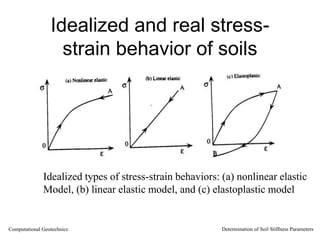
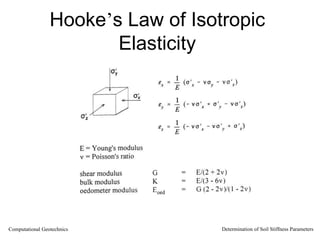
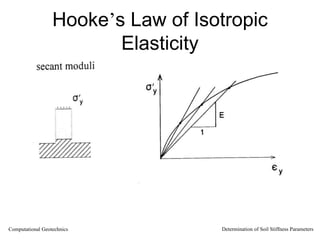
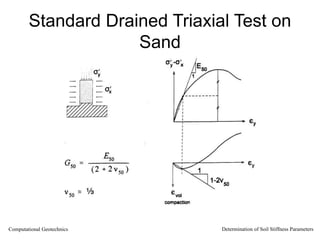
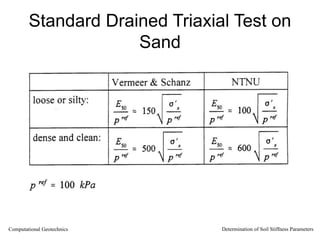
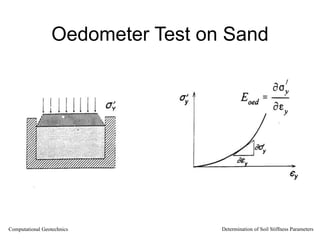
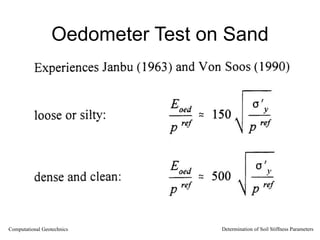
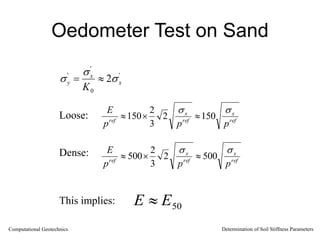
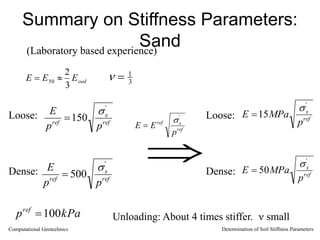
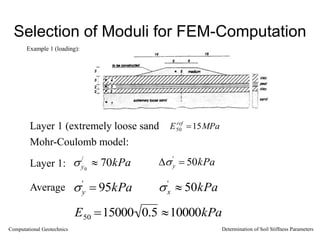
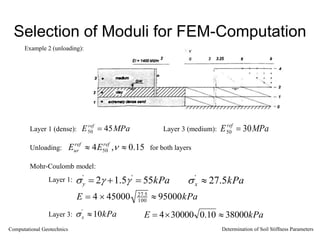
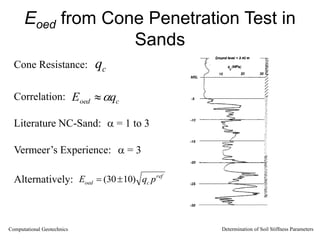
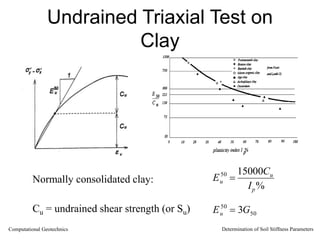
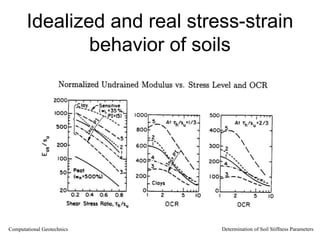
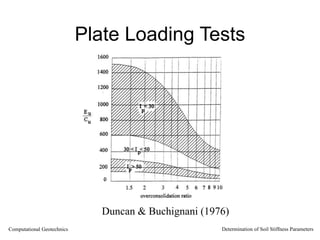
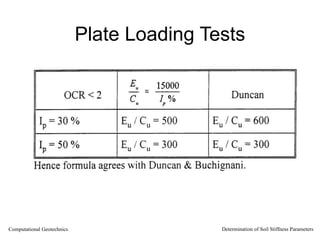
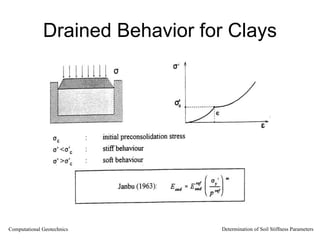
The document discusses methods for determining soil stiffness parameters from laboratory and in-situ tests. It provides equations to estimate the Young's modulus (E) of sand from triaxial compression tests, oedometer tests and cone penetration tests. It suggests values for E of 15 MPa for loose sand and 50 MPa for dense sand based on laboratory tests. For clays, it suggests estimating E from undrained shear strength (Cu) or 3 times the shear modulus (G). The document emphasizes that empirical relationships only provide estimates and that laboratory tests are needed to accurately determine soil stiffness.