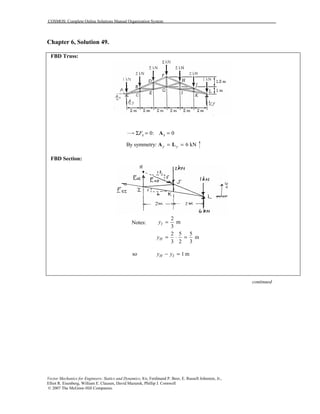
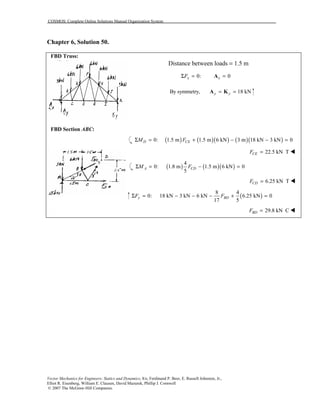
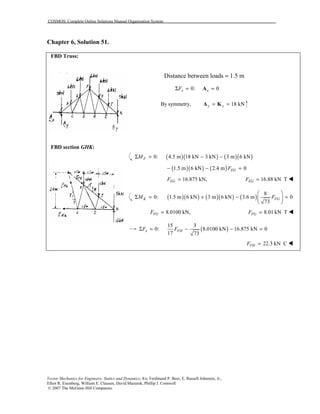
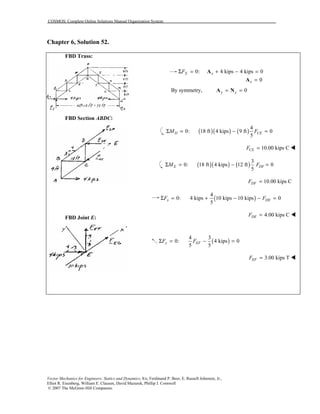
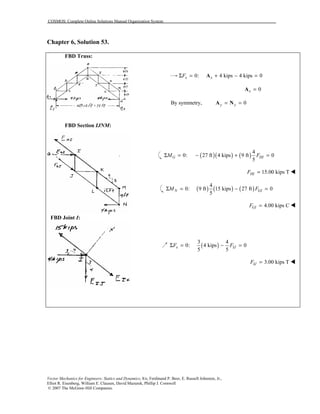
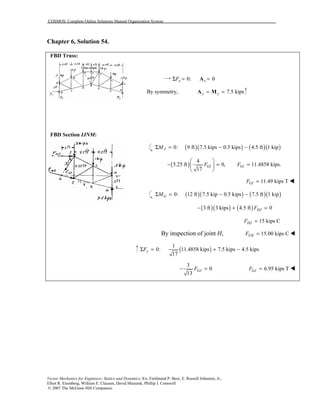
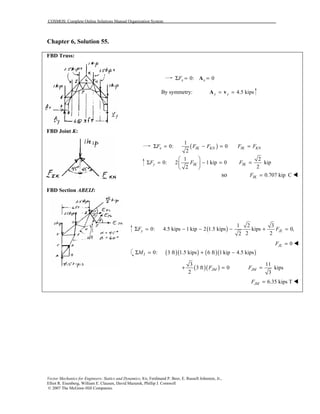
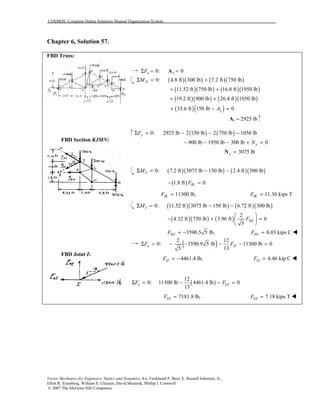
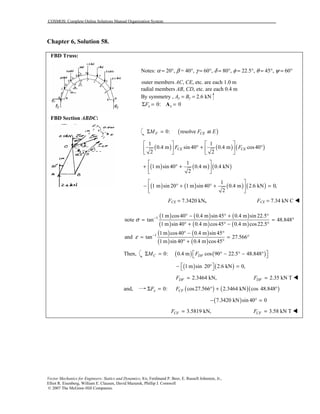
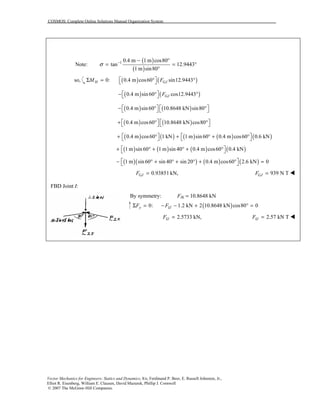
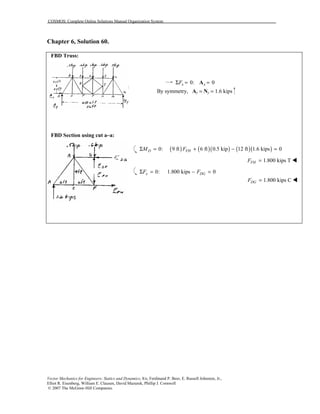
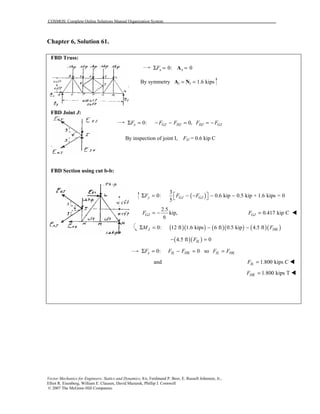
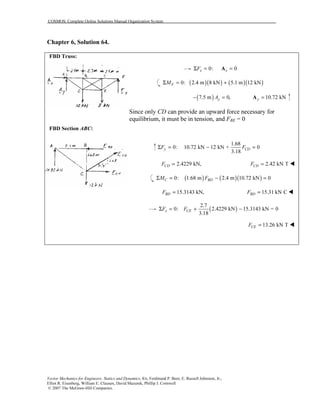
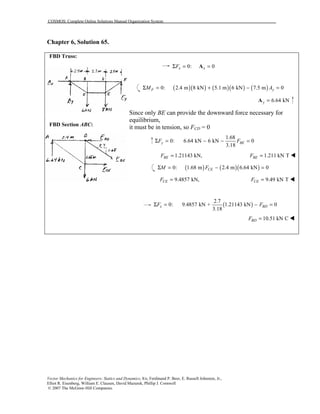
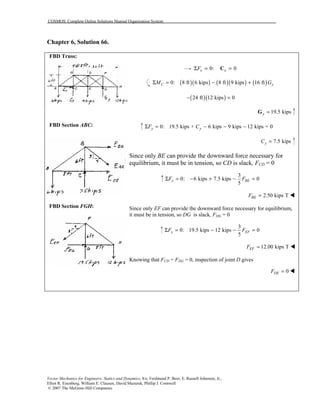
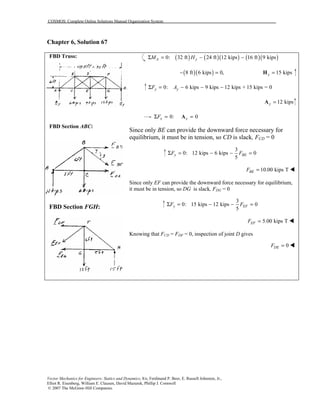
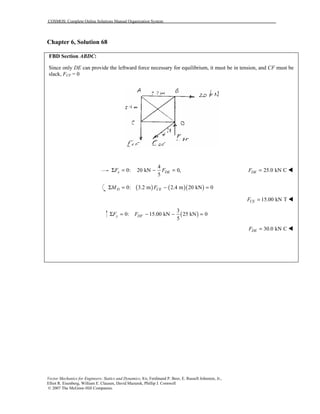
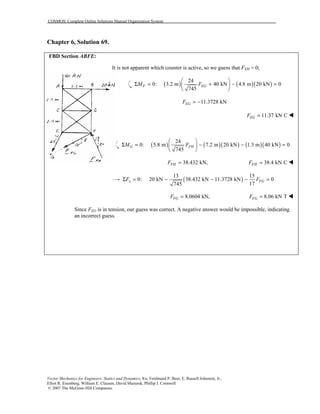
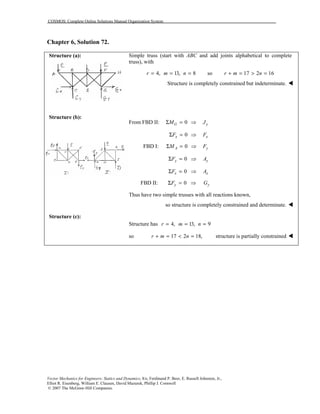
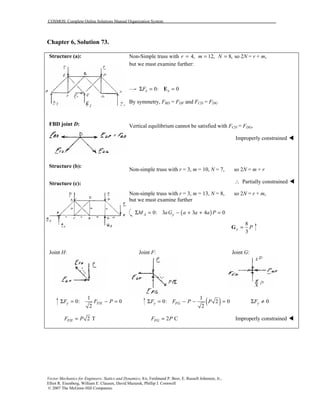
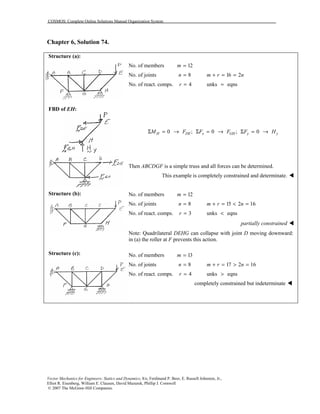
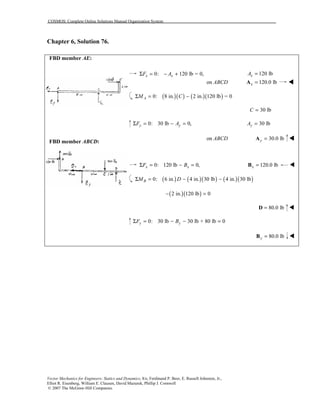
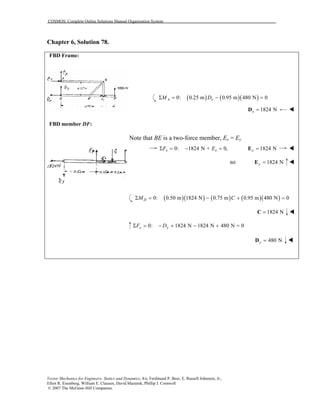
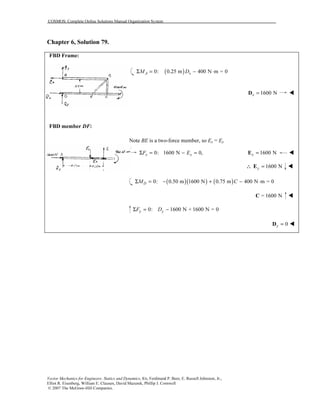
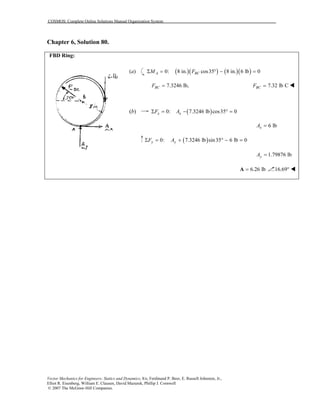
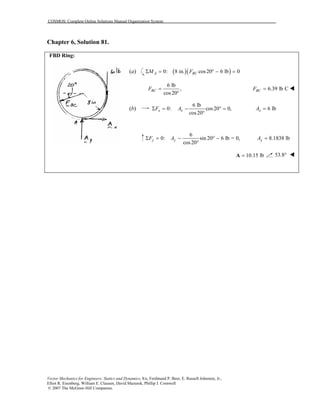
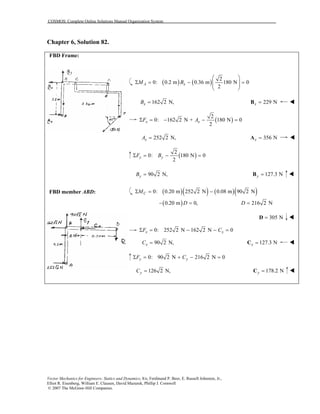
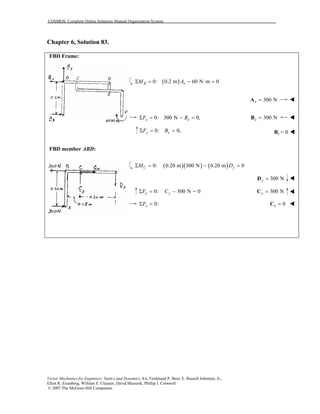
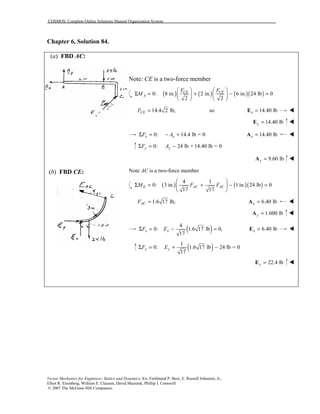
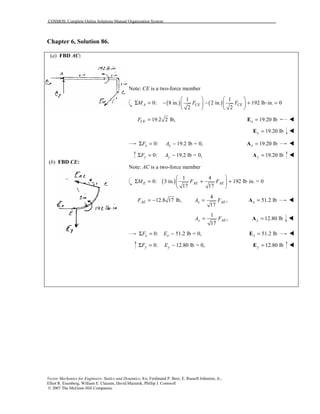
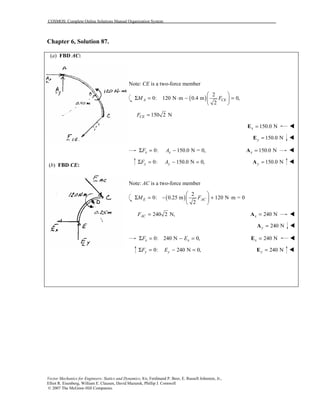
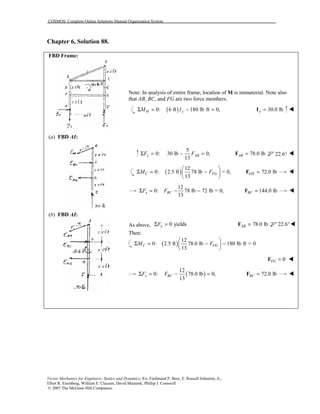
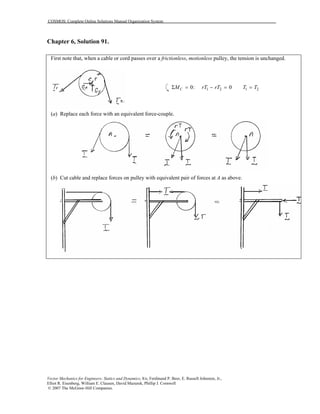
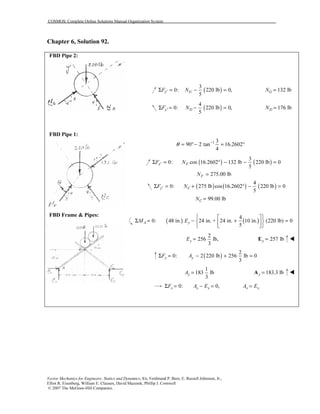
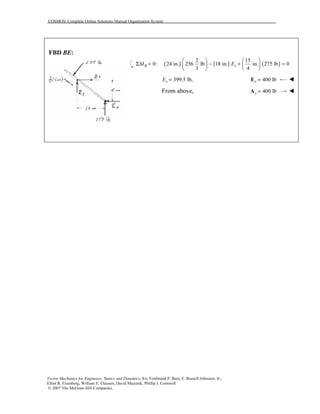
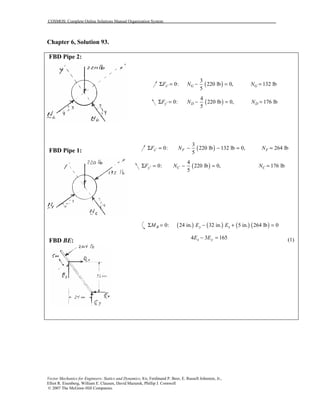
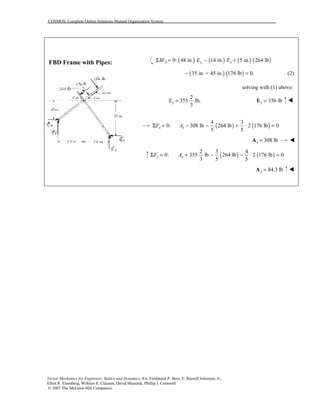
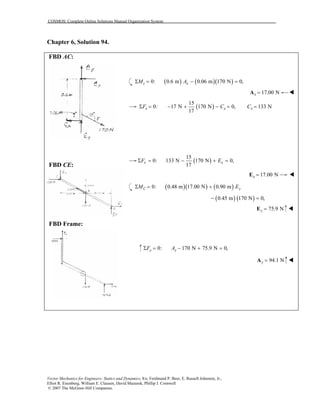
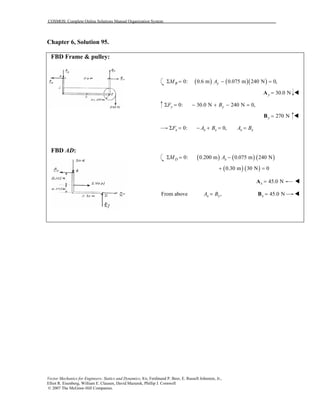
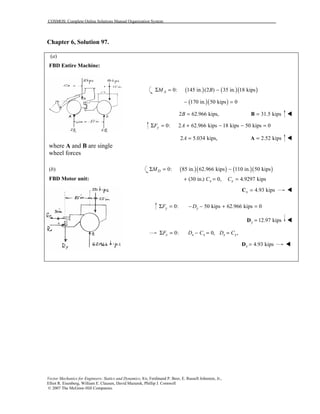
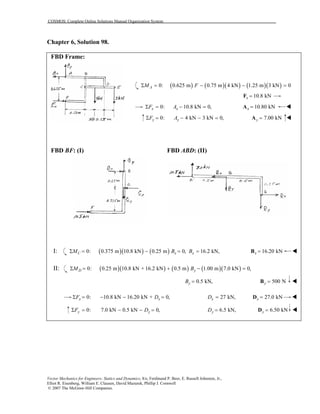
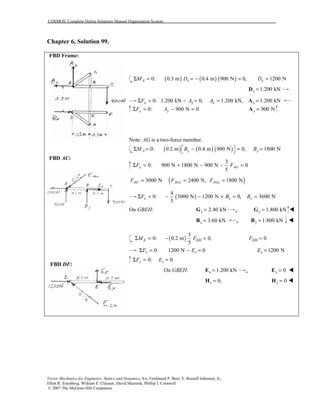
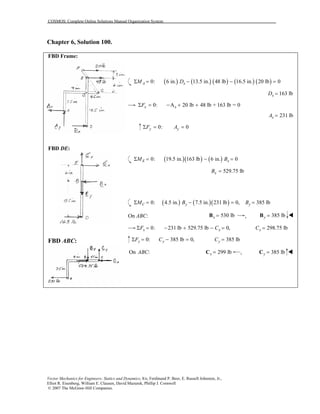
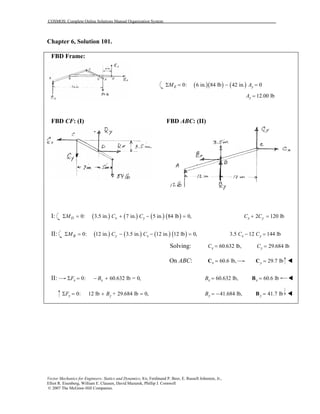
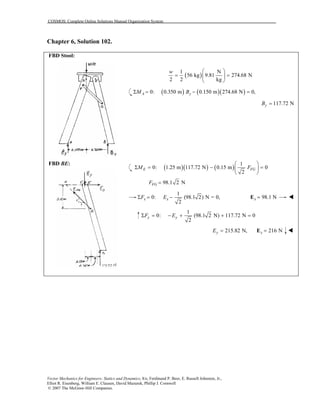
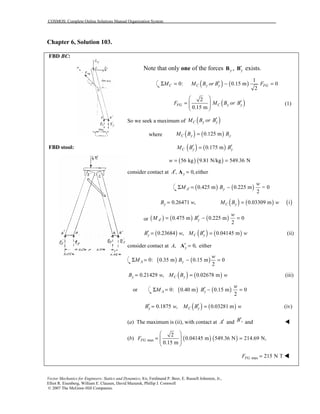
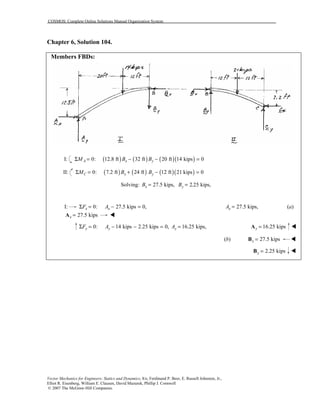
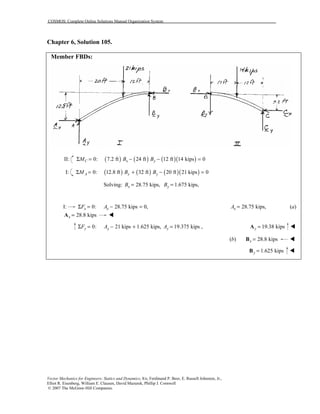
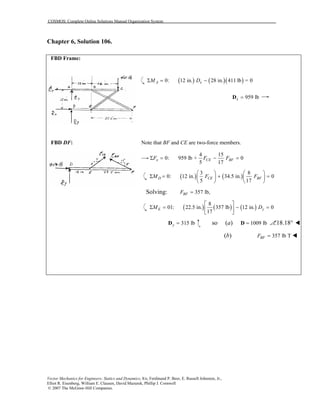
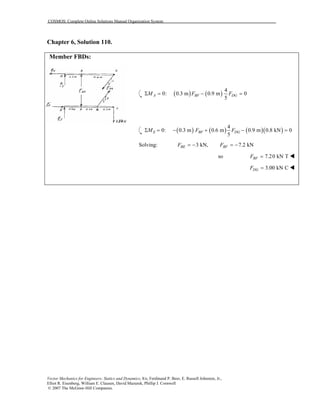
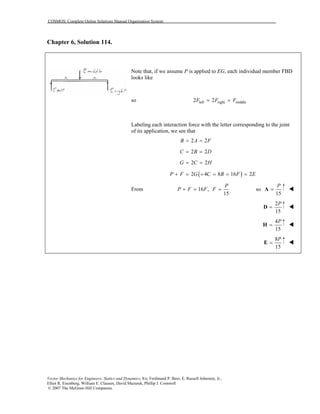
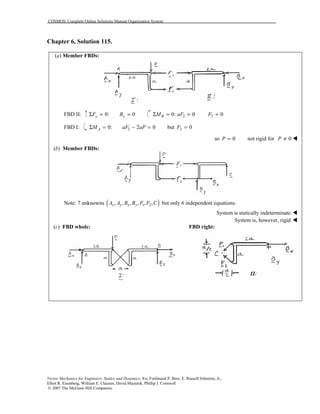
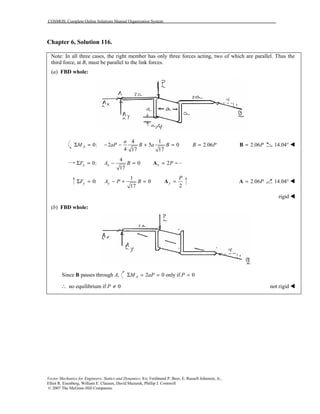
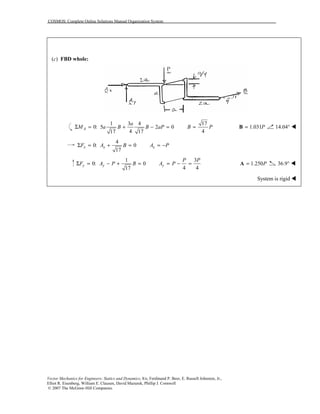
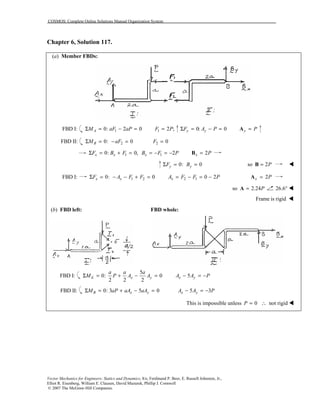
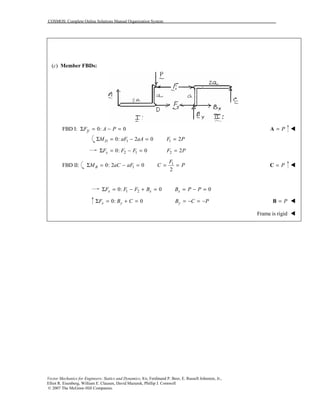
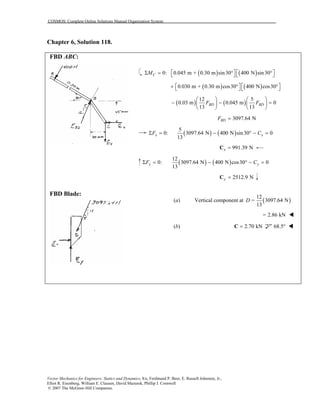
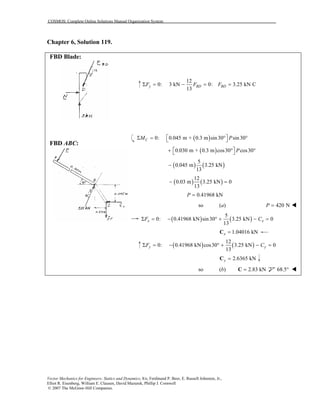
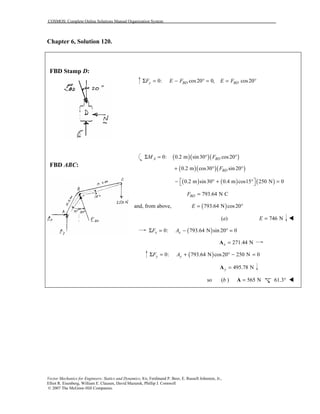
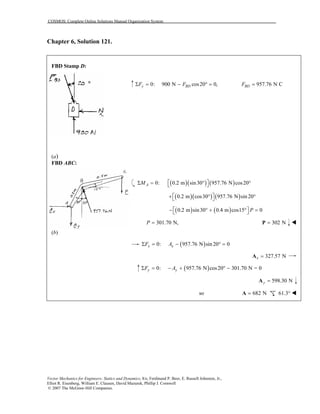
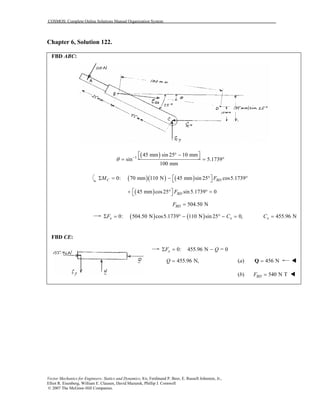
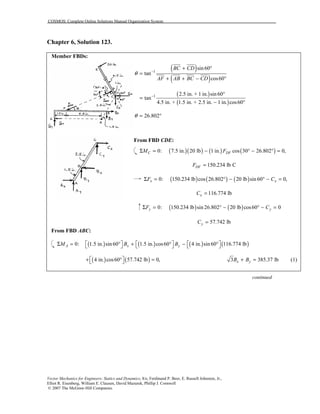
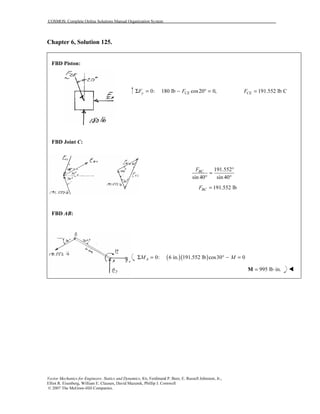
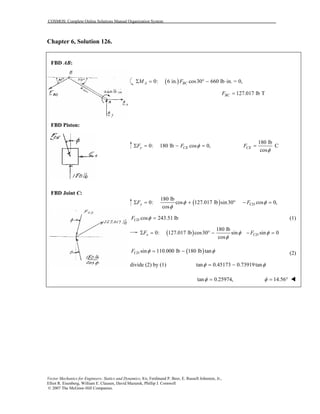
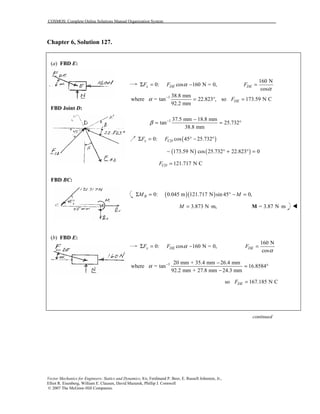
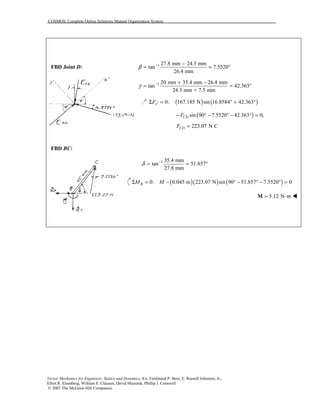
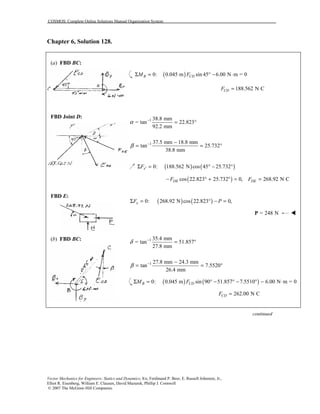
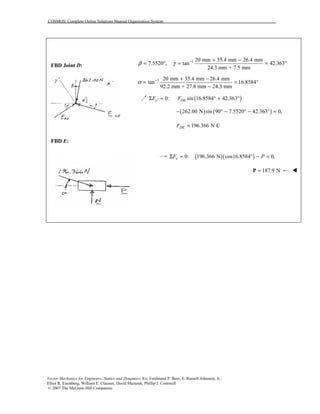
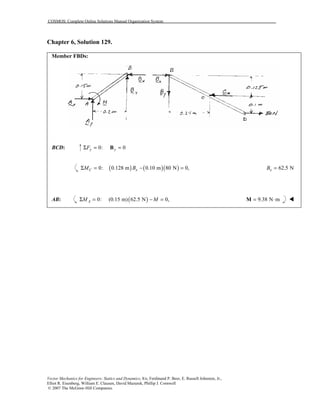
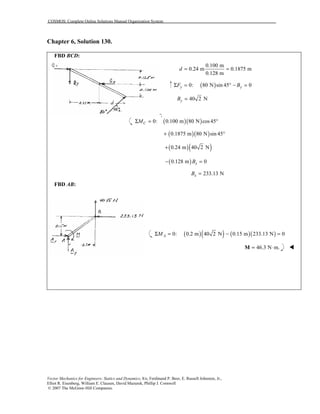
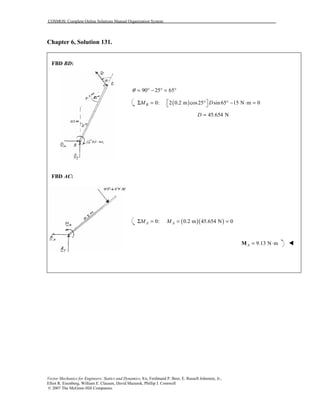
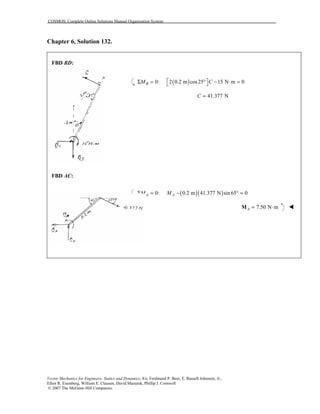
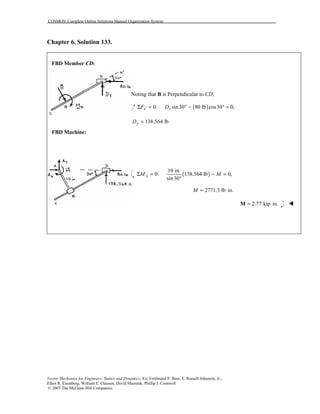
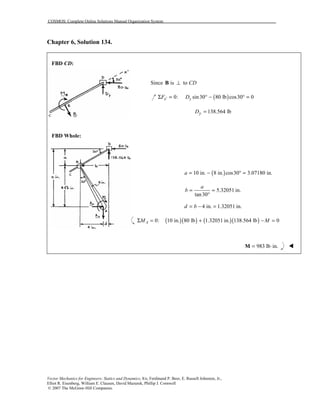
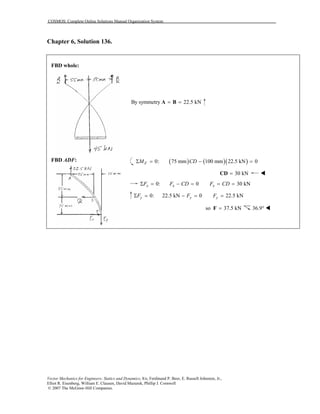
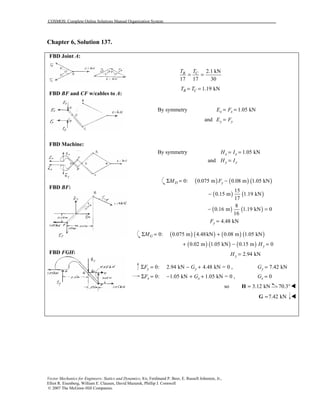
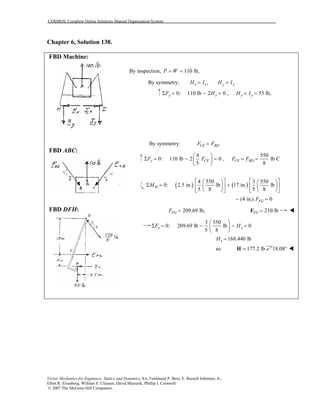
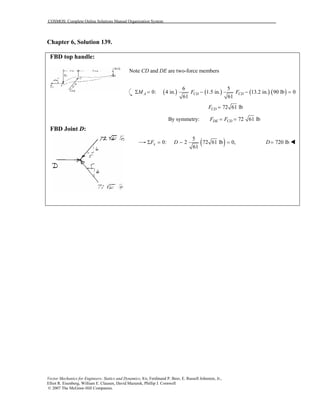
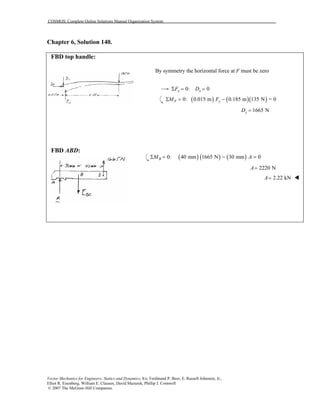
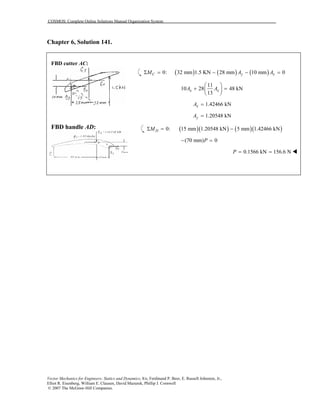
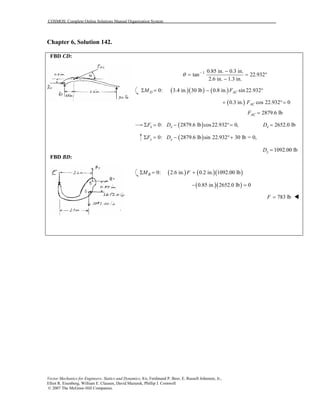
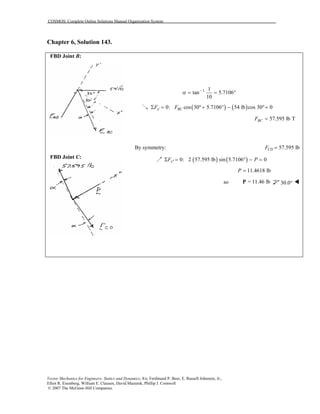
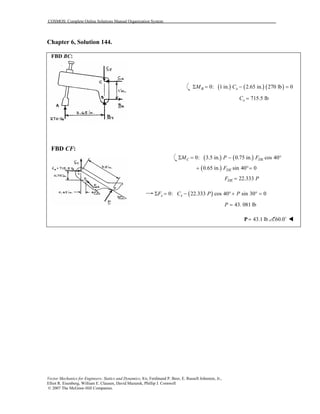
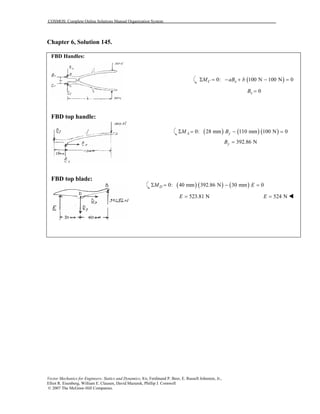
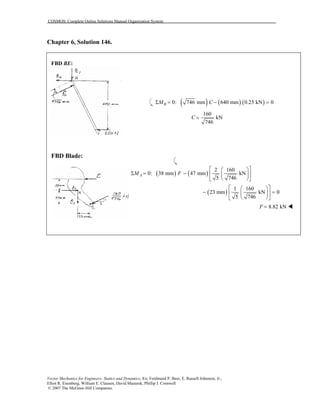
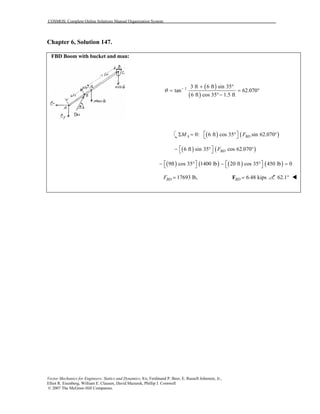
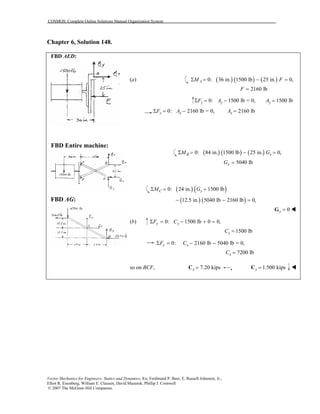
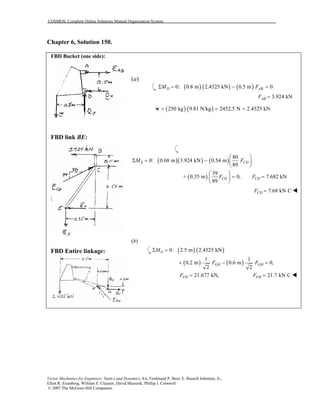
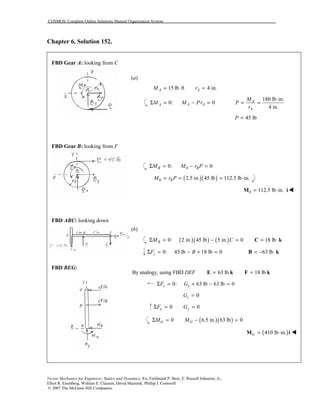
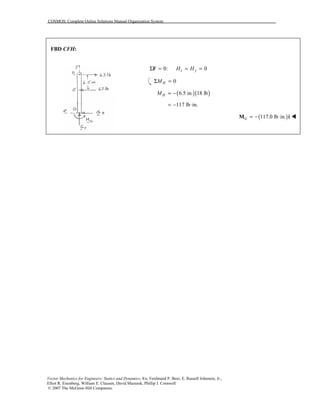
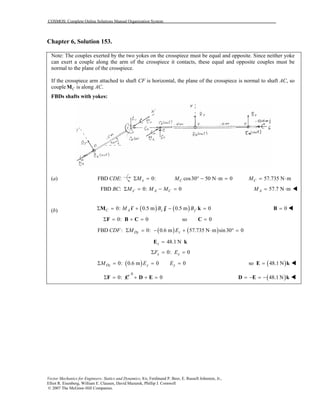
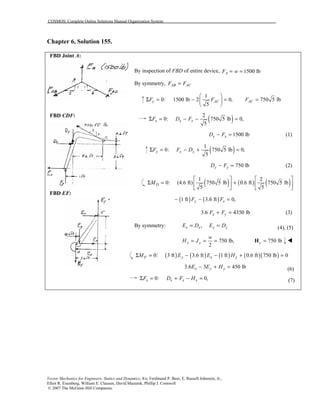
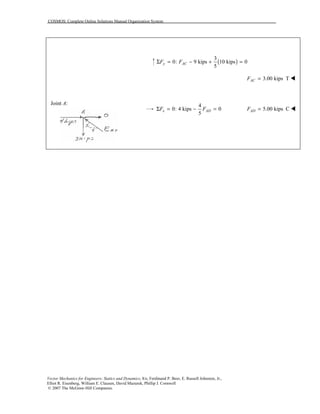
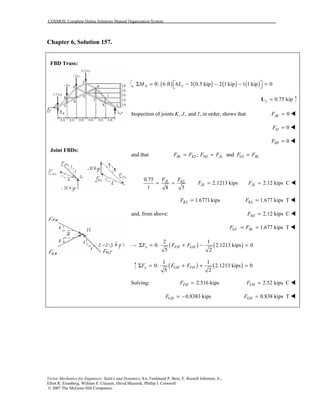
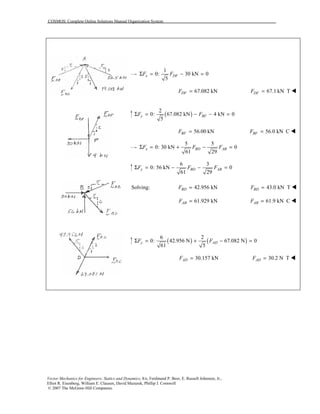
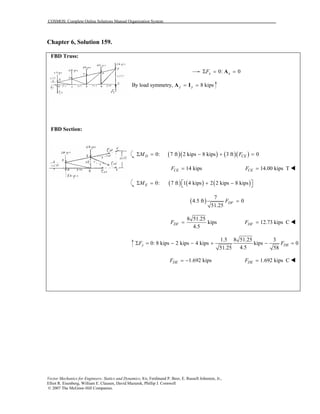
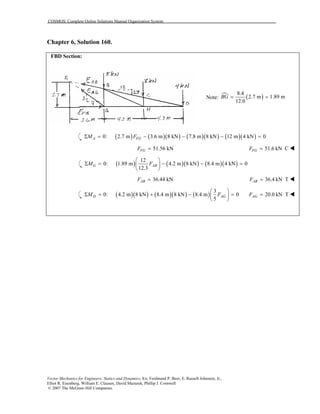
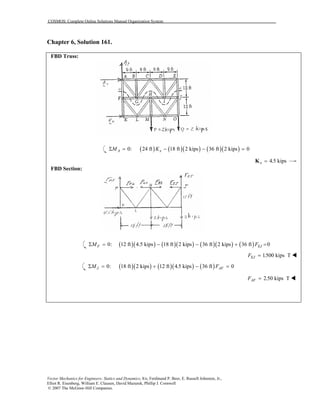
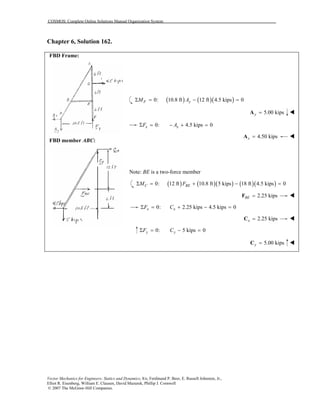
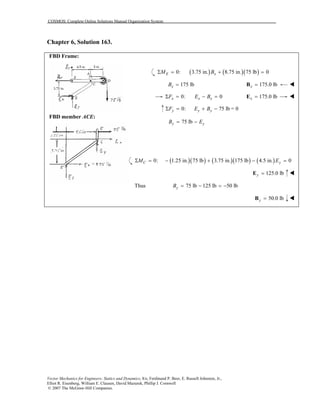
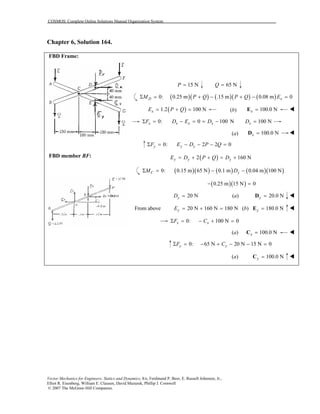
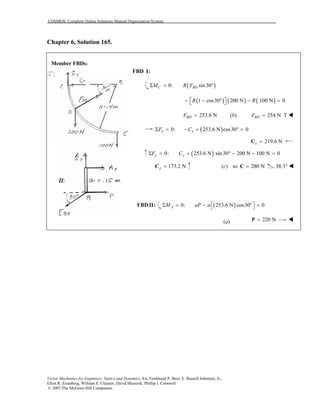
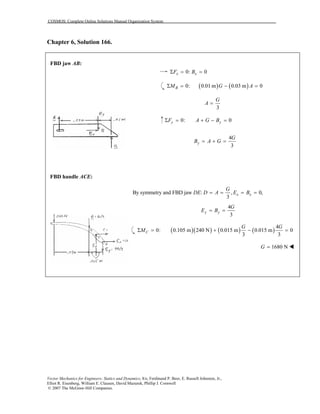
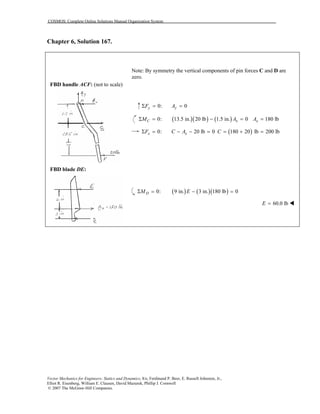
This document contains 12 solutions to statics problems involving truss structures. Each solution includes free body diagrams of the joints in the truss and the application of equilibrium equations to solve for member forces. Reactions and member forces are calculated and summarized for each truss configuration.